Its an established fact that Mars was once a warmer and wetter place, with liquid water covering much of its surface. But between 4.2 and 3.7 billion years ago, the planet lost its atmosphere, which caused most of its surface water to disappear. Today, much of that water remains hidden beneath the surface in the form of water ice, which is largely restricted to the polar regions.
In recent years, scientists have also learned of ice deposits that exist in the equatorial regions of Mars, though it was unlcear how deep they ran. But according to a new study led by the U.S. Geological Survey, erosion on the surface of Mars has revealed abundant deposits of water ice. In addition to representing a major research opportunity, these deposits could serve as a source of water for Martian settlements, should they ever be built.
The study, titled “Exposed subsurface ice sheets in the Martian mid-latitudes“, recently appeared in Science. The study was led by Colin M. Dundas, a researcher with the U.S. Geological Survey, and included members from the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory (LPL) at the University of Arizona, Johns Hopkins University, the Georgia Institute of Technology, the Planetary Science Institute, and the Institute for Geophysics at the University of Texas at Austin.

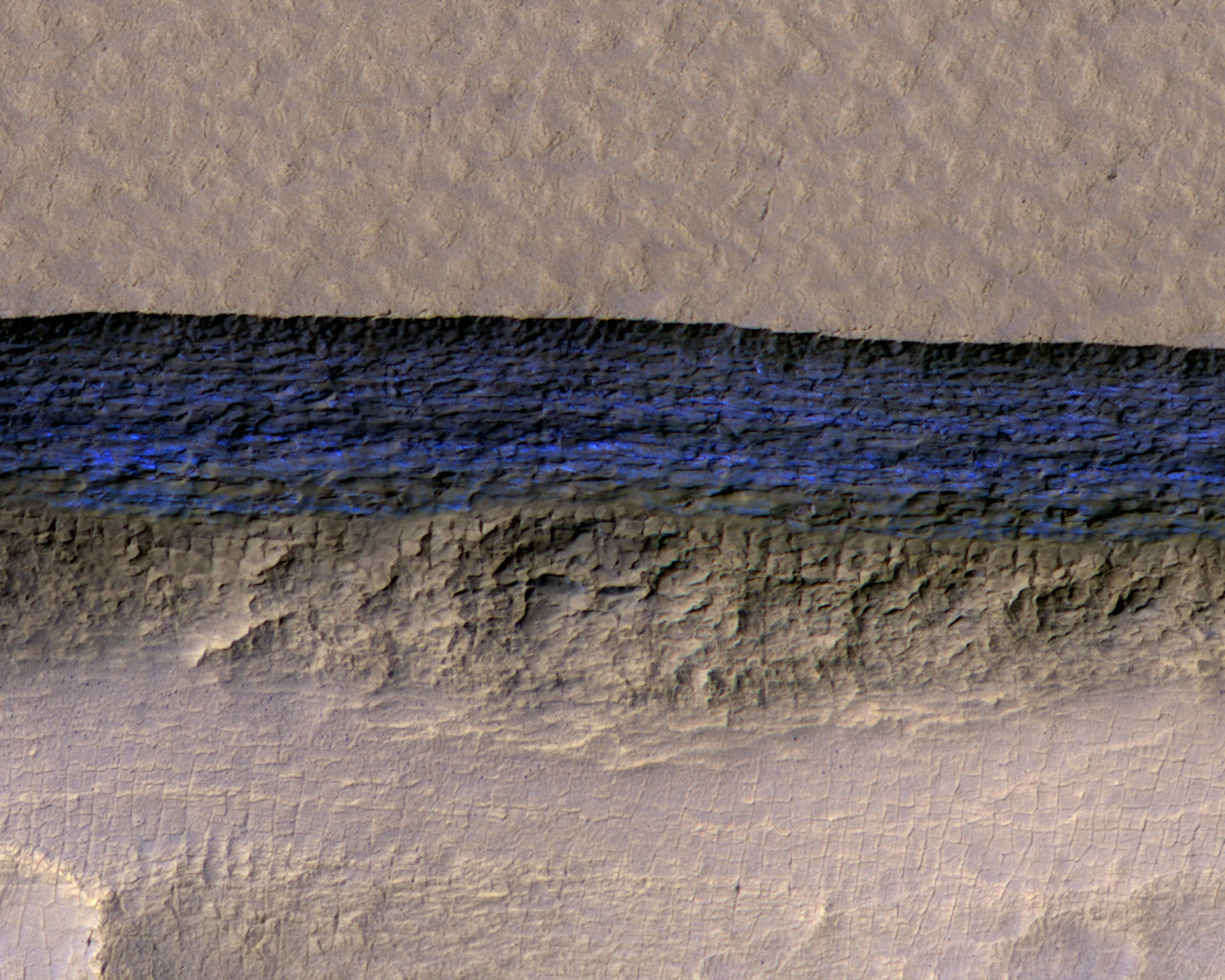
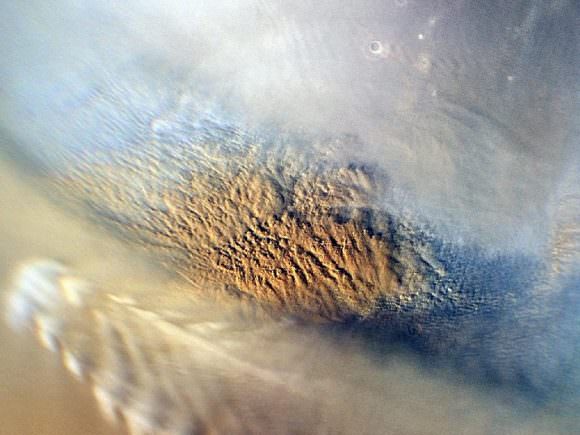
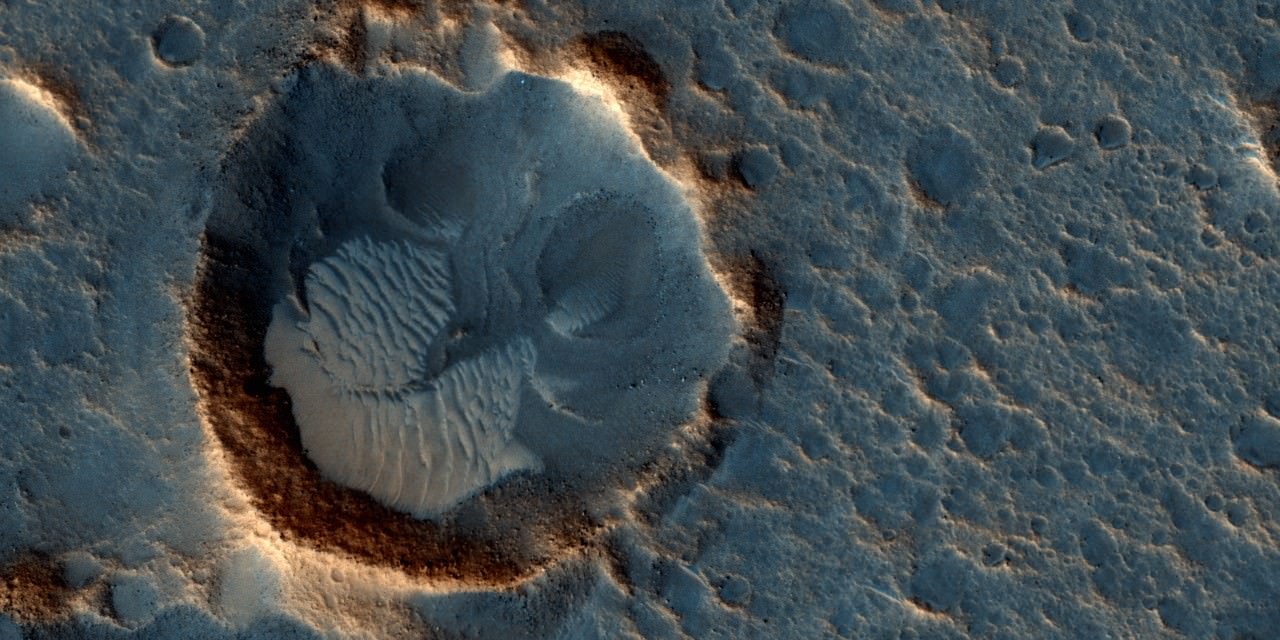
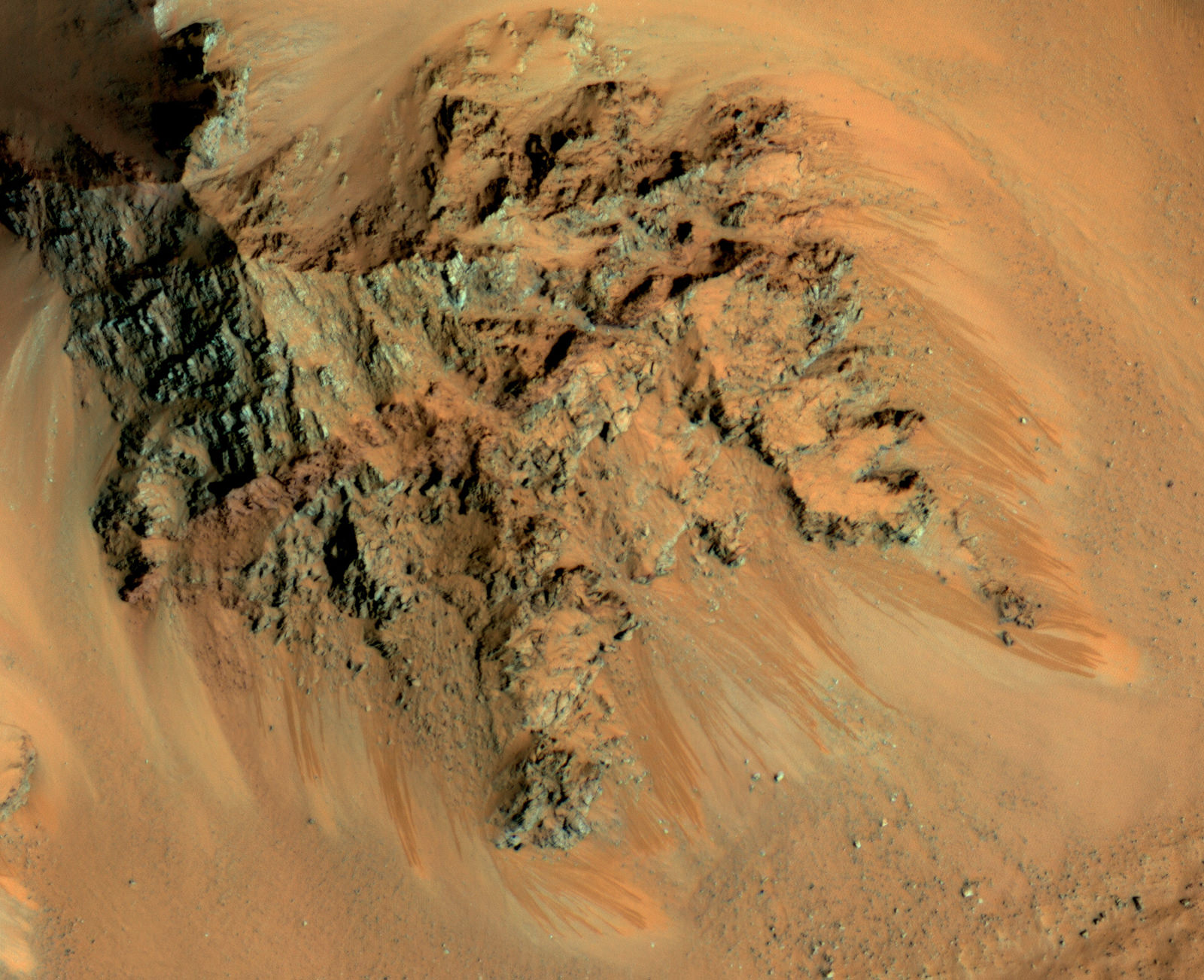
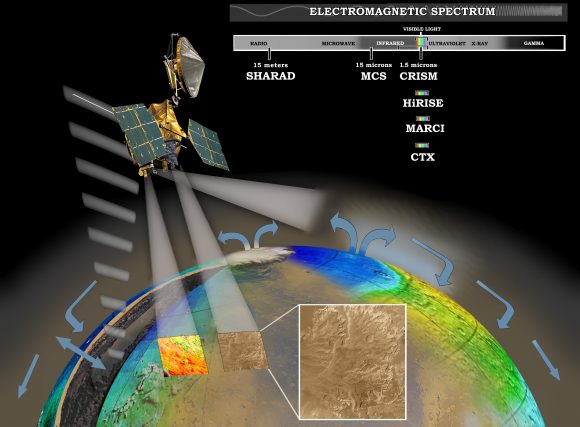
For the sake of their study, the team consulted data obtained by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) aboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). This data revealed eight locations in the mid-latitude region of Mars where steep slopes created by erosion exposed substantial quantities of sub-surface ice. These deposits could extend as deep as 100 meters (328 feet) or more.
The fractures and steep angles indicate that the ice is cohesive and strong. As Dundas explained in a recent NASA press statement:
“There is shallow ground ice under roughly a third of the Martian surface, which records the recent history of Mars. What we’ve seen here are cross-sections through the ice that give us a 3-D view with more detail than ever before.”
These ice deposits, which are exposed in cross-section as relatively pure water ice, were likely deposited as snow long ago. They have since become capped by a layer of ice-cemented rock and dust that is between one to two meters (3.28 to 6.56 ft) thick. The eight sites they observed were found in both the northern and southern hemispheres of Mars, at latitudes from about 55° to 58°, which accounts for the majority of the surface.
It would be no exaggeration to say that this is a huge find, and presents major opportunities for scientific research on Mars. In addition to affecting modern geomorphology, this ice is also a preserved record of Mars’ climate history. Much like how the Curiosity rover is currently delving into Mars’ past by examining sedimentary deposits in the Gale Crater, future missions could drill into this ice to obtain other geological records for comparison.

These ice deposits were previously detected by the Mars Odyssey orbiter (using spectrometers) and ground-penetrated radar aboard the MRO and the ESA’s Mars Express orbiter. NASA also sent the Phoenix lander to Mars in 2008 to confirm the findings made by the Mars Odyssey orbiter, which resulted in it finding and analyzing buried water ice located at 68° north latitude.
However, the eight scarps that were detected in the MRO data directly exposed this subsurface ice for the first time. As Shane Byrne, the University of Arizona Lunar and Planetary Laboratory and a co-author on the study, indicated:
“The discovery reported today gives us surprising windows where we can see right into these thick underground sheets of ice. It’s like having one of those ant farms where you can see through the glass on the side to learn about what’s usually hidden beneath the ground.”
These studies would also help resolve a mystery about how Mars’ climate changes over time. Today, Earth and Mars have similarly-tiled axes, with Mars’ axis tilted at 25.19° compared to Earth’s 23.439°. However, this has changed considerably over the course of eons, and scientists have wondered how increases and decreases could result in seasonal changes.

Basically, during periods where Mars’ tilt was greater, climate conditions may have favored a buildup of ice in the middle-latitudes. Based on banding and color variations, Dundas and his colleagues have suggested that layers in the eight observed regions were deposited in different proportions and with varying amounts of dust based on varying climate conditions.
As Leslie Tamppari, the MRO Deputy Project Scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, said:
“If you had a mission at one of these sites, sampling the layers going down the scarp, you could get a detailed climate history of Mars. It’s part of the whole story of what happens to water on Mars over time: Where does it go? When does ice accumulate? When does it recede?”
The presence of water ice in multiple locations throughout the mid-latitudes on Mars is also tremendous news for those who want to see permanent bases constructed on Mars someday. With abundant water ice just a few meters below the surface, and which is periodically exposed by erosion, it would be easily accessible. It would also mean bases need not be built in polar areas in order to have access to a source of water.
This research was made possible thanks to the coordinated use of multiple instruments on multiple Mars orbiters. It also benefited from the fact that these missions have been studying Mars for extended periods of time. The MRO has been observing Mars for 11 years now, while the Mars Odyssey probe has been doing so for 16. What they have managed to reveal in that time has provided all kinds of opportunities for future missions to the surface.