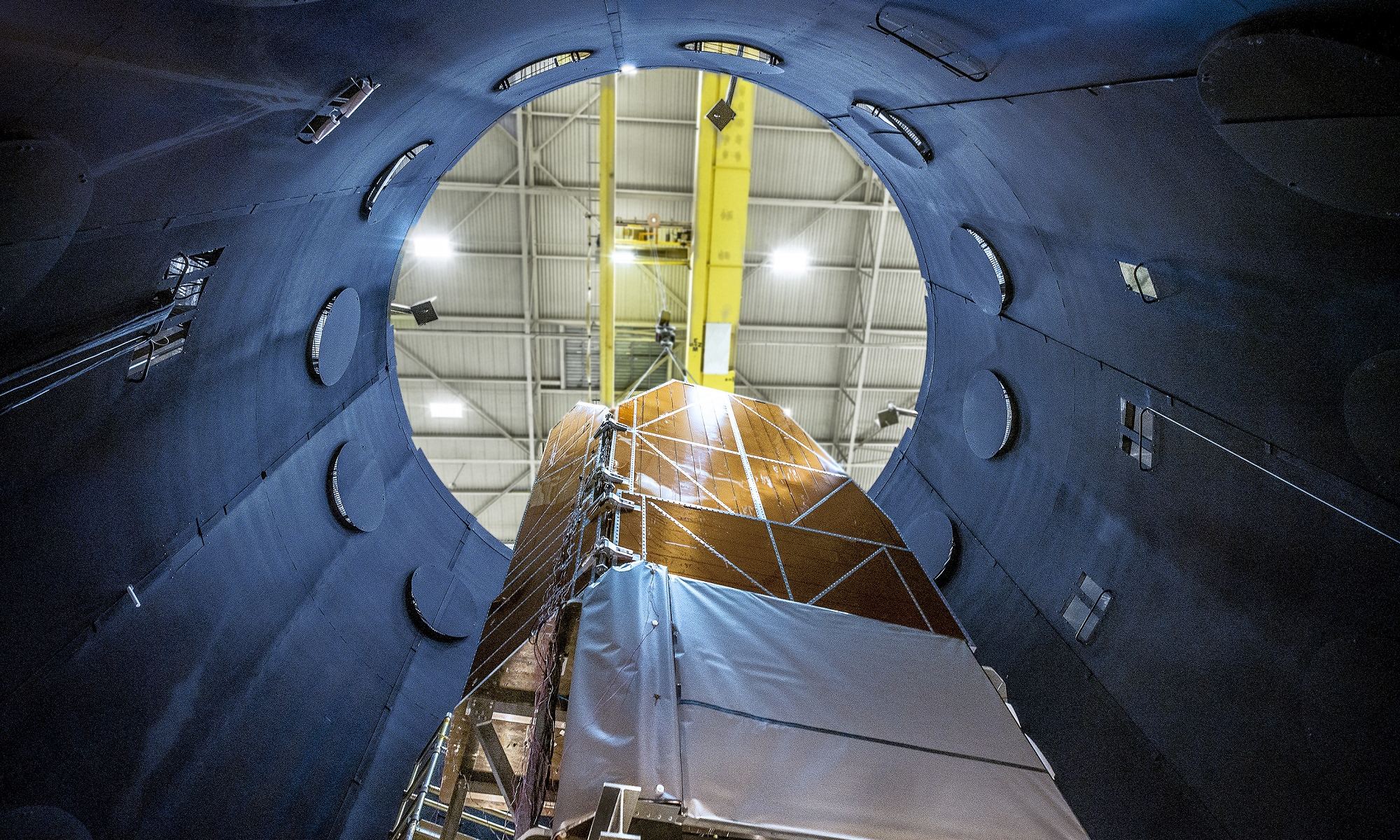
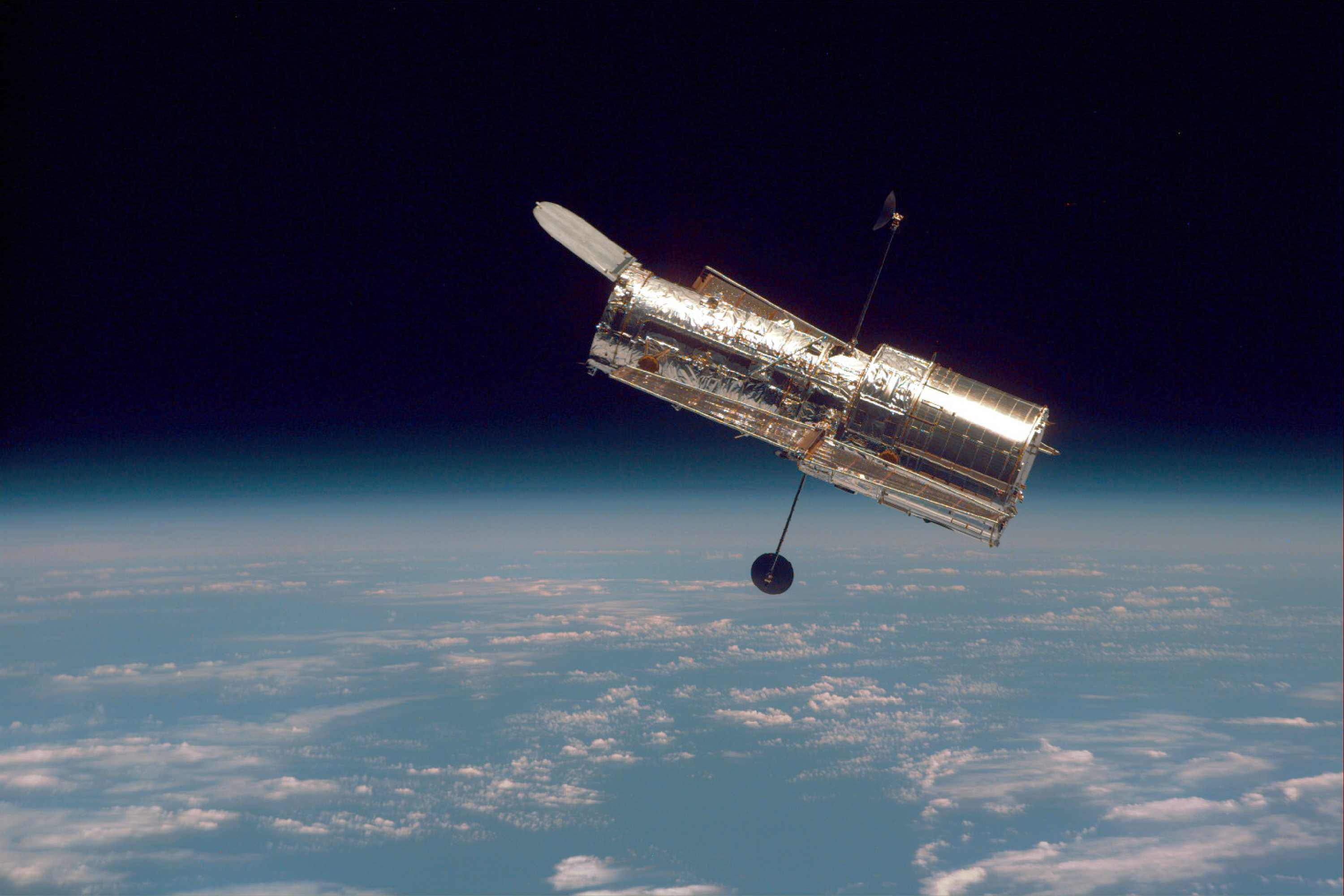
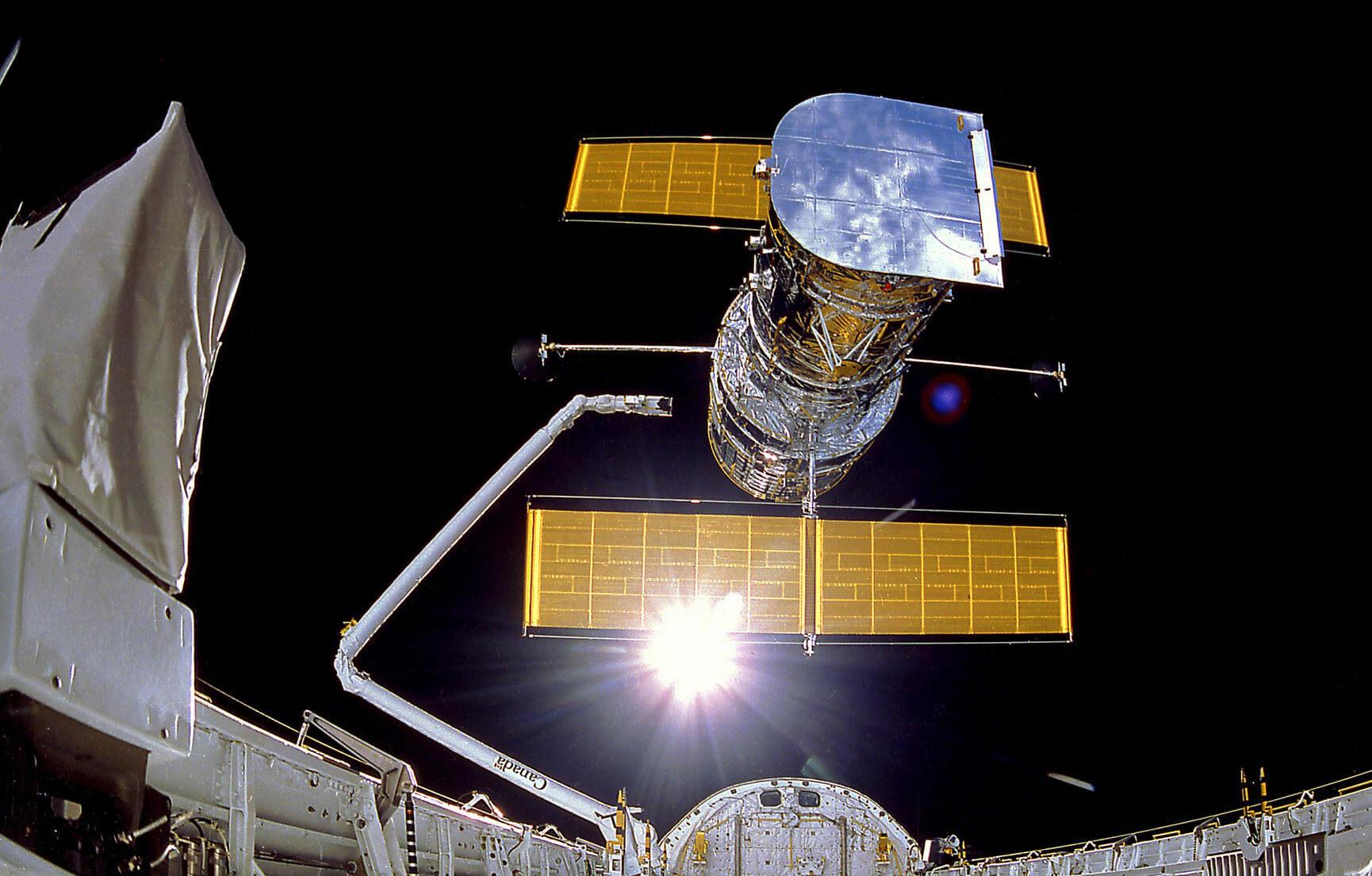
By 2027, the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope – or Roman Space Telescope (RST), for short – will take to space and build on the legacy of the venerable Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Combing a large primary mirror, a camera as sensitive as its predecessors, and next-generation surveying capabilities, Roman will have the power of “One-Hundred Hubbles.” It’s little wonder then why the telescope is named after Dr. Roman (1925 – 2018), NASA’s first Chief Astronomer and the “Mother of Hubble.”
As part of its journey towards realization, this next-generation space telescope recently passed a crucial milestone. This would be the all-important Mission Critical Design Review (CDR), signaling that all design and developmental engineering work is complete. With this milestone reached, the next-generation space telescope is now ready to move from the conceptual stage into the fabrication and assembly phase.
Continue reading “Nancy Grace Roman Just Passed a Critical Design Review”