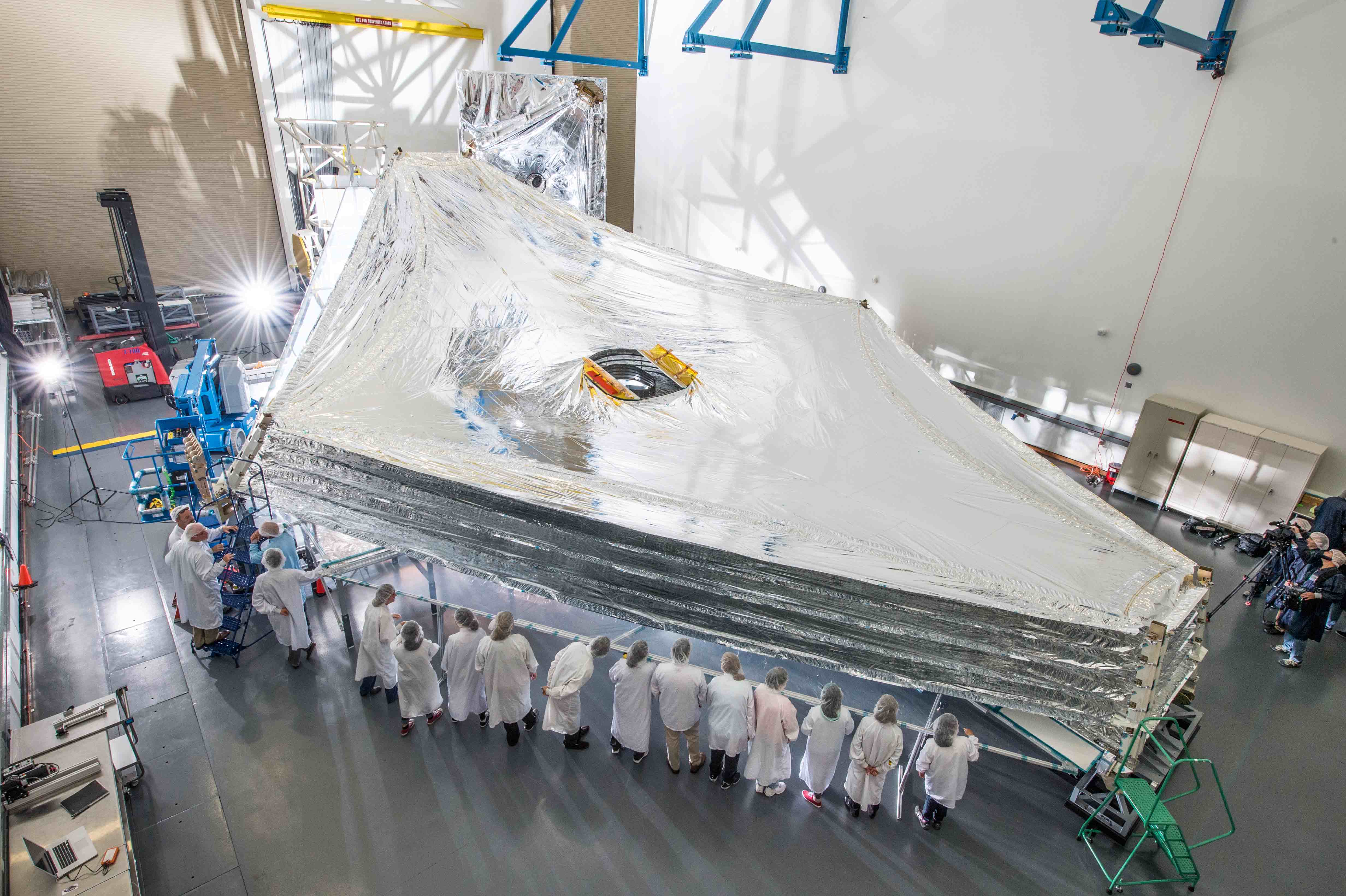
GODDARD SPACE FLIGHT CENTER, MD – The huge Sunshield test unit for NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has been successfully unfurled for the first time in a key milestone ahead of the launch scheduled for October 2018.
Engineers stacked and expanded the tennis-court sized Sunshield test unit last week inside the cleanroom at a Northrop Grumman facility in Redondo Beach, California.
NASA reports that the operation proceeded perfectly the first time during the test of the full-sized unit.
The Sunshield and every other JWST component must unfold perfectly and to precise tolerances in space because it has not been designed for servicing or repairs by astronaut crews voyaging beyond low-Earth orbit into deep space, William Ochs, Associate Director for JWST at NASA Goddard told me in an exclusive interview.
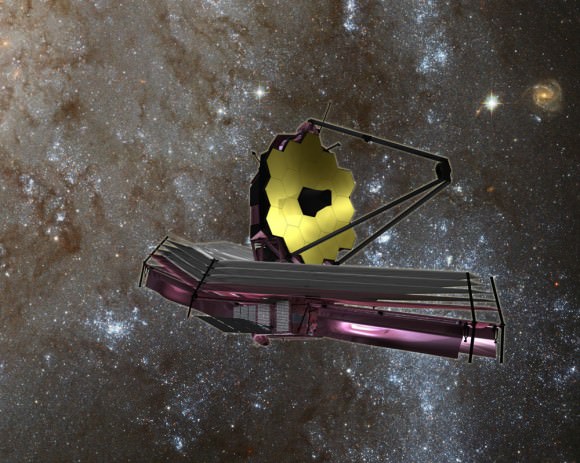
The five layered Sunshield is the largest component of the observatory and acts like a parasol.
Its purpose is to protect Webb from the suns heat and passively cool the telescope and its quartet of sensitive science instruments via permanent shade to approximately 45 kelvins, -380 degrees F, -233 C.
The kite-shaped Sunshield provides an effective sun protection factor or SPF of 1,000,000. By comparison suntan lotion for humans has an SPF of 8 to 40.

The extreme cold is required for the telescope to function in the infrared (IR) wavelengths and enable it to look back in time further than ever before to detect distant objects.
The shield separates the observatory into a warm sun-facing side and a cold anti-sun side.
Its five thin membrane layers also provides a stable thermal environment to keep the telescopes 18 primary mirror segments properly aligned for Webb’s science investigations.
JWST is the successor to the 24 year old Hubble Space Telescope and will become the most powerful telescope ever sent to space.
The Webb Telescope is a joint international collaborative project between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
NASA has overall responsibility and Northrop Grumman is the prime contractor for JWST.
Webb will launch folded up inside the payload fairing of an ESA Ariane V ECA rocket from the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana.
In launch configuration, the Sunshield will surround the main mirrors and instruments like an umbrella.
During the post launch journey to the L2 observing orbit at the second Sun-Earth Lagrange point nearly a million miles (1.5 million Km) from Earth, the telescopes mirrors and sunshield will begin a rather complex six month long unfolding and calibration process.
The science instruments have been mounted inside the ISIM science module and are currently undergoing critical vacuum chamber testing at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center which provides overall management and systems engineering.

The mirror segments have arrived at NASA Goddard where I’ve had the opportunity to observe and report on work in progress.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing JWST, MMS, ISS, Curiosity, Opportunity, SpaceX, Orbital Sciences, Boeing, Orion, MAVEN, MOM, Mars and more Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.