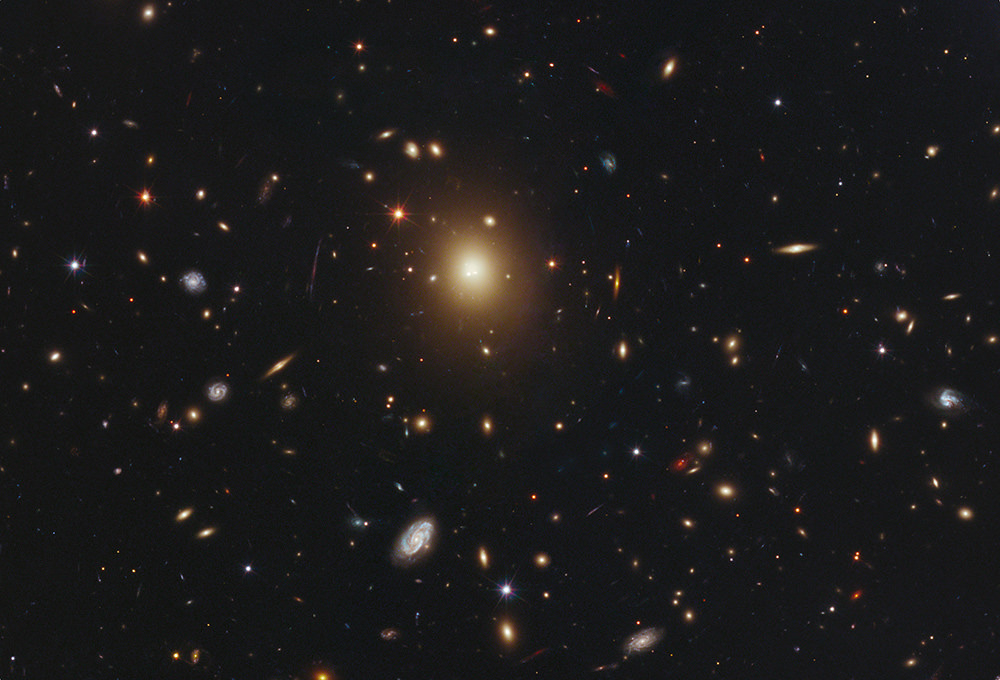
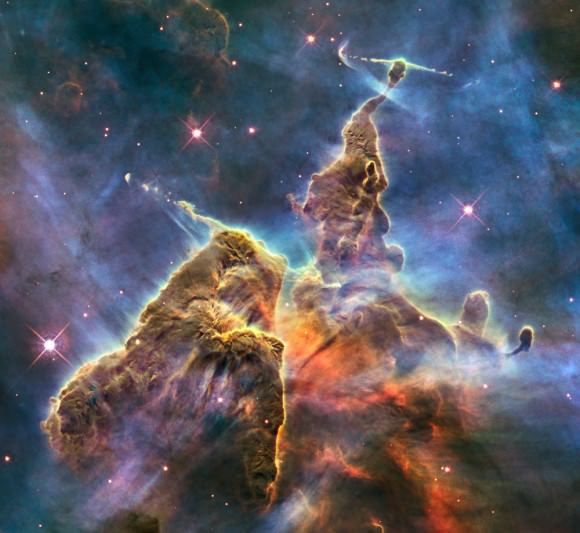
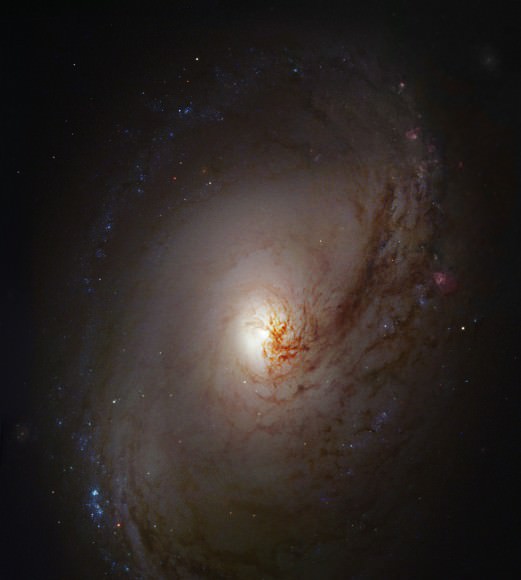
Its massive gravitational field warping space, the huge elliptical galaxy A2261-BCG, seems to have a diffuse halo of stars instead of a bright central galactic core. Image credit: NASA/ESA Hubble
Bloated far beyond the size of normal galaxies, one or more black holes may have puffed up an elliptical galaxy to a whopping size, according to astronomers. To their surprise, however, the black holes are missing.
Normally, scientists measure a concentrated peak of light surrounding the central black hole surrounded by a fuzzy halo of stars. Instead, astronomers, using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, find that the galaxy, known as A2261-BCG, is just a diffuse, bloated foggy patch of light. The intensity of starlight remains even across the entire galaxy. Past Hubble observations show supermassive black holes, each weighing billions of times more than our Sun, reside at the cores of nearly all galaxies.
“Expecting to find a black hole in every galaxy is sort of like expecting to find a pit inside a peach,” explained astronomer and co-author Tod Lauer in a press release. Lauer is with the National Optical Astronomy Observatory in Tucson, Ariz. “With this Hubble observation, we cut into the biggest peach and we can’t find the pit. We don’t know for sure that the black hole is not there, but Hubble shows that there’s no concentration of stars in the core.”
So where are the black holes?
Astronomers, in a paper that appeared in the September 10 issue of The Astrophysical Journal, have two ideas, both involving galactic billiards, for the galaxy’s puffy appearance. In one scenario, a pair of merging black holes gravitationally stir up then scatter the galaxy’s stars. In another, the merging black holes are ejected leaving the swarm of stars with no gravitational anchor allowing them to wander outward.
Galaxy cores tend to be sized proportionally to the wheeling expanse of the host galaxy. In the case of A2261-BCG, which spans about a million light-years (10 times that of our Milky Way Galaxy), the central region is three times larger than other very luminous galaxies, according to the paper. The monster galaxy is the most massive and brightest galaxy in the Abell 2261 galaxy cluster.
Team leader Marc Postman of the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Md., said in the press release that the galaxy stood out in the Hubble image. “When I first saw the image of this galaxy, I knew right away it was unusual,” Postman explained. “The core was very diffuse and very large. The challenge was then to make sense of all the data, given what we knew from previous Hubble observations, and come up with a plausible explanation for the intriguing nature of this particular galaxy.”
The team admits the ejected black-hole ideas sound far-fetched, “but that’s what makes observing the universe so intriguing — sometimes you find the unexpected,” said Postman.
As a follow-up, the team is searching for the sound of material falling into the black hole using the Very Large Array (VLA) radio telescope in New Mexico. Comparing the VLA data with Hubble images will allow the researchers to confirm the existence of a black hole and map its location.
Source: Hubblesite