[/caption]
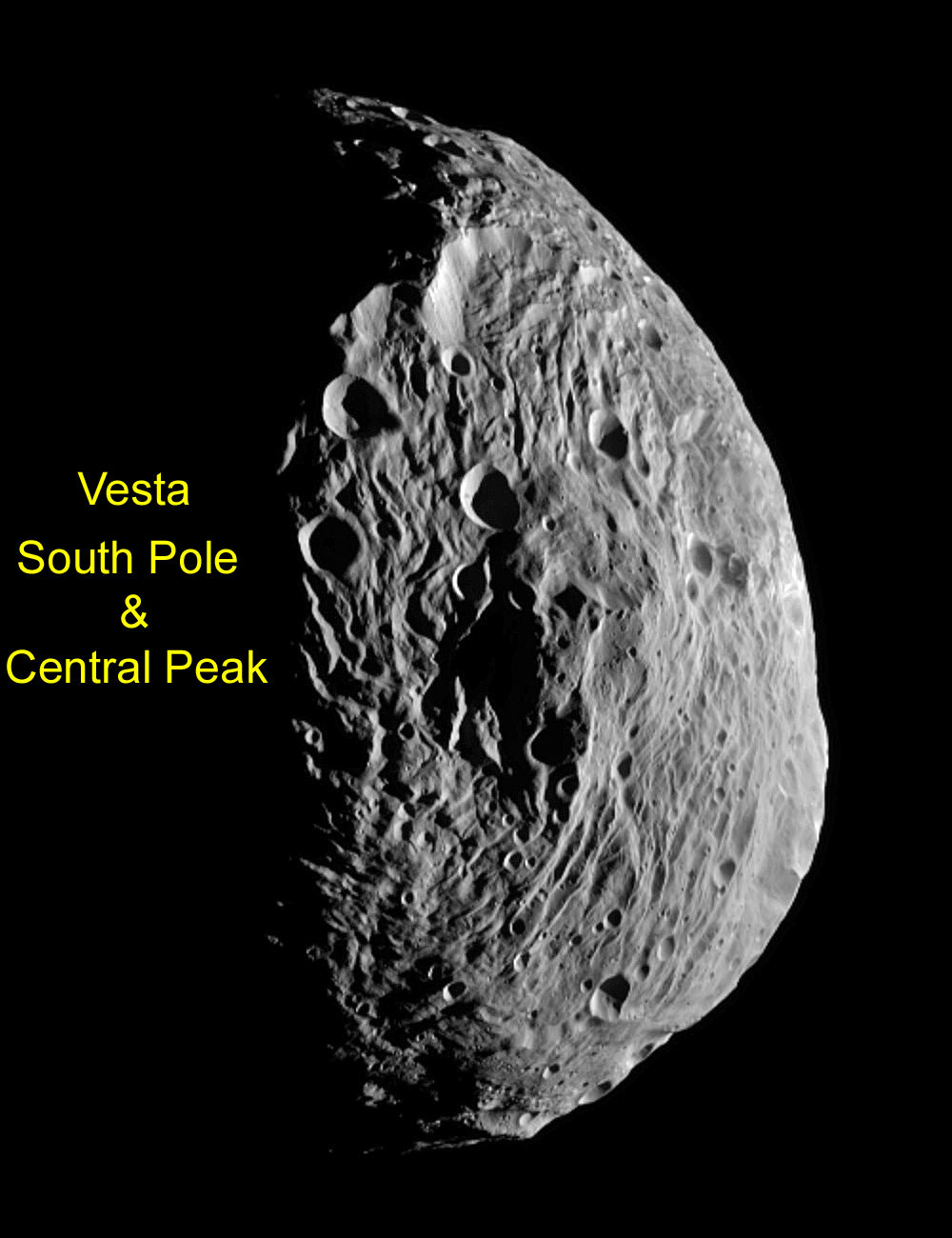
NASA’s Dawn Asteroid Orbiter is now spiraling down ever closer to the protoplanet Vesta – since arriving on July 16 – and capturing magnificent new high resolution images of the huge impact basin at the South Pole that dominates the surface. See enhanced image here.
The Dawn team just released a new image taken by the framing camera on July 18 as the orbiter flew from the day side to the night side at an altitude of 10,500 kilometers above Vesta, the second most massive body in the main Asteroid Belt between Mars and Jupiter.
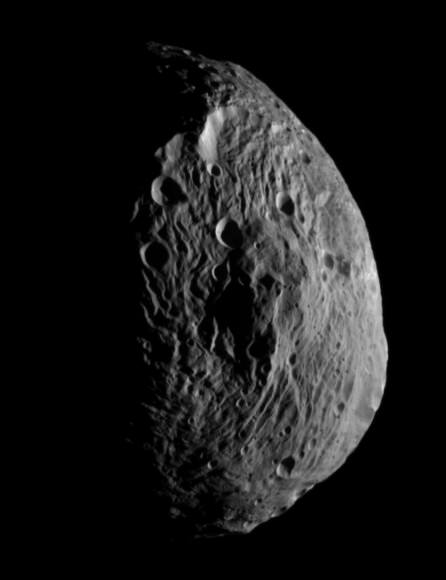

“I find this picture very dramatic !” exclaimed Dr. Marc Rayman, Dawn Chief Engineer from the NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., in an interview with Universe Today.
“Dawn acquired this image after it had flown past the terminator and its orbit began taking it over the night side of Vesta.”
“After having this view, the spacecraft resumed gradually spiraling around its new home, heading for survey orbit where it will begin intensive observations of Vesta,” Rayman told me.
Dawn will reach the initial science survey orbit in early August, approximately 1700 miles above the battered surface. Vesta turns on its axis once very five hours and 20 minutes.
Vesta suffered an enormous cosmic collision eons ago that apparently created a gigantic impact basin in the southern hemisphere and blasted enormous quantities of soil, rocks and dust into space. Some 5% of all meteorites found on Earth originate from Vesta.
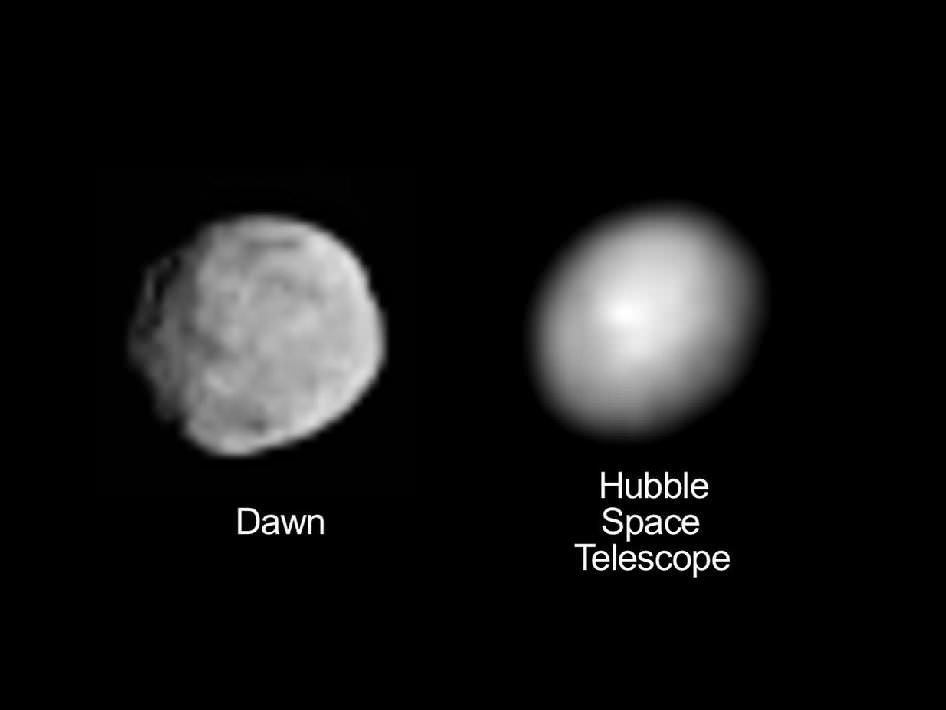
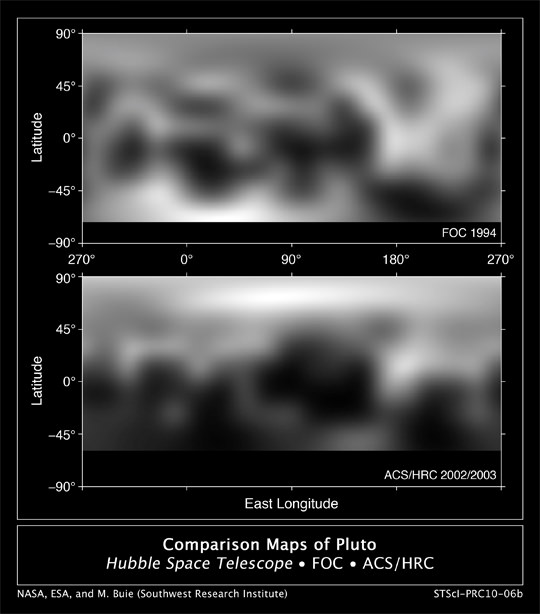
“The south pole region was declared to be a large impact basin after the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) data and images were obtained,” elaborated Prof. Chris Russell, Dawn Principal Investigator from UCLA.
“Now that we have higher resolution images we see that this region is unlike any other large impact on a small body but much of our experience here is on icy bodies of similar size,” Russell told me.
Dawn’s new images of Vesta taken at close range from just a few thousand miles away, now vastly exceed those taken by Hubble as it circled in Earth orbit hundreds of millions of miles away and may cause the science team to reevaluate some long held theories.
“The team is looking forward to obtaining higher resolution data over this region to look for confirmatory evidence for the impact hypothesis. They are not yet willing to vote for or against the HST interpretation. Needless to say the team got very excited by this image,” said Russell.
Dawn will orbit Vesta for one year before heading to its final destination, the Dwarf Planet Ceres.

Read my prior features about Dawn
First Ever Vesta Vistas from Orbit – in 2D and 3D
Dawn Exceeds Wildest Expectations as First Ever Spacecraft to Orbit a Protoplanet – Vesta
Dawn Closing in on Asteroid Vesta as Views Exceed Hubble
Dawn Begins Approach to Asteroid Vesta and Snaps First Images
Revolutionary Dawn Closing in on Asteroid Vesta with Opened Eyes