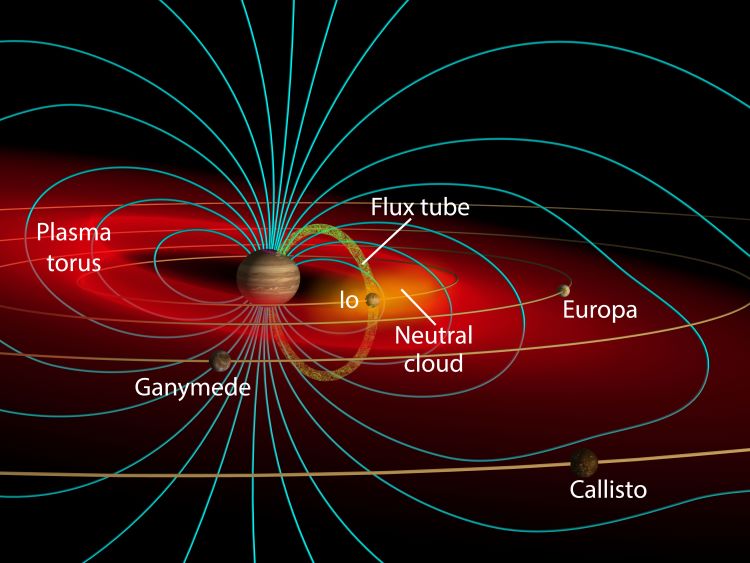
NASA’s Juno mission continues to orbit Jupiter, gathering data on its atmosphere, composition, gravitational field, magnetic field, and radiation environment. This data is helping scientists to learn more about the planet’s formation, internal structure, mass distribution, and what is driving its powerful winds. Periodically, the spacecraft also performs flybys of Jupiter’s largest satellites (the Galilean Moons), acquiring stunning images and vital data on their surfaces. These include optical and thermal images of Io’s many active volcanoes, Europa’s icy terrain, and infrared images of Ganymede.
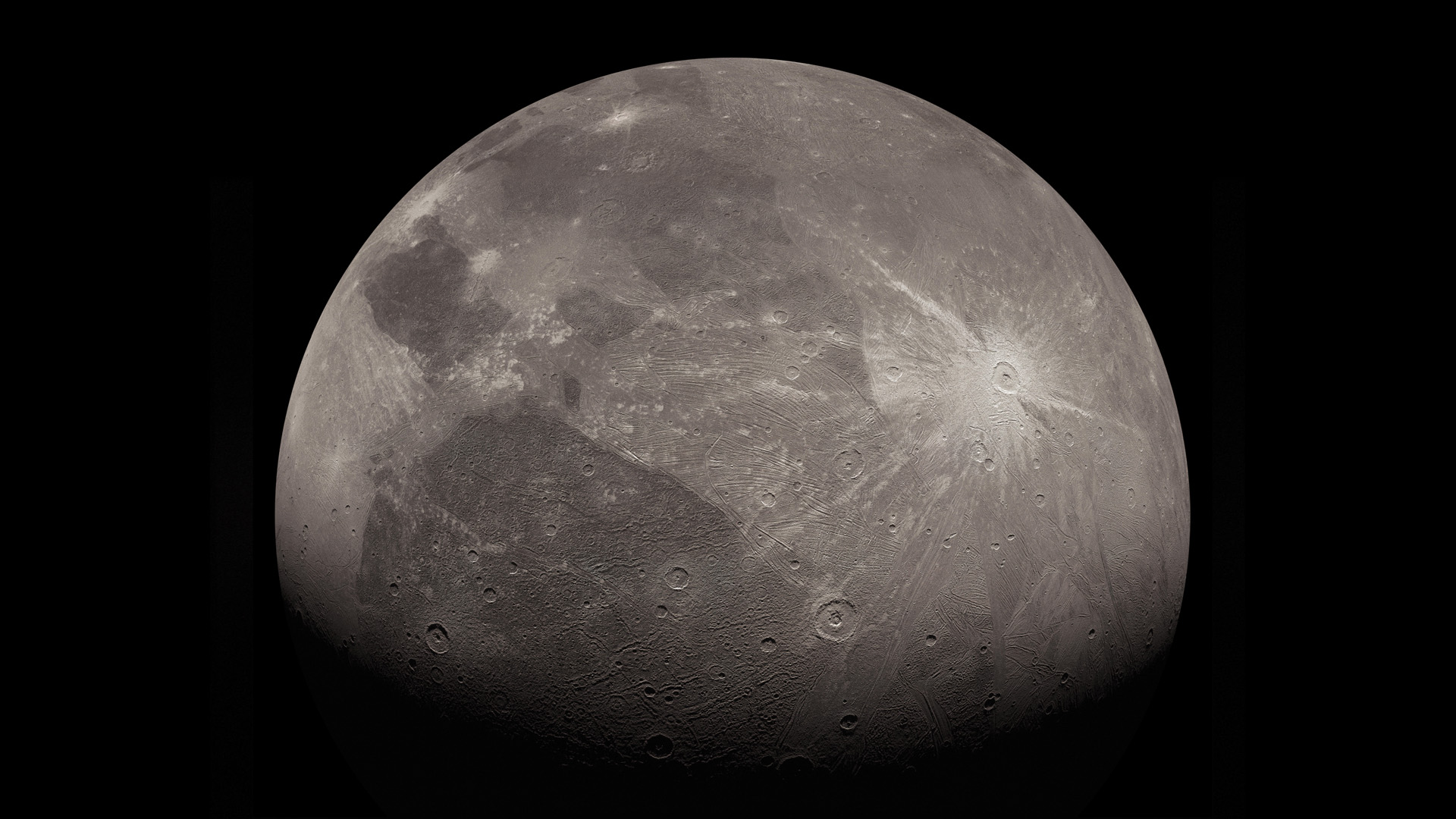
During its last flyby of Ganymede (June 7th, 2021), Juno collected infrared images and spectra on the moon’s surface using its Jovian InfraRed Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) instrument. According to a recent study by an international team of researchers, this data revealed the presence of salt minerals and organic molecules on the icy moon’s surface. The findings could help scientists better understand the origin of Ganymede, the composition of its interior ocean, and the way material is exchanged between the surface and interior. In short, it could help scientists determine if life exists deep inside Ganymede’s ocean.
Continue reading “Juno Spots Salts and Organic Molecules on Ganymede’s Surface”