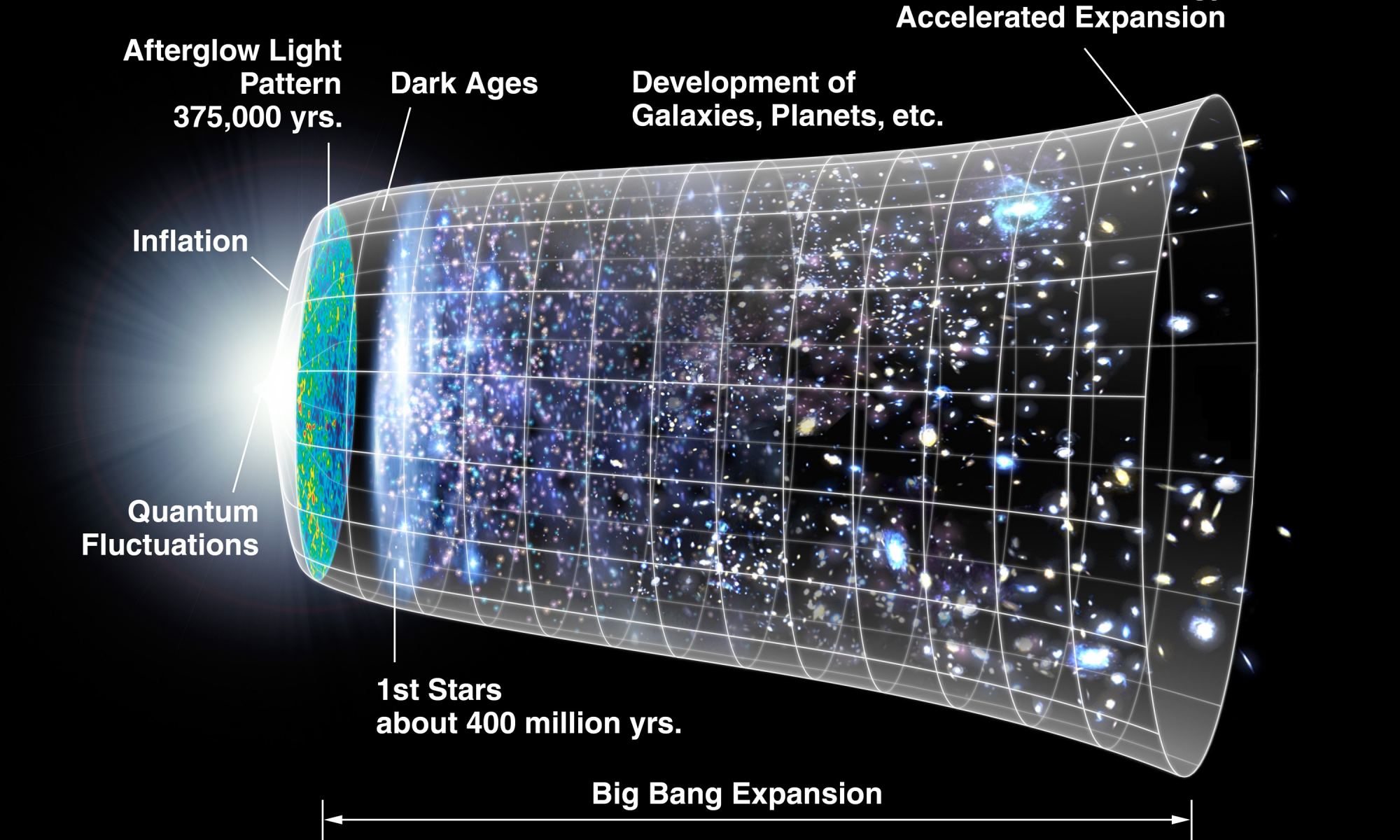
According to the most widely-accepted cosmological theories, the Universe began roughly 13.8 billion years ago in a massive explosion known as the Big Bang. Ever since then, the Universe has been in a constant state of expansion, what astrophysicists know as the Hubble Constant. For decades, astronomers have attempted to measure the rate of expansion, which has traditionally been done in two ways. One consists of measuring expansion locally using variable stars and supernovae, while the other involves cosmological models and redshift measurements of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB).
Unfortunately, these two methods have produced different values over the past decade, giving rise to what is known as the Hubble Tension. To resolve this discrepancy, astronomers believe that some additional force (like “Early Dark Energy“) may have been present during the early Universe that we haven’t accounted for yet. According to a team of particle physicists, the Hubble Tension could be resolved by a “New Early Dark Energy” (NEDE) in the early Universe. This energy, they argue, would have experienced a phase transition as the Universe began to expand, then disappeared.
Continue reading “Could a Dark Energy Phase Change Relieve the Hubble Tension?”