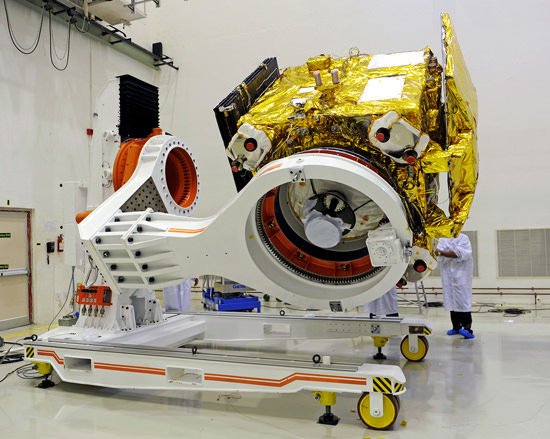
Two days out from her history making date with destiny, India’s Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) successfully completed a crucial test firing of the spacecraft’s main liquid engine to confirm its operational readiness for the critical Mars Orbital Insertion (MOI) engine firing on Wednesday morning Sept. 24 IST (Tuesday evening Sept. 23 EDT).
Engineers at the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) which designed and developed MOM successfully fired the probes 440 Newton Liquid Apogee Motor (LAM) earlier today, Sept. 22, 2014, for a duration of 3.968 seconds at 1430 hrs IST (Indian Standard Time), according to today’s announcement from ISRO.
“We had a perfect burn for four seconds as programmed. MOM will now go-ahead with the nominal plan for Mars Orbital Insertion,” said ISRO.
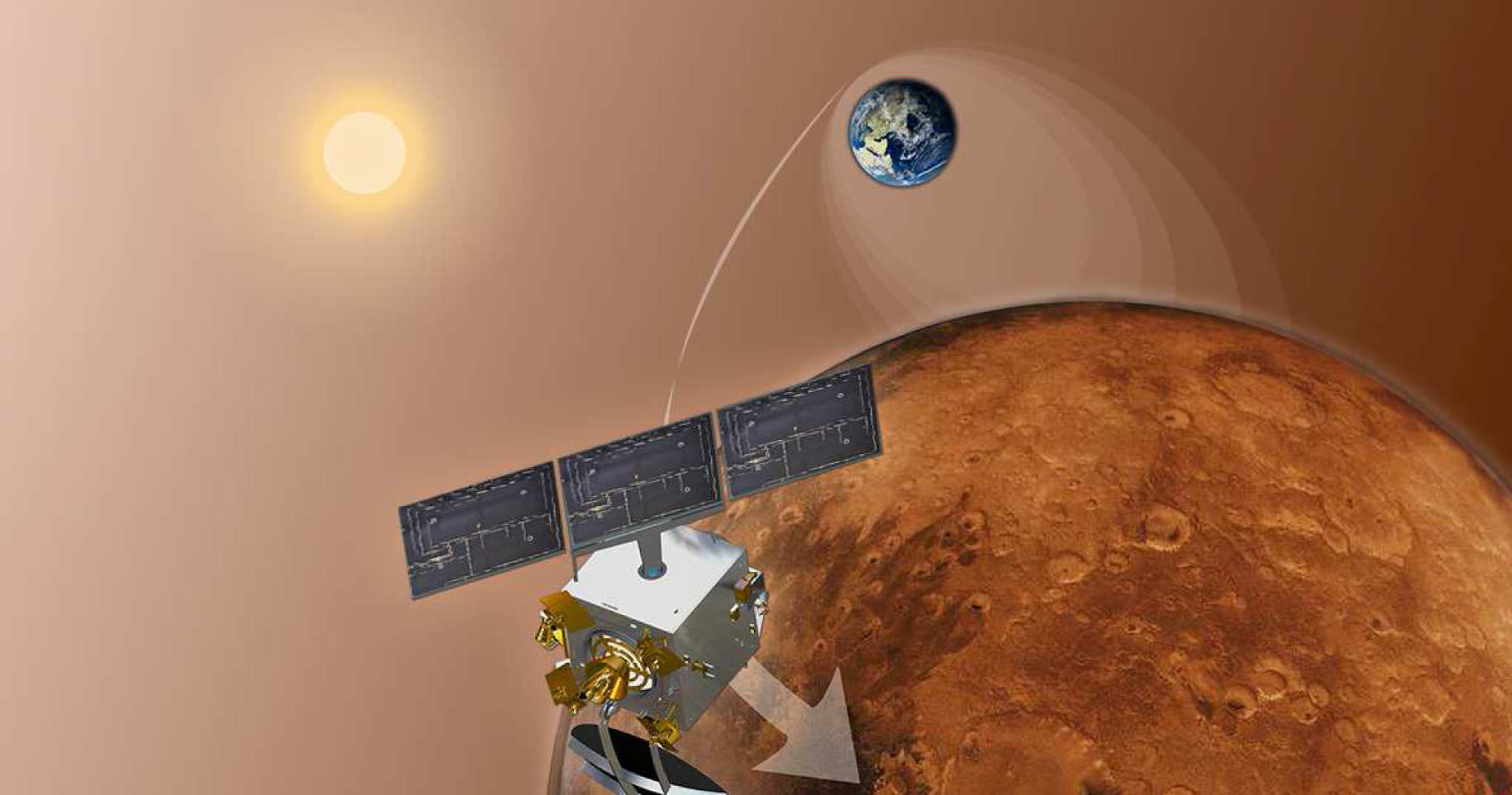
MOM counts as India’s first interplanetary voyager and the nation’s first manmade object to orbit the 4th rock from our Sun – if all goes well.
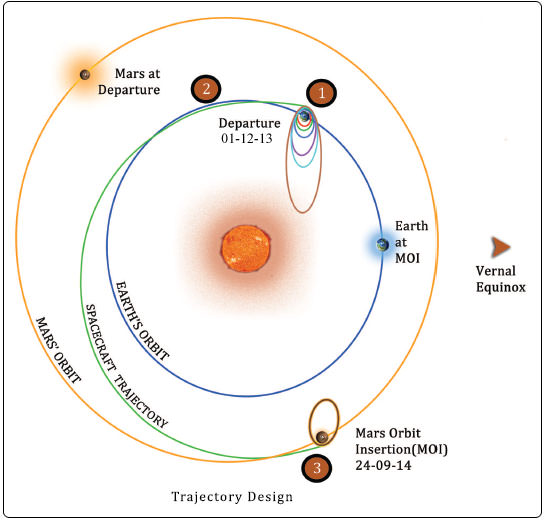
The LAM was last fired over nine months ago on December 01, 2013 to inject MOM into a ten month long interplanetary Trans Mars Trajectory.
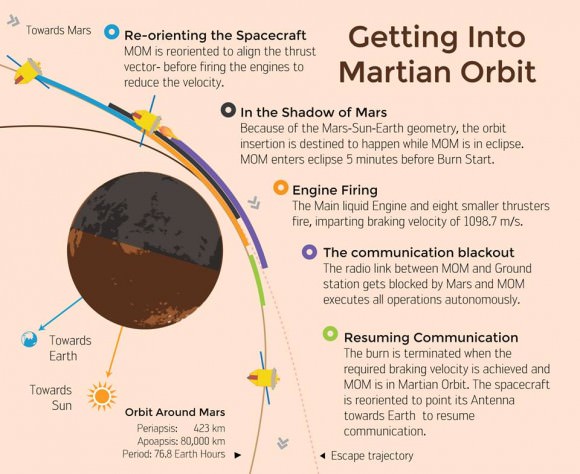
Today’s operation verified that LAM is fully operational to perform the do-or-die MOI braking burn on Sept. 24 targeted for 07:17:32 hrs IST (Sept. 23, 9:47:32 p.m. EDT) that will place the probe into a highly elliptical 377 km x 80,000 km orbit around the Red Planet.
You can watch all the action live on ISRO’s website during the streaming webcast starting at 6:45 IST (9:15 p.m. EDT): http://www.isro.org/
The burn was also marks the spacecraft’s final Trajectory Correction Maneuver known as TCM-4 and changed its velocity by 2.18 meters/second.
“The trajectory has been corrected,” said ISRO.
The $69 Million probe is being continuously monitored by the Indian Deep Space Network (IDSN) and NASA JPL’s Deep Space Network (DSN) to maintain its course.
ISRO space engineers are taking care to precisely navigate MOM to keep it on course during its long heliocentric trajectory from Earth to Mars through a series of in flight Trajectory Correction Maneuvers (TCMs).
The last TCM was successfully performed on June 11 by firing the spacecraft’s 22 Newton thrusters for a duration of 16 seconds. TCM-1 was conducted on December 11, 2013 by firing the 22 Newton Thrusters for 40.5 seconds.
Engineers determined that a TCM planned for August was not needed.
On “D-Day” as ISRO calls it, the LAM and the eight smaller 22 Newton liquid fueled engines are scheduled to fire for a duration of about 24 minutes.
The MOI braking burn will be carried out fully autonomously since MOM will be eclipsed by Mars due to the Sun-Earth-Mars geometry about five minutes prior to initiation of the engine firing.
Round trip radio signals communicating with MOM now take some 21 minutes.
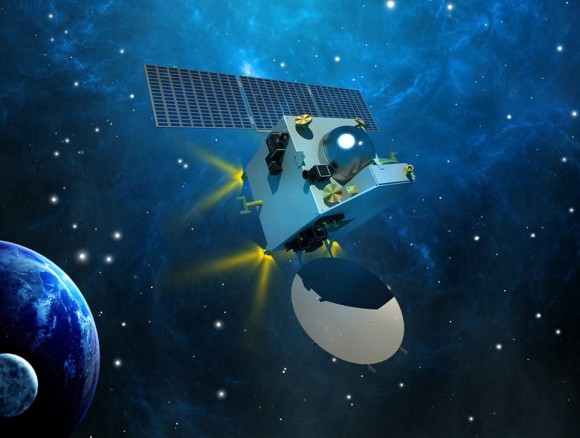
The 1,350 kilogram (2,980 pound) probe has been streaking through space for over ten months.
MOM follows hot on the heels of NASA’s MAVEN spacecraft which successfully achieved Red Planet orbit less than a day ago on Sunday, Sept. 22, 2014.
“We wish a successful MOI for MOM,” said Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN principal investigator with the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics at the University of Colorado, Boulder (CU/LASP) at MAVEN’s post MOI briefing earlier today.
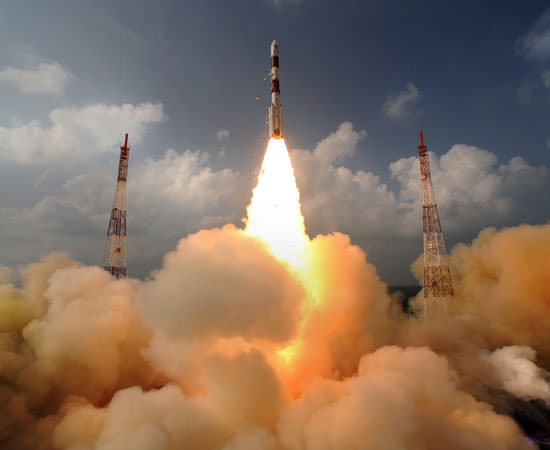
MOM was launched on Nov. 5, 2013 from India’s spaceport at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, atop the nation’s indigenous four stage Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) which placed the probe into its initial Earth parking orbit.
Watch this cool animation showing the interplanetary path of MOM and MAVEN from Earth to Mars sent to me be an appreciative reader – Sankaranarayanan K V:
Although MOM’s main objective is a demonstration of technological capabilities, she will also study the planet’s atmosphere and surface.
The probe is equipped with five indigenous instruments to conduct meaningful science – including a tri-color imager (MCC) and a methane gas sniffer (MSM) to study the Red Planet’s atmosphere, morphology, mineralogy and surface features. Methane on Earth originates from both geological and biological sources – and could be a potential marker for the existence of Martian microbes.
Both MAVEN’s and MOM’s goal is to study the Martian atmosphere , unlock the mysteries of its current atmosphere and determine how, why and when the atmosphere and liquid water was lost – and how this transformed Mars’ climate into its cold, desiccated state of today.
If all goes well, India will join an elite club of only four who have launched probes that successfully investigated the Red Planet from orbit or the surface – following the Soviet Union, the United States and the European Space Agency (ESA).
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing MOM, MAVEN, Rosetta, Opportunity, Curiosity, Mars rover and more Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.