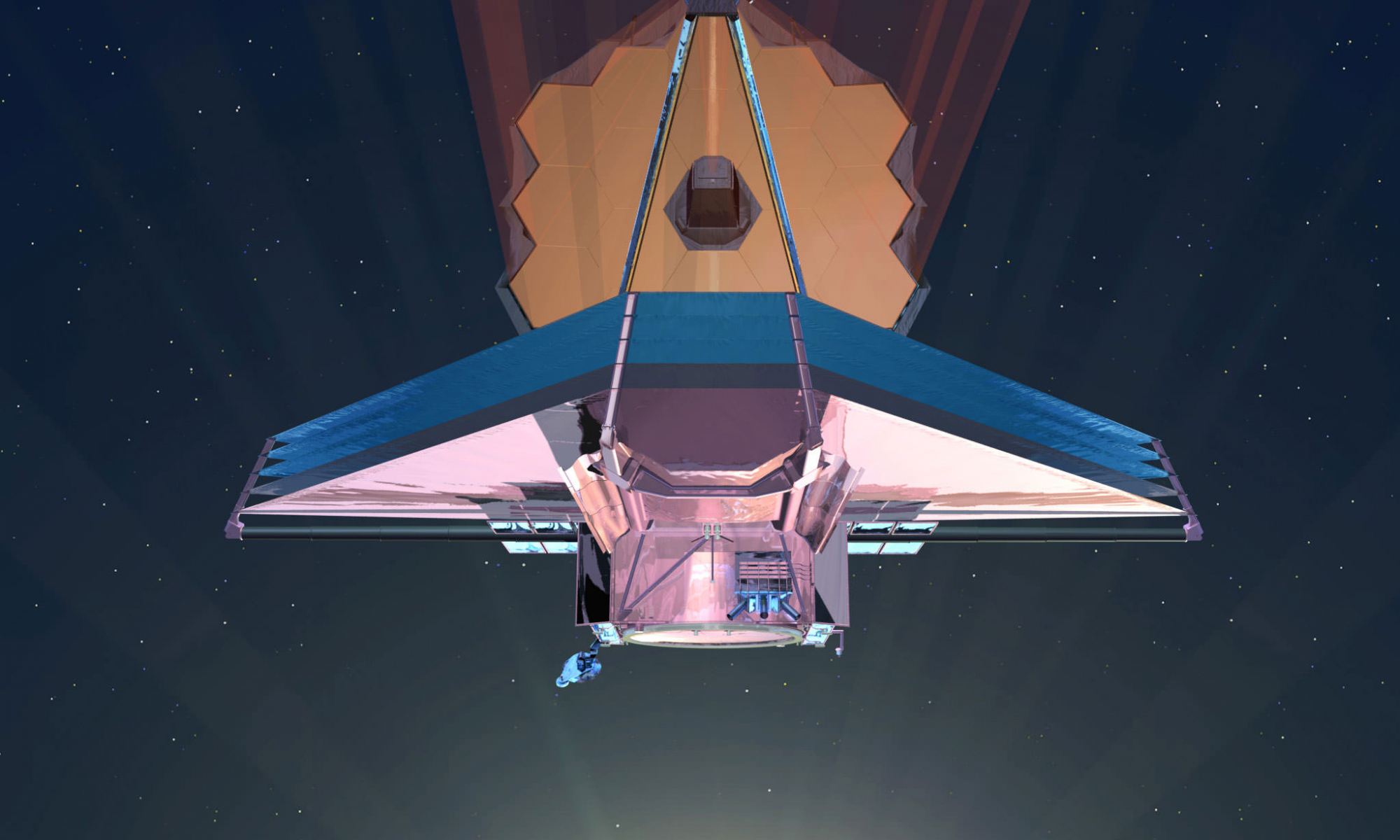
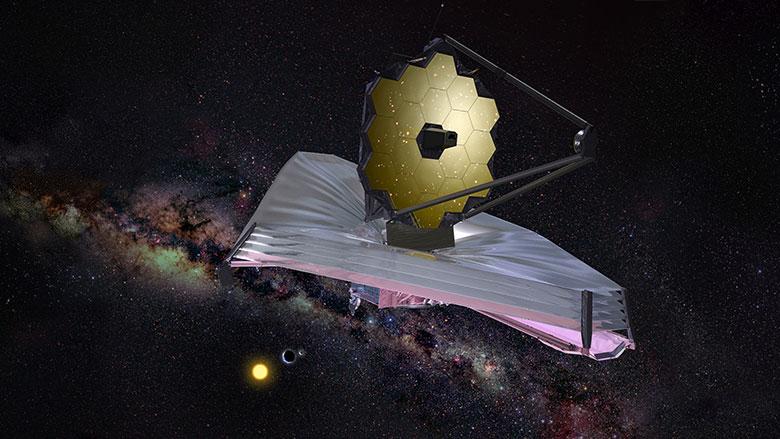
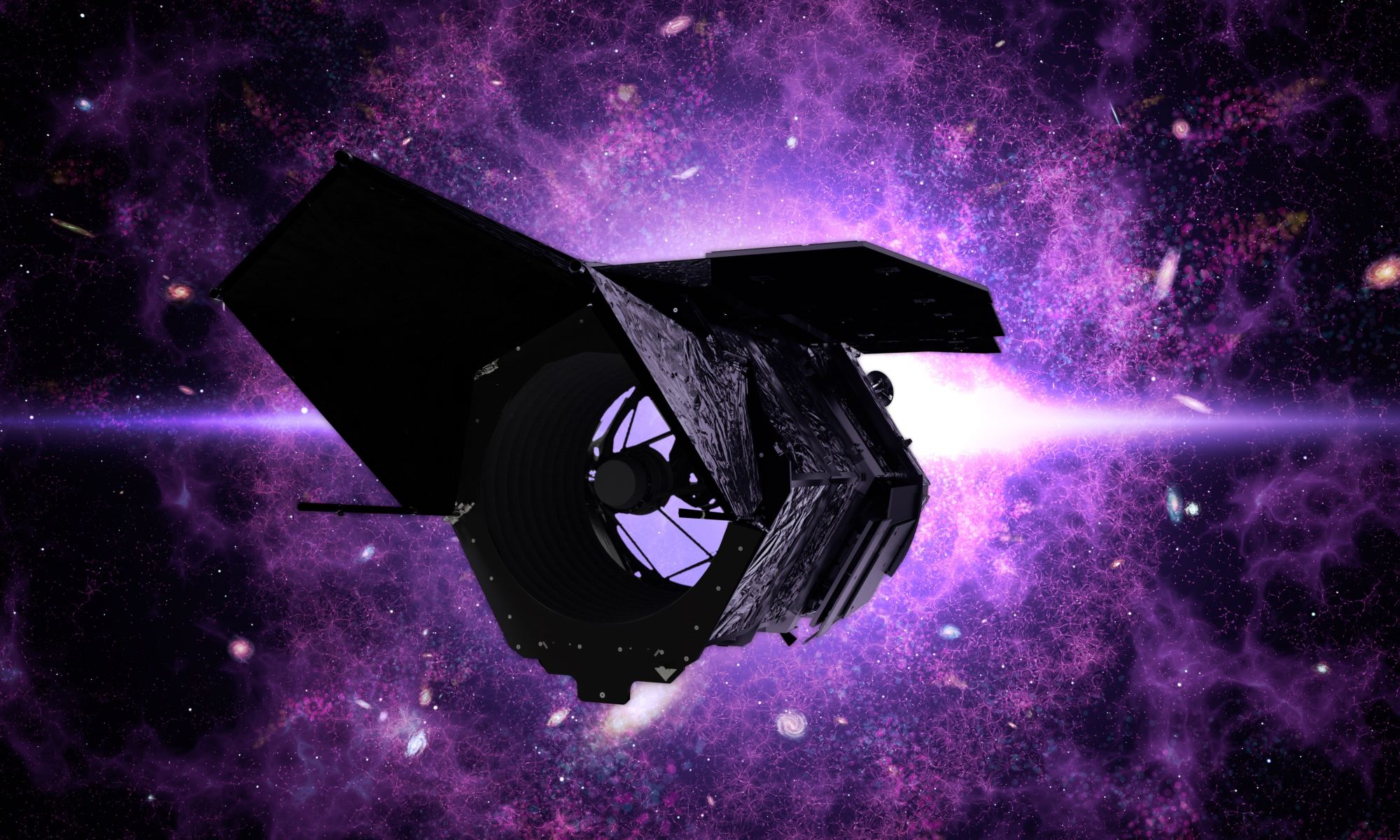
In November (or early December) of this year, after many excruciating delays, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) will finally launch to space. As the most advanced and complex observatory ever deployed, the James Webb will use its advanced suite of instruments to observe stars, exoplanets, and galaxies in the near and mid-infrared spectrum. In the process, it will address some of the most enduring mysteries about the nature of the Universe.
When the time comes, the James Webb will fly aboard an Ariane 5 rocket from the European Space Agency (ESA) launch facility near the town of Korou, French Guayana. Overnight on August 17th, 2021, the upper stage of that Ariane 5 began making its way in its cargo container from the ArianeGroup facility in Bremen, Germany, to Neustadt port, where it will board a ship bound for the ESA spaceport in French Guiana.
Continue reading “James Webb’s Upper Stage is off to the Launch Site”