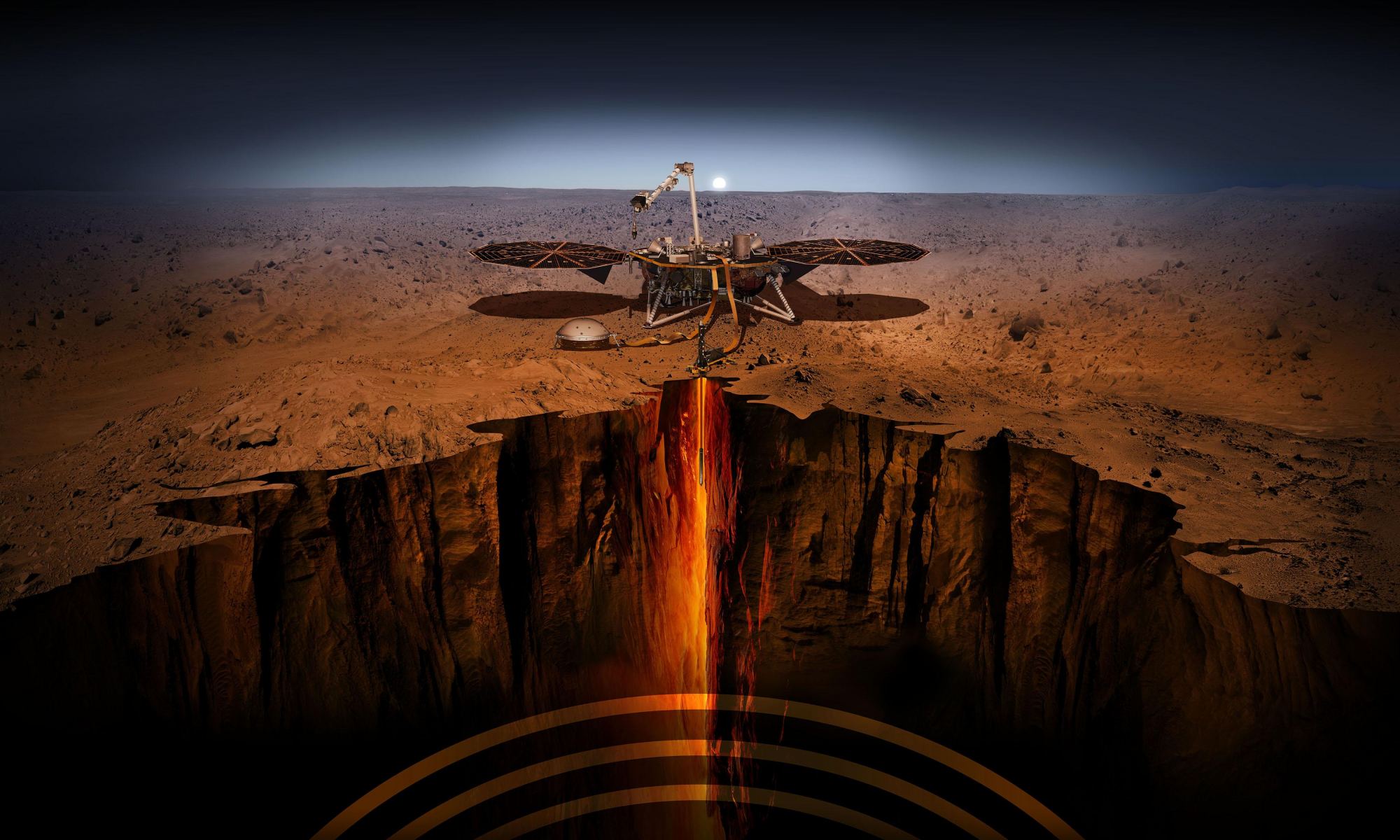
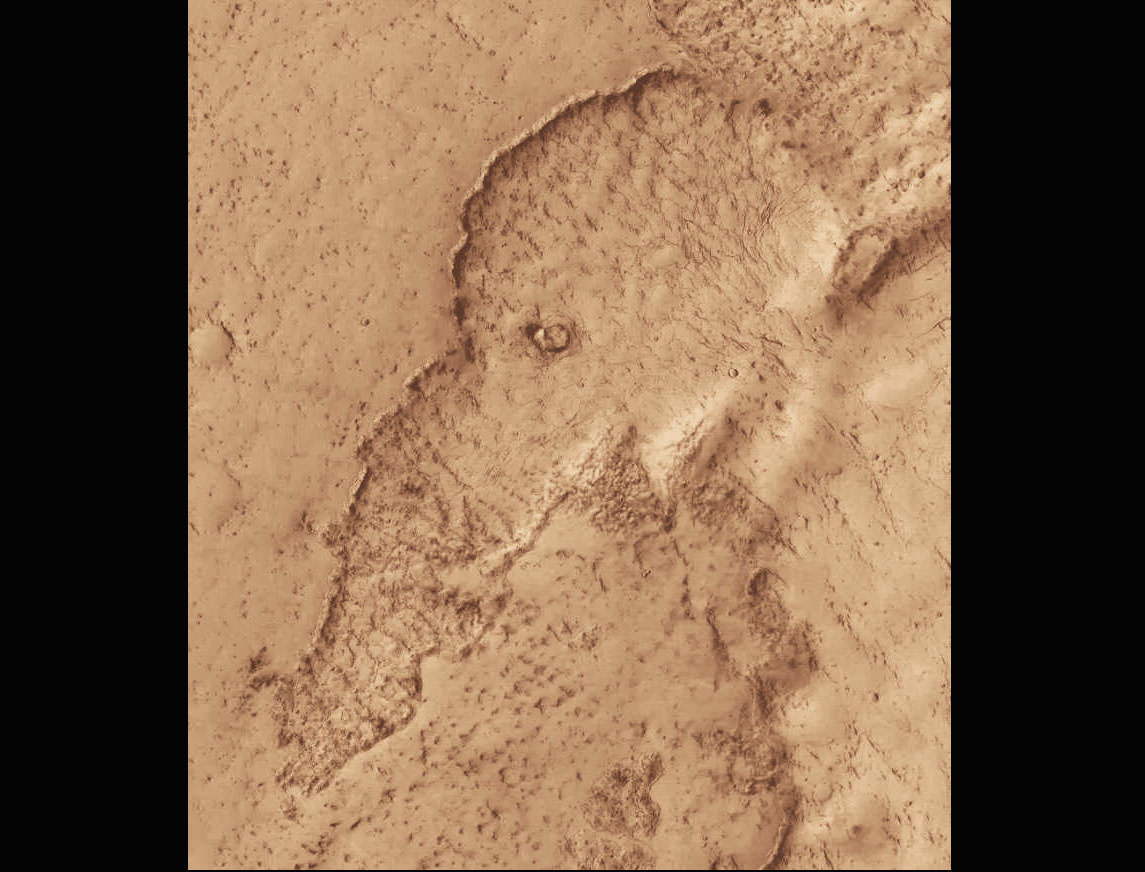
Billions of years ago, Mars was a much different place than it is today. Its atmosphere was thicker and warmer, liquid water flowed on its surface, and the planet was geologically active. Due to its lower gravity, this activity led to the largest volcanoes in the Solar System (Olympus Mons and the Thetis Mons region) and the longest, deepest canyon in the world (Valles Marineris). Unfortunately, Mars’ interior began to cool rapidly, its inner core solidified, and geological activity largely stopped. For some time, geologists have believed that Mars was essentially “dead” in the geological sense.
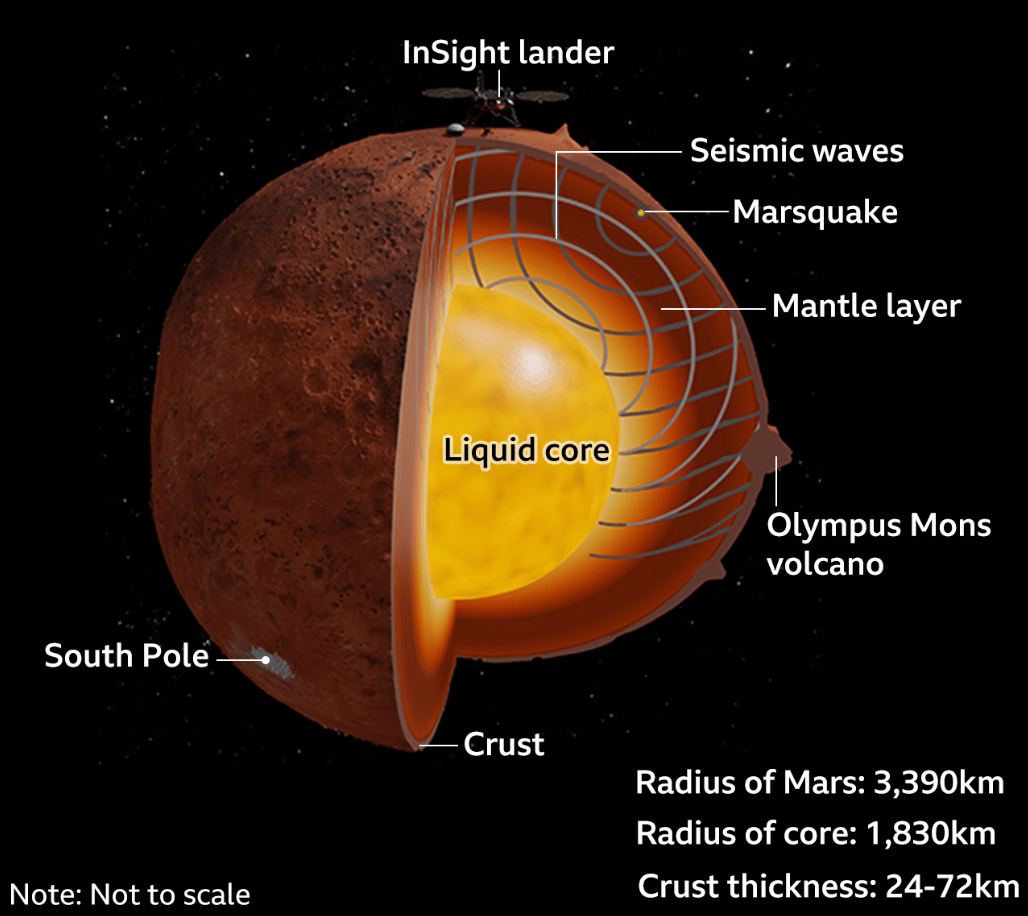
However, recent studies have provided seismic and geophysical evidence that Mars may still be “slightly alive.” In a recent study, scientists from the University of Arizona (ASU) challenged conventional views of Martian geodynamic evolution by discovering evidence of an active mantle plume pushing its way through the crust, causing earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. Combined with some serious marsquakes recorded by NASA’s InSight lander, these finding suggests that there is still some powerful volcanic action beneath the surface of Mars.
Continue reading “There's a Giant Magma Plume on Mars, Bulging the Surface out Across a Vast Region”