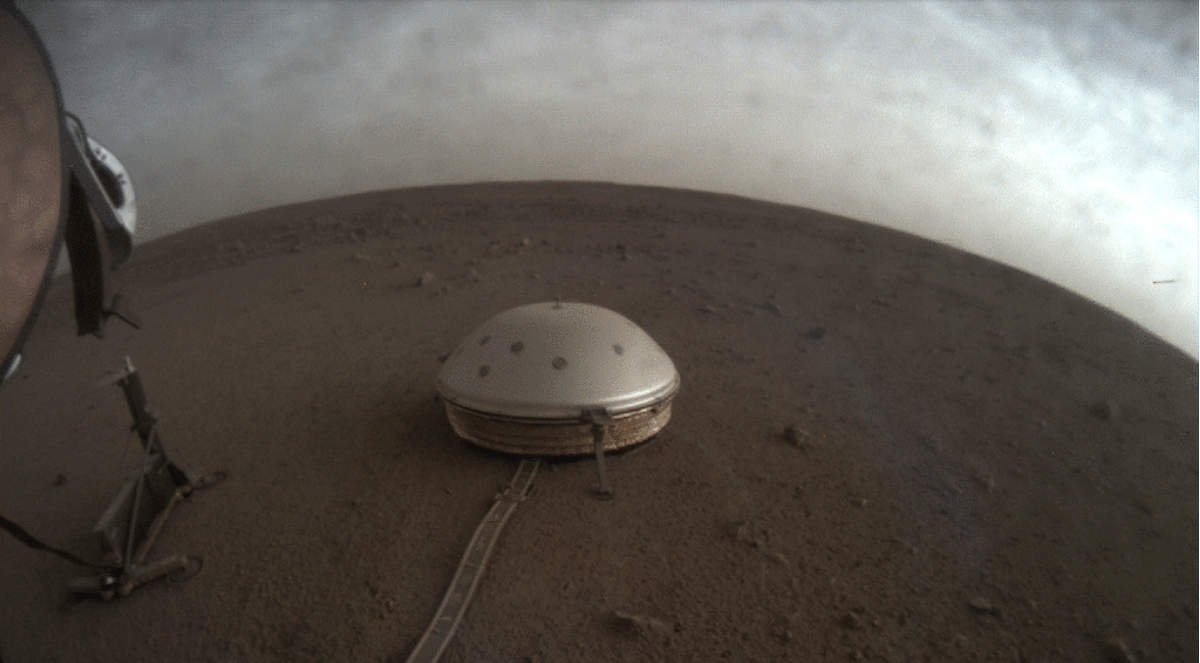
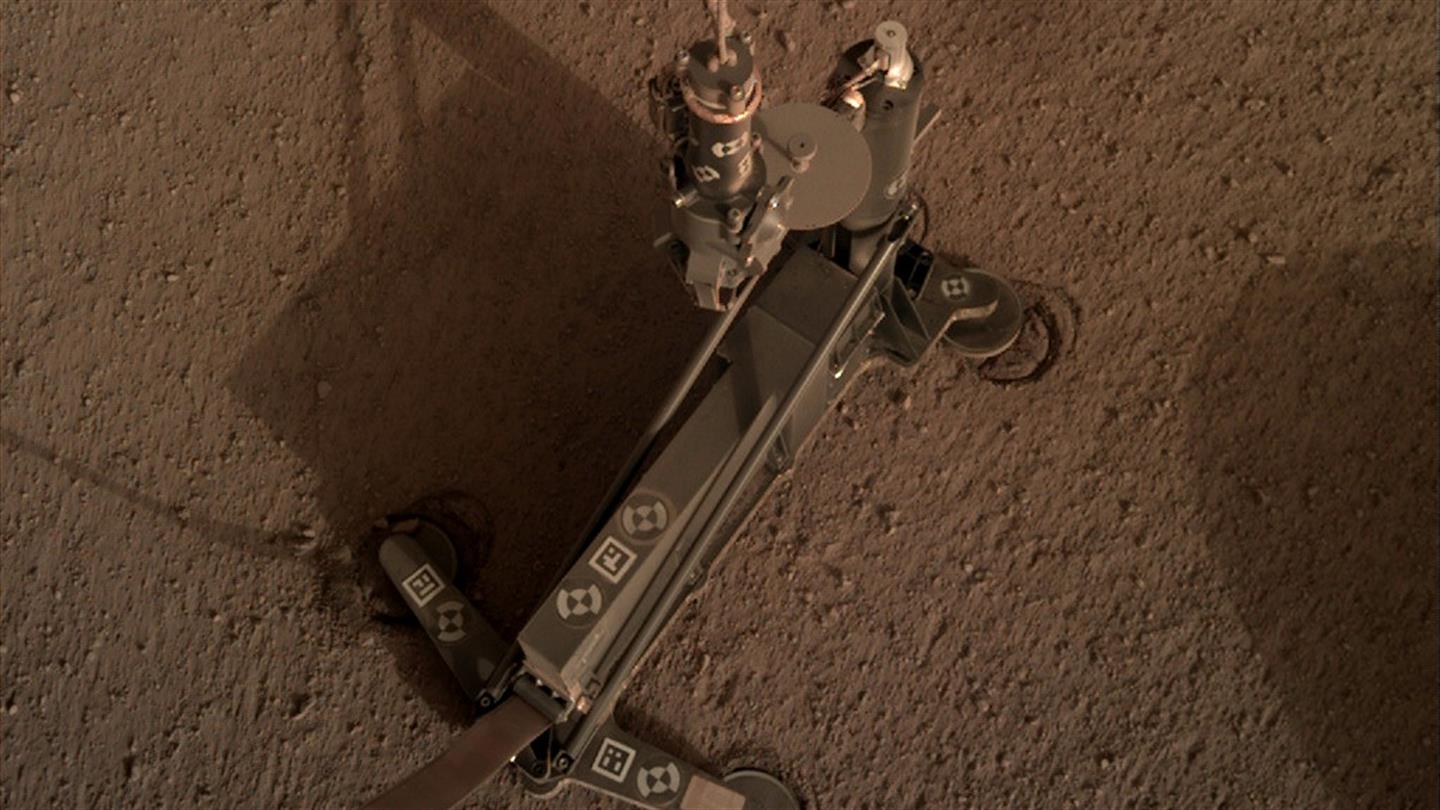
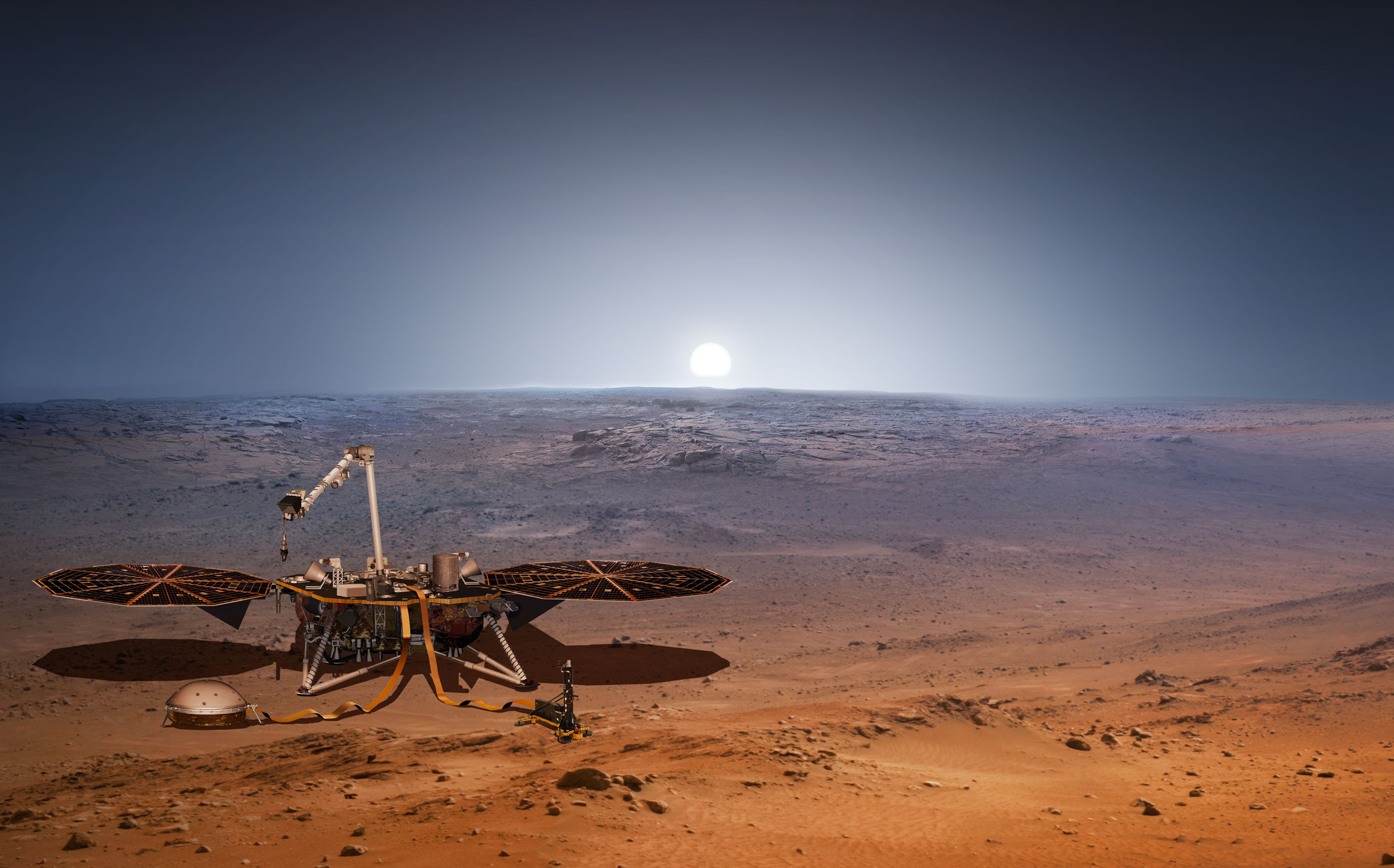
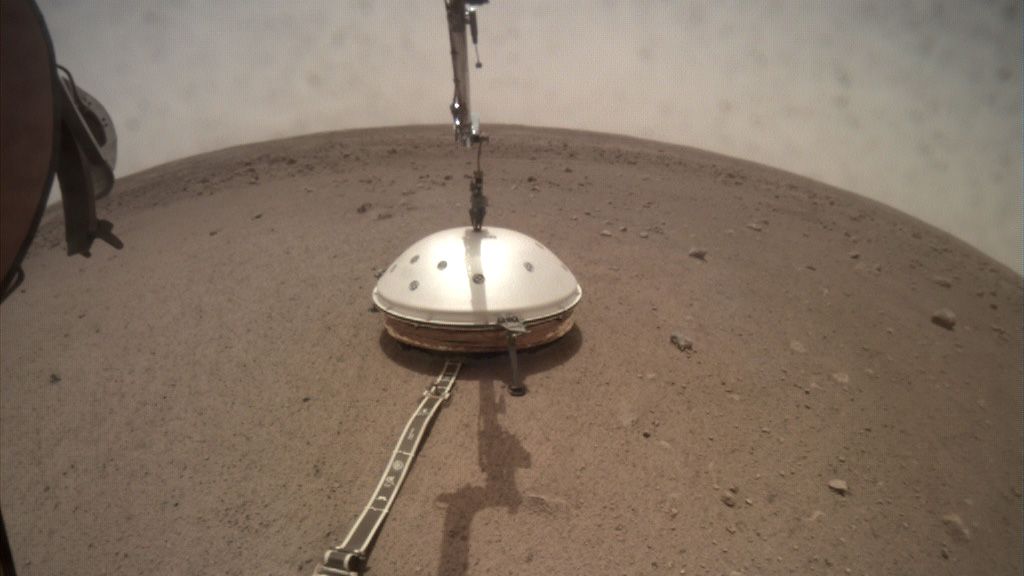
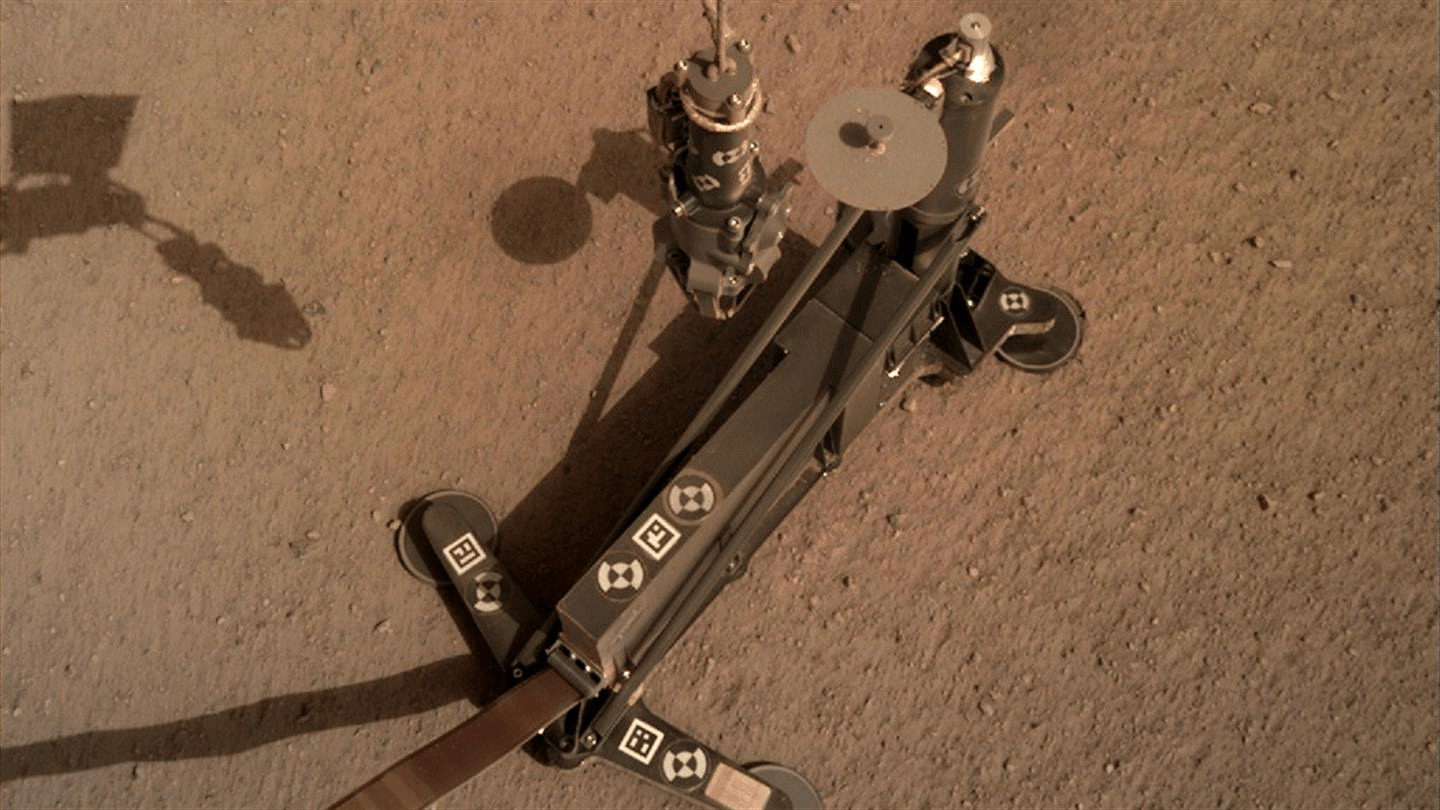
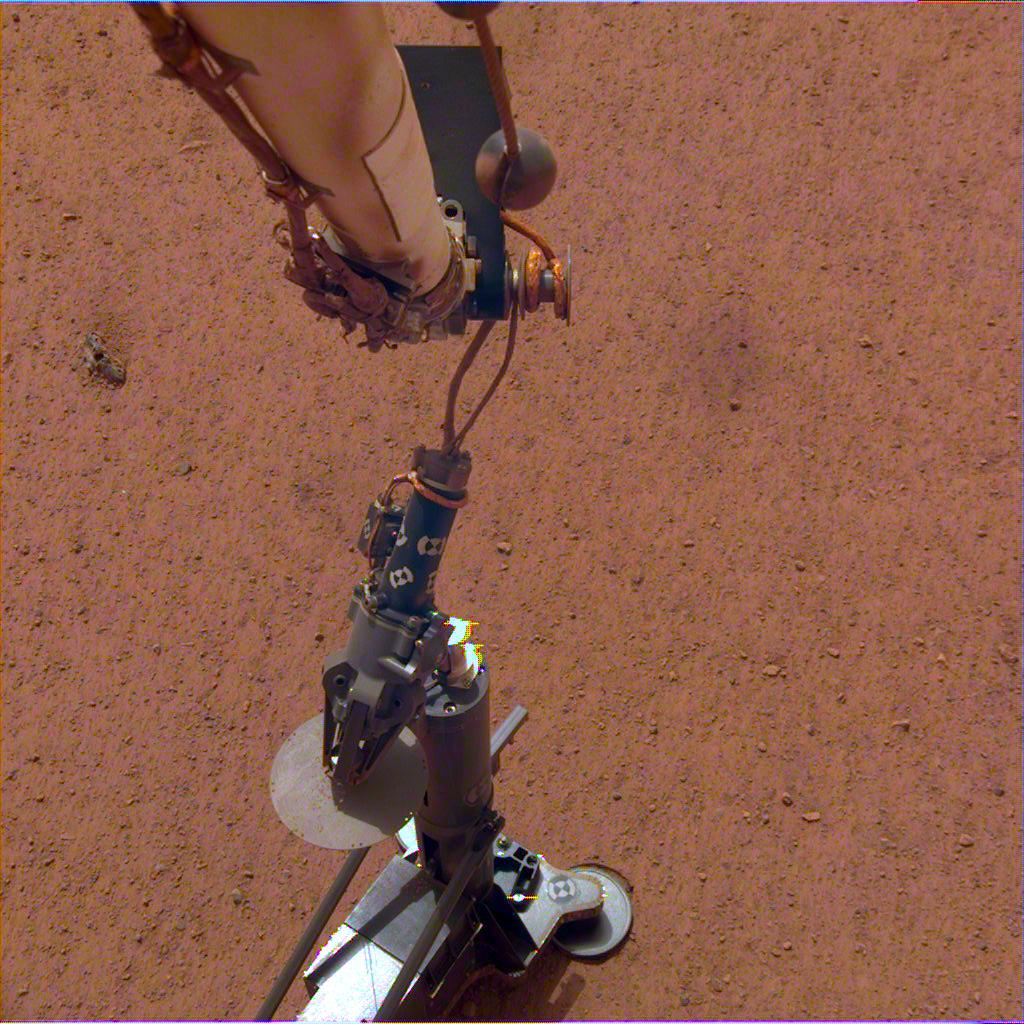
The SEIS (Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure) instrument on NASA’s InSight lander has sensed 21 Marsquakes since it was deployed on December 19th, 2018. It actually sensed over 100 events to date, but only 21 of them have been identified as Marsquakes. SEIS is extremely sensitive so mission scientists expected these results.
SEIS is a key part of InSight, NASA’s mission to understand the interior of Mars. Along with other instruments, it’ll help scientists understand what’s going on inside Mars.
Continue reading “InSight Has Already Detected 21 Marsquakes”