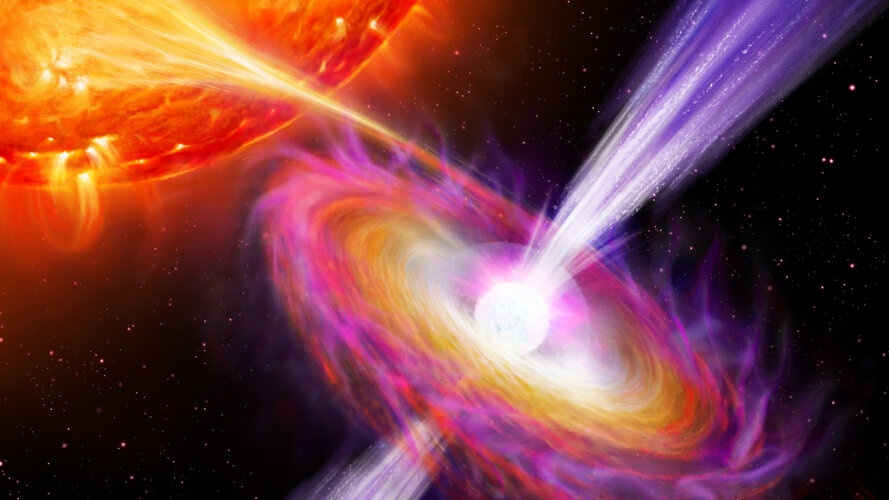
It’s a well known fact that black holes absorb anything that falls into them. Often before material ‘vanishes’ inside it forms into an accretion disk around them. Like the progenitor stars, the black holes have powerful magnetic fields and these can generate jets that blast away from the black hole. A similar process occurs in neutron stars that are orbiting other stars and recent observations holes have shown that some material in the jets travel at speeds 35-40% the speed of light.
Continue reading “Neutron Stars are Jetting Material Away at 40% the Speed of Light”Rapidly Spinning Black Hole is Spitting Out Blobs of Plasma
Black holes, those beguiling singularities that sit on the precipice of the known and the unknown, keep surprising us with their behaviour. As organizations like the Event Horizon Telescope have made clear, there’s a lot we don’t know about the holes, and worse than that, we don’t even know how much we don’t know.
Now scientists have observed a new phenomenon that adds to the black hole mystique: a rapidly spinning black hole that ejects massive blobs of plasma.
Continue reading “Rapidly Spinning Black Hole is Spitting Out Blobs of Plasma”Astronomers See A Dead Star Come Back To Life Thanks To A Donor Star
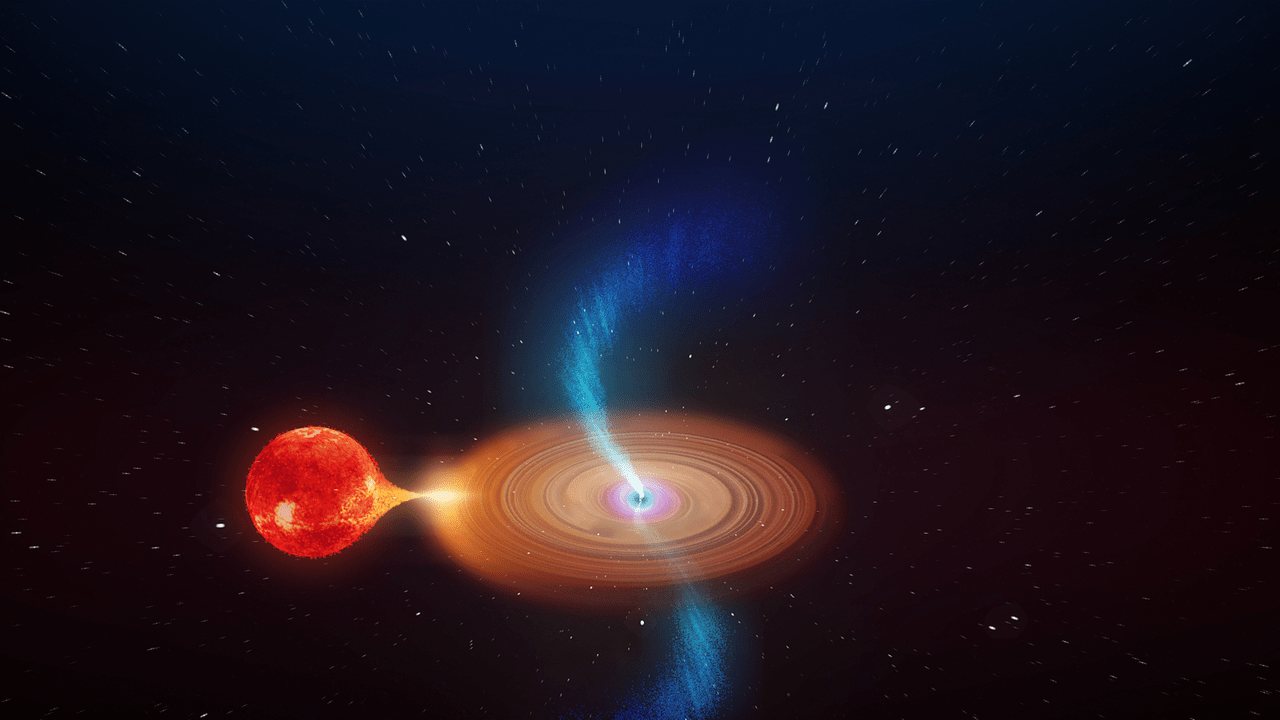
It’s not exactly an organ donor, but a star in the direction of the hyper-populated core of the Milky Way donating some of its mass to a dormant neighbor. The result? The dormant neighbor sprung back to life with an X-ray burst captured by the ESA‘s INTEGRAL (INTErnational Gamma-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory) space observatory.
“INTEGRAL caught a unique moment in the birth of a rare binary system” – Enrico Bozzo, University of Geneva.
The neighbors have likely been paired together for billions of years, which is not in itself noteworthy: stars often live in binary pairs. But the pair spotted by INTEGRAL on August 13th 2017 is very unusual. The donor star is a red giant, and the recipient is a neutron star. So far, astronomers only know of 10 of these pairs, called ‘symbiotic X-ray binaries’.
To understand what’s happening between these neighbors, we have to look at stellar evolution.
The donor star is in its red giant phase. That’s when a star in the same mass range as our star reaches the later stage of its life. As its mass is depleted, gravity can’t hold the star together in the same way it has for the early part of its life. The star expands outwards by millions of kilometers. As it does so, it sheds stellar material from its outer layers in a solar wind that travels several hundreds of km/sec.
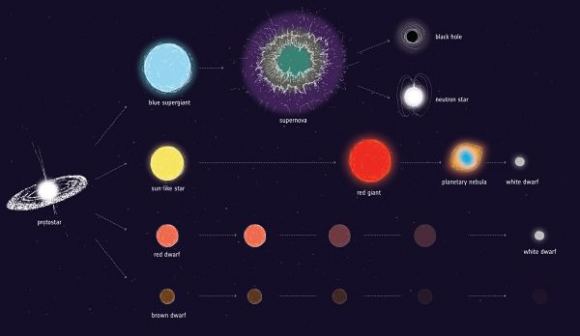
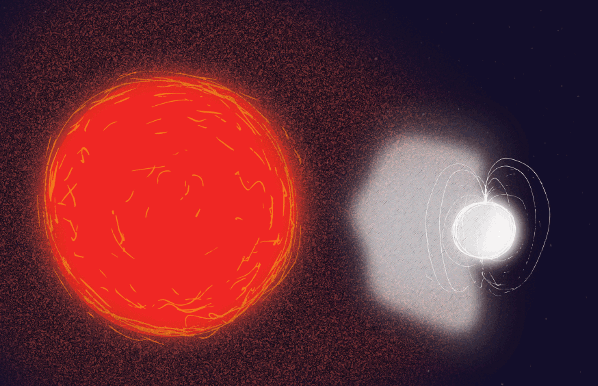
Its neighbor is in a different state. It’s a star that had an initial mass of about 25 to 30 times the Sun. When a star this big approaches the end of its life, it suffers a different fate. Stars this large live fast, and burn through their fuel quickly. Then, they explode as supernovae, in this case leaving a corpse behind. In the binary system captured by INTEGRAL, the corpse is a spinning neutron star with a magnetic field.
Neutron stars are dense. In fact, they’re some of the densest stellar objects we know of, packing as much mass as one-and-a-half of our Suns into an object that’s only about 10 km across.
When the red giant’s stellar wind met the neutron star, the neutron star slowed its rate of spin, and burst into life, emitting high-energy x-rays.
“INTEGRAL caught a unique moment in the birth of a rare binary system,” says Enrico Bozzo from University of Geneva and lead author of the paper that describes the discovery. “The red giant released a sufficiently dense slow wind to feed its neutron star companion, giving rise to high-energy emission from the dead stellar core for the first time.”
After INTEGRAL spotted the x-ray burst from the binary, other observations quickly followed. The ESA’s XMM Newton and NASA’s NuSTAR and Swift space telescopes got to work, along with ground-based telescopes. These observations confirmed what initial observations showed: this is a very peculiar pair of stars.
“…we believe we saw the X-rays turning on for the first time.” – Erik Kuulkers, ESA INTEGRAL Project Scientist.
The neutron star spins very slowly, taking about 2 hours to revolve, which is remarkable since other neutron stars can spin many times per second. The magnetic field of the neutron star was also much stronger than expected. But the magnetic field around a neutron star is thought to weaken over time, making this a relatively young neutron star. And a red giant is old, so this is a very odd pairing of old red giant with young neutron star.
One possible explanation is that the neutron star didn’t form from a supernova, but from a white dwarf. In that scenario, the white dwarf would’ve collapsed into a neutron star after a very long period of feeding on material from the red giant. That would explain the disparity in ages of the two stars in the system.

“These objects are puzzling,” says Enrico. “It might be that either the neutron star magnetic field does not decay substantially with time after all, or the neutron star actually formed later in the history of the binary system. That would mean it collapsed from a white dwarf into a neutron star as a result of feeding off the red giant over a long time, rather than becoming a neutron star as a result of a more traditional supernova explosion of a short-lived massive star.”
The next question is how long will this process go on? Is it short-lived, or the beginning of a long-term relationship?
“We haven’t seen this object before in the past 15 years of our observations with INTEGRAL, so we believe we saw the X-rays turning on for the first time,” says Erik Kuulkers, ESA’s INTEGRAL project scientist. “We’ll continue to watch how it behaves in case it is just a long ‘burp’ of winds, but so far we haven’t seen any significant changes.”
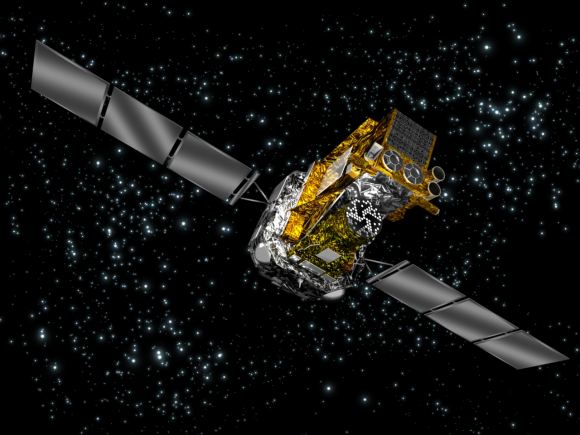
The INTEGRAL space observatory was launched in 2002 to study some of the most energetic phenomena in the universe. It focuses on things like black holes, neutron stars, active galactic nuclei and supernovae. INTEGRAL is a European Space Agency mission in cooperation with the United States and Russia. Its projected end date is December, 2018.