NASA keeps a close eye on the bacteria inhabiting the International Space Station with a program called the Microbial Observatory (M.O.) The ISS is home to a variety of microbes, some of which pose a threat to the health of astronauts. As part of their monitoring, the M.O. has discovered antibiotic resistant bacteria on the toilet seat on the ISS.
Continue reading “Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria has been Found on the Space Station’s Toilet”
This is What Icebergs Look Like at the End of Their Lives. This One’s 18 Years Old
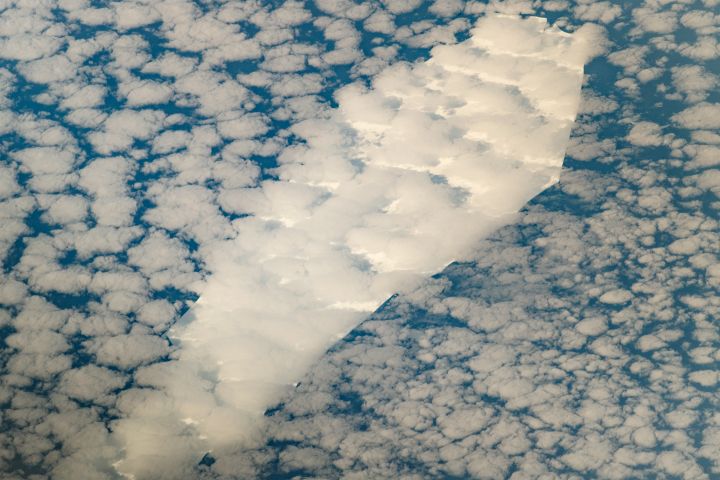

Nothing lasts forever, especially an iceberg drifting away from its frigid home. This coffin-shaped iceberg was spotted by astronauts on the International Space Station as it drifted northwards. It split off from a much larger iceberg about 18 years ago, and is moving into warmer and warmer waters.
Soyuz Launch Carrying Two Astronauts is Forced to Abort, Landing Safely Back on Earth
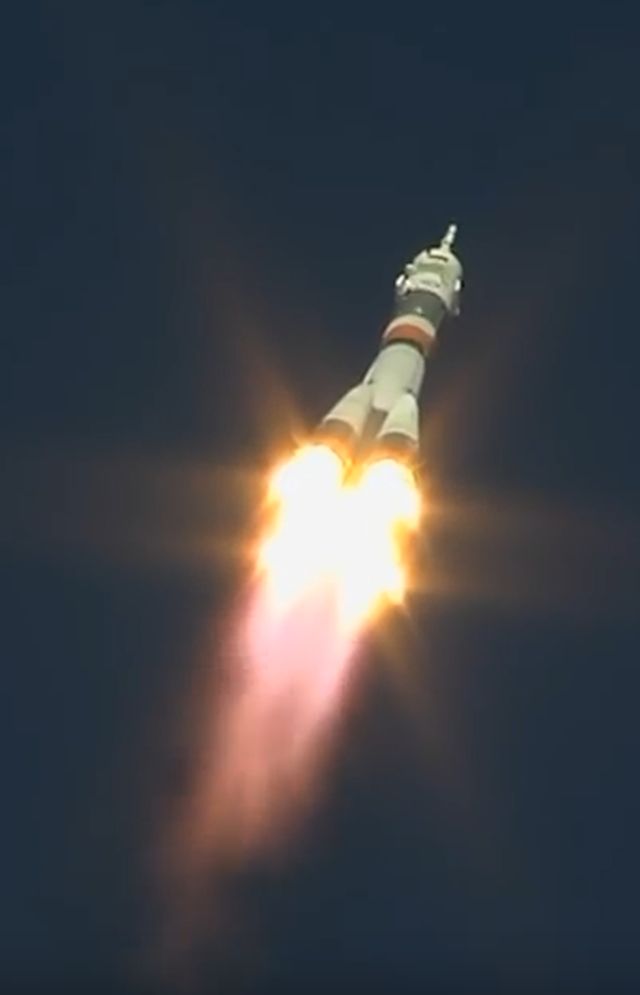

The Soyuz MS-10 spacecraft carrying crew to the ISS was aborted shortly after launch on Thursday, Oct. 11th when its booster failed. The spacecraft executed an emergency ballistic landing with a sharp angle of descent. Both crew members on board—American astronaut Nick Hague and Russian cosmonaut Alexey Ovchinin—exited the capsule safely and are in good condition.
Stare Down from Space into the Churning Maw of Hurricane Florence
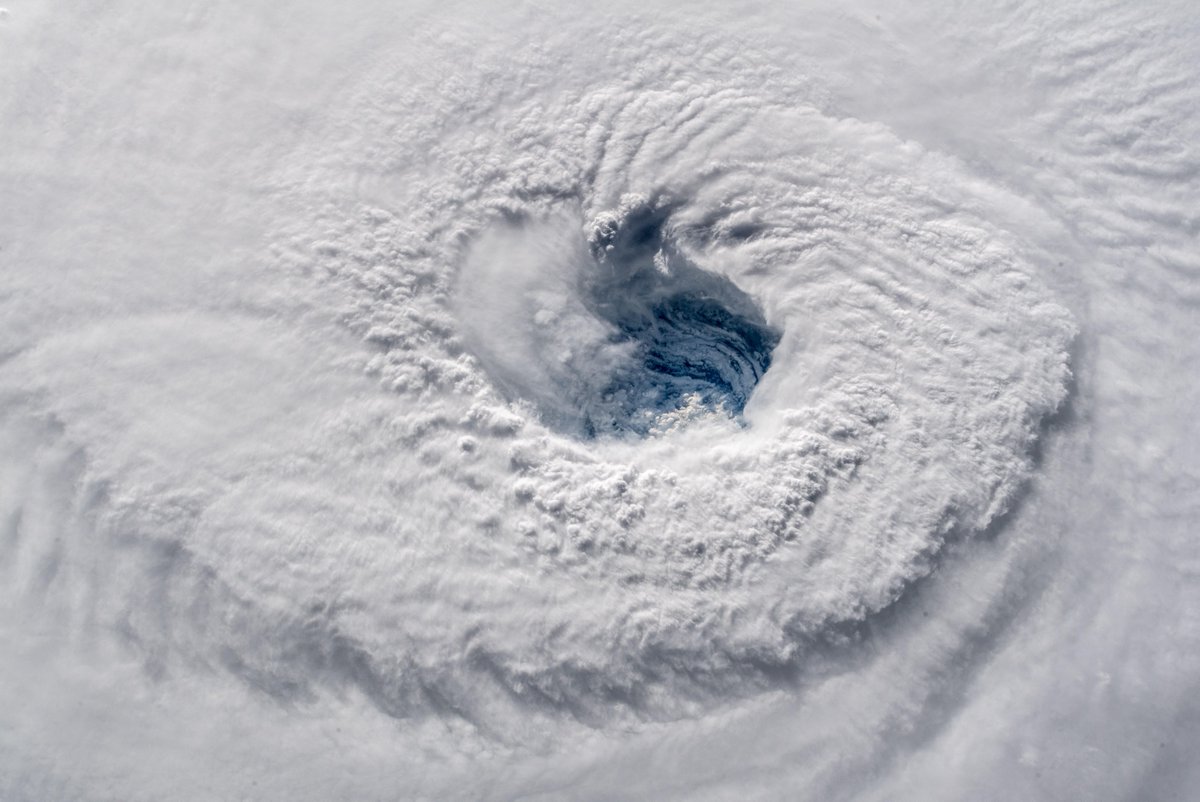

Even if you know nothing about hurricanes, an unavoidable sense of doom and destruction overtakes you when you look at this image of Hurricane Florence as it moves inexorably toward North and South Carolina.
Even if you didn’t know that the powerful storm is forecast to gain strength as it hits the coast on Friday, or that it will dump several months of rain onto the region in a mere few days, or that the storm surge could reach as high as 9 to 13 ft. If you didn’t know all those things, the picture of Florence taken from space would still fill you with foreboding.
Continue reading “Stare Down from Space into the Churning Maw of Hurricane Florence”
7% of Scott Kelly’s Genes Changed After a Year in Space

On March 1st, 2016, American astronaut Scott Kelly returned to Earth after spending a total of 340 days aboard the International Space Station (ISS). As part of NASA’s goal to send astronauts on long-duration space flights to Mars and beyond, this record-setting stay in space was designed to test the limit of human endurance in a microgravity environment.
Also known as the Twin Study, this experiment consisted of Kelly spending nearly a year in space while his identical twin (Mark Kelly) remained on Earth. Since Kelly’s return, the two have been subjected to medical tests to see what long-term effects microgravity has had of Scott’s Kelly’s physique. The final results of this test, which were just released, reveal that Scott has experienced changes at the genetic level.
The study was conducted by NASA’s Human Research Program, and the preliminary findings were released at their Investigator’s Workshop on the week of January 23rd, 2017. According to these findings, Scott Kelly showed indications of inflammation, changes in his telomeres and telomerase (parts of the chromosonal system related to aging), a decrease in bone density and gastrointestinal changes – all of which were expected.

As NASA reported in their preliminary findings:
“By measuring large numbers of metabolites, cytokines, and proteins, researchers learned that spaceflight is associated with oxygen deprivation stress, increased inflammation, and dramatic nutrient shifts that affect gene expression… After returning to Earth, Scott started the process of readapting to Earth’s gravity. Most of the biological changes he experienced in space quickly returned to nearly his preflight status. Some changes returned to baseline within hours or days of landing, while a few persisted after six months.”
At the same time, the study took into account possible genomic and cognitive changes between the two brothers. These findings were recently clarified by NASA, which indicated that 93% of Scott Kelly’s genes returned to normal after he returned to Earth while the remaining 7% points were missing. These were attributed to “longer-term changes in genes related to his immune system, DNA repair, bone formation networks, hypoxia, and hypercapnia.”
In other words, in addition to the well-documented effects of microgravity – such as muscle atrophy, bone density loss and loss of eyesight – Scott Kelly also experienced health effect caused by a deficiency in the amount of oxygen that was able to make it to his tissues, an excess of CO2 in his tissues, and long-term effects in how his body is able to maintain and repair itself.
At the same time, the report indicated that Scott Kelly experienced no significant changes when it came to cognitive performance. The preliminary findings touched on this, indicating that Scott showed a slight decrease in speed and accuracy when undergoing cognitive performance testing compared to his brother. This decrease was more pronounced when he first landed, but was attributed to readjustment to Earth’s gravity.
Mathias Basner – a professor at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who was in charge of conducting the tests – also found no real difference in cognition between 6 month and 12 month missions. This is especially important since typical stays aboard the ISS last six months, whereas long term missions to Mars would take 150-300 days – depending on the alignment of the planets and the speed of the spacecraft.
A two way trip to Mars, as well as the time spent in Mars lower-gravity environment (37.6 % that of Earth’s), could take multiple years. As such, the Twin Study was intrinsic to NASA’s efforts to prepare for its proposed “Journey to Mars“, which is expected to take place sometime in the 2030s. These and other studies being conducted aboard the ISS seek to determine what the long-term effects on astronaut health will be, and how they can be mitigated.
The NASA Twin Study was the result of a partnership between 10 individual investigations, 12 colleges and universities, NASA’s biomedical labs and the National Space Biomedical Research Institute Consortium.
Scott Kelly’s stay in space and the Twin Study will also be the subject of a PBS documentary titled “Beyond a Year in Space“. Be sure to check out the teaser trailer here:
Further Reading: MLive
Astronaut Scott Tingle Was Able To Control A Ground-Based Robot… From Space.
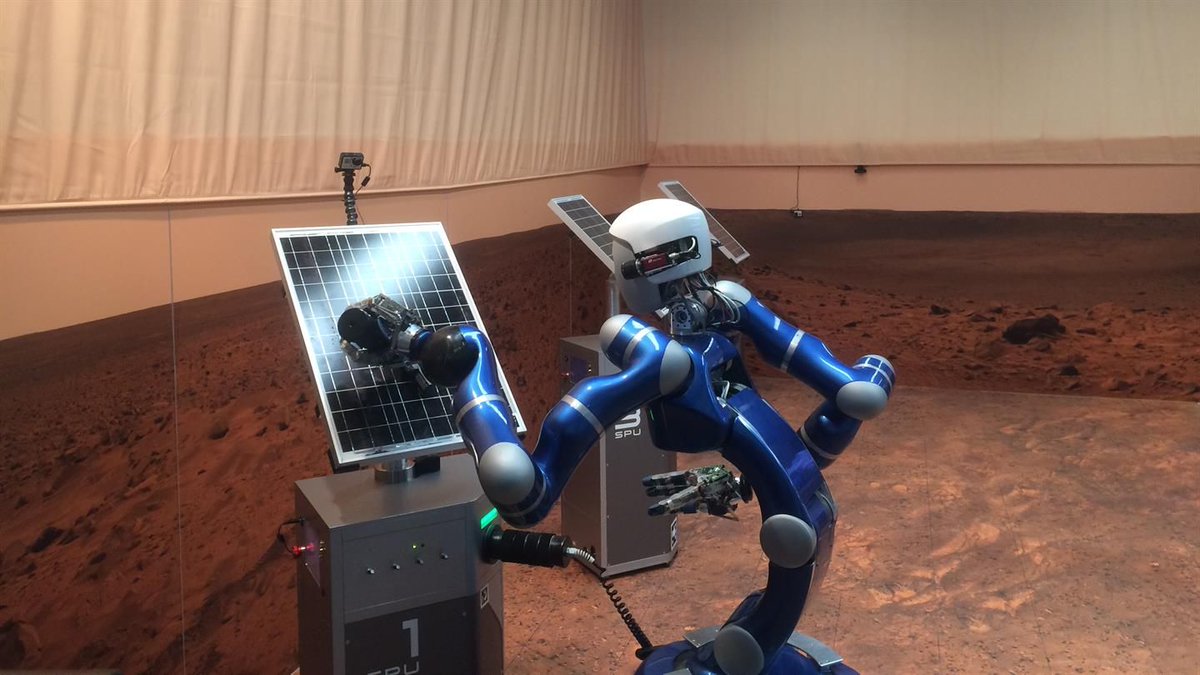

If something called “Project METERON” sounds to you like a sinister project involving astronauts, robots, the International Space Station, and artificial intelligence, I don’t blame you. Because that’s what it is (except for the sinister part.) In fact, the Meteron Project (Multi-Purpose End-to-End Robotic Operation Network) is not sinister at all, but a friendly collaboration between the European Space Agency (ESA) and the German Aerospace Center (DLR.)
The idea behind the project is to place an artificially intelligent robot here on Earth under the direct control of an astronaut 400 km above the Earth, and to get the two to work together.
“Artificial intelligence allows the robot to perform many tasks independently, making us less susceptible to communication delays that would make continuous control more difficult at such a great distance.” – Neil Lii, DLR Project Manager.
On March 2nd, engineers at the DLR Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics set up the robot called Justin in a simulated Martian environment. Justin was given a simulated task to carry out, with as few instructions as necessary. The maintenance of solar panels was the chosen task, since they’re common on landers and rovers, and since Mars can get kind of dusty.

The first test of the METERON Project was done in August. But this latest test was more demanding for both the robot and the astronaut issuing the commands. The pair had worked together before, but since then, Justin was programmed with more abstract commands that the operator could choose from.
American astronaut Scott Tingle issued commands to Justin from a tablet aboard the ISS, and the same tablet also displayed what Justin was seeing. The human-robot team had practiced together before, but this test was designed to push the pair into more challenging tasks. Tingle had no advance knowledge of the tasks in the test, and he also had no advance knowledge of Justin’s new capabilities. On-board the ISS, Tingle quickly realized that the panels in the simulation down here were dusty. They were also not pointed in the optimal direction.
This was a new situation for Tingle and for Justin, and Tingle had to choose from a range of commands on the tablet. The team on the ground monitored his choices. The level of complexity meant that Justin couldn’t just perform the task and report it completed, it meant that Tingle and the robot also had to estimate how clean the panels were after being cleaned.
“Our team closely observed how the astronaut accomplished these tasks, without being aware of these problems in advance and without any knowledge of the robot’s new capabilities,” says DLR engineer Daniel Leidner.
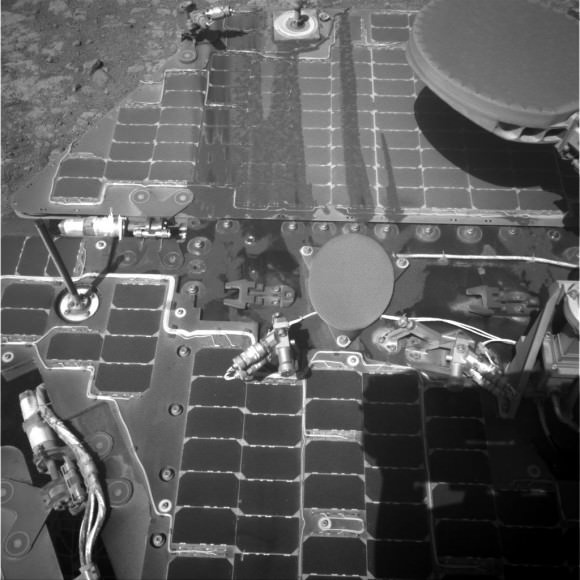

The next test will take place in Summer 2018 and will push the system even further. Justin will have an even more complex task before him, in this case selecting a component on behalf of the astronaut and installing it on the solar panels. The German ESA astronaut Alexander Gerst will be the operator.
If the whole point of this is not immediately clear to you, think Mars exploration. We have rovers and landers working on the surface of Mars to study the planet in increasing detail. And one day, humans will visit the planet. But right now, we’re restricted to surface craft being controlled from Earth.
What METERON and other endeavours like it are doing, is developing robots that can do our work for us. But they’ll be smart robots that don’t need to be told every little thing. They are just given a task and they go about doing it. And the humans issuing the commands could be in orbit around Mars, rather than being exposed to all the risks on the surface.
“Artificial intelligence allows the robot to perform many tasks independently, making us less susceptible to communication delays that would make continuous control more difficult at such a great distance,” explained Neil Lii, DLR Project Manager. “And we also reduce the workload of the astronaut, who can transfer tasks to the robot.” To do this, however, astronauts and robots must cooperate seamlessly and also complement one another.
That’s why these tests are important. Getting the astronaut and the robot to perform well together is critical.
“This is a significant step closer to a manned planetary mission with robotic support,” says Alin Albu-Schäffer, head of the DLR Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics. It’s expensive and risky to maintain a human presence on the surface of Mars. Why risk human life to perform tasks like cleaning solar panels?
“The astronaut would therefore not be exposed to the risk of landing, and we could use more robotic assistants to build and maintain infrastructure, for example, with limited human resources.” In this scenario, the robot would no longer simply be the extended arm of the astronaut: “It would be more like a partner on the ground.”
Special Skinsuits Could Help Astronauts Avoid Back Pain When Their Spines Expand In Space
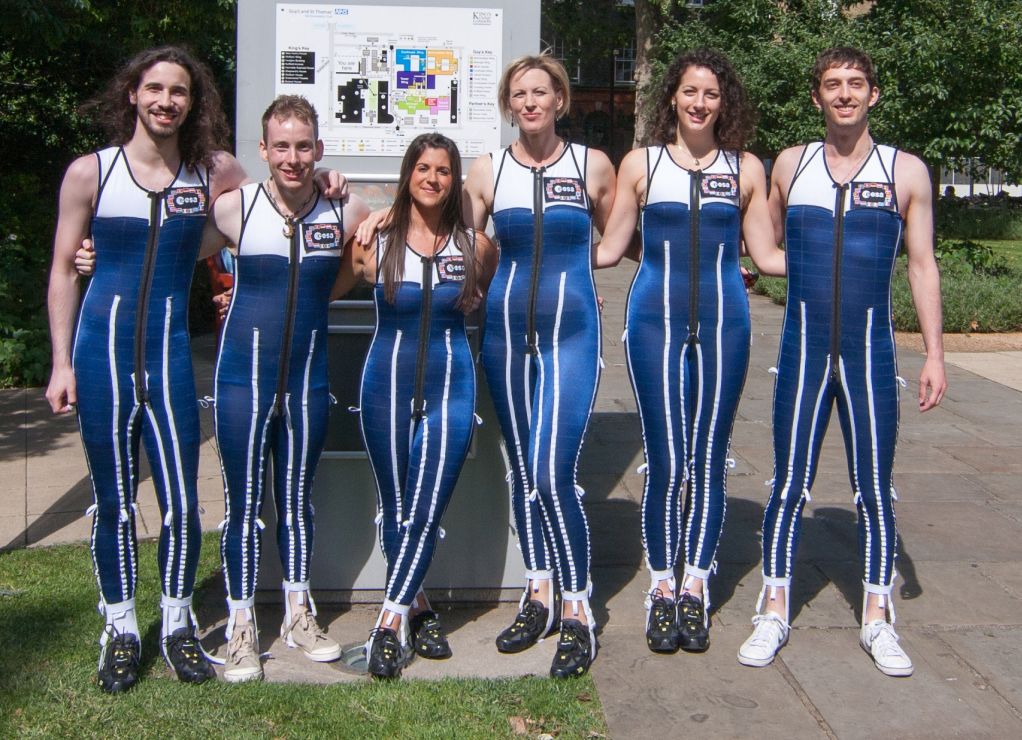

The microgravity in space causes a number of problems for astronauts, including bone density loss and muscle atrophy. But there’s another problem: weightlessness allows astronauts’ spines to expand, making them taller. The height gain is permanent while they’re in space, and causes back pain.
A new SkinSuit being tested in a study at King’s College in London may bring some relief. The study has not been published yet.
The constant 24 hour microgravity that astronauts live with in space is different from the natural 24 hour cycle that humans go through on Earth. Down here, the spine goes through a natural cycle associated with sleep.
Sleeping in a supine position allows the discs in the spine to expand with fluid. When we wake up in the morning, we’re at our tallest. As we go about our day, gravity compresses the spinal discs and we lose about 1.5 cm (0.6 inches) in height. Then we sleep again, and the spine expands again. But in space, astronauts spines have been known to grow up to 7 cm. (2.75 in.)
Study leader David A. Green explains it: “On Earth your spine is compressed by gravity as you’re on your feet, then you go to bed at night and your spine unloads – it’s a normal cyclic process.”
In microgravity, the spine of an astronaut is never compressed by gravity, and stays unloaded. The resulting expansion causes pain. As Green says, “In space there’s no gravitational loading. Thus the discs in your spine may continue to swell, the natural curves of the spine may be reduced and the supporting ligaments and muscles — no longer required to resist gravity – may become loose and weak.”
The SkinSuit being developed by the Space Medicine Office of ESA’s European Astronaut Centre and the King’s College in London is based on work done by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). It’s a spandex-based garment that simulates gravity by squeezing the body from the shoulders to the feet.

The Skinsuits were tested on-board the International Space Station by ESA astronauts Andreas Mogensen and Thomas Pesquet. But they could only be worn for a short period of time. “The first concepts were really uncomfortable, providing some 80% equivalent gravity loading, and so could only be worn for a couple of hours,” said researcher Philip Carvil.
Back on Earth, the researchers worked on the suit to improve it. They used a waterbed half-filled with water rich in magnesium salts. This re-created the microgravity that astronauts face in space. The researchers were inspired by the Dead Sea, where the high salt content allows swimmers to float on the surface.
“During our longer trials we’ve seen similar increases in stature to those experienced in orbit, which suggests it is a valid representation of microgravity in terms of the effects on the spine,” explains researcher Philip Carvil.

Studies using students as test subjects have helped with the development of the SkinSuit. After lying on the microgravity-simulating waterbed both with and without the SkinSuit, subjects were scanned with MRI’s to test the SkinSuit’s effectiveness. The suit has gone through several design revisions to make it more comfortable, wearable, and effective. It’s now up to the Mark VI design.
“The Mark VI Skinsuit is extremely comfortable, to the point where it can be worn unobtrusively for long periods of normal activity or while sleeping,” say Carvil. “The Mk VI provides around 20% loading – slightly more than lunar gravity, which is enough to bring back forces similar to those that the spine is used to having.”
“The results have yet to be published, but it does look like the Mk VI Skinsuit is effective in mitigating spine lengthening,” says Philip. “In addition we’re learning more about the fundamental physiological processes involved, and the importance of reloading the spine for everyone.”
A New Kind of Propulsion System That Doesn’t Need Propellant. It Converts Electricity into Thrust and Vice Versa.
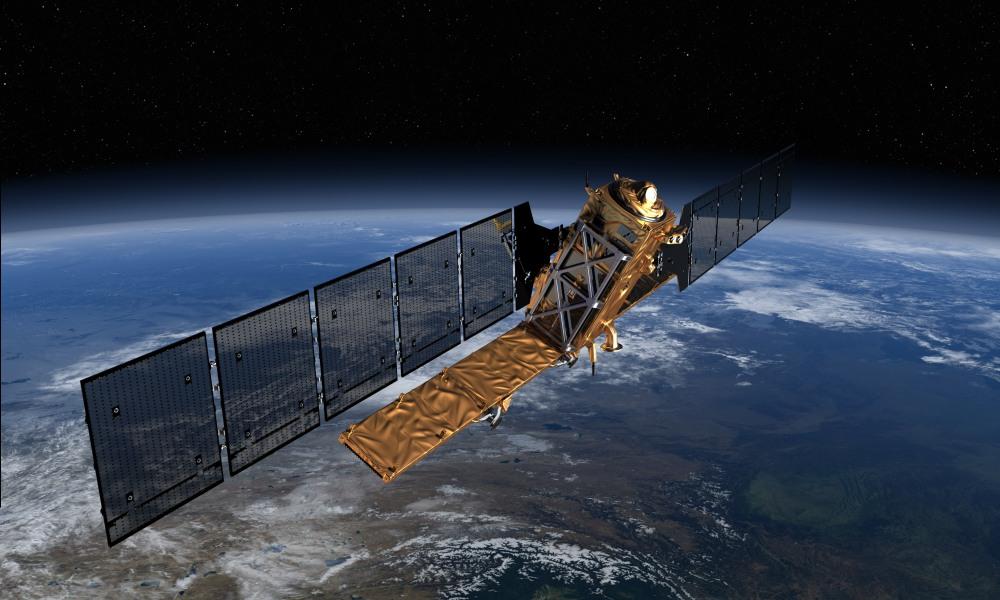

Some of the best things in science are elegant and simple. A new propulsion system being developed in Spain is both those things, and could help solve a growing problem with Earth’s satellites: the proliferation of space junk.
Researchers at Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) and the Universidad Politécnica de Madrid (UPM) in Spain are patenting a new kind of propulsion system for orbiting satellites that doesn’t use any propellant or consumables. The system is basically a tether, in the form of an aluminum tape a couple kilometers long and a couple inches wide, that trails out from the satellite. The researchers call it a space tie.
“This is a disruptive technology because it allows one to transform orbital energy into electrical energy and vice versa without using any type of consumable”. – Gonzalo Sánchez Arriaga, UC3M.
The lightweight space tie is rolled up during launch, and once the satellite is in orbit, it’s deployed. Once deployed, the tape can either convert electricity into thrust, or thrust into electricity. The Spanish researchers behind this say that the space-ties will be used in pairs.
The system is based on what is called a “low-work-function” tether. A special coating on the tether has enhanced electron emission properties on receiving sunlight and heat. These special properties allow it to function in two ways. “This is a disruptive technology because it allows one to transform orbital energy into electrical energy and vice versa without using any type of consumable,” said Gonzalo Sánchez Arriaga, Ramón y Cajal researcher at the Bioengineering and Aerospace Engineering Department at UC3M.
As a satellite loses altitude and gets closer to Earth, the tether converts that thrust-caused-by-gravity into electricity for the spacecraft systems to use. When it comes to orbiting facilities like the International Space Station (ISS), this tether system could solve an annoying problem. Every year the ISS has to burn a significant amount of propellant to maintain its orbit. The tether can generate electricity as it moves closer to Earth, and this electricity could replace the propellant. “With a low- work function tether and the energy provided by the solar panel of the ISS, the atmospheric drag could be compensated without the use of propellant”, said Arriaga.
“Unlike current propulsion technologies, the low-work function tether needs no propellant and it uses natural resources from the space environment such as the geomagnetic field, the ionospheric plasma and the solar radiation.” – Gonzalo Sánchez Arriaga, UC3M.
For satellites with ample on-board power, the tether would operate in reverse. It would use electricity to provide thrust to the space craft. This is especially useful to satellites near the end of their operational life. Rather than languish in orbit for a long time as space junk, the derelict satellite could be forced to re-enter Earth’s atmosphere where it would burn up harmlessly.
The space-tie system is based on what’s called Lorentz drag. Lorentz drag is an electrodynamic effect. (Electrodynamics enthusiasts can read all about it here.) I won’t go too deeply into it because I’m not a physicist, but the Spanish researchers suggest that the Lorentz drag can be easily observed by watching a magnet fall through a copper tube. Here’s a video.
Space organizations have shown interest in the low-work-function tether, and the Spanish team is getting the word out to experts in the USA, Japan, and Europe. The next step is the manufacture of prototypes. “The biggest challenge is its manufacturing because the tether should gather very specific optical and electron emission properties,” says Sánchez Arriaga.
The Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness has awarded the Spanish team a grant to investigate materials for the system. The team has also submitted a proposal to the European Commission’s Future and Emerging Technologies (FET-Open) consortium for funding. “The FET-OPEN project would be foundational because it considers the manufacturing and characterization of the first low-work-function tether and the development of a deorbit kit based on this technology to be tested on a future space mission. If funded, it would be a stepping stone to the future of low-work-function tethers in space” Sanchez Arriaga concluded.
In this video, Gonzalo Sanchez Arriaga explains how the system works. If you don’t speak Spanish, just turn on subtitles.
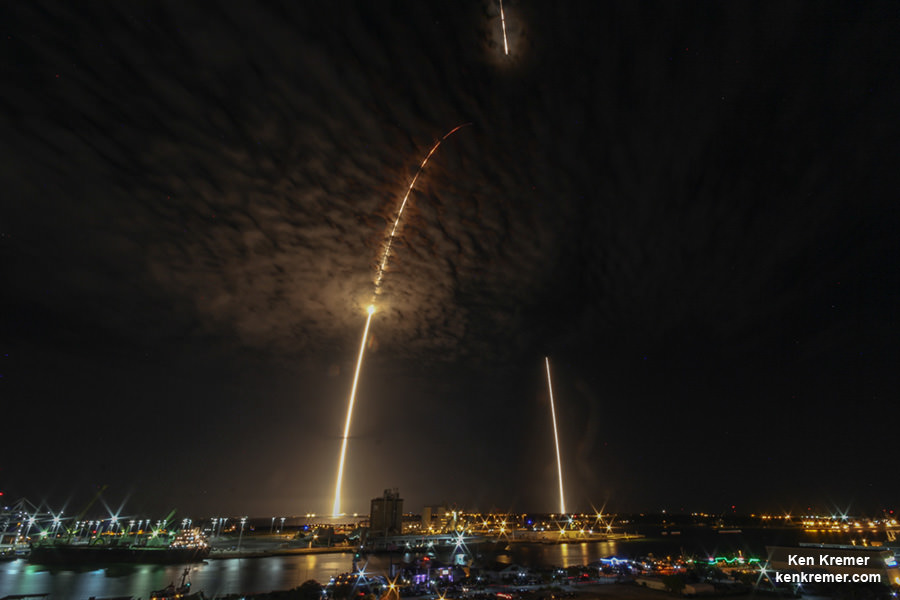
SpaceX Resuming Launches from Damaged Pad 40 on Dec. 4 with Station Resupply Flight for NASA; Covert Zuma Remains on Hold
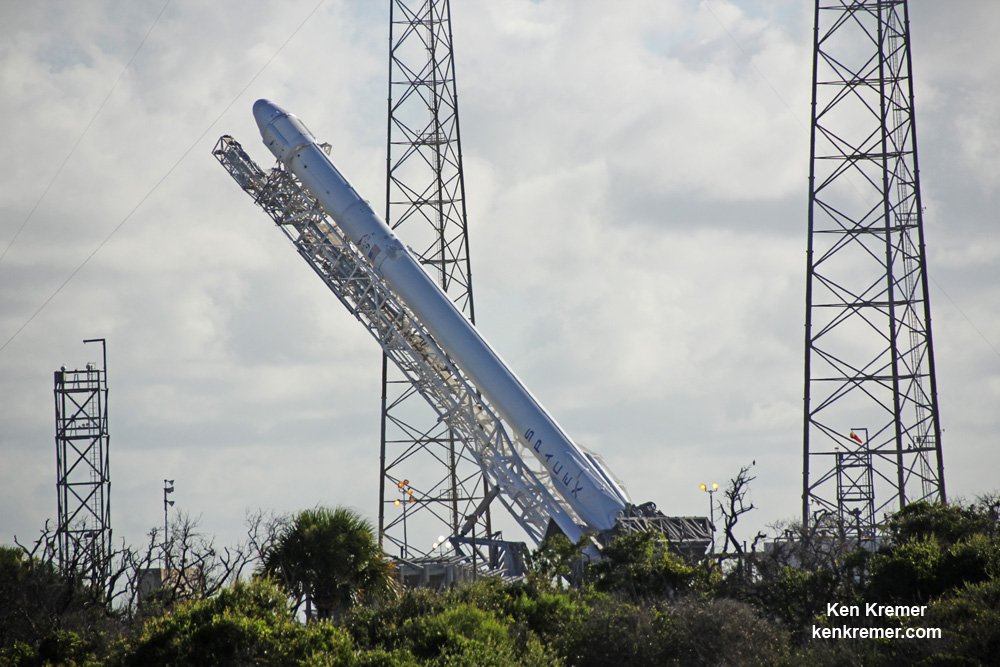


KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – After postponing last week’s liftoff of the covert ‘Zuma’ spy satellite due to last minute concerns about the reliability of the payload fairing encapsulating it while poised for liftoff at KSC pad 39, SpaceX is set to at last resume launches from their previously damaged and now repaired Cape Canaveral pad 40 with a cargo resupply mission for NASA to the International Space Station (ISS) on Dec 4.
NASA and SpaceX have jointly decided to move forward with the Dragon CRS-13 cargo blastoff apparently because the mission does not involve use of the problematical payload fairing that halted last weeks planned Falcon 9 launch with the rocket and the mysterious Zuma payload.
Zuma was ready and waiting at pad 39A for the GO to launch that never came.
Then after a series of daily delays SpaceX ultimately announced a ‘stand down’ for super secret Zuma at pad 39A on Friday, Nov. 17, for the foreseeable future.
SpaceX engineers also had to deal with the after effects of a fire that broke out on a Merlin engine test stand during preparations for a hot fire test that resulted from a leak during a ‘LOX drop’ that halted testing of the Block 5 version of the Merlin 1D.
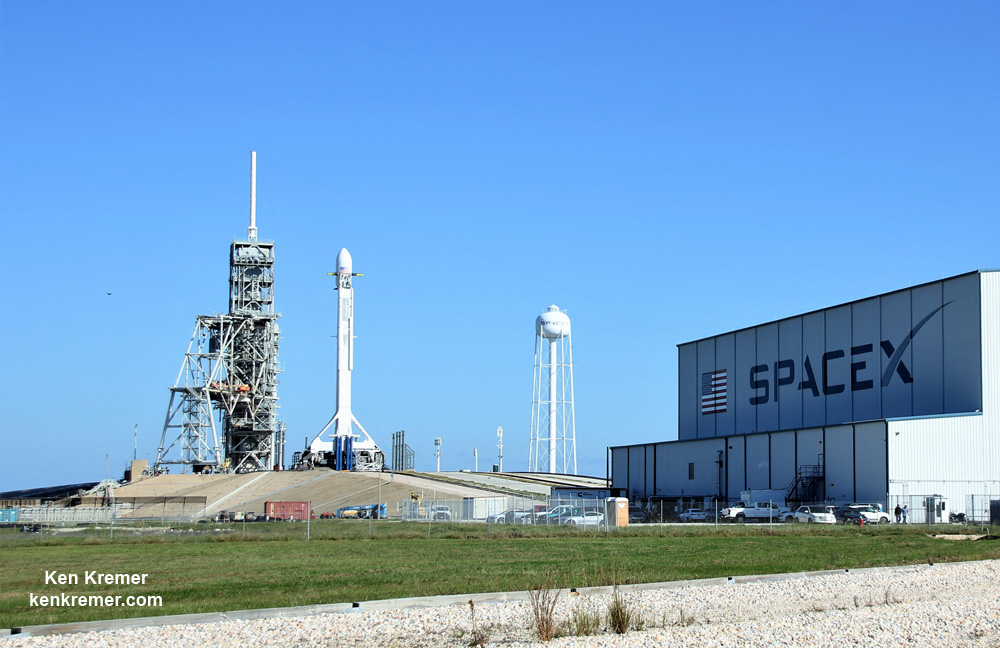

Since SpaceX’s gumdrop shaped Dragon cargo freighter launches as a stand alone aerodynamically shielded spacecraft atop the Falcon 9, it does not require additional protection from atmospheric forces and friction housed inside a nose cone during ascent to orbit unlike satellites with many unprotected exposed surfaces, critical hardware and delicate instruments.
Thus Dragon is deemed good to go since there currently appear to be no other unresolved technical issues with the Falcon 9 rocket.
“NASA commercial cargo provider SpaceX is targeting its 13th commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station for no earlier than 2:53 p.m. EST Monday, Dec. 4,” NASA announced on the agency blog and social media accounts.
The Dec. 4 launch date for Dragon CRS-13 was announced by NASA’s space station manager Dan Hartman during the Orbital ATK Antares/Cygnus launch campaign that culminated with a successful blastoff last Sunday, Nov 12 from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility on Virginia’s eastern shore.
But the targeted Dec 4 liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, FL, was cast in doubt after SpaceX disclosed the payload fairing issue related launch delay on Friday.
Since last week SpaceX engineers have been busy taking the time to carefully scrutinize all the pertinent fairing data before proceeding with the top secret Zuma launch.
“We have decided to stand down and take a closer look at data from recent fairing testing for another customer,” said SpaceX spokesman John Taylor last Friday.
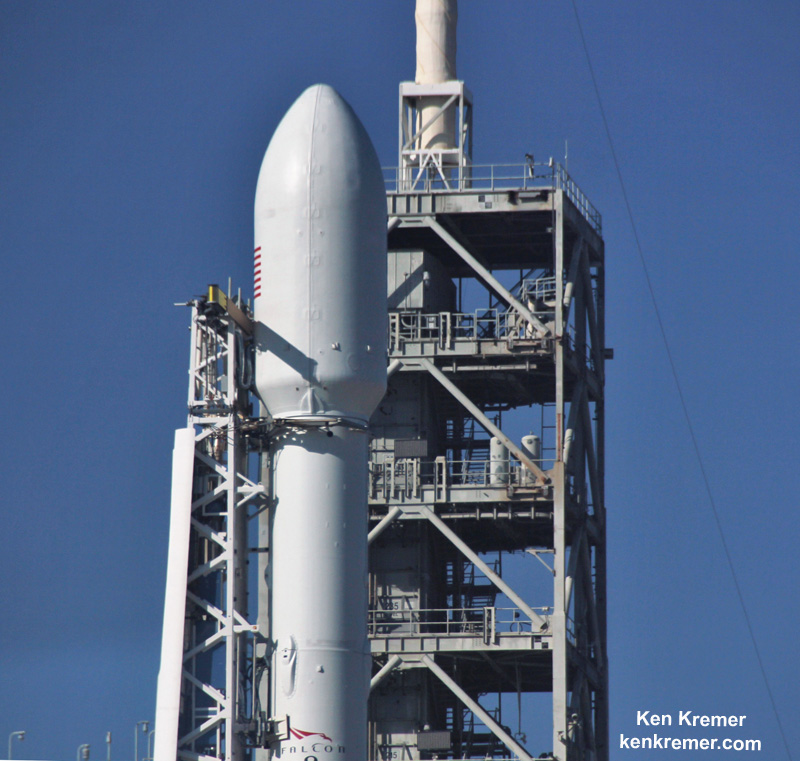

All of SpaceX’s launches this year from Florida’s Spaceport have taken place from NASA’s historic Launch Complex-39A at the Kennedy Space Center.
Pad 39A became SpaceX’s only operational Florida Space Coast launch pad following a catastrophic launch pad accident last year on Sept. 1, 2016 that took place during a routine fueling test that suddenly ended in a devastating explosion and fire that completely consumed the Falcon 9 rocket and Amos-6 payload and heavily damaged the pad and support infrastructure.
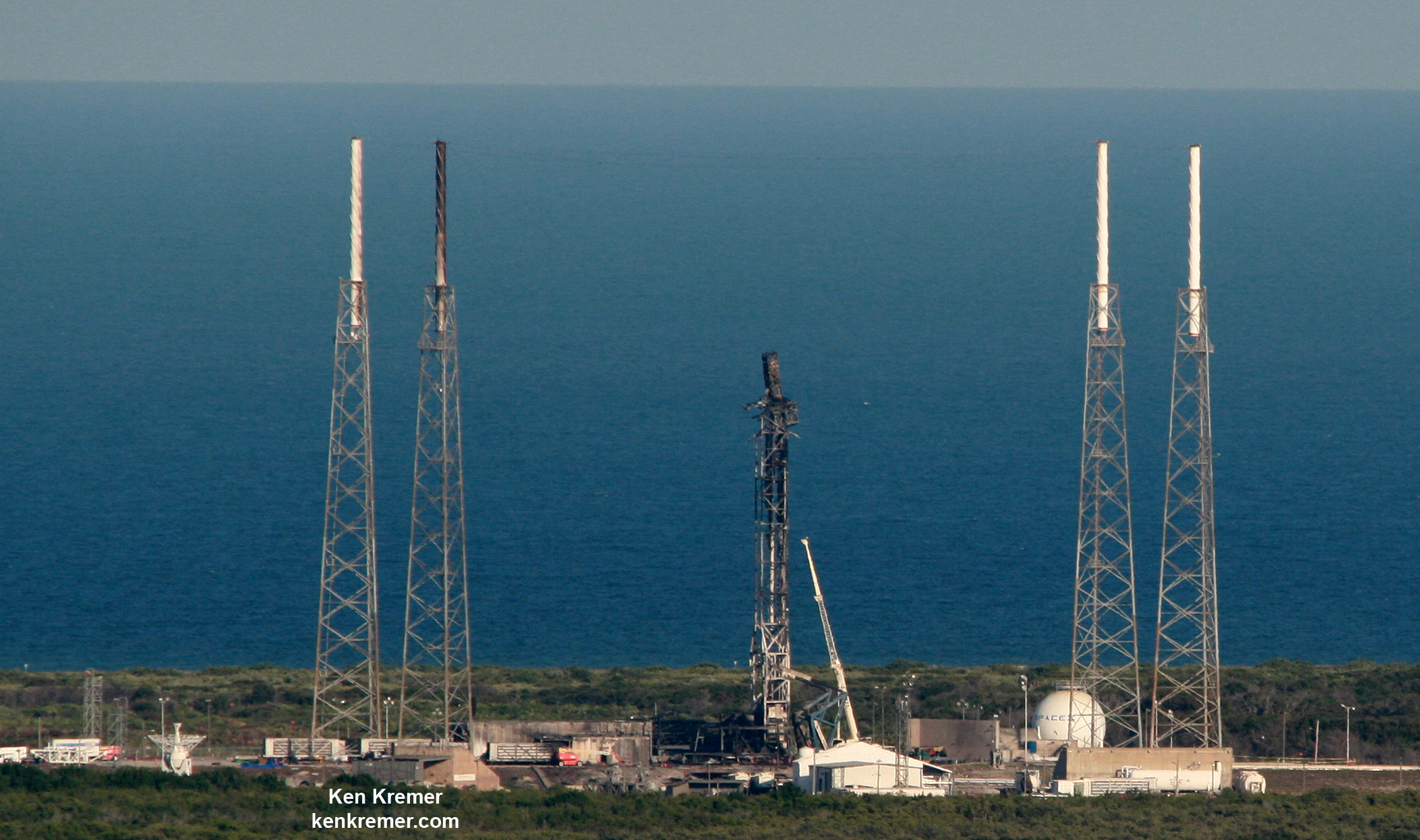

Since the Amos-6 accident workers raced to finish refurbishments to NASA’s long dormant pad 39A to transform into operational status and successfully launched a dozen missions this year.
Simultaneously additional crews have been hard at work to repair damaged pad 40 so that flights can resume there as soon as possible for the bulk of NASA, commercial and military contracted missions.
Meanwhile SpaceX wants to upgrade pad 39A to launch the Falcon Heavy and crewed Dragon flight. But those launches cant take place until pad 40 resumes operational status.
The Dragon CRS-13 mission was recently announced as the maiden mission for the reopening of pad 40.
Altogether Dragon CRS-13 will count as the fourth SpaceX Dragon liftoff of 2017.
The 20-foot high, 12-foot-diameter Dragon CRS-13 vessel will carry about 3 tons of science and supplies to the orbiting outpost and stay about 4 weeks.
It will be a reused Dragon that previously flew on the CRS-6 mission.
“The Dragon [CRS-13] spacecraft will spend about a month attached to the space station,” NASA said.
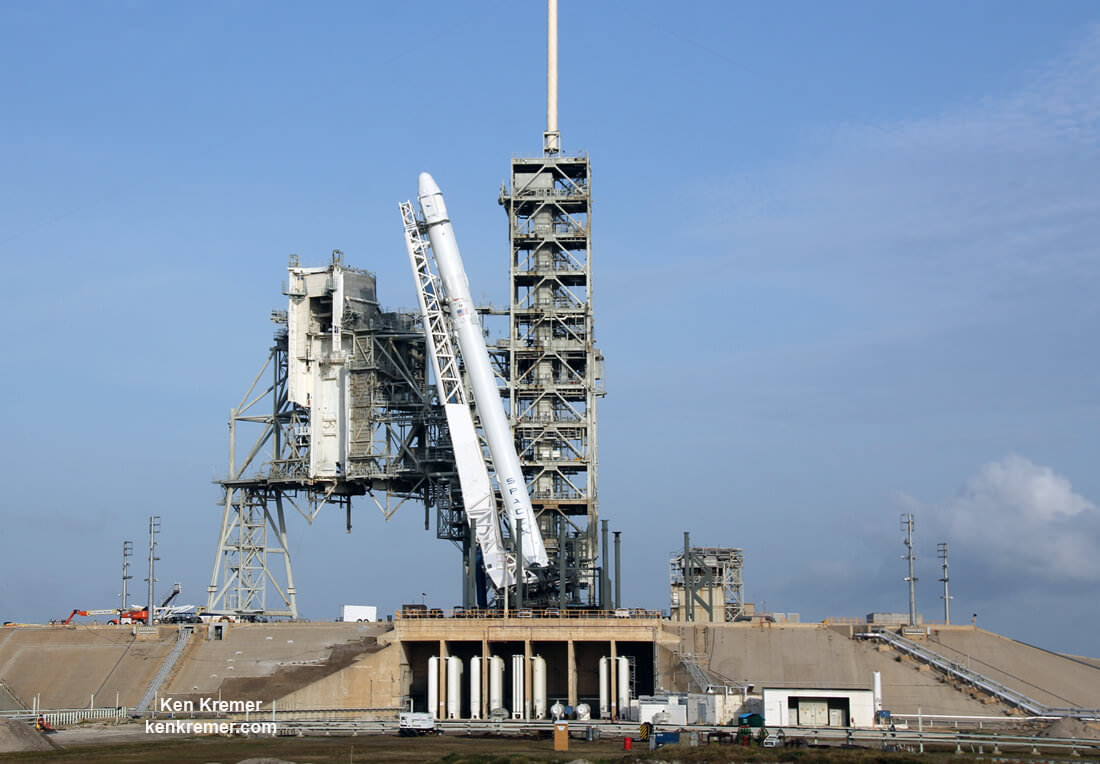

The prior Dragon CRS-12 resupply ship launched from pad 39A on Aug. 14, 2017 from KSC pad 39A and carried more than 6,400 pounds ( 2,900 kg) of science experiments and research instruments, crew supplies, food water, clothing, hardware, gear and spare parts to the million pound orbiting laboratory complex.
Dragon CRS-9 was the last ISS resupply mission to launch from pad 40 on July 18, 2016.
The recently arrived Orbital ATK Cygnus cargo ship is expected to depart the station from the Earth facing Unity node on Dec. 3 to make way for Dragon’s berthing at the Harmony node.

Watch for Ken’s continuing onsite coverage of SpaceX CRS-13, Zuma and KoreaSat-5A & Orbital ATK OA-8 Cygnus and NASA and space mission reports direct from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.


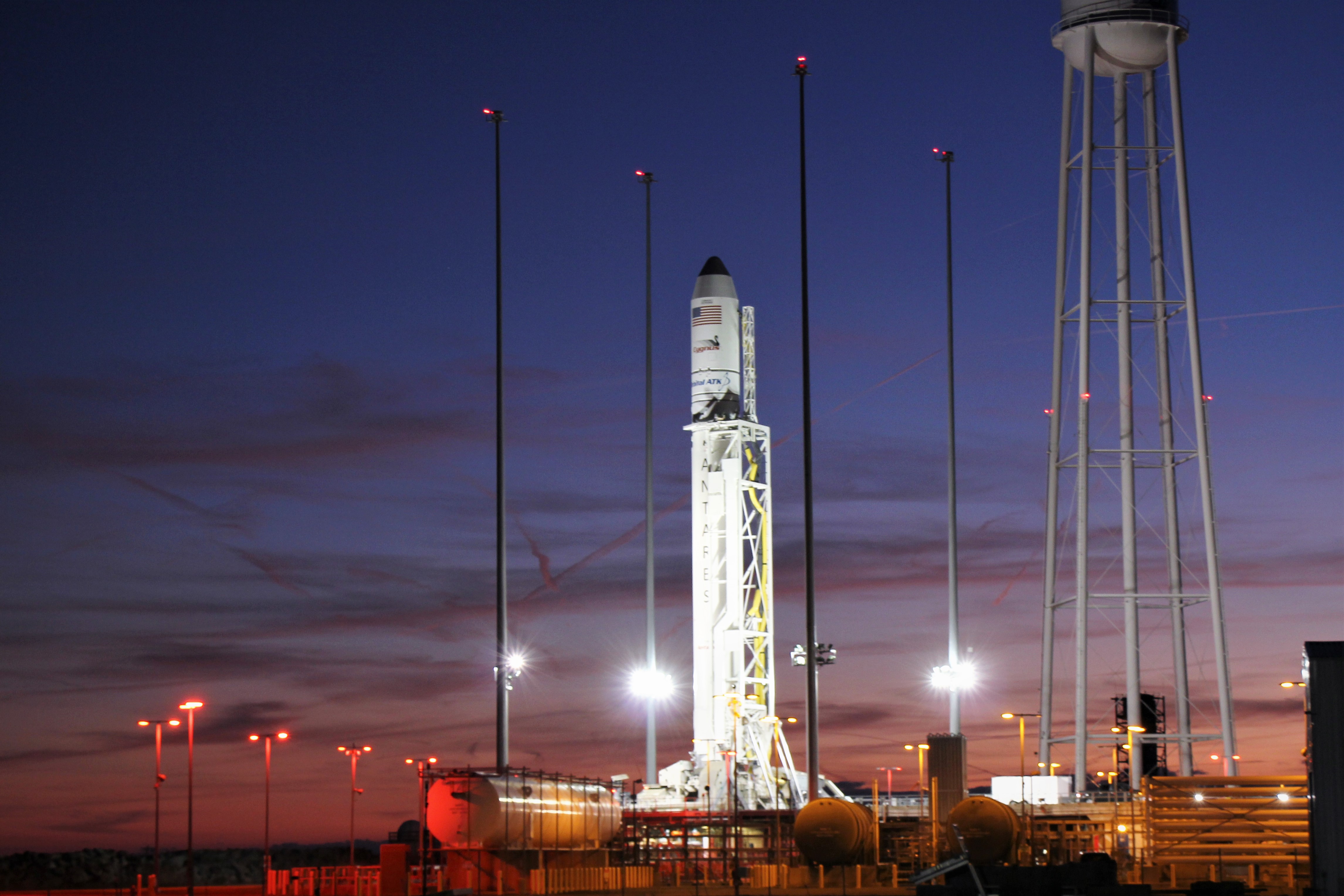
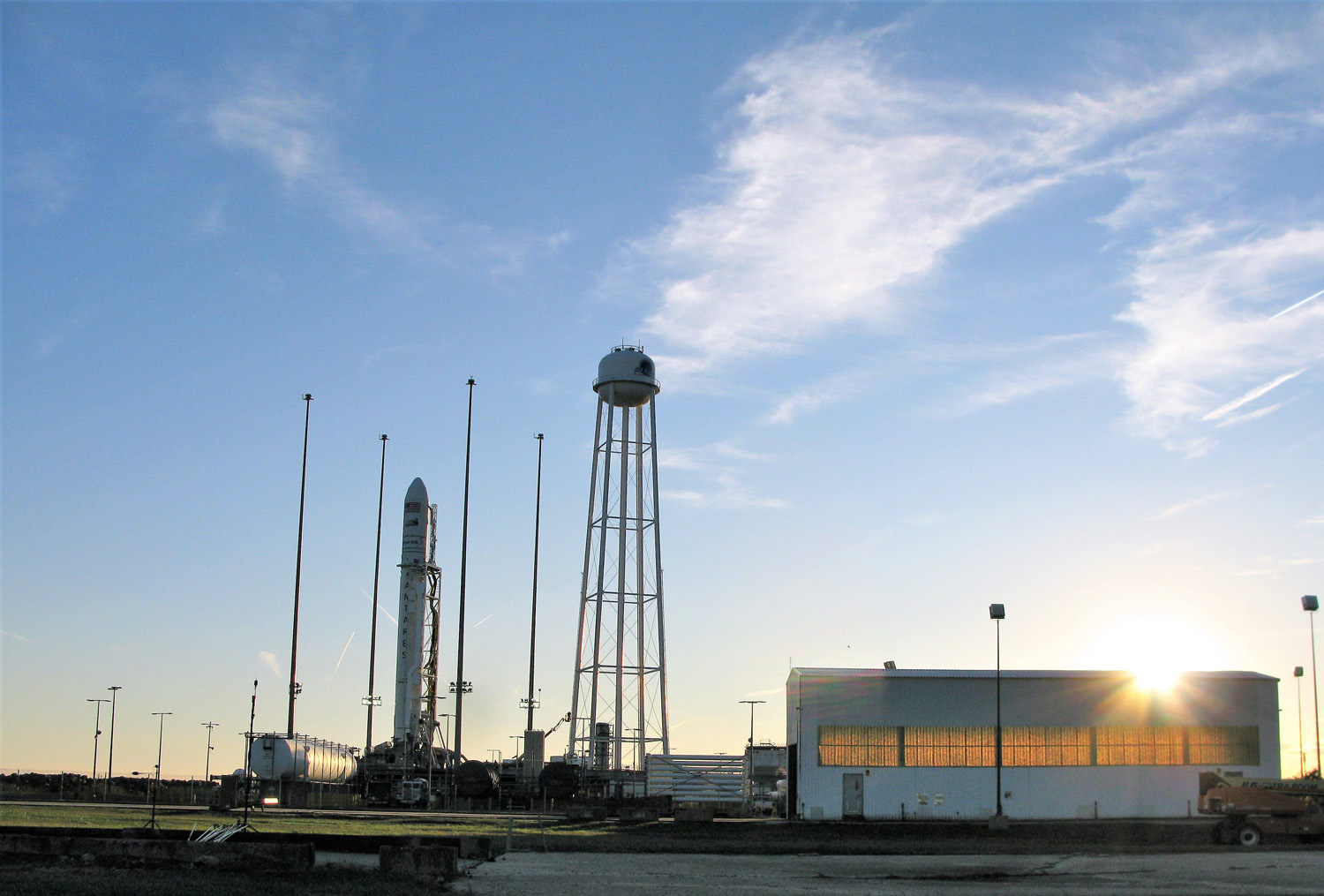
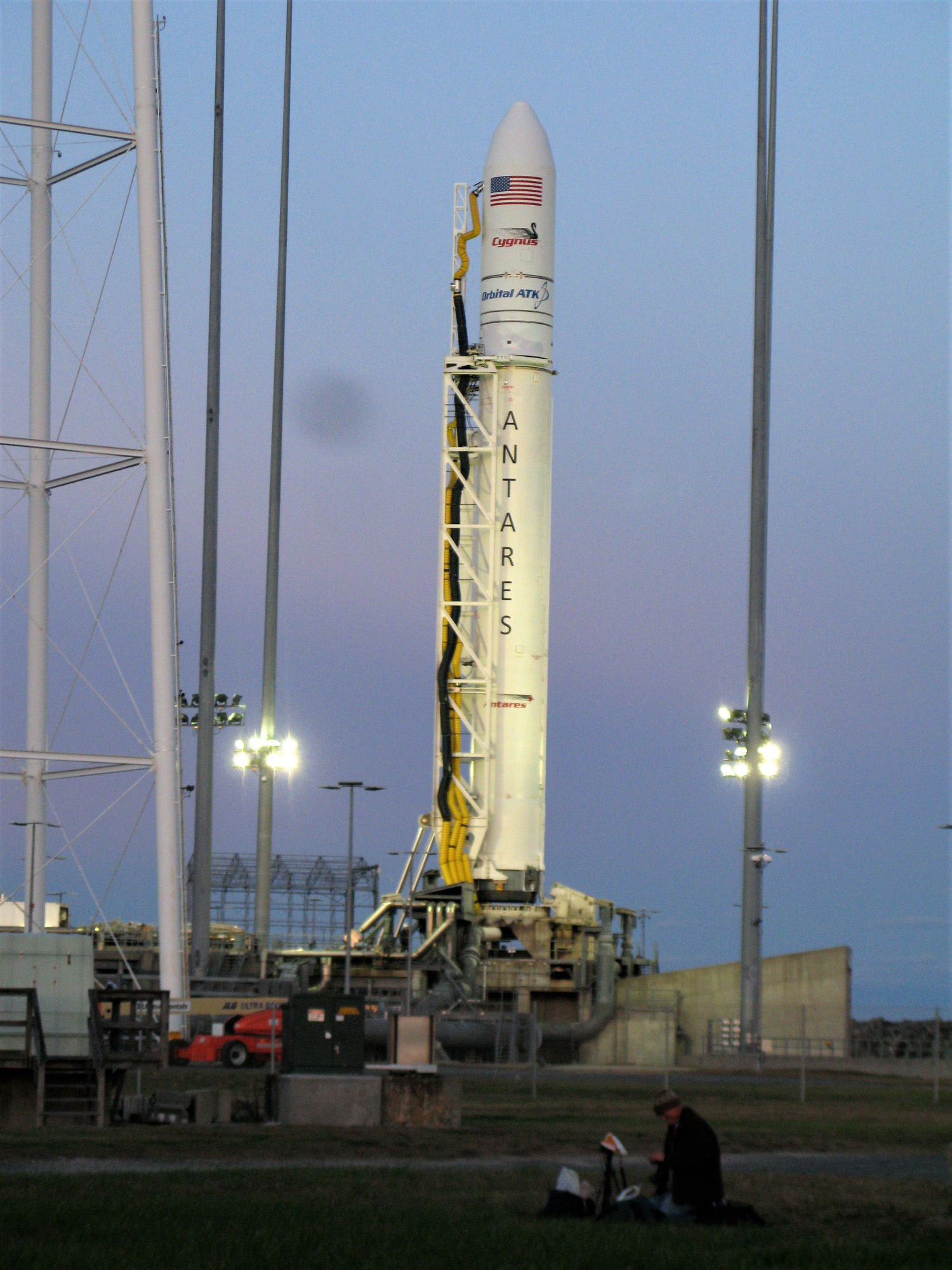
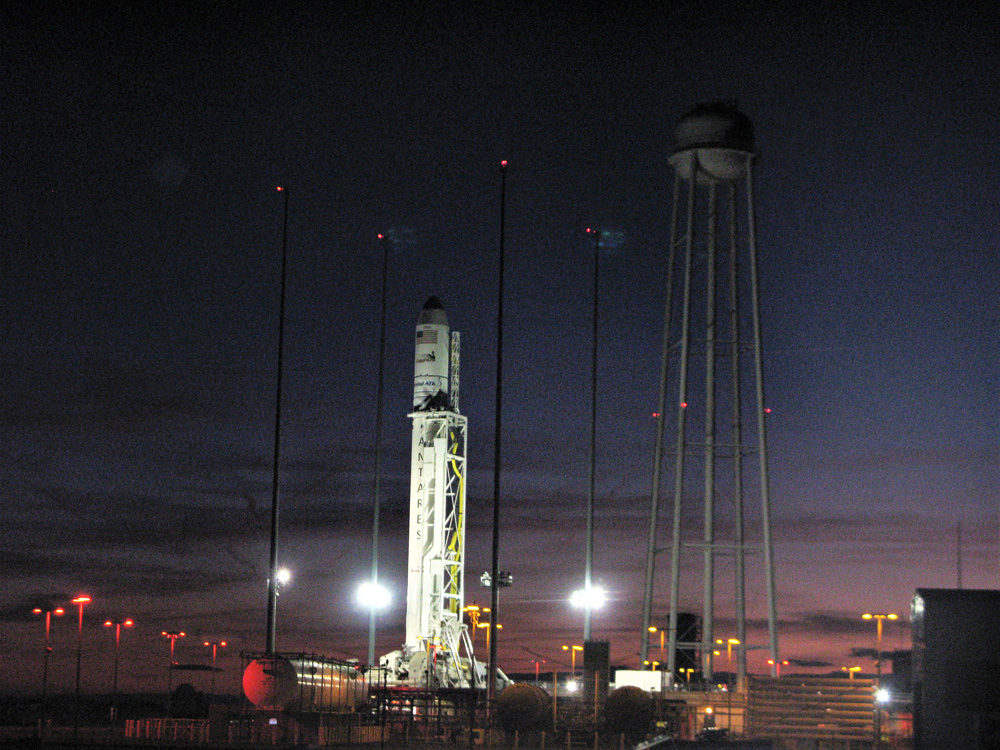
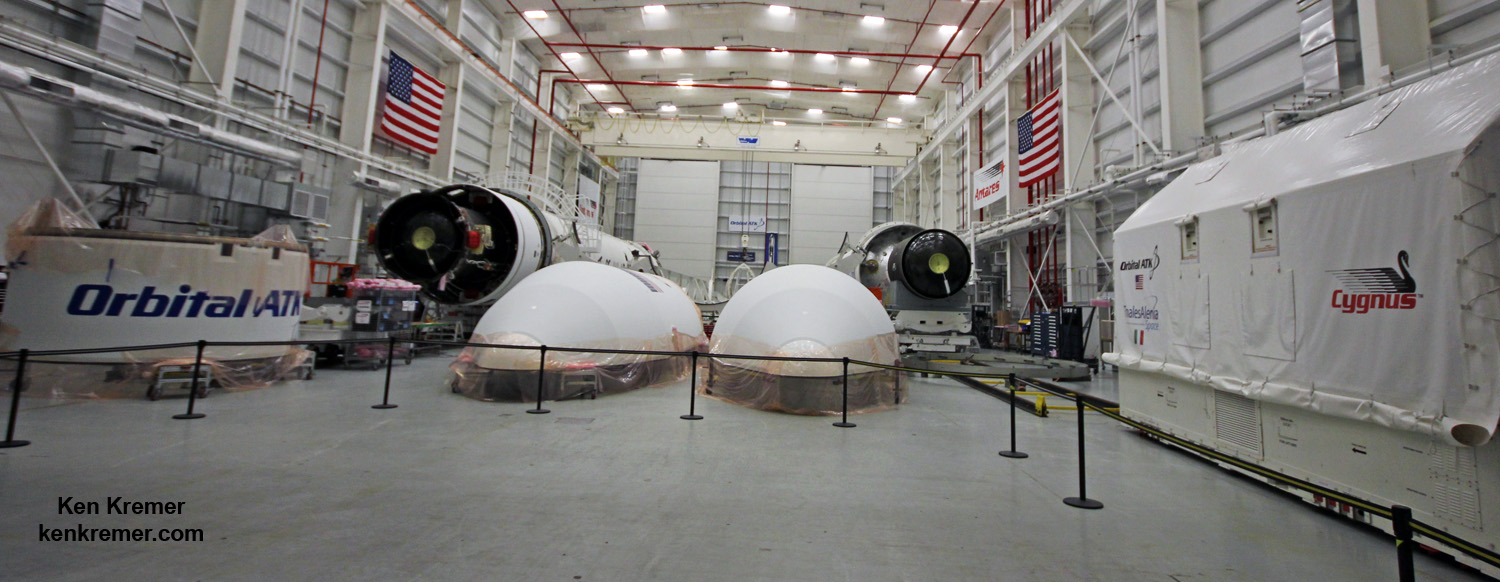
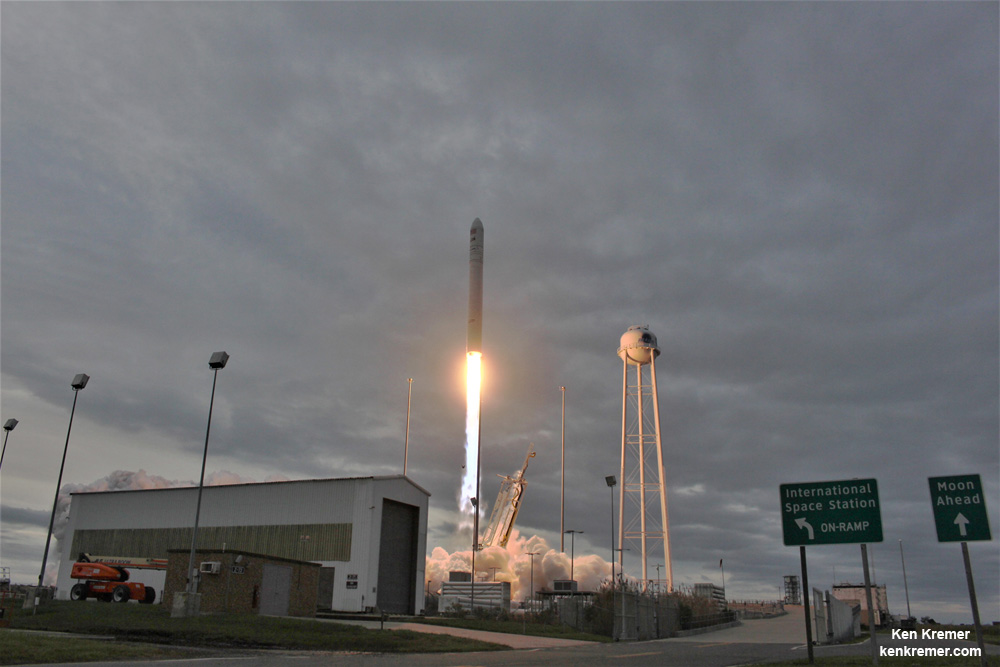
Station Astronauts Unload Cygnus Science; Antares Launch Gallery
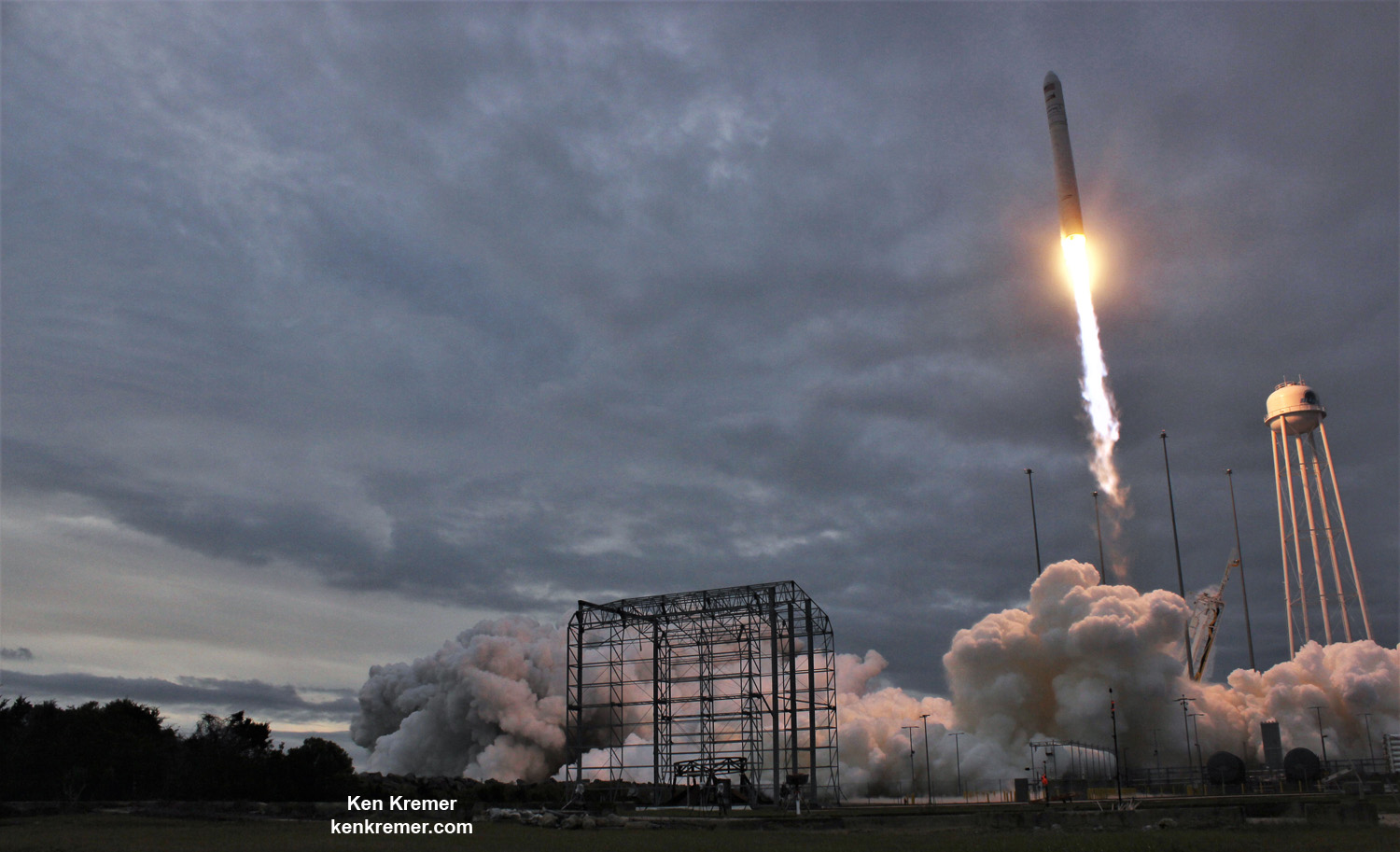


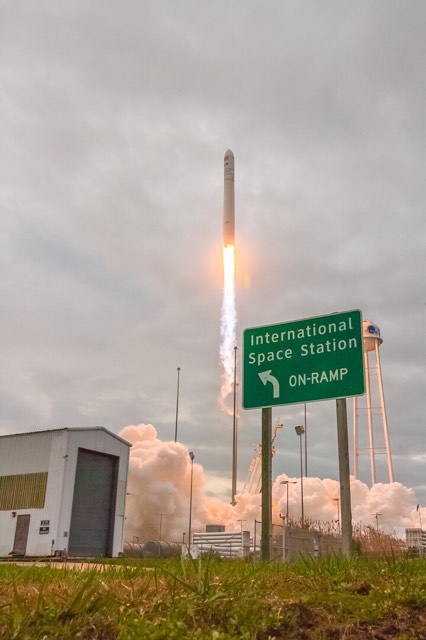
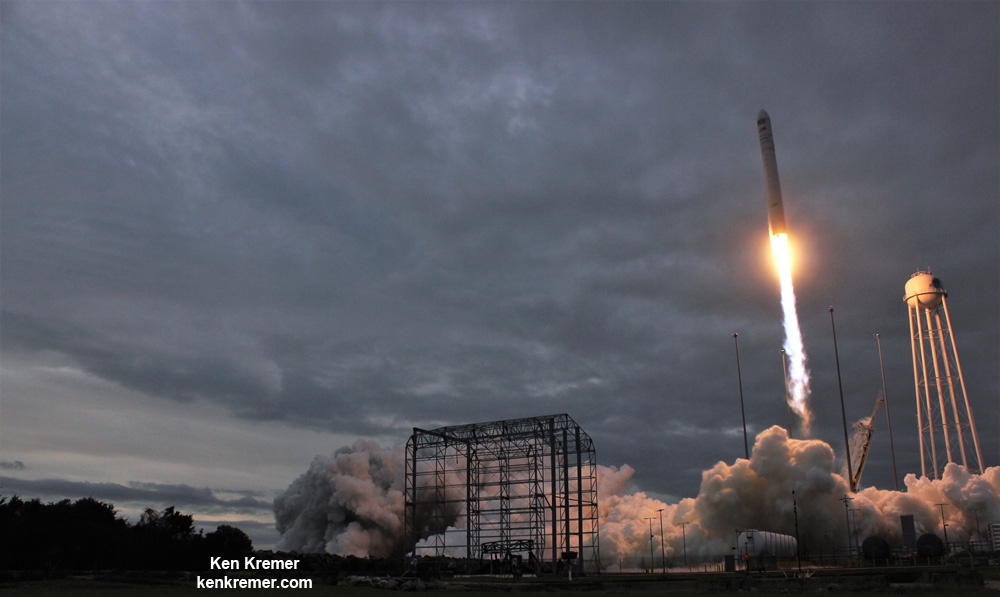
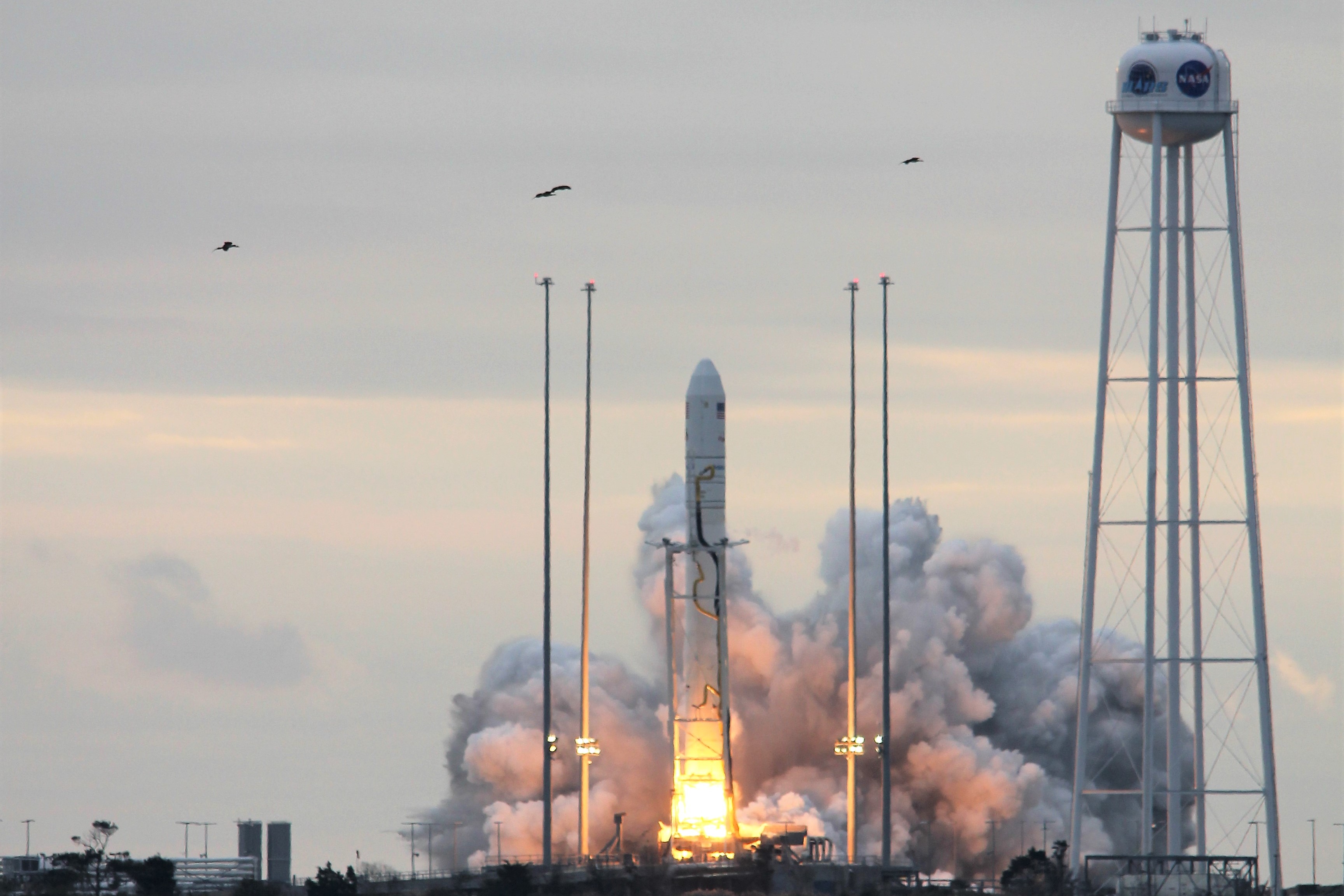
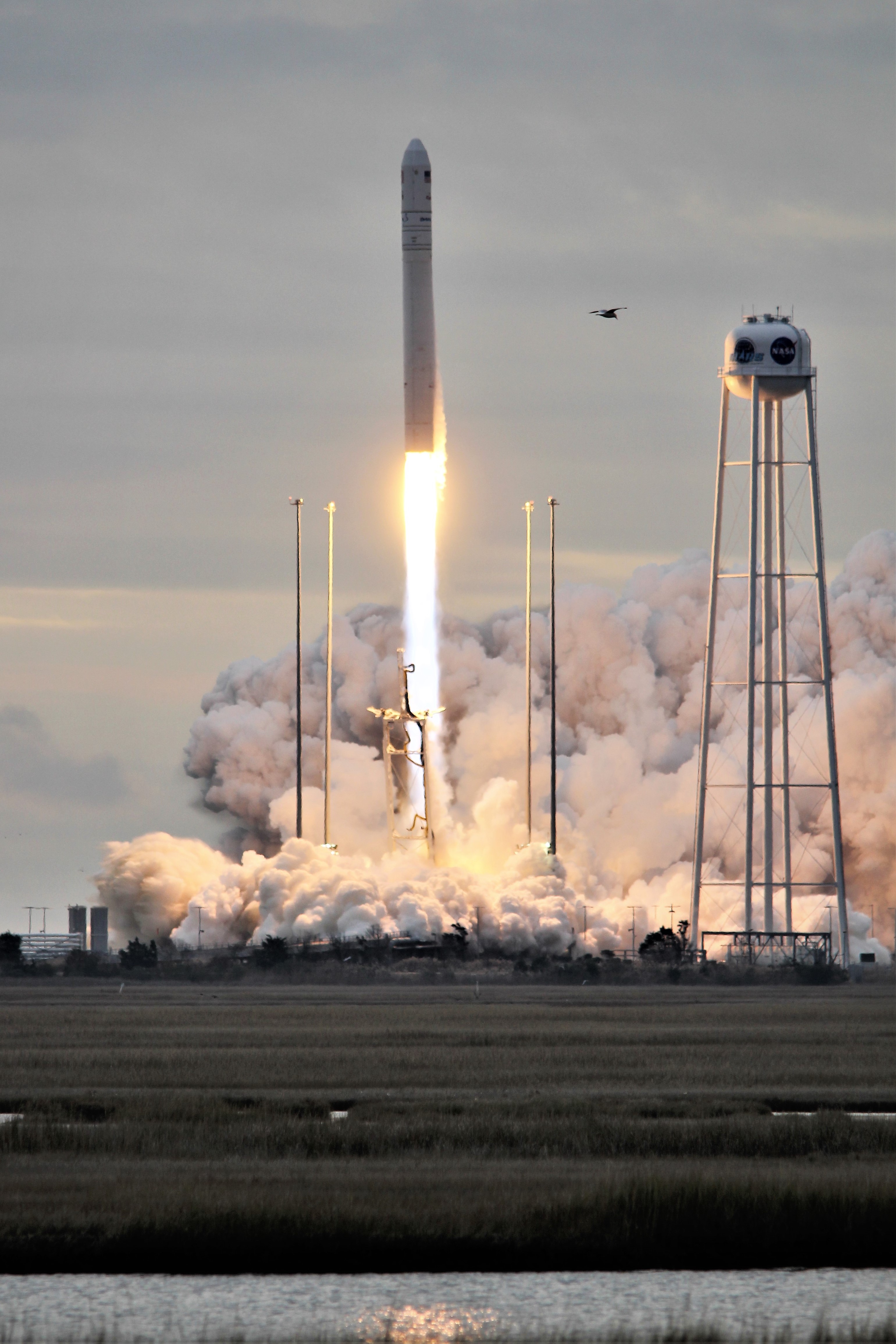
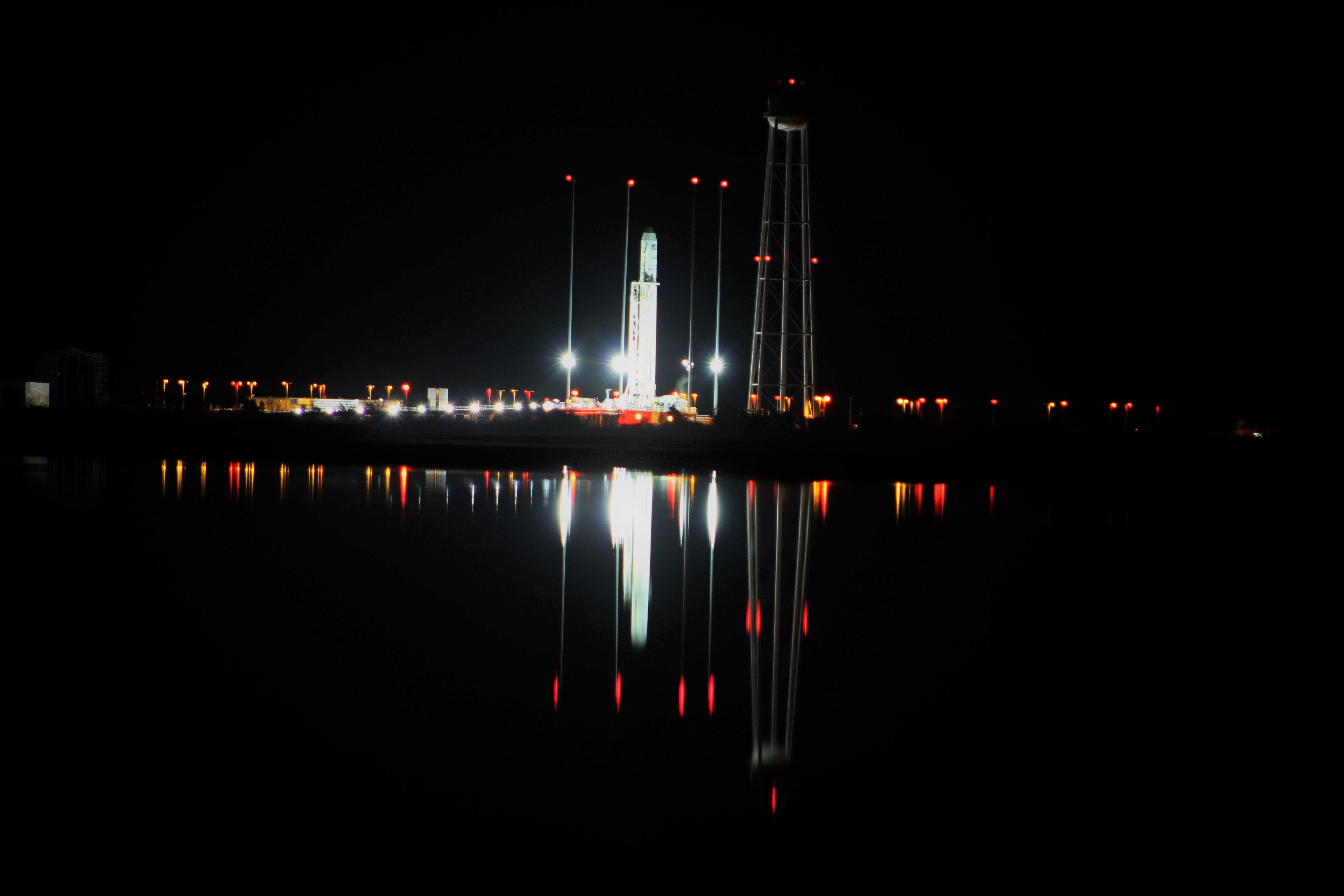
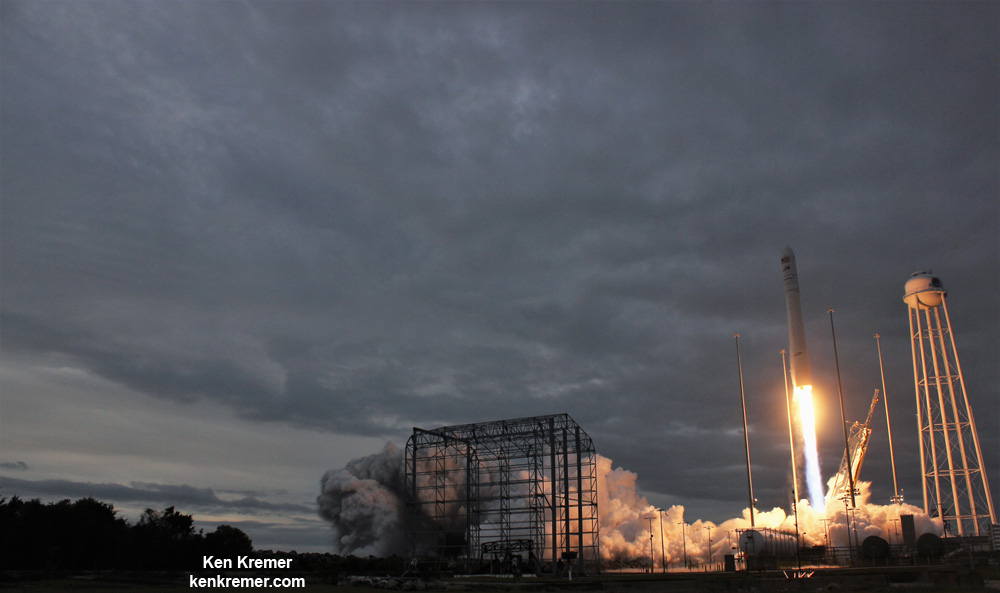
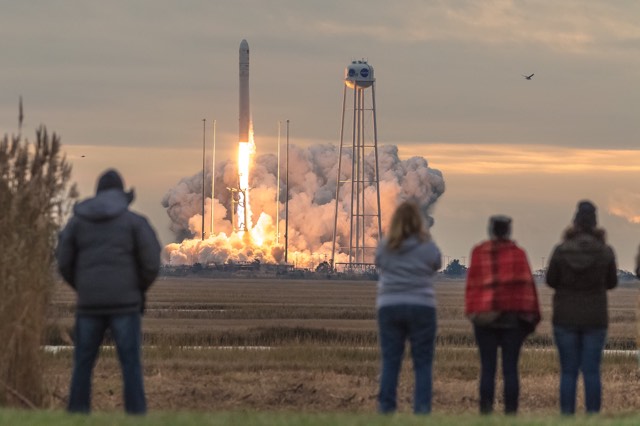
NASA WALLOPS FLIGHT FACILITY, VA – Astronauts aboard the International Space Station are now busily unloading nearly four tons of science experiments, research gear, station equipment and crew supplies – following the spectacular launch of the Orbital ATK Antares rocket earlier this week on Sunday Nov. 12 from Virginia’s eastern shore that propelled the Cygnus cargo freighter to an on time arrival two days later on Tuesday Nov. 14.
The Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft was christened the S.S. Gene Cernan and named in honor of NASA’s Apollo 17 lunar landing commander; Gene Cernan.
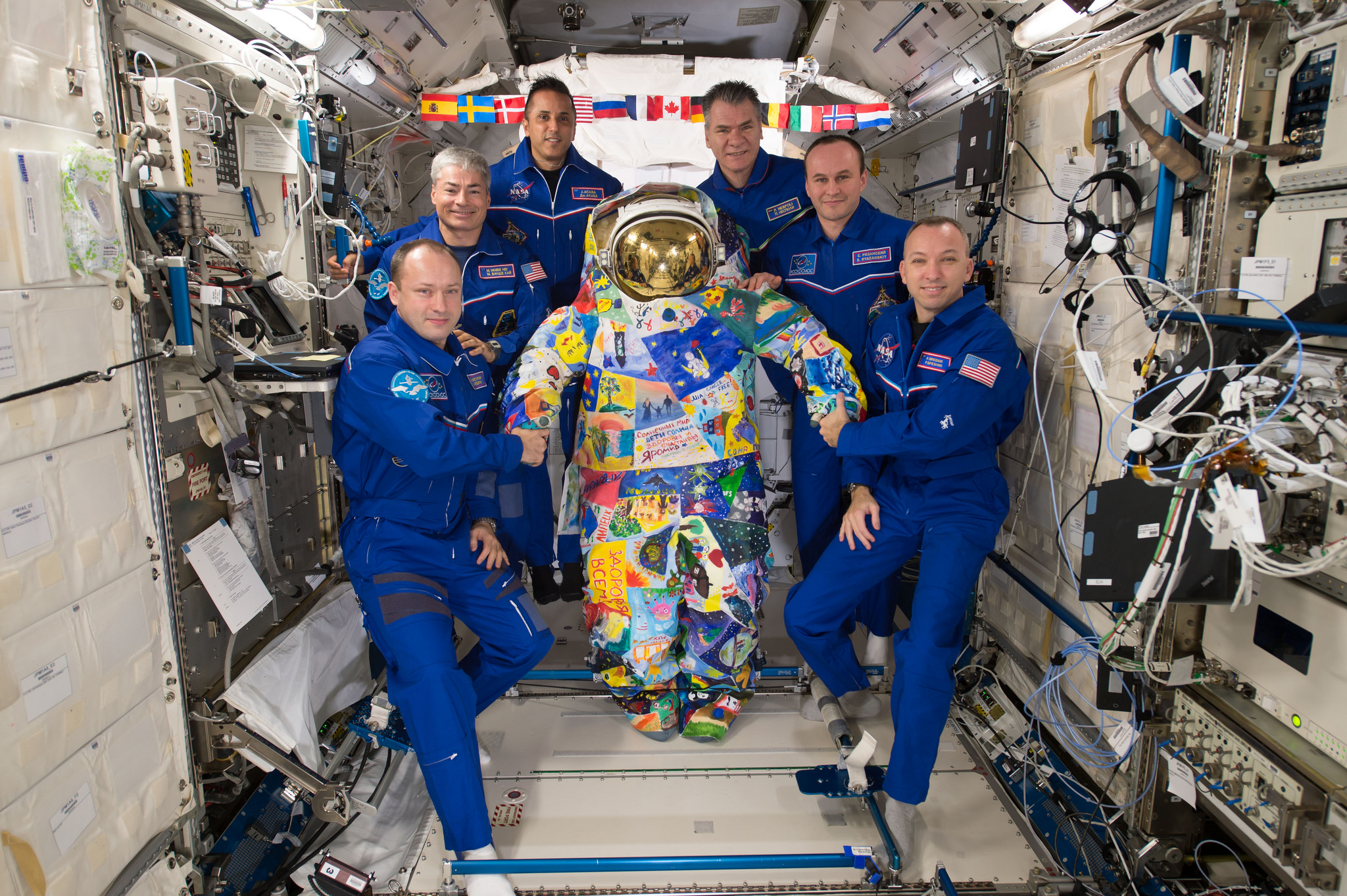
Among the goodies delivered by the newly arrived S.S. Gene Cernan Cygnus OA-8 supply run to resident the crew of six astronauts and cosmonauts from the US, Russia and Italy are ice cream, pizza and presents for the holidays. They are enjoying the fruits of the earthy labor of thousands of space workers celebrating the mission’s success.

The journey began with the flawless liftoff of the two stage Antares rocket shortly after sunrise Sunday at 7:19 a.m. EST, Nov. 12, rocket from Pad-0A at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia.
Check out the expanding gallery of launch imagery and videos captured by this author and several space colleagues of Antares prelaunch activities around the launch pad and through Sunday’s stunningly beautiful sunrise blastoff.
After a carefully choreographed series of intricate thruster firings to raise its orbit in an orbital pursuit over the next two days, the Cygnus spacecraft on the OA-8 resupply mission for NASA arrived in the vicinity of the orbiting research laboratory.
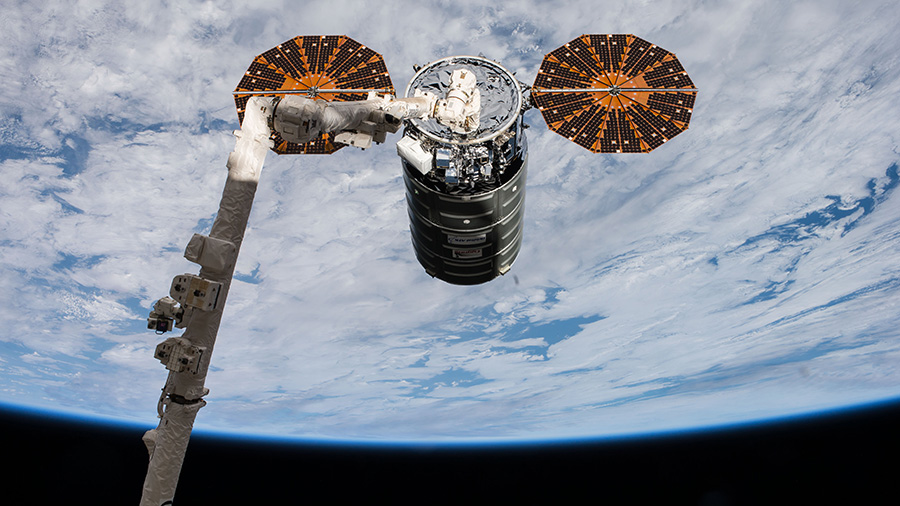

Expedition 53 Flight Engineer Paolo Nespoli of ESA (European Space Agency) assisted by NASA astronaut Randy Bresnik then deftly maneuvered the International Space Station’s 57.7-foot-long (17.6 meter-long) Canadarm2 robotic arm to grapple and successfully capture the Cygnus cargo freighter at 5:04 a.m., Tuesday Nov. 14.
The station was orbiting 260 statute miles over the South Indian Ocean at the moment Nespoli grappled the S.S. Gene Cernan Cygnus spacecraft with the Canadian-built robotic arm.
Ground controllers at NASA’s Mission Control at the Johnson Space Center in Texas, then maneuvered the arm and robotic hand grappling Cygnus towards the exterior hull and berthed the cargo ship at the Earth-facing port of the stations Unity module.
The berthing operation was completed at 7:15 a.m. after all 16 bolts were driven home for hard mating as the station was flying 252 miles over the North Pacific in orbital night.

The Cygnus spacecraft dubbed OA-8 is Orbital ATK’s eighth contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA to the International Space Station under the unmanned Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) program to stock the station with supplies on a continuing and reliable basis.

Altogether over 7,400 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware launched to the orbital laboratory and its crew of six for investigations that will occur during Expeditions 53 and 54.
The S.S. Gene Cernan manifest includes equipment and samples for dozens of scientific investigations including those that will study communication and navigation, microbiology, animal biology and plant biology. The ISS science program supports over 300 ongoing research investigations.
Apollo 17 was NASA’s final lunar landing mission. Gere Cernan was the last man to walk on the Moon.

Among the experiments flying aboard Cygnus are the coli AntiMicrobial Satellite (EcAMSat) mission, which will investigate the effect of microgravity on the antibiotic resistance of E. coli, the Optical Communications and Sensor Demonstration (OCSD) project, which will study high-speed optical transmission of data and small spacecraft proximity operations, the Rodent Research 6 habitat for mousetronauts who will fly on a future SpaceX cargo Dragon.
Cygnus will remain at the space station until Dec. 4, when the spacecraft will depart the station and release 14 CubeSats using a NanoRacks deployer, a record number for the spacecraft.
It will then be commanded to fire its main engine to lower its orbit and carry out a fiery and destructive re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean as it disposes of several tons of trash.

The Cygnus OA-8 manifest includes:
Crew Supplies 2,734.1 lbs. / 1,240 kg
Science Investigations 1631.42 lbs. / 740 kg
Spacewalk Equipment 291.0 lbs. / 132 kg
Vehicle Hardware 1,875.2 lbs. / 851 kg
Computer Resources 75.0 lbs. / 34 kg
Total Cargo: 7,359.0 lbs. / 3,338 kg
Total Pressurized Cargo with Packaging: 7,118.7 lbs. / 3,229 kg
Unpressurized Cargo (NanoRacks Deployer): 240.3 lbs. / 109 kg
Under the Commercial Resupply Services-1 (CRS-1) contract with NASA, Orbital ATK will deliver approximately 66,000 pounds (30,000 kilograms) of cargo to the space station. OA-8 is the eighth of these missions.
The Cygnus OA-8 spacecraft is Orbital ATK’s eighth contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA to the International Space Station under the unmanned Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) program to stock the station with supplies on a continuing basis.
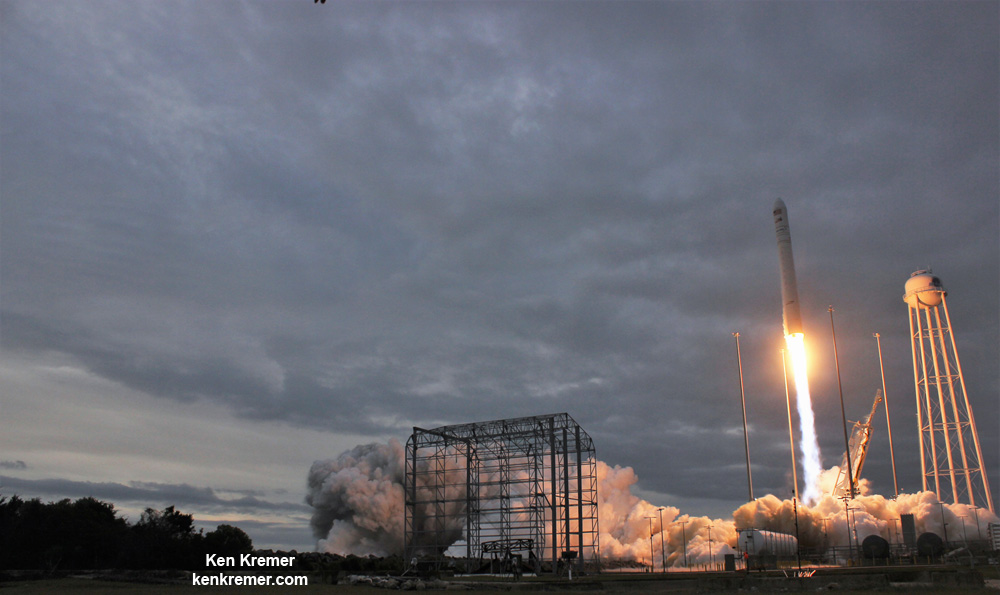

Beginning in 2019, the company will carry out a minimum of six cargo missions under NASA’s CRS-2 contract using a more advanced version of Cygnus.
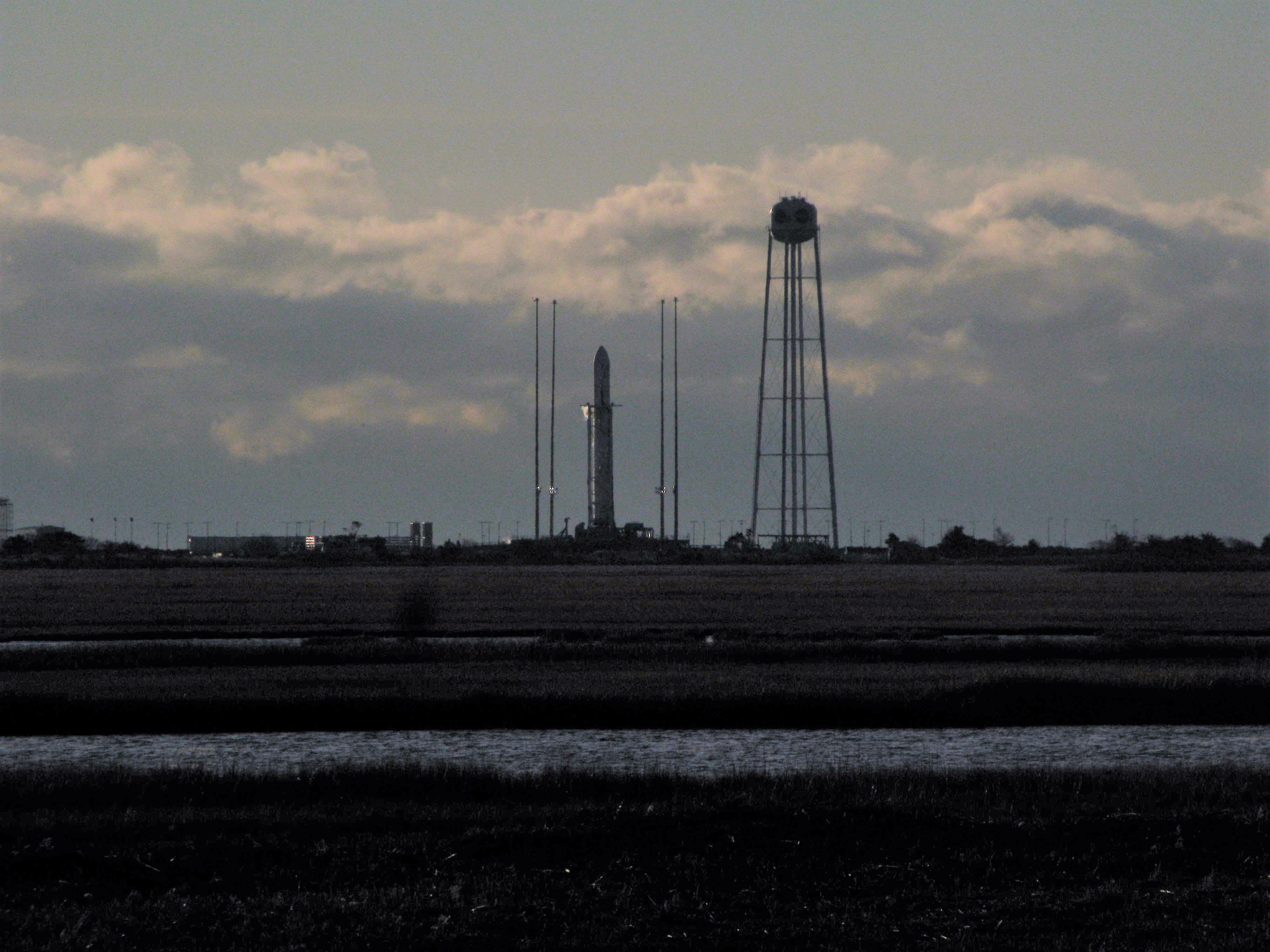

Watch for Ken’s continuing Antares/Cygnus mission and launch reporting from on site at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, VA during the launch campaign.
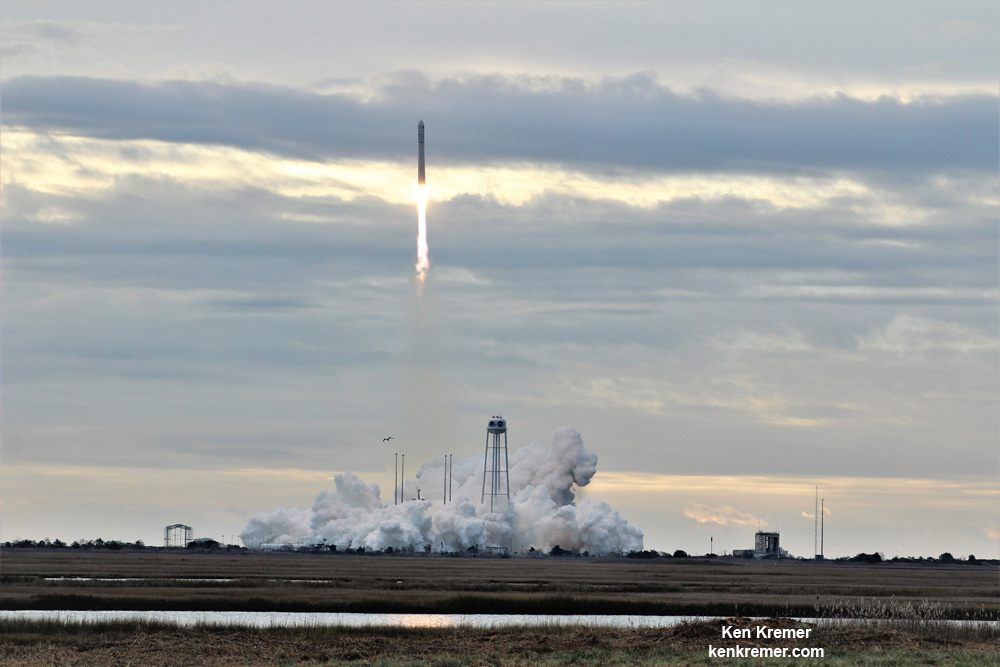

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.