[/caption]
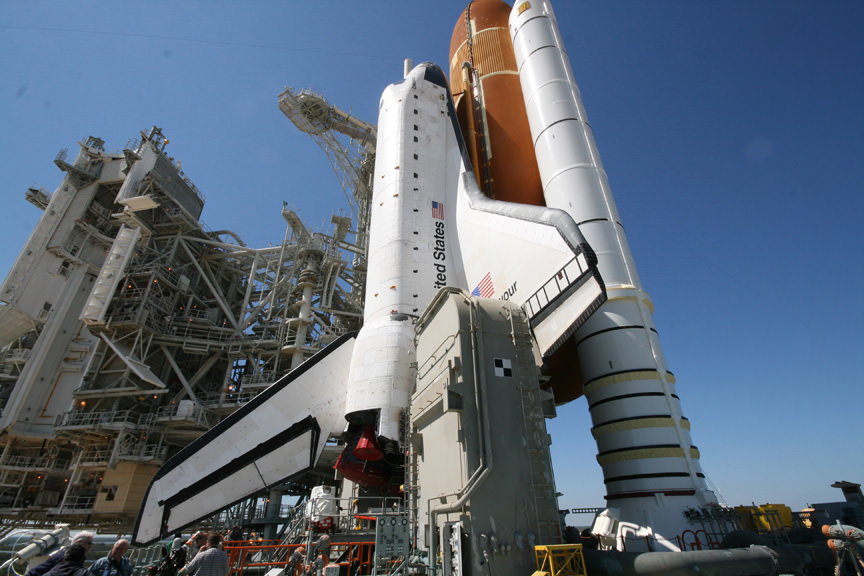
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER – Space Shuttle Endeavour is poised for launch as the countdown clock ticks down to a liftoff from Pad 39 A on Monday morning, May 16 at 8:56 a.m. EDT. The shuttle Mission Management Team (MMT) at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) met today (May 14) and gave the green light to continue launch preparations for the STS-134 mission, which is the final flight of shuttle Endeavour.
The weather forecast remains at a 70 percent favorable chance of acceptable conditions on Monday, according to Shuttle Weather Officer Kathy Winters. The weather outlook drops to only 20 percent favorable on Tuesday in case of a one day delay. The weather rebounds to 80 percent favorable if the launch is postponed by 48 hours.

At a briefing for reporters at KSC today, shuttle launch managers were upbeat about preparations for the launch.
“We had a really good meeting today, unanimous consent from the Mission Management Team to press on with the launch countdown,” said Mike Moses, MMT chairman and manager of shuttle integration at KSC. “Everything’s in really great shape, really no issues at all.”
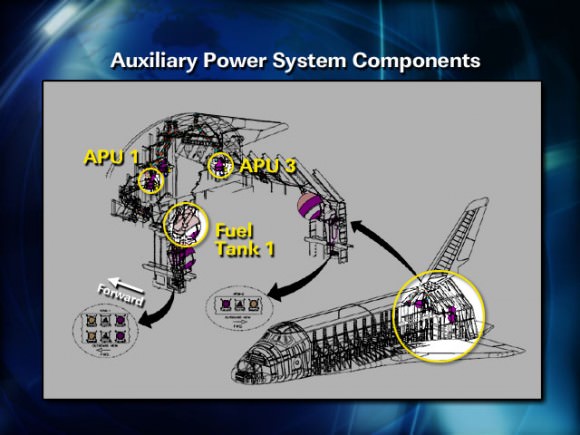
Moses added that no problems are expected with the heaters in the auxiliary power units (APU’s) that caused the launch scrub two weeks ago on April 29.

Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach said, “The countdown is going extremely well and the team is ready to go. Tanking of the External Tank begins just prior to midnight. We are not working any issue at this time.”
Fueling of the External Tank with supercold liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen starts at 11.36 p.m. Sunday night.
Leinbach said that local officials are expecting a crowd of about half a million people to descend on the Florida Space Coast area for the launch.
“You’ll recall for the first launch attempt on that Friday afternoon, the estimate was between 500,000 and 750,000,” he said. “So they’re not quite expecting that big surge, but it’ll still be a heck of a traffic jam after launch.”
Endeavour and her six man crew will deliver the $2 Billion Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer – a particle physics detector searching for dark matter, dark energy and antimatter – to the International Space Station during a 16 day mission that will include 4 spacewalks.
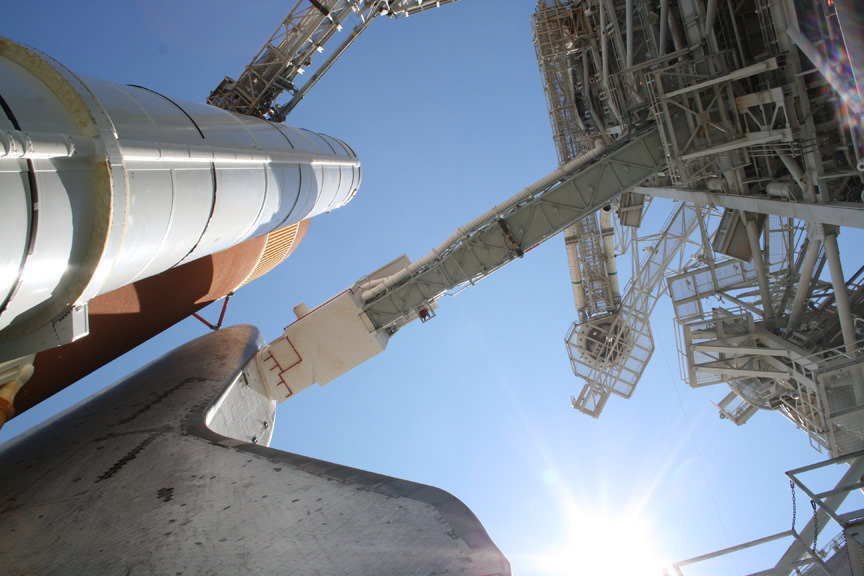
After Endeavour was rolled out to the pad, I had an awesome opportunity to photograph Endeavour at the pad from stunning vantage points all around the launch pad from top to bottom.
Herein is part 2 of my photo album focusing on my visit to the base of the shuttle stack on the mobile launch platform while looking to the heavens and standing directly beneath the External Tank and in between the Twin Solid Rocket Boosters. Part 1 of my photo album concentrated on the view from the upper levels and our visit to the White Room – where the astronauts board the shuttle orbiter to take their seats for the adventure of a lifetime.


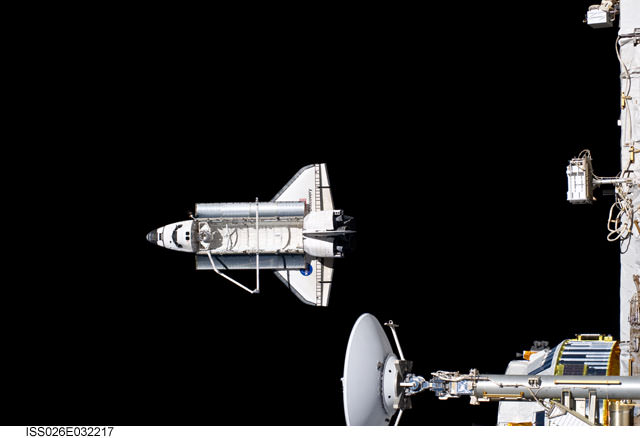
Endeavour will deliver the $2 Billion Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer to the International Space Station which seeks to unveil the Unknown and uncover the birth of the Universe. Credit: Ken Kremer



on top of pad 39 A. Credit: Ken Kremer

If you watch Endeavour’s launch, send me your launch and crowd photos to post in an STS-134 launch gallery here at Universe Today.
Read my related stories about the STS-134 mission here:
Endeavour Astronauts Arrive at Cape for May 16 Launch
NASA Sets May 16 for Last Launch of Endeavour; Atlantis Slips to July
Endeavour’s Final Launch further delayed another Week or more
On the Cusp of Endeavour’s Final Flight
Brush Fires Erupt at Kennedy Space Center during Endeavour’s Last Countdown
Commander Mark Kelly and STS-134 Crew Arrive at Kennedy for Endeavour’s Final Flight
President Obama to Attend Endeavour’s Last Launch on April 29
Shuttle Endeavour Photo Special: On Top of Pad 39A for Final Flight
Endeavour Mated to Rockets for Last Flight Photo Album
Endeavour Rolls to Vehicle Assembly Building for Final Flight
NPR Radio interview including Ken here:
Shuttle Fixes Will Take At Least One Week