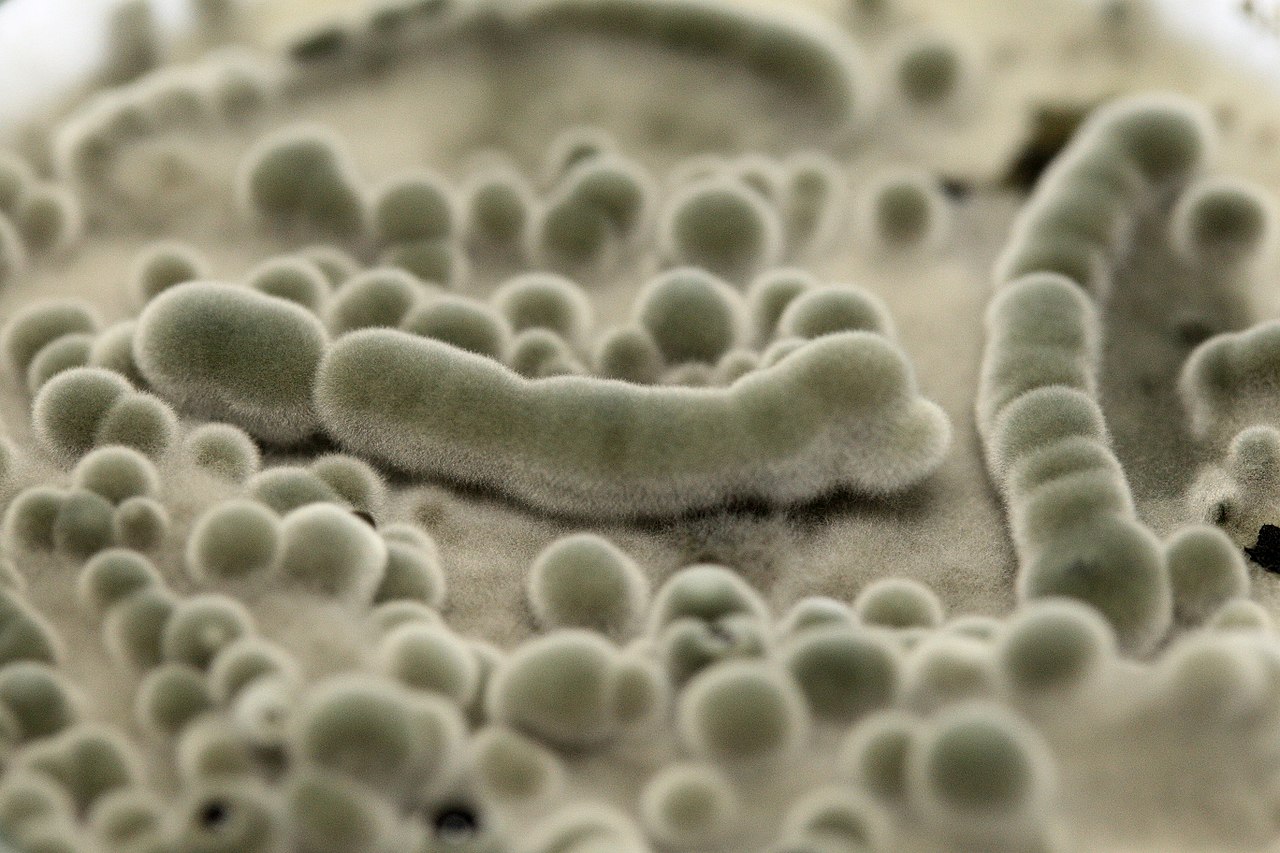
A lack of effective radiation shielding is one of the biggest challenges still to be overcome if humans are to embark on long-term voyages into deep space. On Earth, the planet’s powerful magnetosphere protects us from the deadliest forms of radiation – those produced by solar flares, and galactic cosmic rays arriving from afar – that stream through the Solar System. Astronauts on the International Space Station, some 408km above the Earth, receive elevated levels of radiation, but are close enough to Earth that they still receive some shielding, and can stay on orbit for up to a year. The same can’t be said for astronauts traveling further out, to the Moon, for example, or, someday, to Mars. Future deep space voyagers will need to bring their own shielding with them – or, as a new paper suggests – grow it along the way.
Continue reading “Fungi Were Able to Absorb Radiation on the ISS. Could Astronauts Grow Their own Radiation Shields in Space?”Blue Origin Announces the “Orbital Reef,” the Space Station they Plan to Build in Orbit
Blue Origin has certainly stepped up its game of late! After stepping down as the CEO of Amazon, Jeff Bezos has made it his personal mission to take the company he founded in 2000 and turn it into a powerhouse of the commercial space sector. Between some high-profile missions involving the New Shepard – which included passengers like Wally Funk, William Shatner, and even himself and his brother – Bezos has also been outspoken about his long-term vision.
Bezos describes this vision as “building a road to space so our children can build the future.” In the latest step towards achieving this, Blue Origin announced a new partnership with Sierra Space to develop a commercial space station in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), known as “Orbital Reef.” This mixed-use space station, which is to be completed by the end of this decade, will facilitate commerce, research, tourism, and facilitate the commercialization of LEO.
Continue reading “Blue Origin Announces the “Orbital Reef,” the Space Station they Plan to Build in Orbit”The Astronauts who Would Have Tested Starliner Have Been Reassigned to an Upcoming SpaceX Crew Dragon Launch
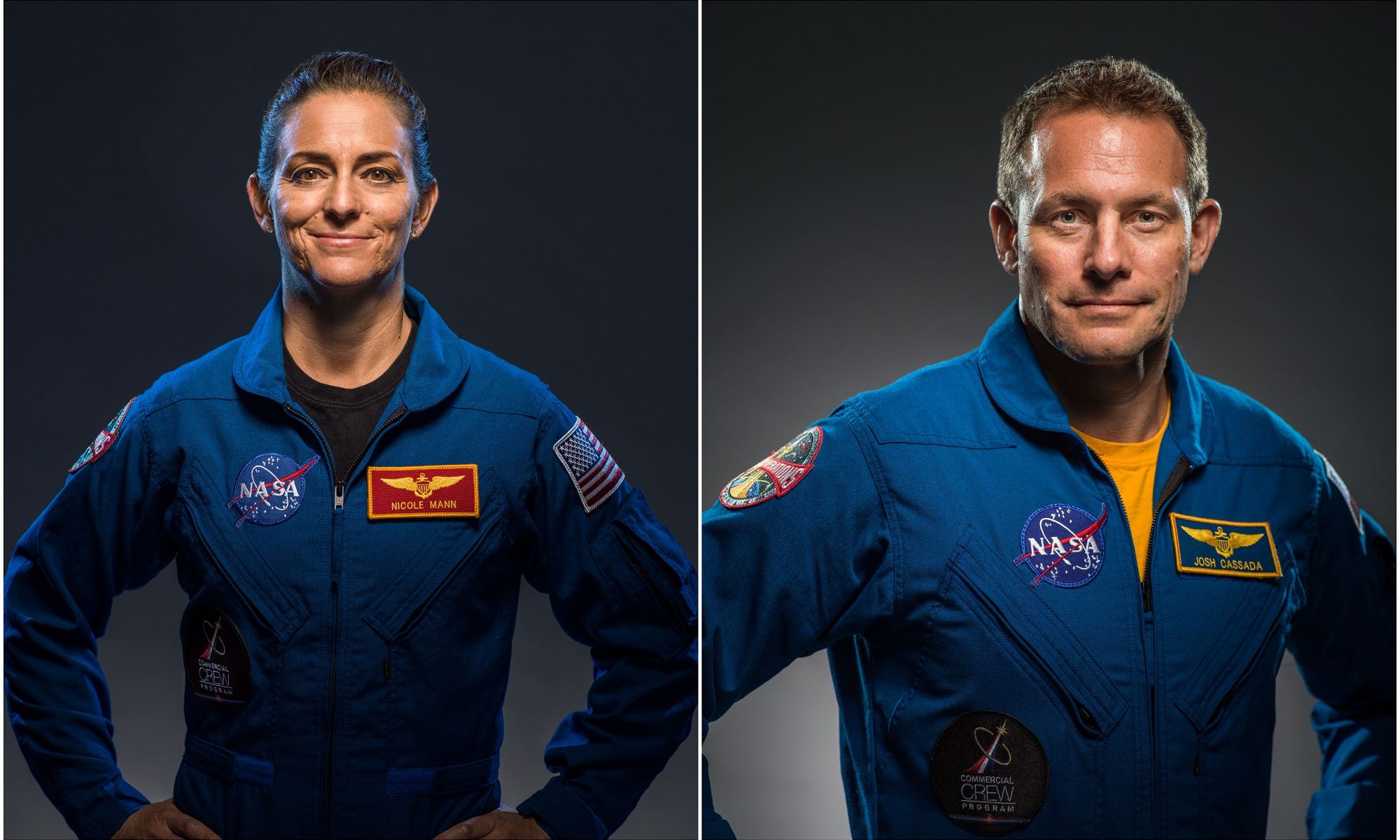

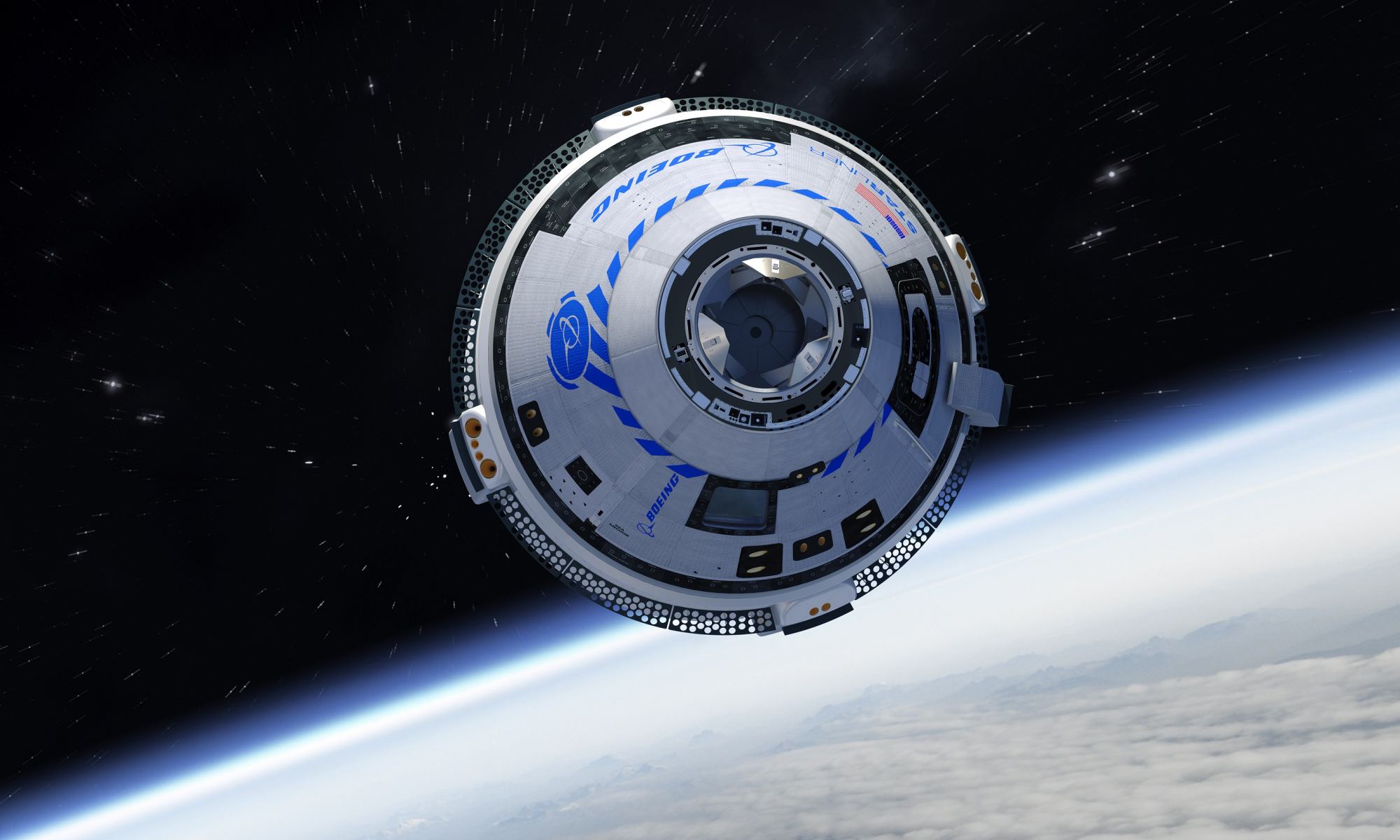
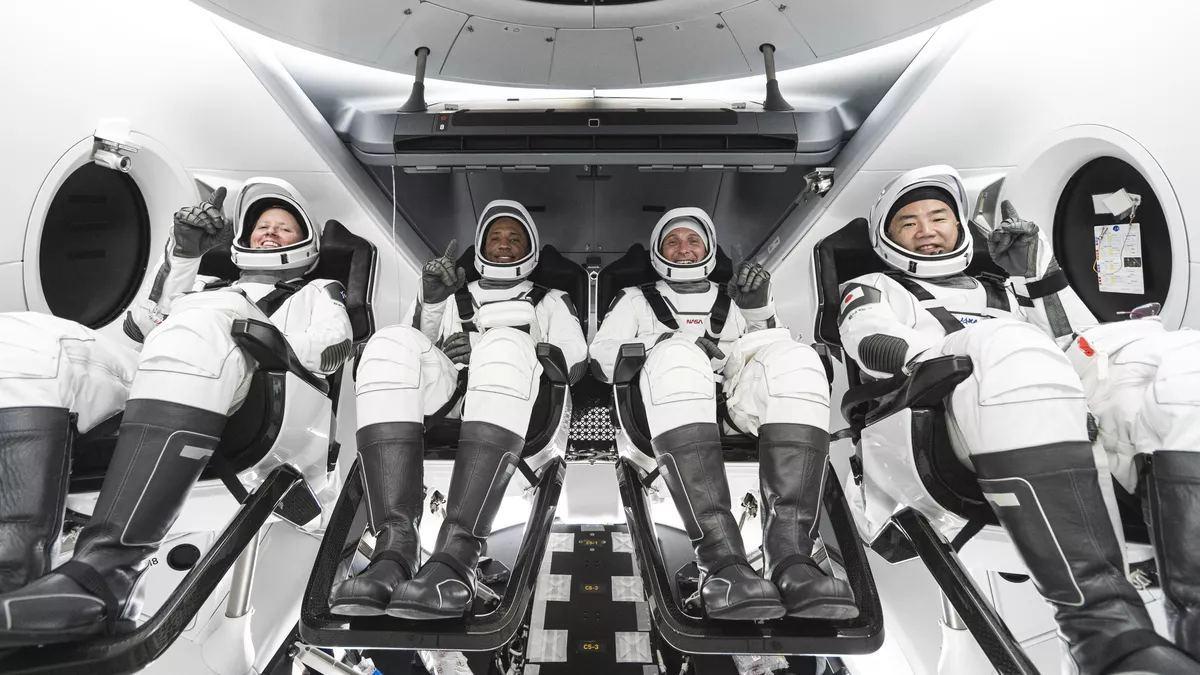
In 2011, NASA announced a bold new program to leverage partnerships between the government and the commercial space sector to restore domestic launch capability. As part of the Commercial Crew Program (CCP), NASA selected Boeing and SpaceX to develop next-generation crew-rated capsules that would transport astronauts and payloads to International Space Station (ISS) and other locations in Low-Earth Orbit (LEO).
While SpaceX has managed to meet all the requirements of the CCP with their Crew Dragon module, Boeing’s Starliner has experienced technical problems and several delays. With the latest delay (caused by the ISS being temporarily pushed out of its orbit), NASA has decided to reassign the astronauts that were scheduled to take the Starliner on its maiden crewed flight (Starliner-1) to the next crewed flight of the SpaceX Crew Dragon to the ISS (Crew-5).
Continue reading “The Astronauts who Would Have Tested Starliner Have Been Reassigned to an Upcoming SpaceX Crew Dragon Launch”Russia’s new Module Kicks the Station out of Position, Causes a Delay for Starliner
On July 28th, the International Space Station (ISS) suffered a mishap after a new Russian module (named Nauka) fired its thrusters just hours after arriving. As a result, the entire station was temporarily pushed out of position, forcibly delaying the Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) mission. This would have been Boeing’s CT-100 Starliner’s second attempt to rendezvous with the ISS as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP).
The ISS managed to correct its orbit shortly thereafter, while the OFT-2 launch was delayed until the next available opportunity (Wednesday, Aug. 4th). Unfortunately, the mission was delayed again due to an issue with one of the valves on the spacecraft’s propulsion system. This prompted the ground crews to move the Starliner and Atlas V launch vehicle back into Vertical Integration Facility (VIF), so they can look for the source of the problem more closely.
Continue reading “Russia’s new Module Kicks the Station out of Position, Causes a Delay for Starliner”Health Issues From Spaceflight Might Originate in the Mitochondria
It’s not easy living and working in space for extended periods of time. As NASA’s Twins Study illustrated, microgravity takes a toll on human physiology, which is followed by a painful transition back to normal gravity (just ask Scott Kelly!) Aside from muscle and bone degeneration, there’s diminished organ function, effects on cardiovascular health, the central nervous system, and “subtle changes” on the genetic level.
Until now, the biggest unanswered question was what the underlying cause of these physical impacts was. But after reviewing all of the data accumulated from decades of research aboard the International Space Station (ISS) – which included the Twins Study and DNA samples taken from dozens of astronauts – an international team of researchers came to the conclusion that mitochondria might be the driving force for these changes.
Continue reading “Health Issues From Spaceflight Might Originate in the Mitochondria”SpaceX’s Resilience Spacecraft has Lifted Off and is Headed for the ISS!
Earlier this evening (Sunday, November 15th, 2020), NASA and SpaceX achieved another historical milestone. Six months after successfully sending astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the ISS with the Demo-2 mission, the US demonstrated the restoration of domestic launch capability by sending the fully-crewed Crew Dragon spacecraft (Resilience) on an operational mission to the ISS.
Continue reading “SpaceX’s Resilience Spacecraft has Lifted Off and is Headed for the ISS!”ISS Crew Return Safely to Earth
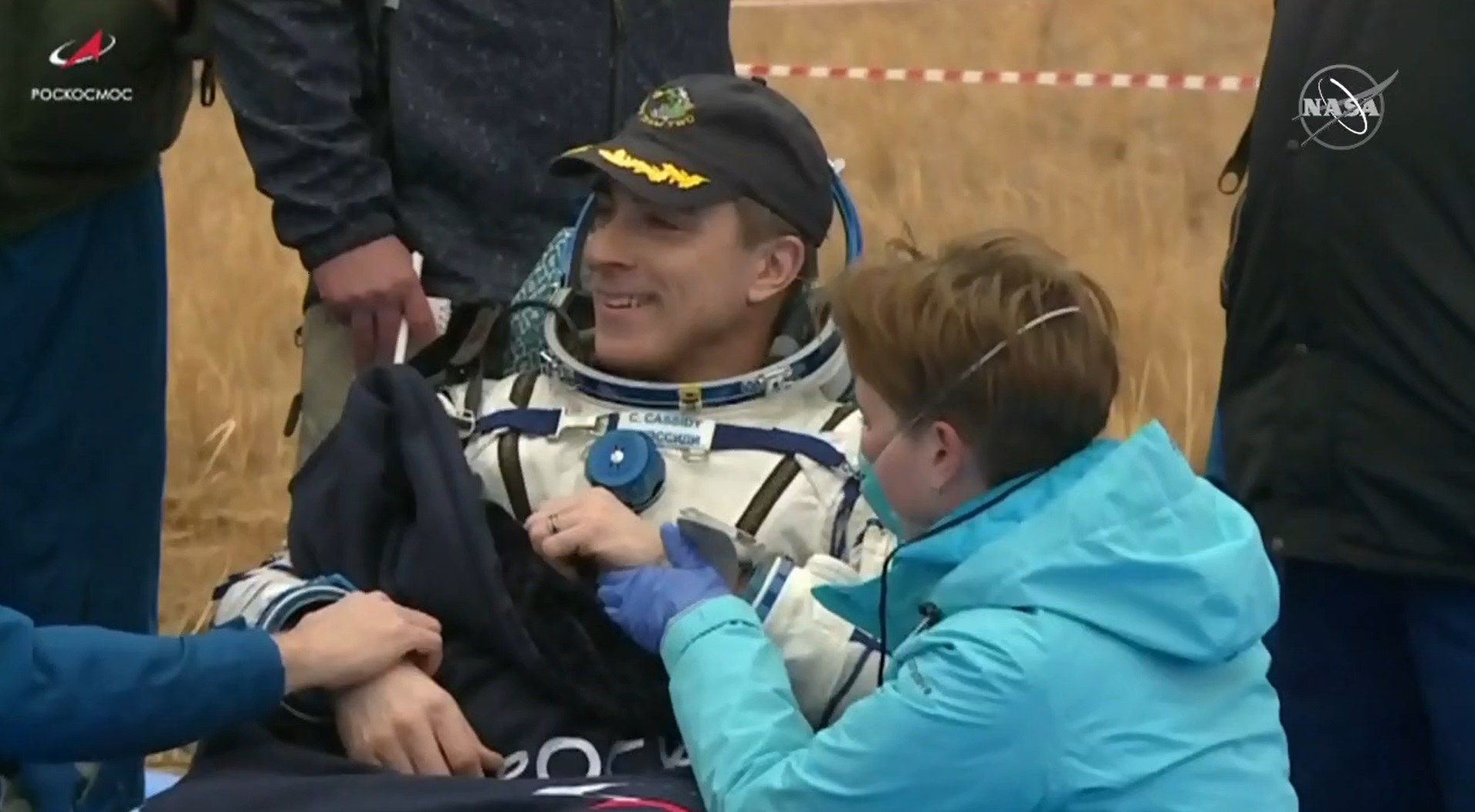
On the evening of Wednesday, Oct. 21st, the crew of Expedition 63 finally returned to Earth after spending 196 days in space. It all began when NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy (commander) and Russian cosmonauts Ivan Vagner and Anatoly Ivanishin (both flight engineers) departed the International Space Station (ISS) aboard their Soyuz spacecraft at 07:32 PM EDT (04:32 PM PDT) and landed in Kazakhstan by 10:54 PM EDT (07:54 PM PDT).
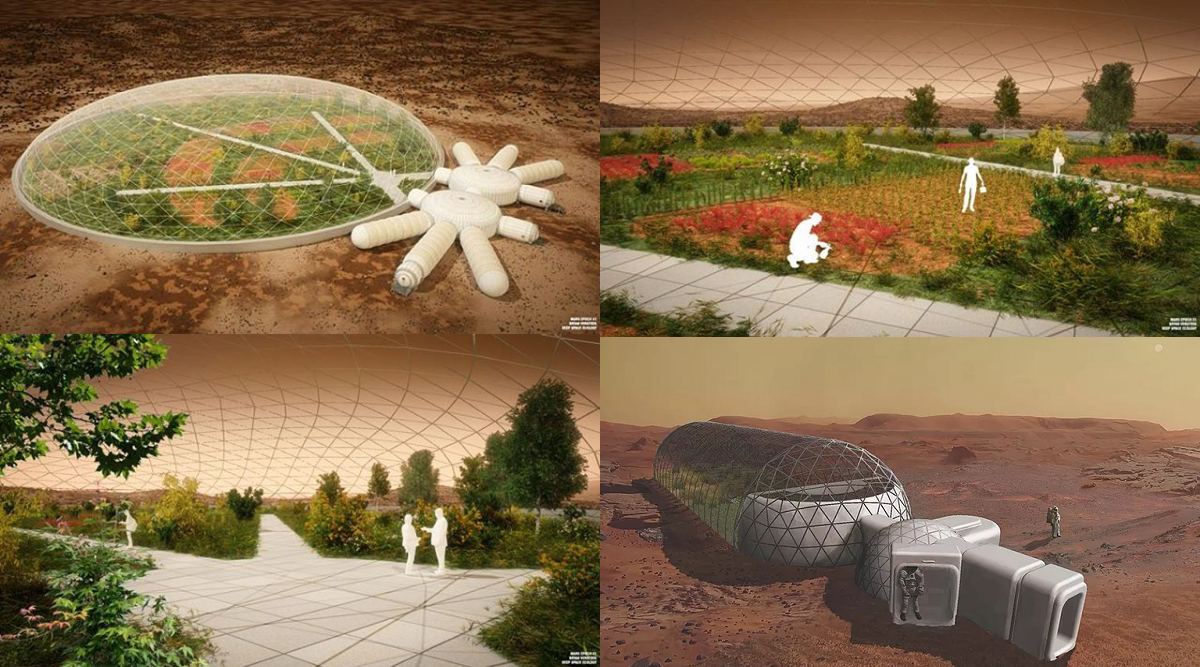
Continue reading “ISS Crew Return Safely to Earth”What Martian Settlers Need to Know About Soil Can Teach us How to Grow Better on Earth
When human beings start living in space for extended periods of time they will need to be as self-sufficient as possible. The same holds true for settlements built on the Moon, on Mars, and other bodies in the Solar System. To avoid being entirely dependent on resupply missions from Earth (which is costly and time-consuming) the inhabitants will need to harvest resources locally – aka. In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU).
This means they’ll have to procure their own sources of water, building materials, and grow their own food. While the ISS has allowed for all kinds of experiments involving hydroponics in space, little has been done to see how soil fares in microgravity (or lower gravity). To address this, Morgan Irons – Chief Science Officer of the Virginia-based startup Deep Space Ecology (DSE) – recently sent her Soil Health in Space experiment to the ISS.
Continue reading “What Martian Settlers Need to Know About Soil Can Teach us How to Grow Better on Earth”The Air Leak on the International Space Station is Worse Than Previously Believed
On Tuesday, Sept. 29th, the Russian State Space Corporation (Roscosmos) announced that astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) had found the source of a suspected leak. The crew of Expedition 63 – NASA astronaut and Commander Chris Cassidy and Russian cosmonauts Anatoly Ivanishin and Ivan Vagner – had been searching for this leak since August, and determined that it was “beyond expected levels.”
Roscosmos also said in a statement that “it was established that the spot is located in the Zvezda (star) service module, which contains scientific equipment.” They also emphasized that the leak “is not dangerous for the life and health of the ISS crew and does not prevent the ISS continuing manned flight.” Nevertheless, the amount of atmosphere lost may require additional oxygen to be pumped into the station.
Continue reading “The Air Leak on the International Space Station is Worse Than Previously Believed”Astronauts Come Back to Earth on August 2nd, Completing the Full Crew Dragon Test
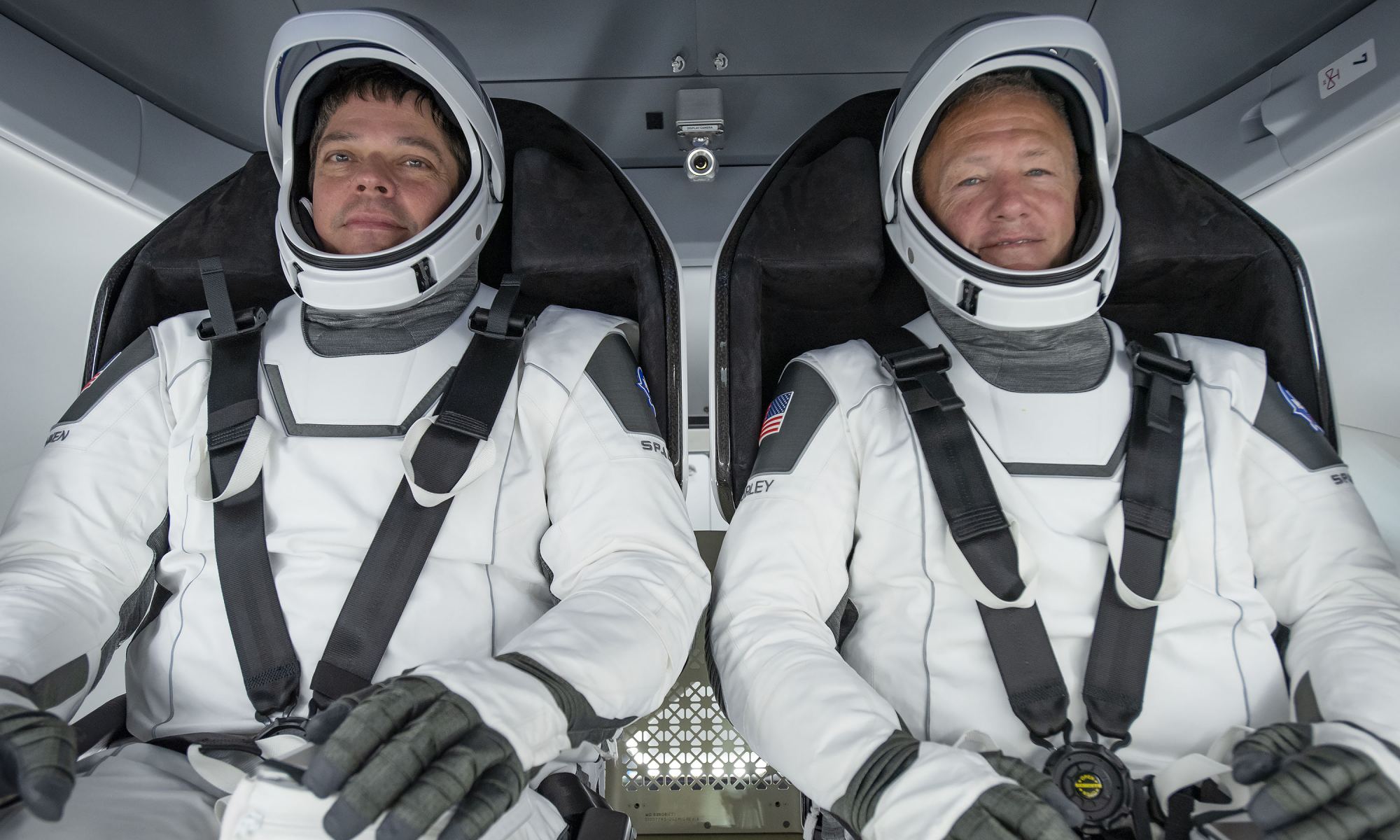

On May 30th, SpaceX and NASA made history when a Crew Dragon spacecraft carrying two astronauts (Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley) launched atop a Falcon 9 rocket and rendezvoused with the International Space Station (ISS). With this one flight, NASA and SpaceX demonstrated that the US once again has domestic launch capability, something they have not enjoyed since the retirement of the Space Shuttle in 2011.
In one week, Sunday, August 2nd, Robert and Douglas will be returning to Earth using the same Crew Dragon spacecraft (named Endeavour) that took them to the ISS. This is the most crucial part of Demo-2 flight, where the spacecraft is tasked with bringing the astronauts home, safe and sound. As you can imagine, there are a lot of people who are understandably nervous, not the least of which is SpaceX founder Elon Musk.
Continue reading “Astronauts Come Back to Earth on August 2nd, Completing the Full Crew Dragon Test”