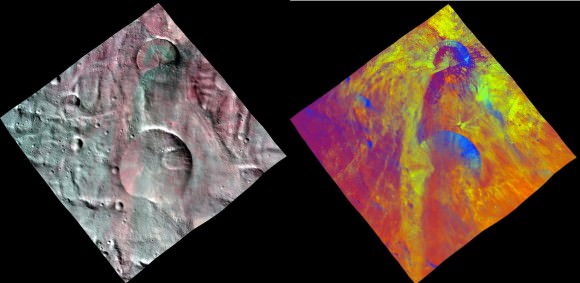
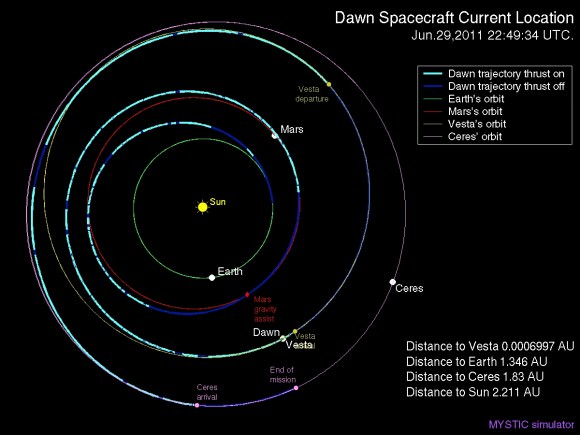
[/caption]
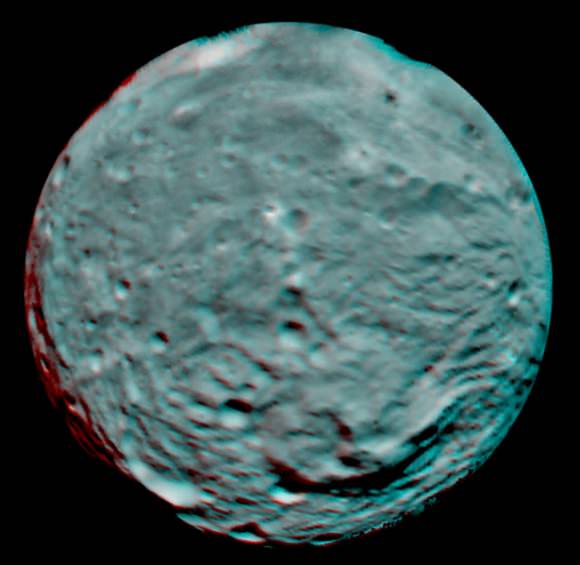
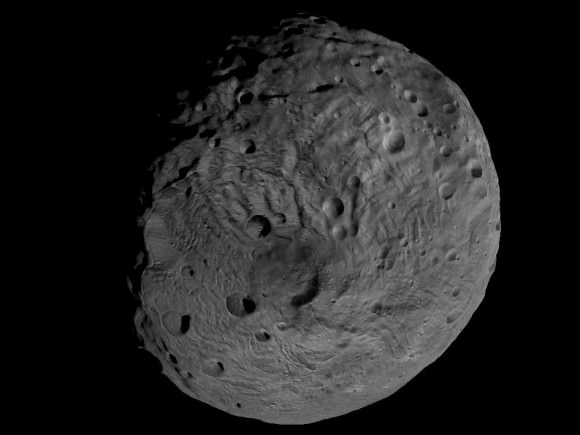
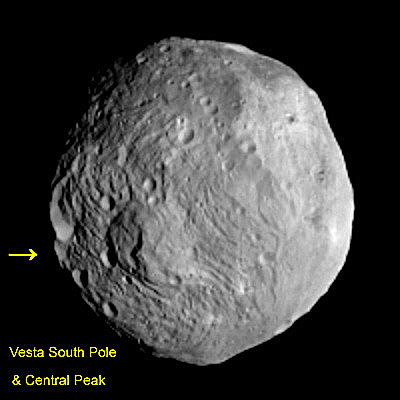
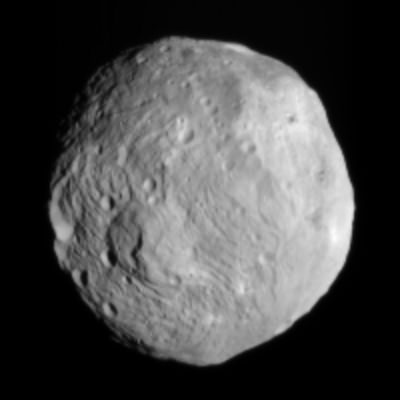
NASA’s Dawn mission is getting a whopping boost in science observing time at the closest orbit around Asteroid Vesta as the probe passes the midway point of its 1 year long survey of the colossal space rock. And the team informs Universe Today that the data so far have surpassed all expectations and they are very excited !
Dawn’s bonus study time amounts to an additional 40 days circling Vesta at the highest resolution altitude for scientific measurements. That translates to a more than 50 percent increase beyond the originally planned length of 70 days at what is dubbed the Low Altitude Mapping Orbit, or LAMO.
“We are truly thrilled to be able to spend more time observing Vesta from low altitude,” Dr. Marc Rayman told Universe Today in an exclusive interview. Rayman is Dawn’s Engineer at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, Calif.
“It is very exciting indeed to obtain such a close-up look at a world that even a year ago was still just a fuzzy blob.”
The big extension for a once-in-a-lifetime shot at up close science was all enabled owing to the hard work of the international science team in diligently handling any anomalies along the pathway through interplanetary space and since Dawn achieved orbit in July 2011, as well as to the innovative engineering of the spacecraft’s design and its revolutionary ion propulsion system.
“This is a reflection of how well all of our work at Vesta has gone from the beginning of the approach phase in May 2011,” Rayman told me.

Credit: Gregory J. Whiffen, JPL
Dawn’s initially projected 10 week long science campaign at LAMO began on Dec. 12, 2011 at an average distance of 210 kilometers (130 miles) from the protoplanet and was expected to conclude on Feb. 20, 2012 under the original timeline. Thereafter it would start spiraling back out to the High Altitude Mapping Orbit, known as HAMO, approximately 680 kilometers above the surface.
“With the additional 40 days it means we are now scheduled to leave LAMO on April 4. That’s when we begin ion thrusting for the transfer to HAMO2,” Rayman stated.
And the observations to date at LAMO have already vastly surpassed all hopes – using all three of the onboard science instruments provided by the US, Germany and Italy.
“Dawn’s productivity certainly is exceeding what we had expected,” exclaimed Rayman.
“We have acquired more than 7500 LAMO pictures from the Framing Camera and more than 1 million LAMO VIR (Visible and Infrared) spectra which afford scientists a much more detailed view of Vesta than had been planned with the survey orbit and the high altitude mapping orbit (HAMO). It would have been really neat just to have acquired even only a few of these close-up observations, but we have a great bounty!”
“Roughly around half of Vesta’s surface has been imaged at LAMO.”
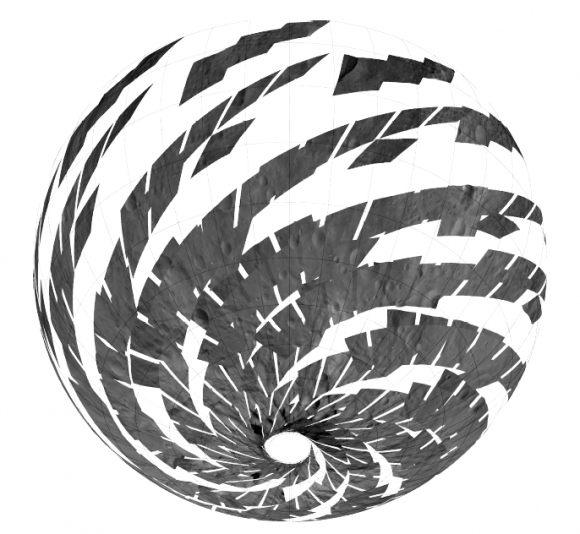

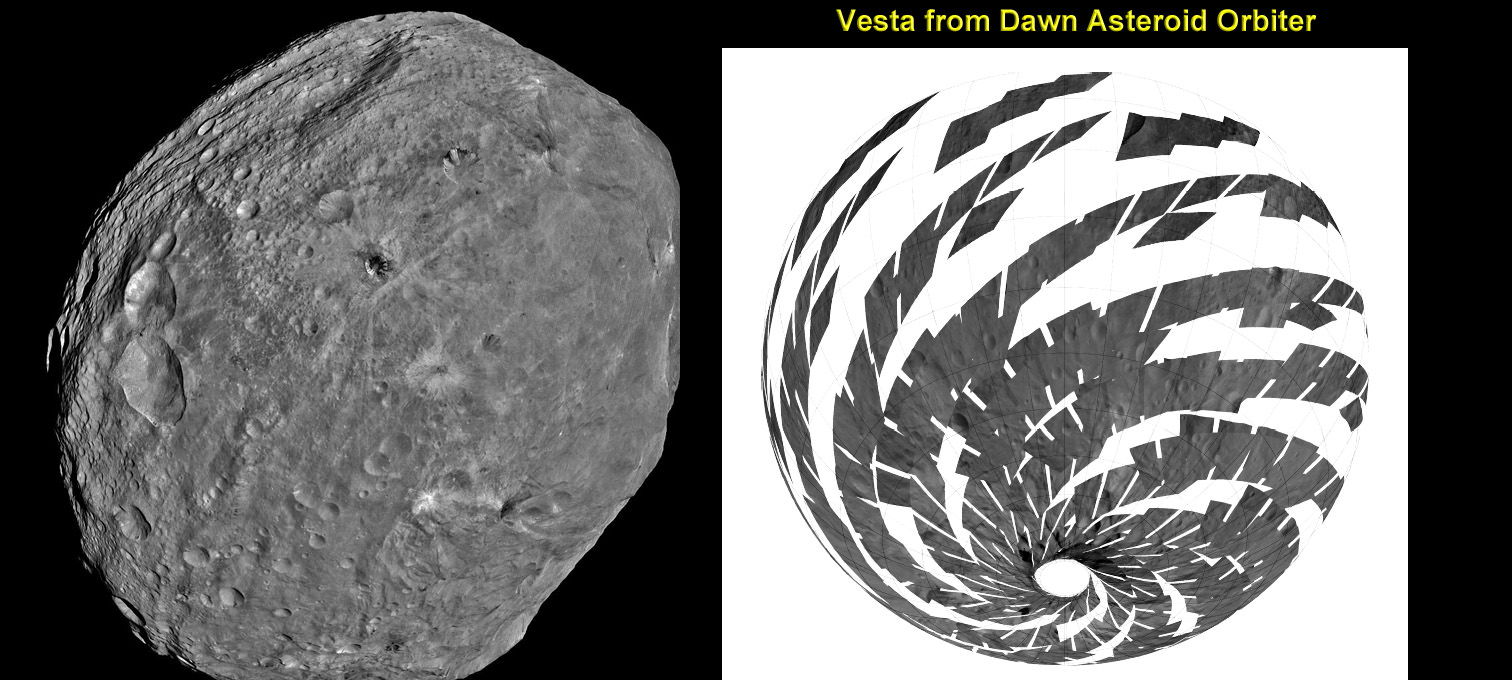
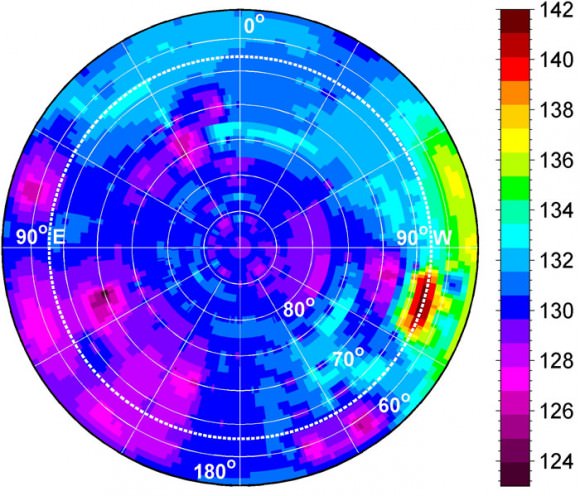
This mosaic shows the location of the data acquired by VIR (visible and infrared spectrometer) during the HAMO (high-altitude mapping orbit) phase of the Dawn mission from August to October 2011. Dawn is now making the same observations at the now extended LAMO (low-altitude mapping orbit) phase of the Dawn mission from December 2011 to April 2012. VIR can image Vesta in a number of different wavelengths of light, ranging from the visible to the infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum. This mosaic shows the images taken at a wavelength of 550 nanometers, which is in the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. During HAMO VIR obtained more than 4.6 million spectra of Vesta. It is clear from this image that the VIR observations are widely distributed across Vesta, which results in a global view of the spectral properties of Vesta’s surface. This image shows Vesta’s southern hemisphere (lower part of the image) and equatorial regions (upper part of the image). NASA’s Dawn spacecraft obtained these VIR images with its visible and infrared spectrometer in September and October 2011. The distance to the surface of Vesta is around 700 kilometers (435 miles) and the average image resolution is 170 meters per pixel. Credit: NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ UCLA/ ASI/ INAF/ IAPS
The bonus time at LAMO will now be effectively used to help fill in the gaps in surface coverage utilizing all 3 science instruments. Therefore perhaps an additional 20% to 25% extra territory will be imaged at the highest possible resolution. Some of this will surely amount to enlarged new coverage and some will be overlapping with prior terrain, which also has enormous research benefits.
“There is real value even in seeing the same part of the surface multiple times, because the illumination may be different. In addition, it helps for building up stereo,” said Rayman.
Researchers will deduce further critical facts about Vesta’s topography, composition, interior, gravity and geologic features with the supplemental measurements.
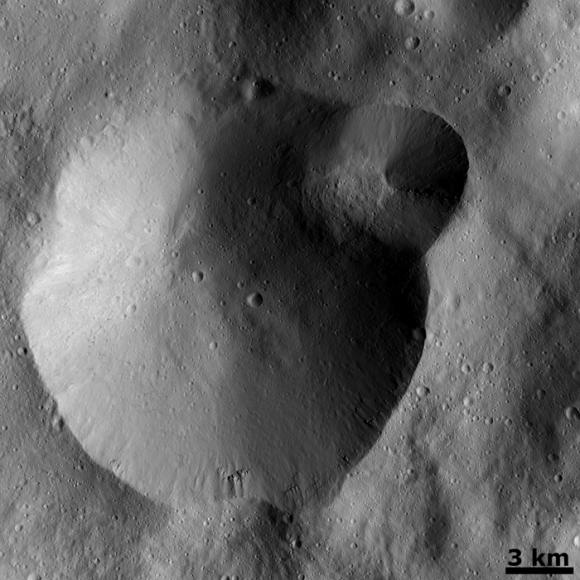

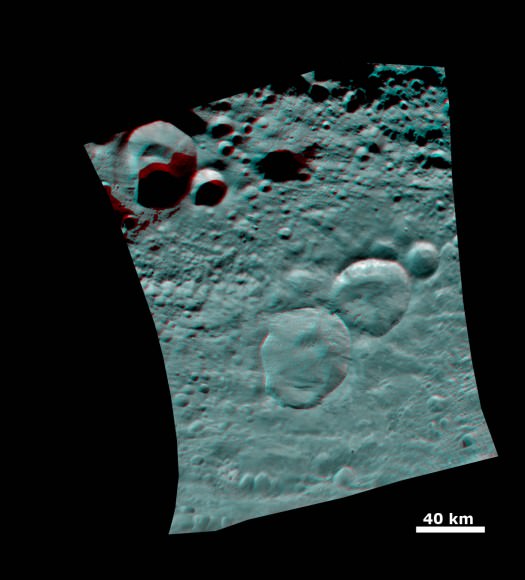
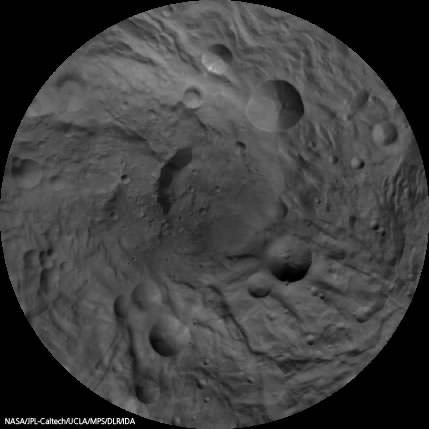
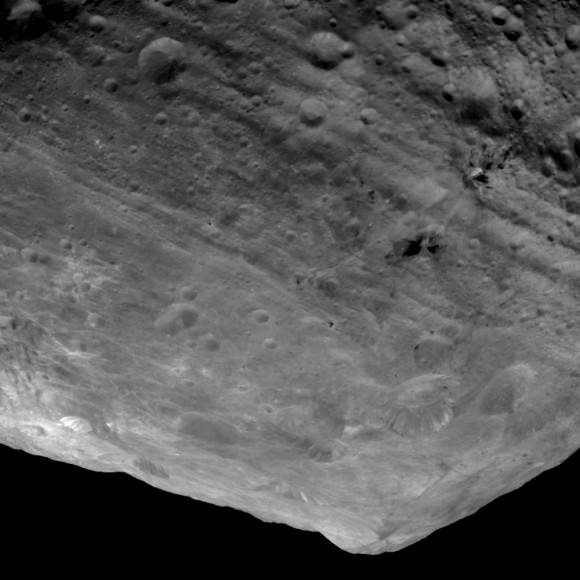
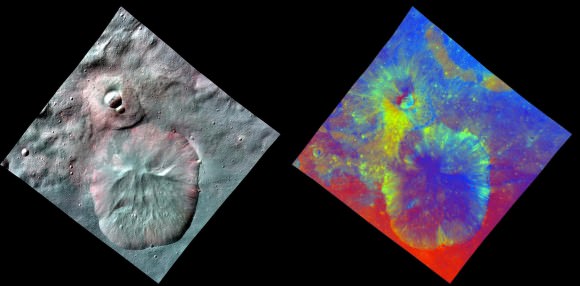
This Dawn FC (framing camera) image shows two overlapping impact craters and was taken on Dec. 18,2011 during the LAMO (low-altitude mapping orbit) phase of the mission. The large crater is roughly 20 kilometers (12 miles) in diameter and the smaller crater is roughly 6 kilometers (4 miles) in diameter. The rims of the craters are both reasonably fresh but the larger crater must be older because the smaller crater cuts across the larger crater’s rim. As the smaller crater formed it destroyed a part of the rim of the pre-existing, larger crater. The larger crater’s interior is more densely cratered than the smaller crater, which also suggests that is it older. In the bottom of the image there is some material slumping from rim of the larger crater towards its center. This image with its framing camera on Dec. 18, 2011. This image was taken through the camera’s clear filter. The distance to the surface of Vesta is 260 kilometers (162 miles) and the image has a resolution of about 22 meters (82 feet) per pixel. Credit: NASA/ JPL-Caltech/ UCLA/ MPS/ DLR/ IDA
The foremost science goals at LAMO are collection of gamma ray and neutron measurements with the GRaND instrument – which focuses on determining the elemental abundances of Vesta – and collection of information about the structure of the gravitational field. Since GRaND can only operate effectively at low orbit, the extended duration at LAMO takes on further significance.
“Our focus is on acquiring the highest priority science. The pointing of the spacecraft is determined by our primary scientific objectives of collecting GRaND and gravity measurements.”
As Dawn continues orbiting every 4.3 hours around Vesta during LAMO, GRaND is recording measurements of the subatomic particles that emanate from the surface as a result of the continuous bombardment of cosmic rays and reveals the signatures of the elements down to a depth of about 1 meter.
“You can think of GRaND as taking a picture of Vesta but in extremely faint light. That is, the nuclear emissions it detects are extremely weak. So our long time in LAMO is devoted to making a very, very long exposure, albeit in gamma rays and neutrons and not in visible light,” explained Rayman.
Now with the prolonged mission at LAMO the team can gather even more data, amounting to thousands and thousands more pictures, hundreds of thousands of more VIR spectra and ultra long exposures by GRaND.
“HAMO investigations have already produced global coverage of Vesta’s gravity field,” said Sami Asmar, a Dawn co-investigator from JPL. Extended investigations at LAMO will likewise vastly improve the results from the gravity experiment.
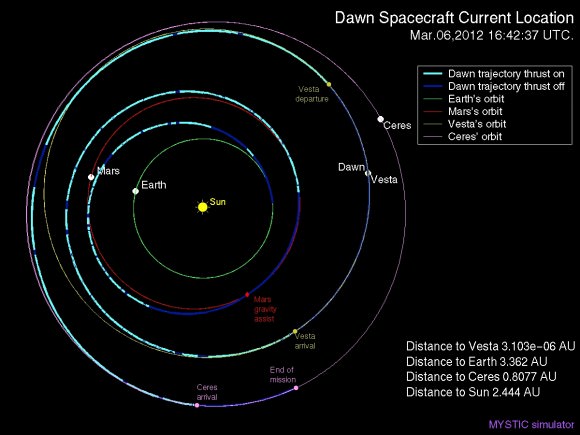
“We always carried 40 days of “margin,” said Rayman, “but no one who was knowledgeable about the myriad challenges of exploring this uncharted world expected we would be able to accomplish all the complicated activities before LAMO without needing to consume some of that margin. So although we recognized that we might get to spend some additional time in LAMO, we certainly did not anticipate it would be so much.”
“As it turned out, although we did have surprises the operations team managed to recover from all of them without using any of those 40 days.”
“This is a wonderful bonus for science,” Rayman concluded.
“We remain on schedule to depart Vesta in July 2012, as planned for the past several years.”
Dawn’s next target is Ceres, the largest asteroid in the main Asteroid Belt between Mars and Jupiter