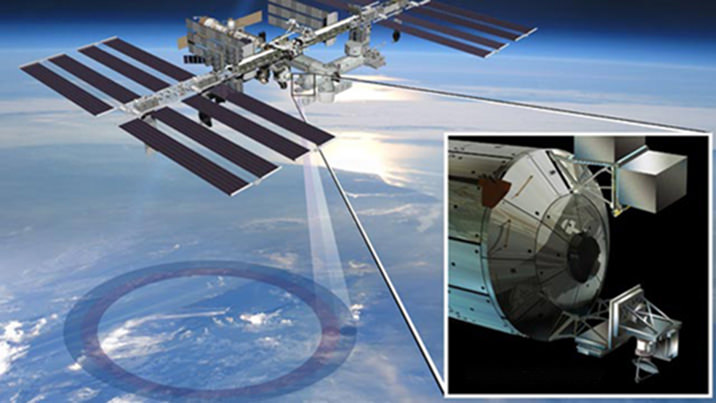
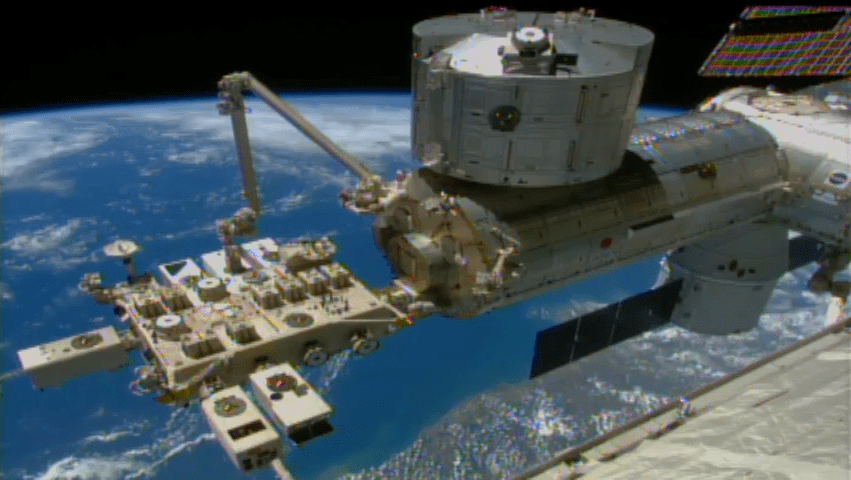
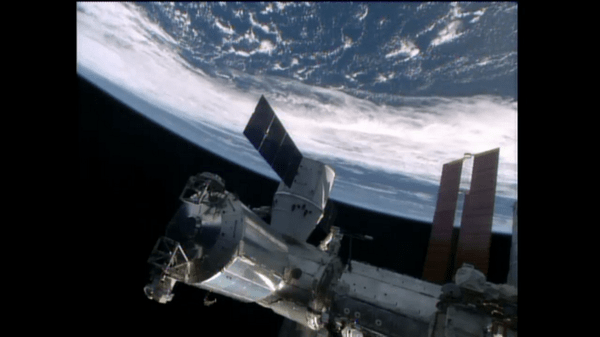
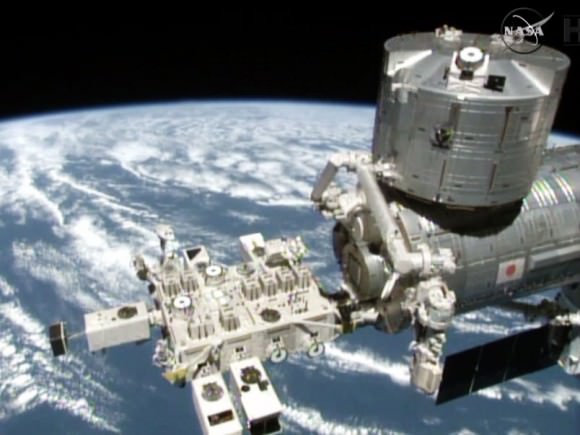
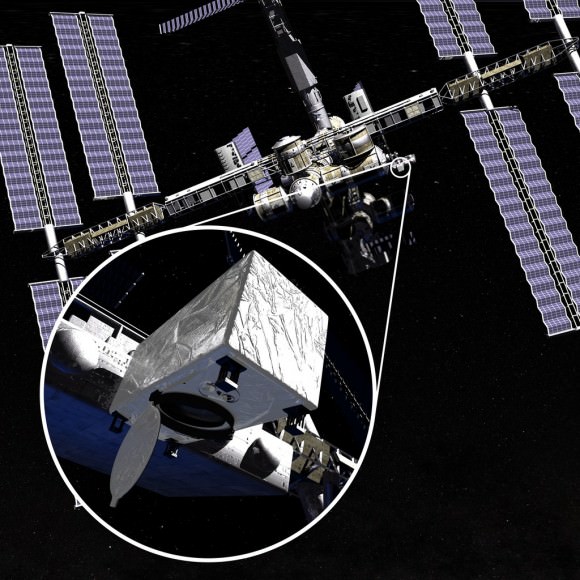
The Japanese robotic arm installs the CATS experiment on an external platform on Japan’s Kibo lab module. The SpaceX Dragon commercial cargo craft is seen at the right center of the image. Credit: NASA TV
See way cool installation video below[/caption]
“Robotic controllers let the CATS out of the bag!” So says NASA spokesman Dan Huot in a cool new NASA timelapse video showing in detail how CATS crawled around the space stations gangly exterior and clawed its way into its new home – topped off with a breathtaking view of our home planet that will deliver science benefits to us down below.
The CATS experiment was installed on the exterior of the International Space Station (ISS) via a first ever type of robotic handoff, whereby one of the stations robotic arms handed the rectangular shaped instrument off to a second robotic arm. Sort of like relays runners passing the baton while racing around the track for the gold medal.
In this case it was all in the name of science. CATS is short for Cloud Aerosol Transport System.
Ground controllers at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston plucked CATS out of the truck of the recently arrived SpaceX Dragon cargo delivery vehicle with the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator (Dextre). Then they passed it off to a Japanese team of controllers at JAXA, manipulating the second arm known as the Japanese Experiment Module Remote Manipulator System. The JAXA team then installed CATS onto an external platform on Japans Kibo laboratory.
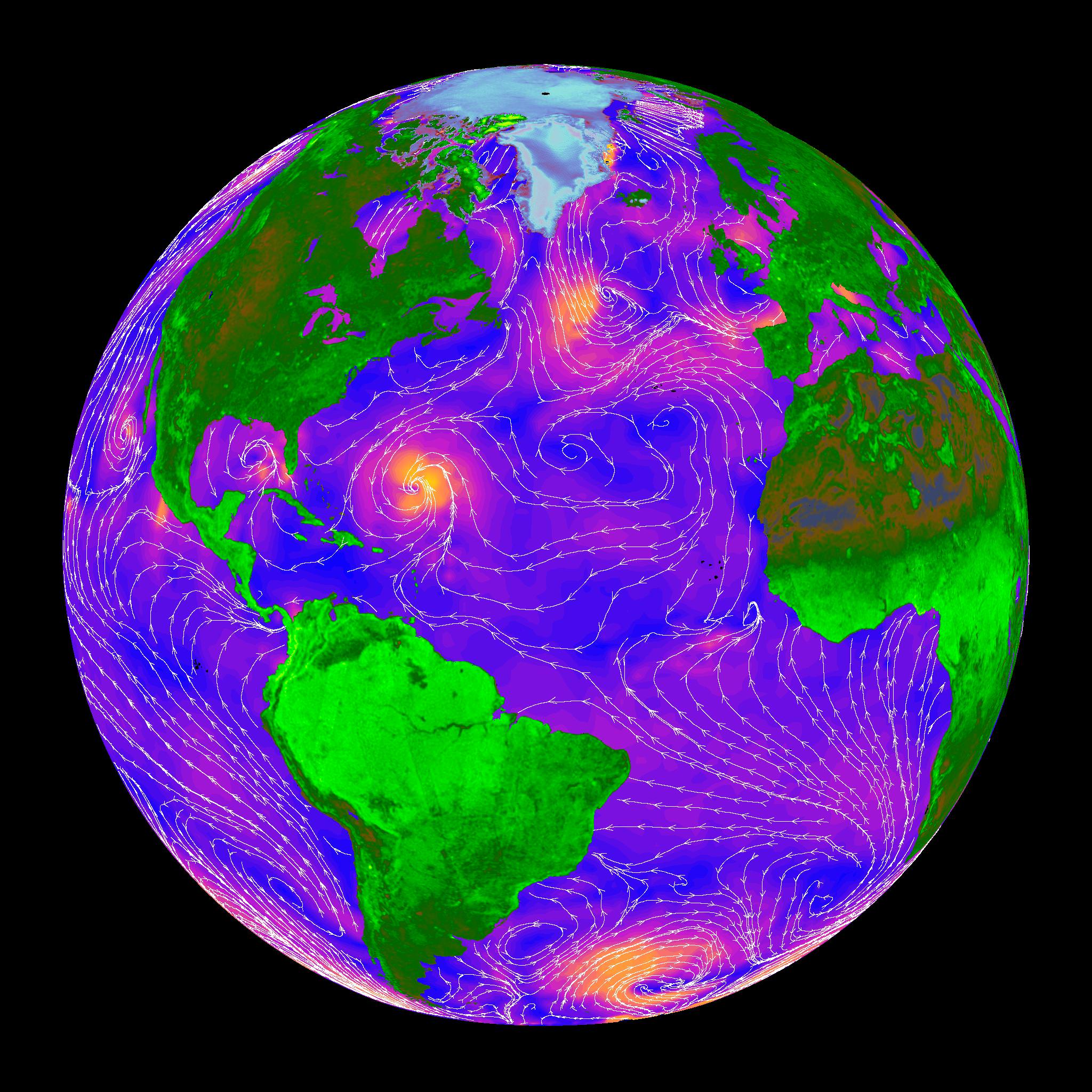
CATS is a new Earth Science instrument dedicated to collecting continuous data about clouds, volcanic ash plumes and tiny airborne particles that can help improve our understanding of aerosol and cloud interactions and improve the accuracy of climate change models.
The remote-sensing laser instrument measures clouds and the location and distribution of pollution, dust, smoke, and other particulates and aerosols in the atmosphere that directly impacts the global climate.
Data from CATS will be used to derive properties of cloud/aerosol layers at three wavelengths: 355, 532, 1064 nm.
Check out this cool NASA ‘Space to Ground’ video showing CATS installation
Video caption: NASA’s Space to Ground on 1/23/15 covers CATS Out of The Bag. This is your weekly update on what’s happening aboard the International Space Station. Got a question or comment? Use #spacetoground to talk to us.
All the movements were conducted overnight by robotic flight controllers on the ground. They installed CATS to an external platform on Japan’s Kibo lab module.
CATS is helping to open a new era on the space station research dedicated to expanding its use as a science platform for making extremely valuable remote sensing observations for Earth Science.
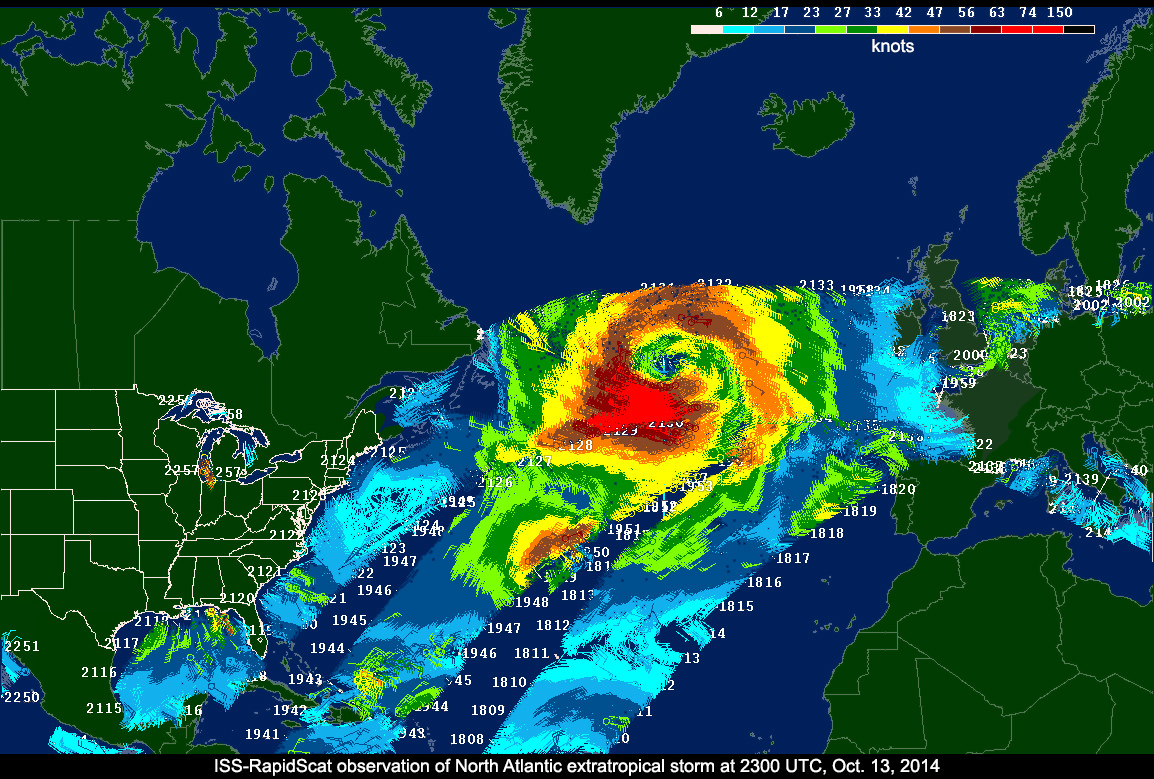
The CATS instrument is the fourth successful NASA Earth science launch out of five scheduled during a 12-month period. And it is the second to be installed on the exterior of the ISS, following ISS-RapidScat that was brought by the SpaceX CRS-4 Dragon.
The fifth launch — the Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite — is scheduled for Jan. 29 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
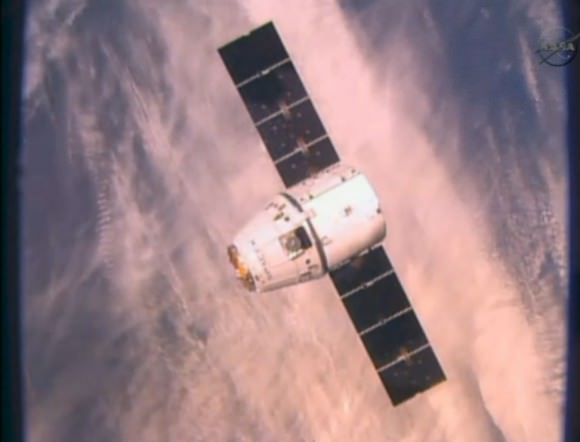
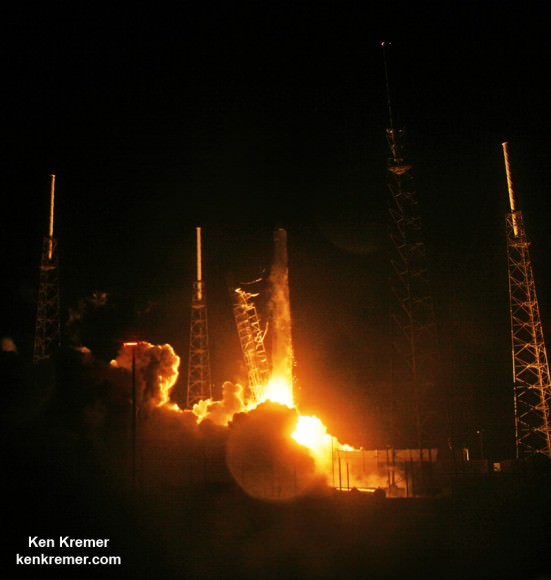
CATS was launched to the station as part of the payload aboard the SpaceX Dragon CRS-5 cargo vessel bolted atop the SpaceX Falcon 9 for the spectacular nighttime blastoff on Jan. 10 at 4:47 a.m. EST from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
CATS was loaded in the unpressurized rear trunk section of Dragon.

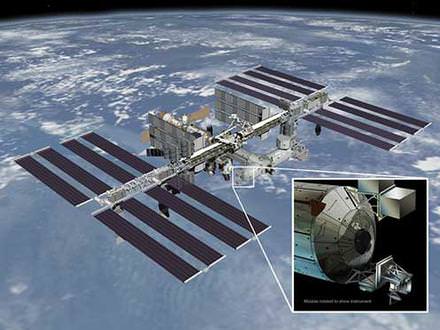
The new CATS experiment delivered by the SpaceX commercial cargo craft will be installed on a platform outside Japan’s Kibo Laboratory module. Credit: NASA
The Dragon CRS-5 spacecraft was loaded with over 5108 pounds (2317 kg) of scientific experiments, technology demonstrations, the CATS science payload, student research investigations, crew supplies, spare parts, food, water, clothing and assorted research gear for the six person crew serving aboard the ISS.
It successfully rendezvoused at the station on Jan. 12 after a two day orbital chase, delivering the critical cargo required to keep the station stocked and humming with science.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.