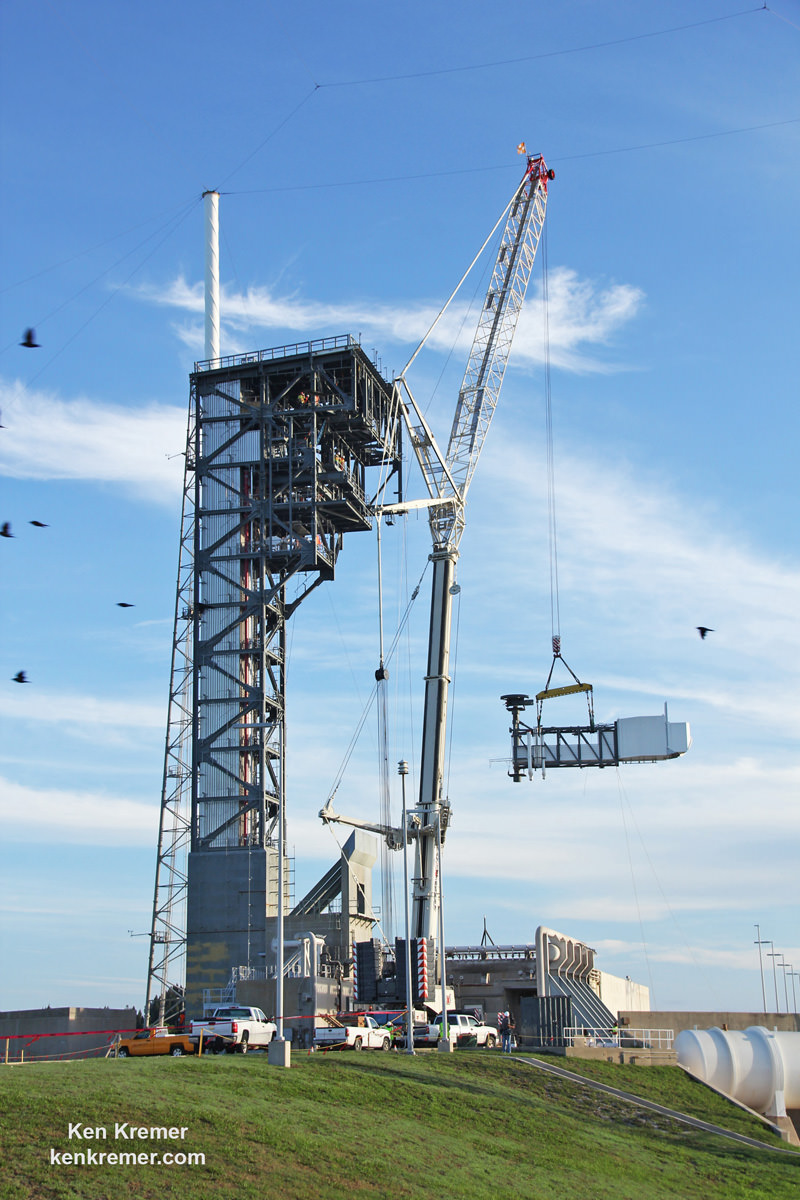
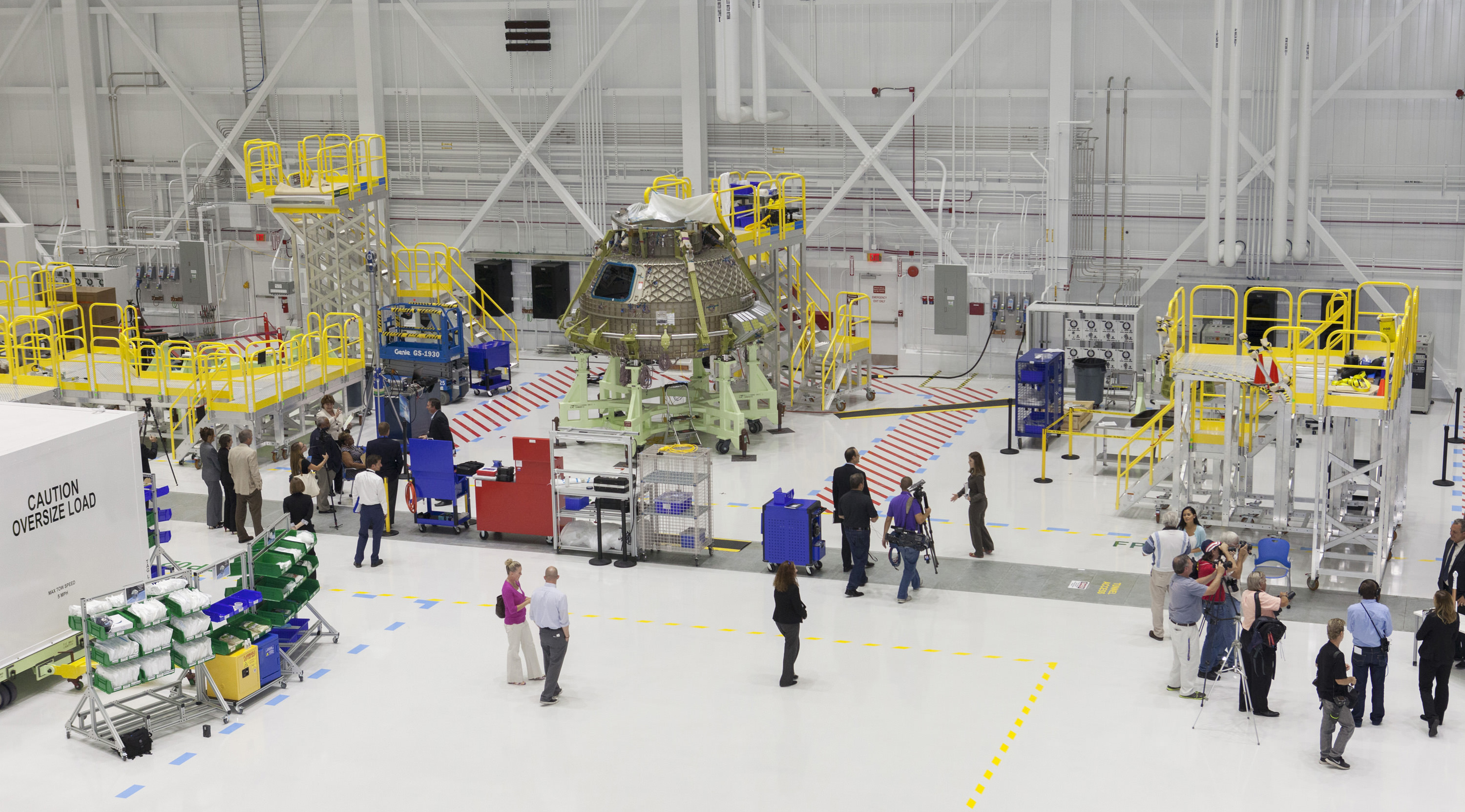
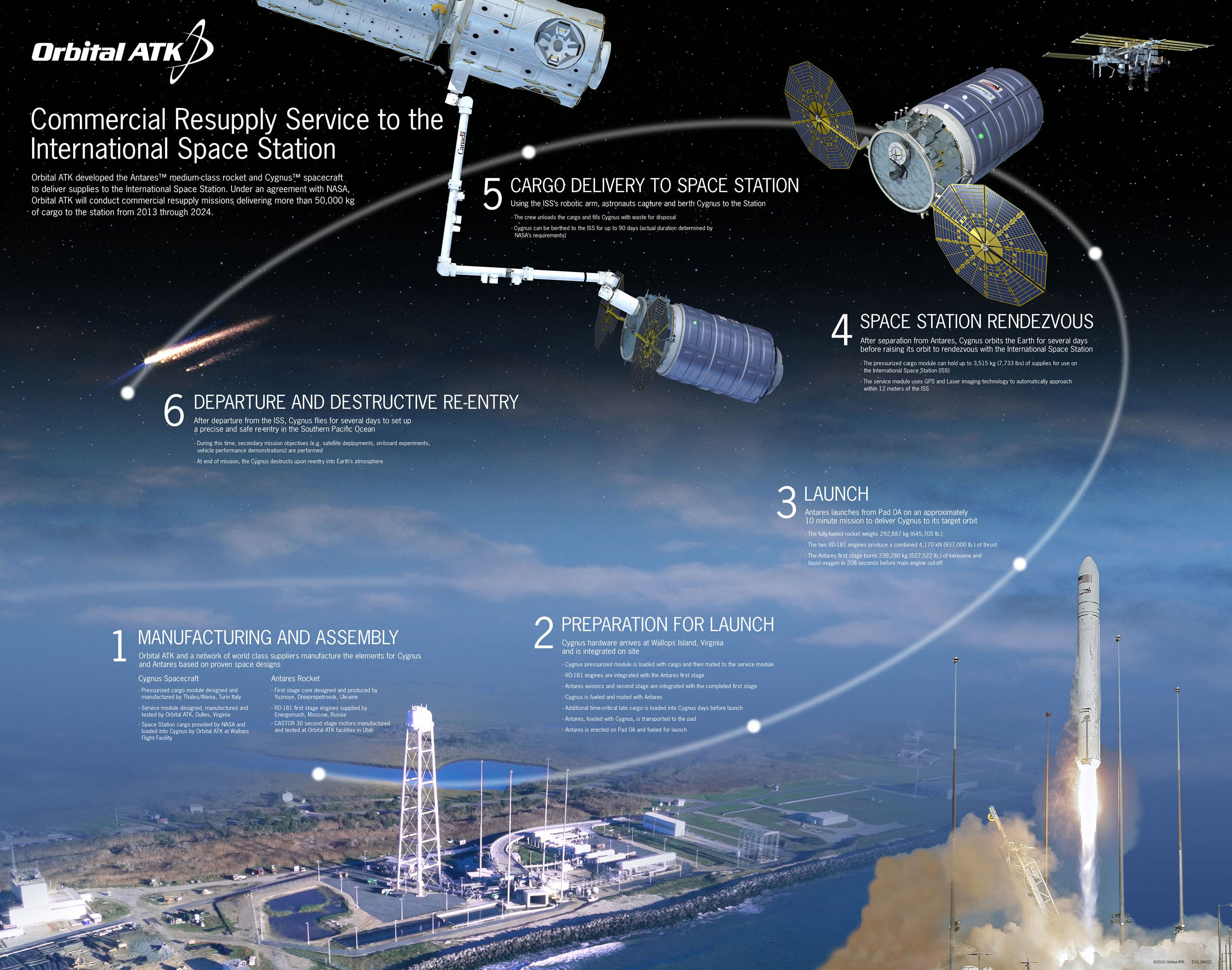
CAPE CANAVERAL AIR FORCE STATION, FL — A new ‘Stairway to Heaven’ which American astronauts will soon stride along as “the last place on Earth” departure point aboard our next generation of human spaceships, was at long last hoisted into place at the ULA Atlas rocket launch pad on Florida’s Space Coast on Monday Aug 15, at an “awesome” media event witnessed by space journalists including Universe Today.
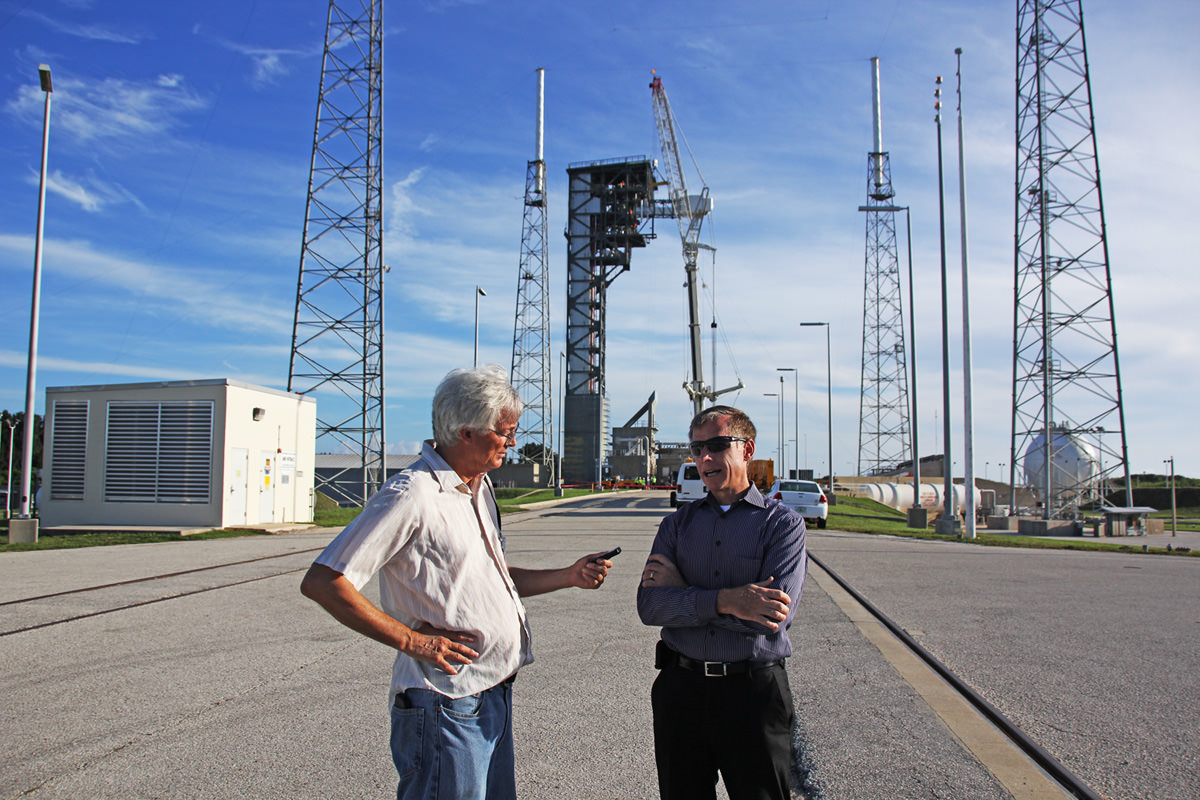
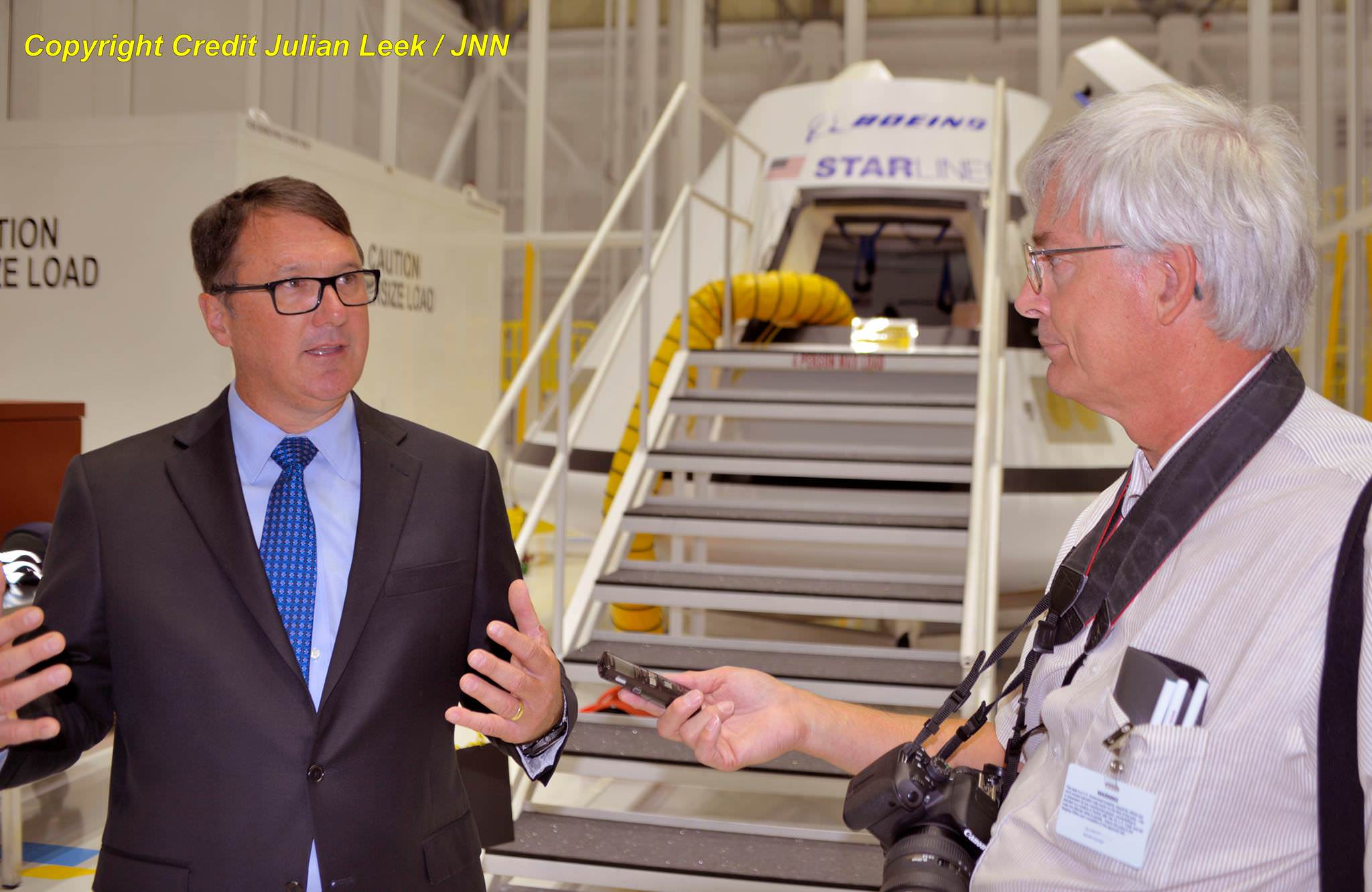
“This is awesome,” Chris Ferguson, a former shuttle commander who is now Boeing’s deputy program manager for the company’s Commercial Crew Program told Universe Today in an exclusive interview at the launch pad – after workers finished installing the spanking new Crew Access Arm walkway for astronauts leading to the hatch of Boeing’s Starliner ‘Space Taxi.’
Starliner will ferry crews to and from the International Space Station (ISS) as soon as 2018.
“It’s great to see the arm up there,” Ferguson elaborated to Universe Today. “I know it’s probably a small part of the overall access tower. But it’s the most significant part!”
“We used to joke about the 195 foot level on the shuttle pad as being ‘the last place on Earth.”
“This will now be the new ‘last place on Earth’! So we are pretty charged up about it!” Ferguson gushed.
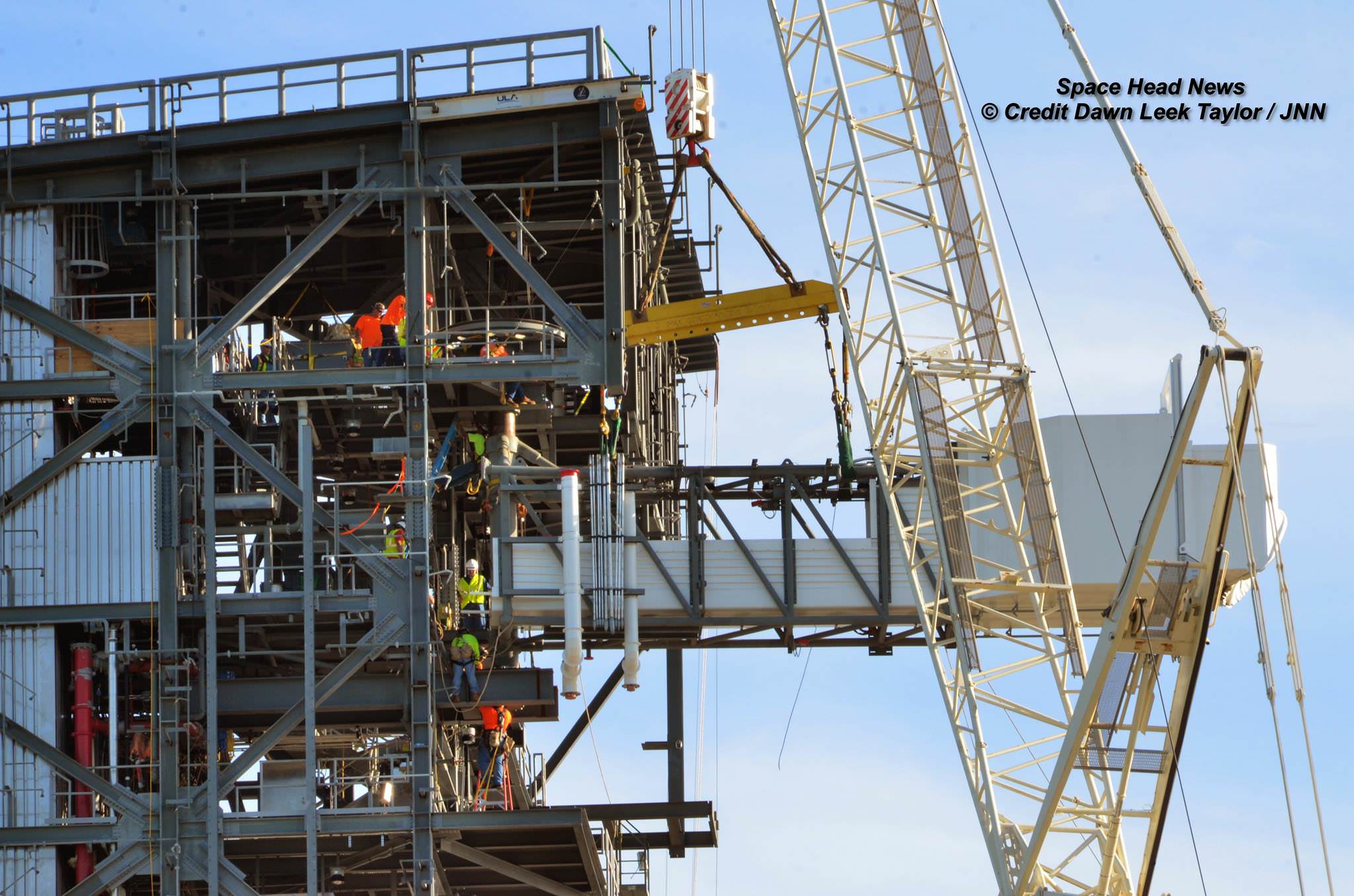

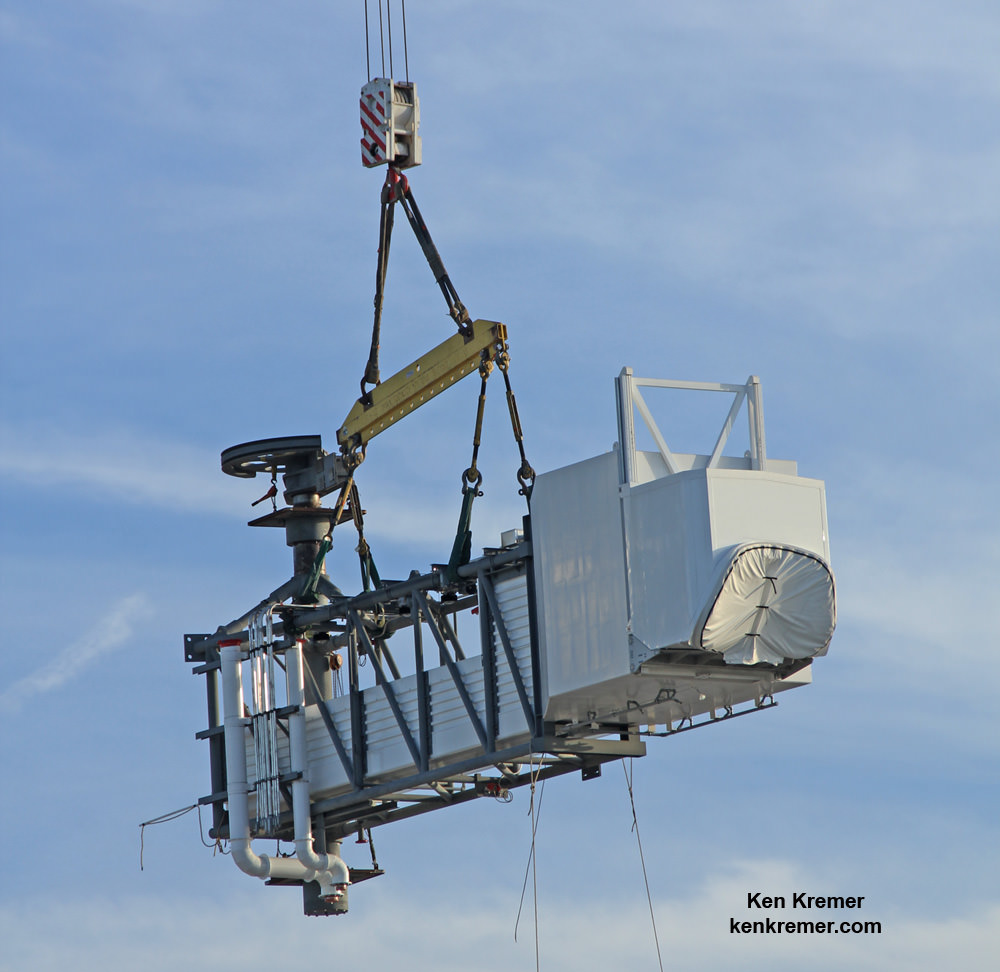
Under hot sunny skies portending the upcoming restoration of America’s ability to once again launch American astronauts from American soil when American rockets ignite, the newly constructed 50-foot-long, 90,000-pound ‘Crew Access Arm and White Room’ was lifted and mated to the newly built ‘Crew Access Tower’ at Space Launch Complex-41 (SLC-41) on Monday morning, Aug. 15.
“We talked about how the skyline is changing here and this is one of the more visible changes.”
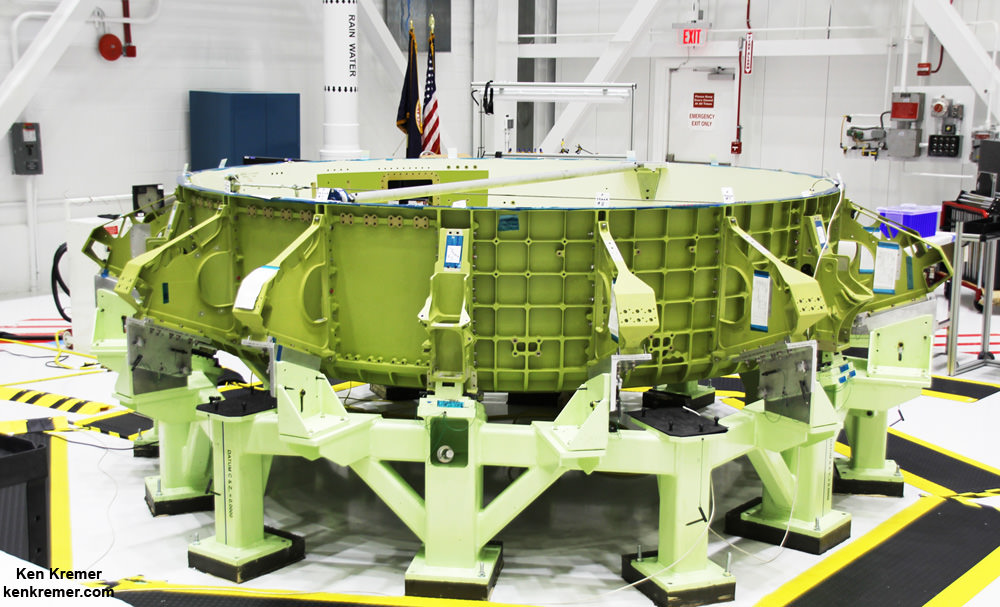
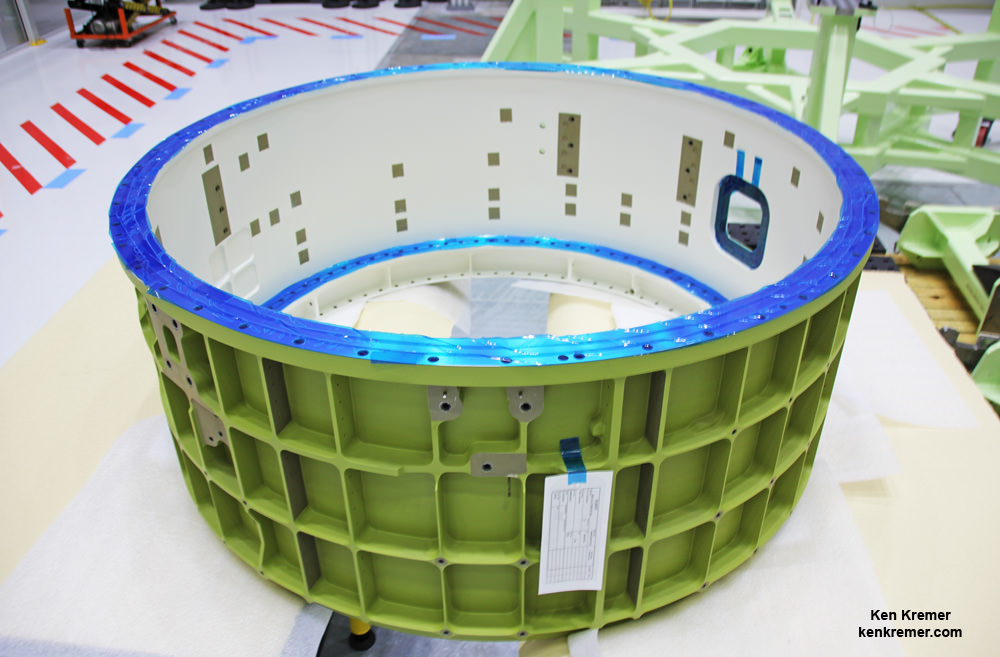
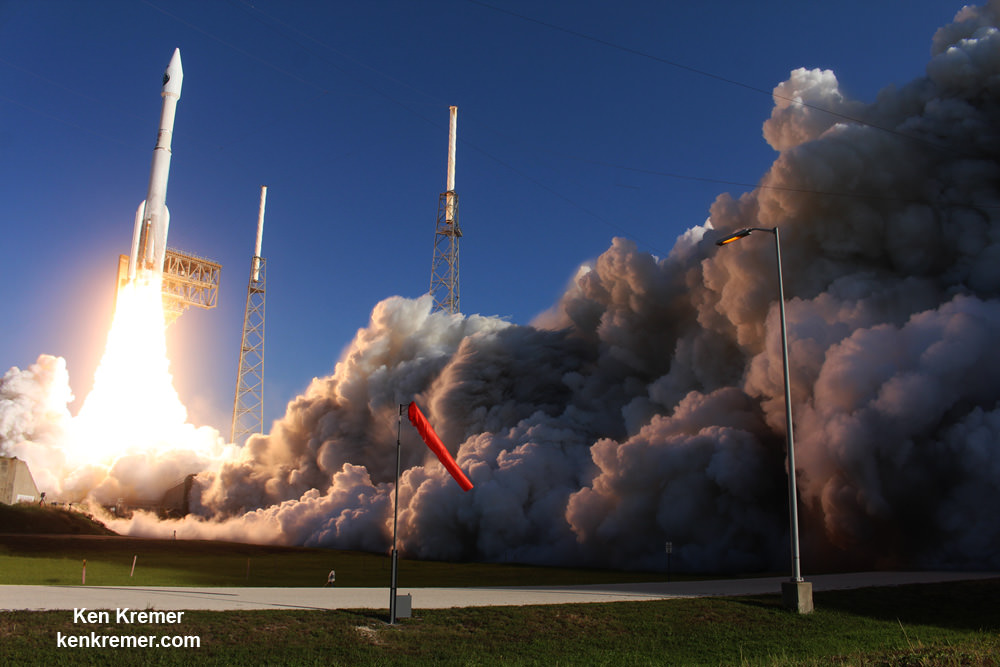
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner crew capsule stacked atop the venerable United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket at pad 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida will launch crews to the massive orbiting science outpost continuously soaring some 250 miles (400 km) above Earth.
Space workers, enthusiasts and dreamers alike have been waiting years for this momentous day to happen. And I was thrilled to observe all the action firsthand along with the people who made it happen from NASA, United Launch Alliance, Boeing, the contractors – as well as to experience it with my space media colleagues.
“All the elements that we talked about the last few years are now reality,” Ferguson told me.
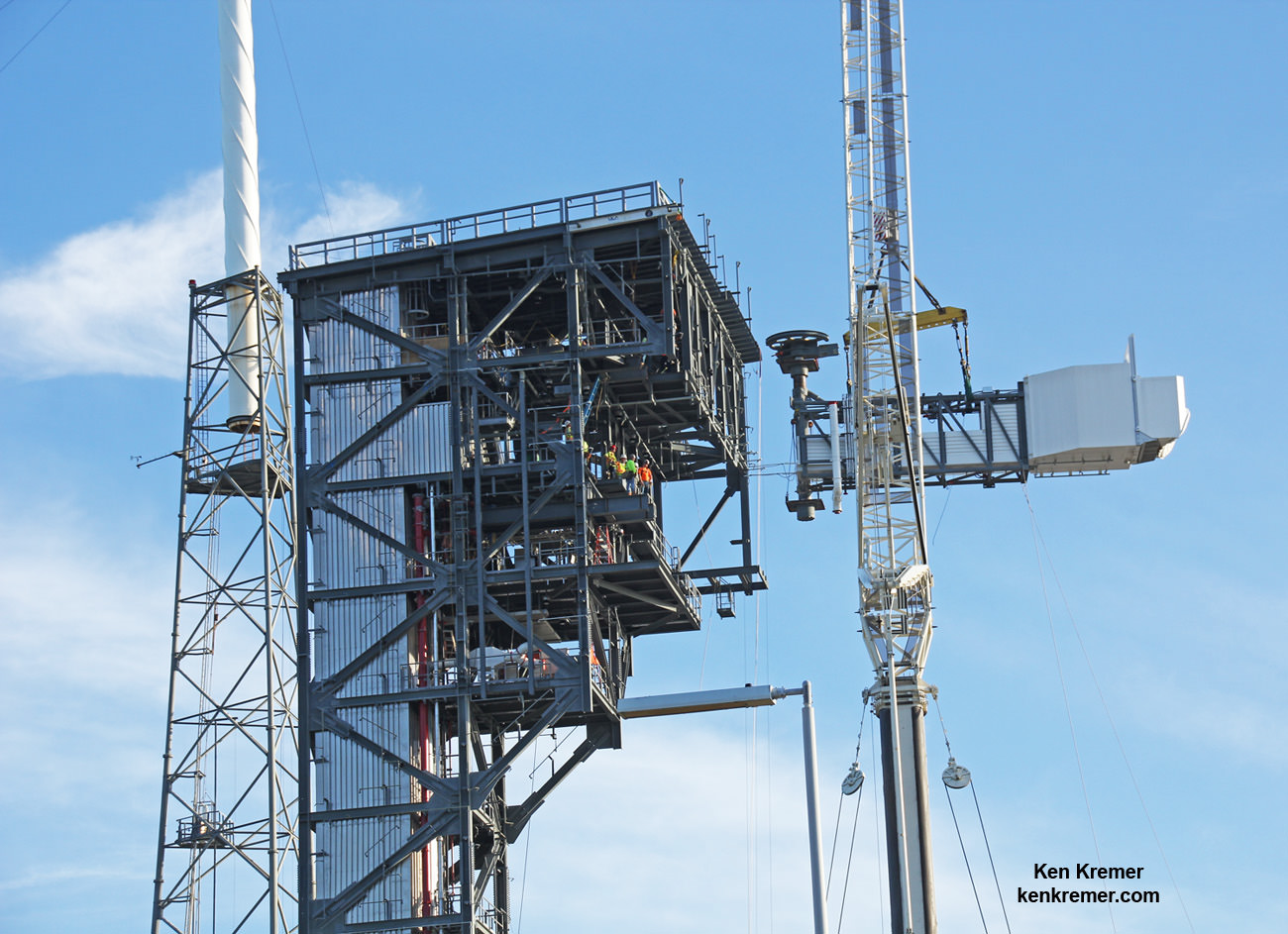

Attaching the access arm is vital and visual proof that at long last America means business and that a renaissance in human spaceflight will commence in some 18 months or less when commercially built American crew capsules from Boeing and SpaceX take flight to the heavens above – and a new space era of regular, robust and lower cost space flights begins.
It took about an hour for workers to delicately hoist the gleaming grey steel and aluminum white ‘Stairway to Heaven’ by crane into place at the top of the tower – at one of the busiest launch pads in the world!
It’s about 130 feet above the pad surface since it’s located at the 13th level of the tower.
The install work began at about 7:30 a.m. EDT as we watched a work crew lower a giant grappling hook and attach cables. Then they carefully raised the arm off the launch pad surface by crane. The arm had been trucked to the launch pad on Aug. 11.
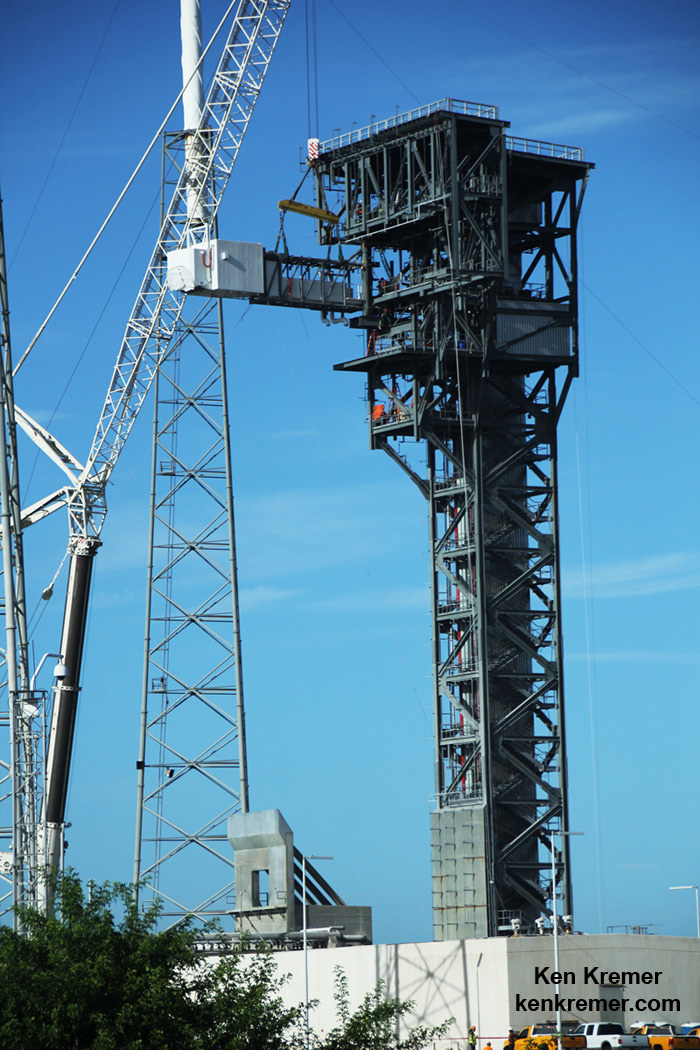
The tower itself is comprised of segmented tiers that were built in segments just south of the pad. They were stacked on the pad over the past few months – in between launches. Altogether they form a nearly 200-foot-tall steel structure.
Another crew stationed in the tower about 160 feet above ground waited as the arm was delicately craned into the designated notch. The workers then spent several more hours methodically bolting and welding the arm to the tower to finish the assembly process.
Indeed Monday’s installation of the Crew Access Arm and White Room at pad 41 basically completes the construction of the first new Crew Access Tower at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station since the Apollo moon landing era of the 1960s.
“It is the first new crew access structure at the Florida spaceport since the space shuttle’s Fixed Service Structures were put in place before Columbia’s first flight in 1981,” say NASA officials.
Overall the steel frame of the massive tower weighs over a million pounds. For perspective, destination ISS now weighs in at about a million pounds in low Earth orbit.
Construction of the tower began about 18 months ago.
“You think about when we started building this 18 months ago and now it’s one of the most visible changes to the Cape’s horizon since the 1960s,” said Ferguson at Monday’s momentous media event. “It’s a fantastic day.”
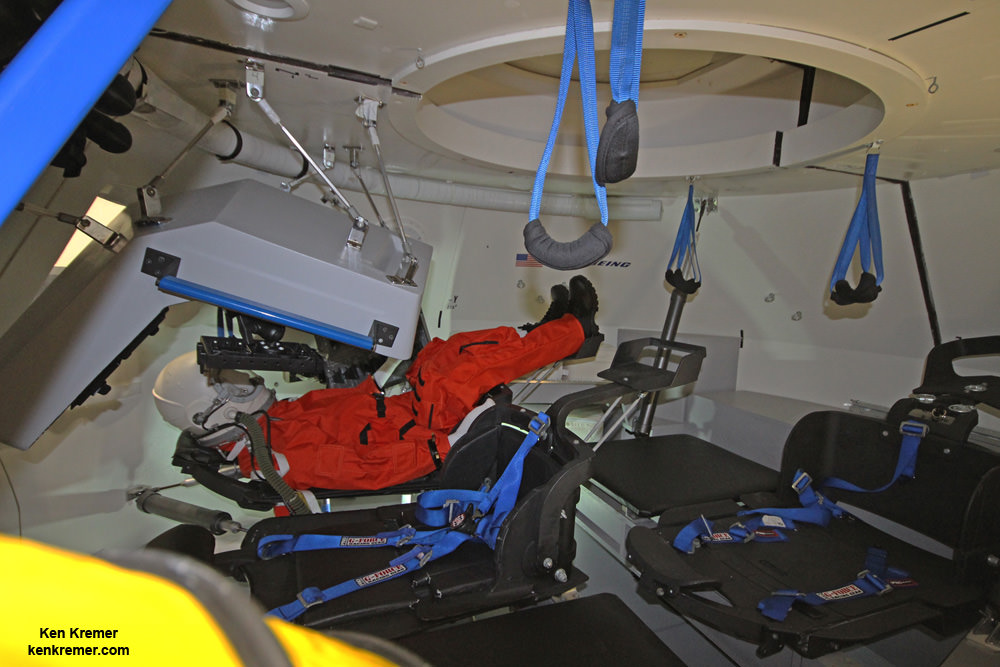
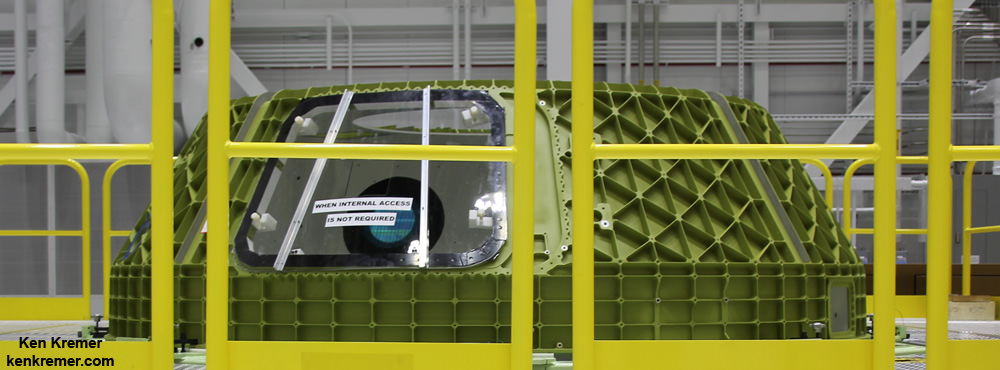
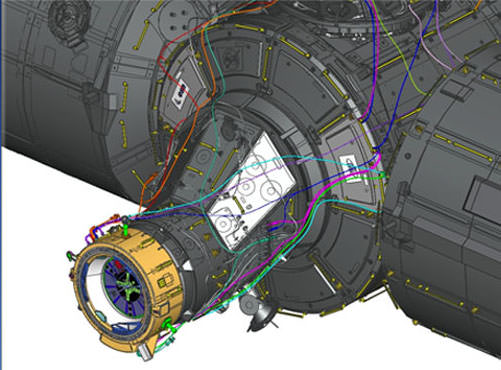
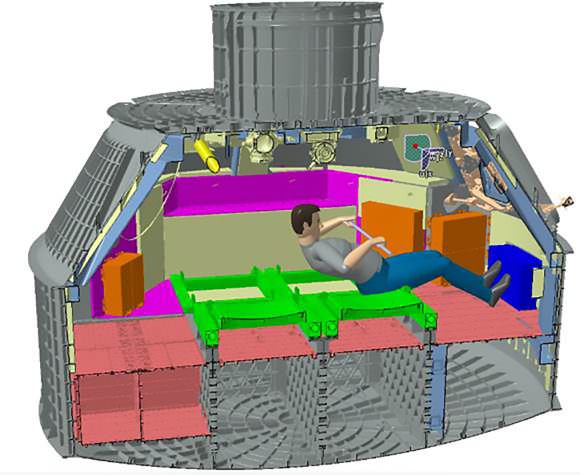
The White Room is an enclosed area at the end of the Crew Access Arm. It big enough for astronauts to make final adjustments to their suits and is spacious enough for technicians to assist the astronauts climbing aboard the spacecraft and get tucked into their seats in the final hours before liftoff.
“You have to stop and celebrate these moments in the craziness of all the things we do,” said Kathy Lueders, manager of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, at the event. “It’s going to be so cool when our astronauts are walking out across this access arm to get on the spacecraft and go to the space station.”
The Crew Access Arm was built by Saur at NASA’s nearby off site facility at Oak Hill.
And when Starliner takes flight it will hearken back to the dawn of the Space Age.
“John Glenn was the first to fly on an Atlas, now our next leap into the future will be to have astronauts launch from here on Atlas V,” said Barb Egan, program manager for Commercial Crew for ULA.
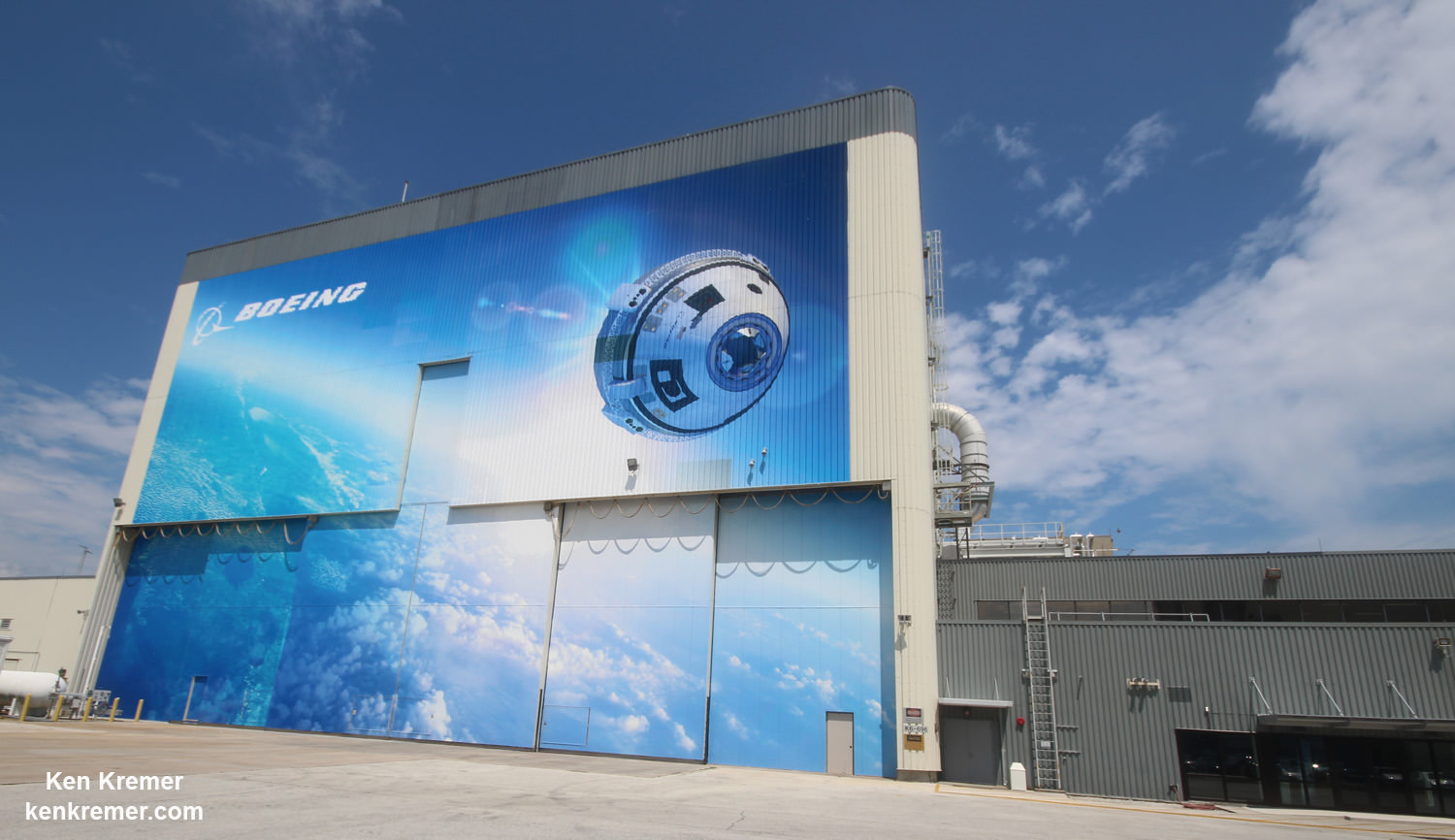
Boeing is manufacturing Starliner in what is officially known as Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida under contract with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP).
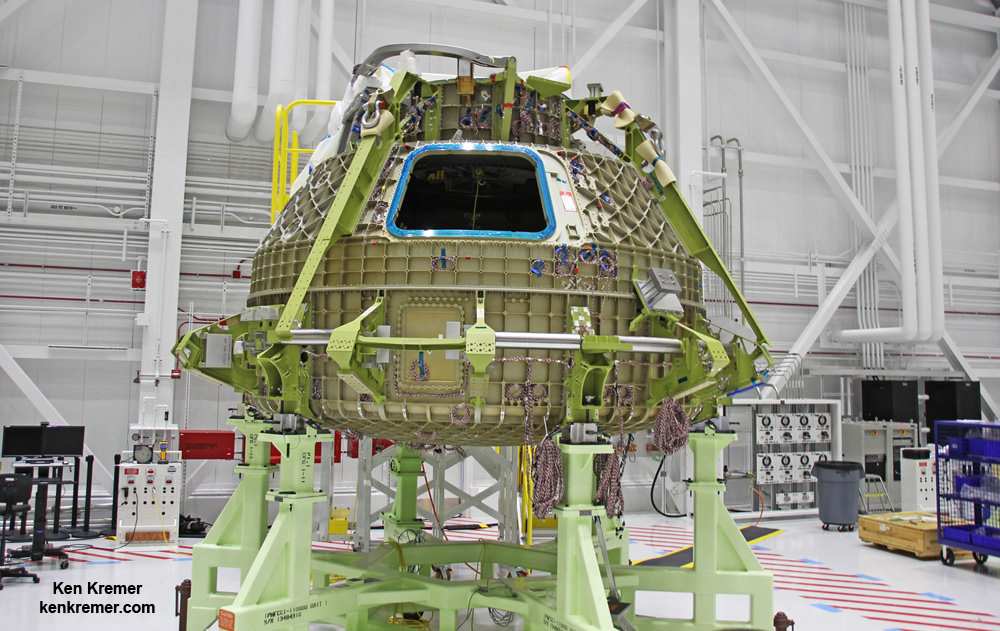

The Boeing CST 100 Starliner is one of two private astronaut capsules – along with the SpaceX Crew Dragon – being developed under a CCP commercial partnership contract with NASA to end our sole reliance on Russia for crew launches back and forth to the International Space Station (ISS).
The goal of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program since its inception in 2010 is to restore America’s capability to launch American astronauts on American rockets from American soil to the ISS, as soon as possible.
Furthermore when the Boeing Starliner and SpaceX Crew Dragon become operational the permanent resident ISS crew will grow to 7 – enabling a doubling of science output aboard the science laboratory.
This significant growth in research capabilities will invaluably assist NASA in testing technologies and human endurance in its agency wide goal of sending humans on a ‘Journey to Mars’ by the 2030s with the mammoth Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion deep space capsule concurrently under full scale development by the agency.
The next key SLS milestone is a trest firing of the RS-25 main engines at NASA Stennis this Thursday, Aug. 18 – watch for my onsite reports!
Boeing was awarded a $4.2 Billion contract in September 2014 by NASA Administrator Charles Bolden to complete development and manufacture of the CST-100 Starliner space taxi under the agency’s Commercial Crew Transportation Capability (CCtCap) program and NASA’s Launch America initiative.
Since the retirement of NASA’s space shuttle program in 2011, the US was been 100% dependent on the Russian Soyuz capsule for astronauts rides to the ISS at a cost exceeding $70 million per seat.
When will Ferguson actually set foot inside the walkway?
“I am hoping to get up there and walk through there in a couple of weeks or so when it’s all strapped in and done. I want to see how they are doing and walk around.”
How does the White Room fit around Starliner and keep it climate controlled?
“The end of the white room has a part that slides up and down and moves over and slides on top of the spacecraft when it’s in place.”
“There is an inflatable seal that forms the final seal to the spacecraft so that you have all the appropriate humidity control and the purge without the Florida atmosphere inside the crew module,” Ferguson replied.

Boeing and NASA are targeting Feb. 2018 for launch of the first crewed orbital test flight on the Atlas V rocket. The Atlas will be augmented with two solid rocket motors on the first stage and a dual engine Centaur upper stage.
How confident is Ferguson about meeting the 2018 launch target?
“The first crew flight is scheduled for February 2018. I am confident.” Ferguson responded.
“And we have a lot of qualification to get through between now and then. But barring any large unforeseen issues we can make it.”

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.