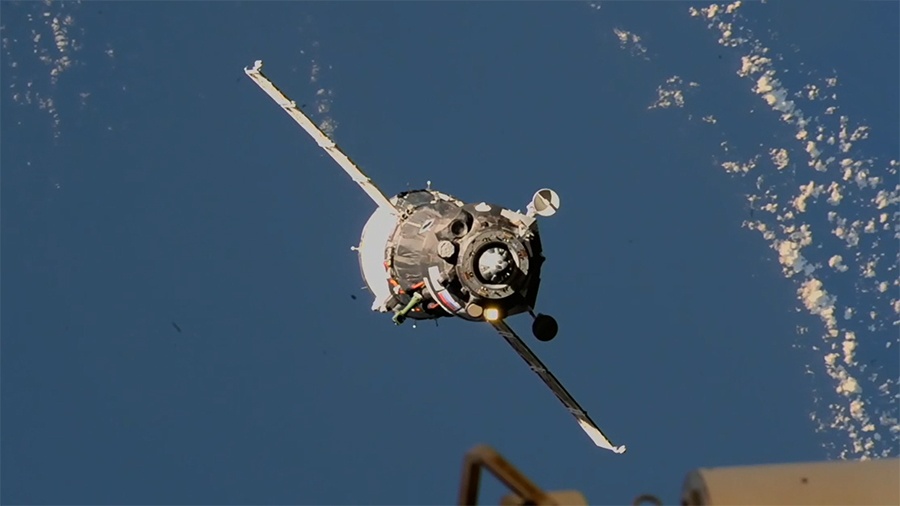
Roscosmos has had quite the run of bad luck lately. In addition to sanctions putting pressure on their space program and the cancellation of agreements (all due to the war in Ukraine), the Russian space agency has experienced several problems in space. On December 14th, 2022, and February 11th, 2023, two space capsules reportedly suffered radiator coolant leaks (Soyuz MS-22 and Progress 82). In addition to delivering fresh supplies to the International Space Station (ISS), one of the spacecraft (M-22) was slated to bring three members of Expedition 68 back to Earth.
Luckily, on February 25th, Russia announced it was sending another Soyuz capsule to replace the M-22 (Soyuz M-23) and retrieve the three crew members, cosmonauts Sergey Prokopyev and Dmitri Petelin, and astronaut Frank Rubio (who will return to Earth now on September 27th). In addition, Tuesday, March 28th, Russia undocked the M-22 from the ISS and successfully brought it home without crew. NASA provided live coverage of the undocking and departure of the uncrewed spacecraft via NASA TV, the agency website, and the NASA app.
Continue reading “Leaky Soyuz Capsule Returns to Earth”