SpaceX and NASA are just days away from a crucial test of a crew capsule escape system that will save astronauts lives in the unlikely event of a launch failure with the Falcon 9 rocket.
Buster the Dummy is already strapped into his seat aboard the SpaceX Crew Dragon test vehicle for what is called the Pad Abort Test, that is currently slated for Wednesday, May 6.
The test is critical for the timely development of the human rated Dragon that NASA is counting on to restore the US capability to launch astronauts from US soil abroad US rockets to the International Space Station (ISS) as early as 2017.
Boeing was also selected by NASA to build the CST-100 spaceship to provide a second, independent crew space taxi capability to the ISS during 2017.
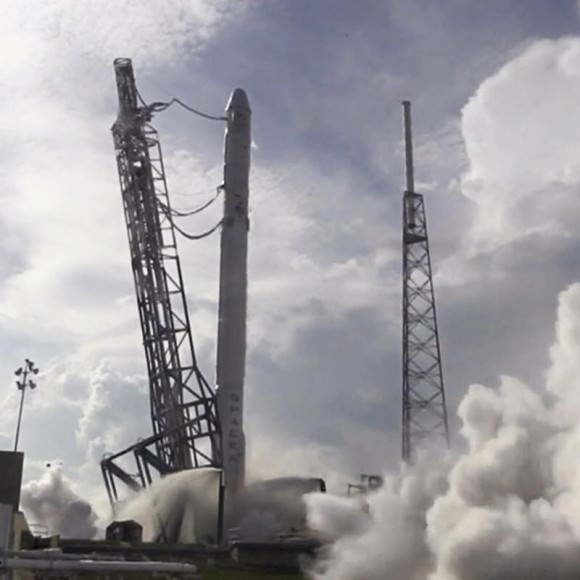
The May 6 pad abort test will be performed from the SpaceX Falcon 9 launch pad from a platform at Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. The test will not include an actual Falcon 9 booster.

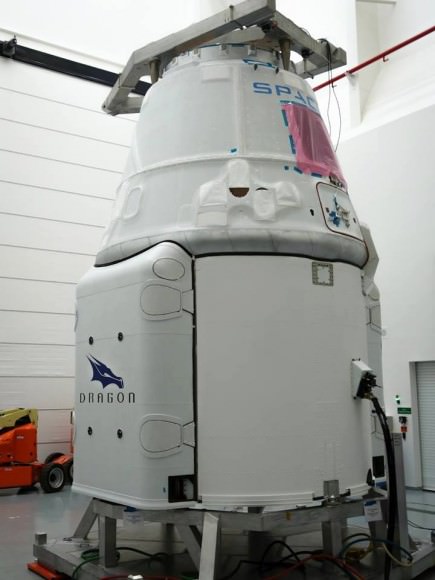
The SpaceX Dragon and trunk together stand about 20 feet tall and are positioned atop the launch mount at SLC-40 for what is clearly labeled as a development test to learn how the Dragon, engines and abort system perform.
Buster will soar along inside the Dragon that will be rapidly propelled to nearly a mile high height solely under the power of eight SpaceX SuperDraco engines.
The trunk will then separate, parachutes will be deployed and the capsule will splashdown about a mile offshore from Florida in the Atlantic Ocean, said Hans Koenigsmann, vice president of Mission Assurance at SpaceX during a May 1, 2015 press briefing on the pad abort test at the Kennedy Space Center, Florida.
The entire test will take about a minute and a half and recovery teams will retrieve Dragon from the ocean and bring it back on shore for detailed analysis.
The test will be broadcast live on NASA TV. The test window opens at 7 a.m. EDT May 6 and extends until 2:30 p.m. EDT. The webcast will start about 20 minutes prior to the opening of the window. NASA will also provide periodic updates about the test at their online Commercial Crew Blog.

The test is designed to simulate an emergency escape abort scenario from the test stand at the launch pad in the unlikely case of booster failing at liftoff or other scenario that would threaten astronauts inside the spacecraft.
The pad abort demonstration will test the ability of a set of eight SuperDraco engines built into the side walls of the crew Dragon to pull the vehicle away from the launch pad in a split second in a simulated emergency to save the astronauts lives in the event of a real emergency.
The SuperDraco engines are located in four jet packs around the base. Each engine produces about 15,000 pounds of thrust pounds of axial thrust, for a combined total thrust of about 120,000 pounds, to carry astronauts to safety, according to Koenigsmann.
“This is what SpaceX was basically founded for, human spaceflight,” said Hans Koenigsmann, vice president of Mission Assurance with SpaceX.
“The pad abort is going to show that we’ve developed a revolutionary system for the safety of the astronauts, and this test is going to show how it works. It’s our first big test on the Crew Dragon.”
SpaceX and NASA hope to refurbish and reuse the same Dragon capsule for another abort test at high altitude later this year. The timing of the in flight abort test hinges on the outcome of the pad abort test.
“No matter what happens on test day, SpaceX is going to learn a lot,” said Jon Cowart, NASA’s partner manager for SpaceX. “One test is worth a thousand good analyses.”

Beside Buster the dummy, who is human-sized, the Dragon is outfitted with 270 sensors to measure a wide range of vehicle, engine, acceleration and abort test parameters.
“There’s a lot of instrumentation on this flight – a lot,” Koenigsmann said. “Temperature sensors on the outside, acoustic sensors, microphones. This is basically a flying instrumentation deck. At the end of the day, that’s the point of tests, to get lots of data.”
Buster will be accelerated to a force of about 4 to 4½ times the force of Earth’s gravity, noted Koenigsmann.
The pad abort test is being done under SpaceX’s Commercial Crew Integrated Capability (CCiCap) agreement with NASA that will eventually lead to certification of the Dragon for crewed missions to low Earth orbit and the ISS.
“The point is to gather data – you don’t have to have a flawless test to be successful,” Cowart said.
The second Dragon flight test follows later in the year, perhaps in the summer. It will launch from a SpaceX pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California and involves simulating an in flight emergency abort scenario during ascent at high altitude at maximum aerodynamic pressure (Max-Q) at about T plus 1 minute, to save astronauts lives.
The pusher abort thrusters would propel the capsule and crew safely away from a failing Falcon 9 booster for a parachute assisted splashdown into the Ocean.
Koenigsmann notes that the SpaceX abort system provides for emergency escape all the way to orbit, unlike any prior escape system such as the conventional launch abort systems (LAS) mounted on top of the capsule.
“Whatever happens to Falcon 9, you will be able to pull out the astronauts and land them safely on this crew Dragon,” said Koenigsmann. “In my opinion, this will make it the safest vehicle that you can possibly fly.”
The SpaceX Dragon V2 and Boeing CST-100 vehicles were selected by NASA last fall for further funding under the auspices of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP), as the worlds privately developed spaceships to ferry astronauts back and forth to the International Space Station (ISS).
Both SpaceX and Boeing plan to launch the first manned test flights to the ISS with their respective transports in 2017.
During the Sept. 16, 2014 news briefing at the Kennedy Space Center, NASA Administrator Charles Bolden announced that contracts worth a total of $6.8 Billion were awarded to SpaceX to build the manned Dragon V2 and to Boeing to build the manned CST-100.
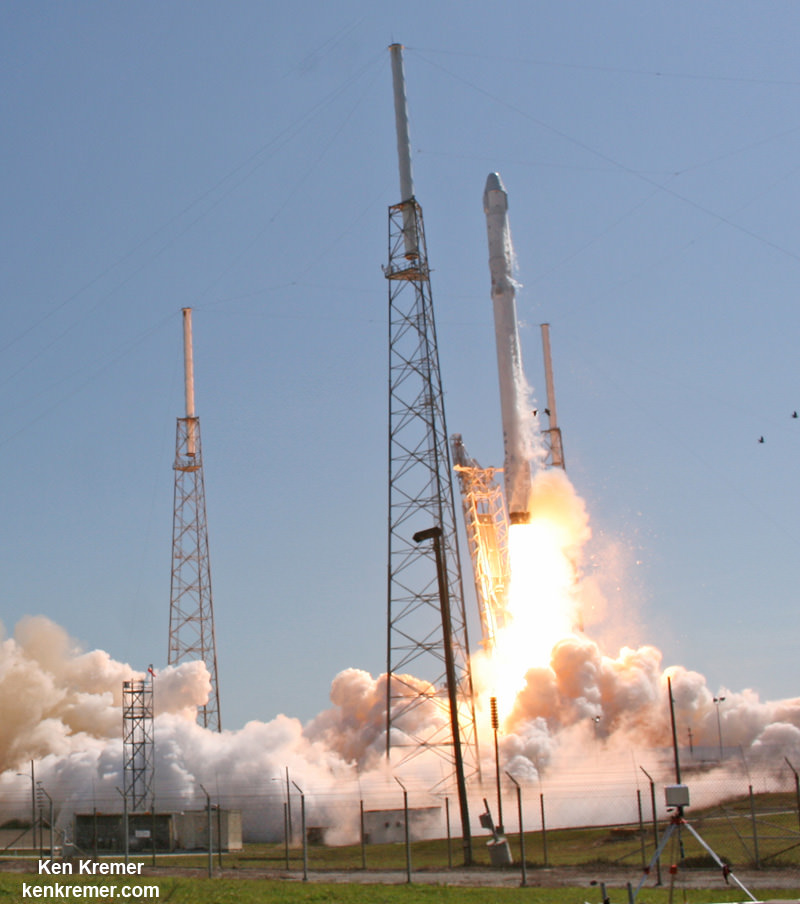
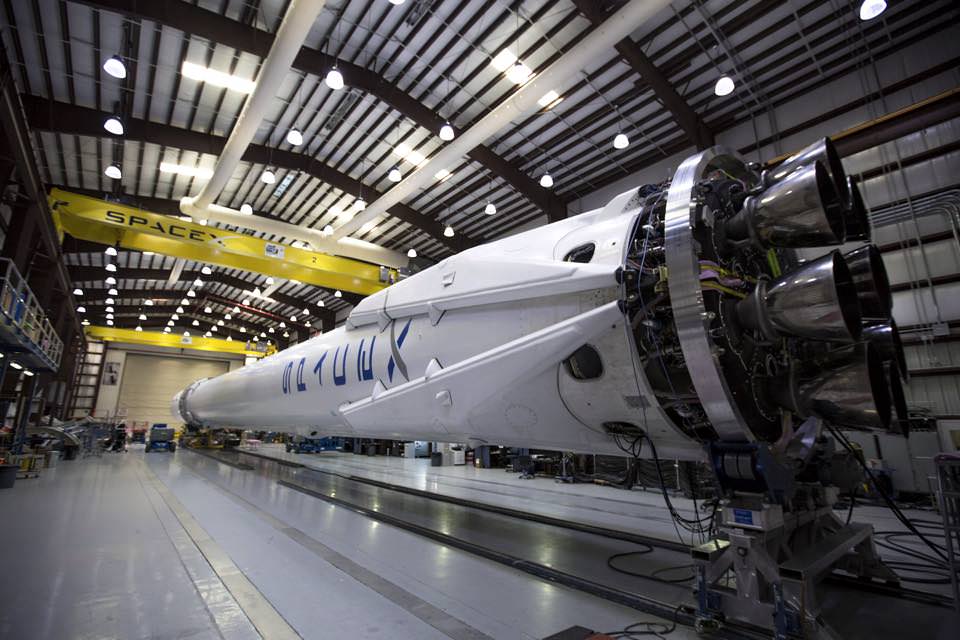
The next Falcon 9 launch is slated for mid-June carrying the CRS-7 Dragon cargo ship on a resupply mission for NASA to the ISS. On April 14, a flawless Falcon 9 launch boosted the SpaceX CRS-6 Dragon to the ISS.
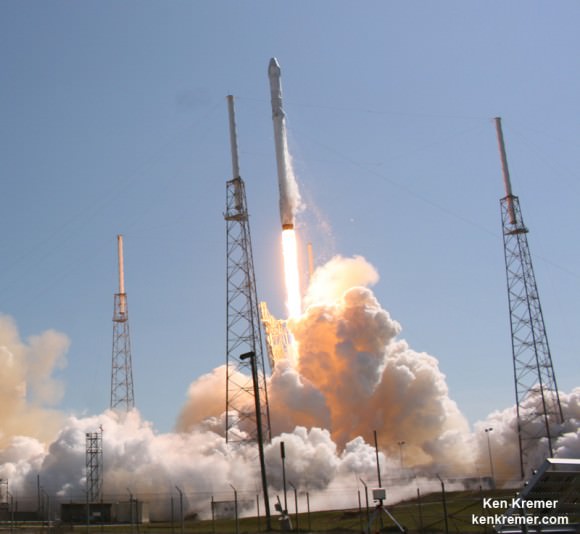

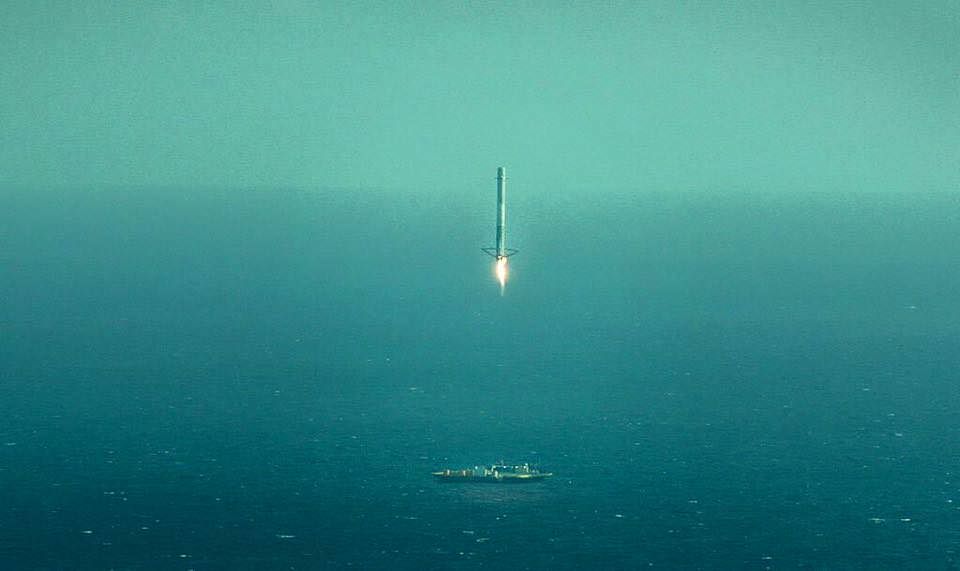
There was no attempt to soft land the Falcon 9 first stage during the most recent launch on April 27. Due to the heavy weight of the TurkmenÄlem52E/MonacoSat satellite there was not enough residual fuel for a landing attempt on SpaceX’s ocean going barge.
The next landing attempt is set for the CRS-7 mission.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.