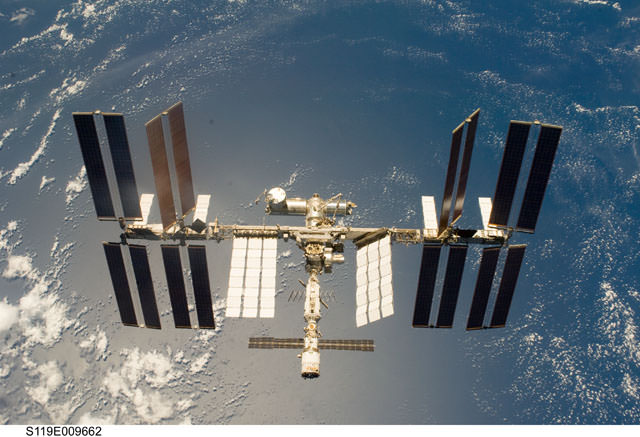
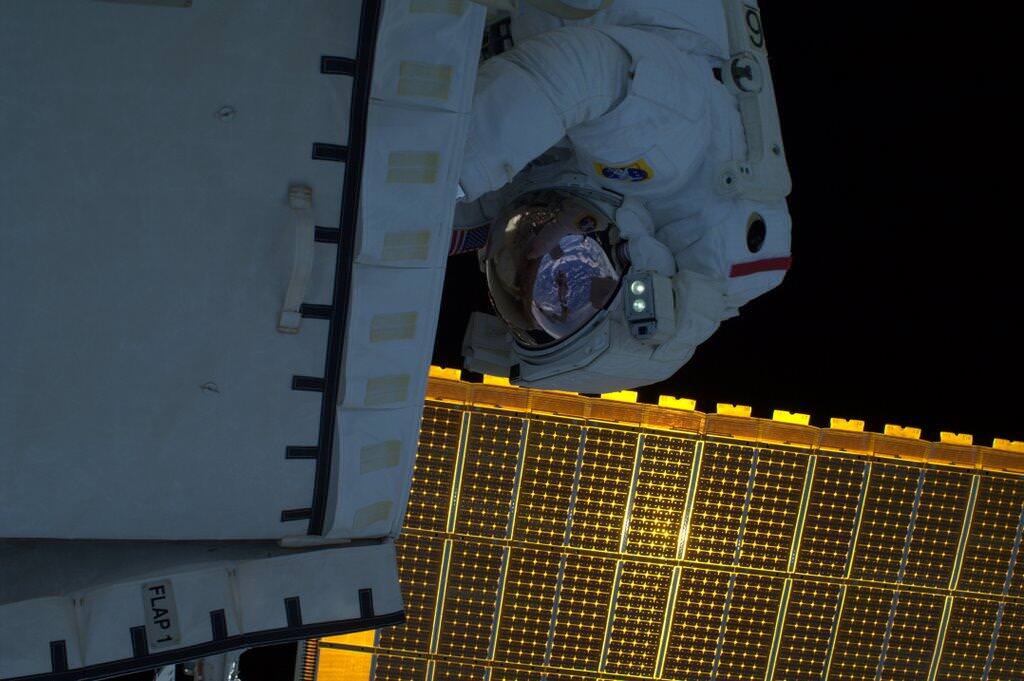
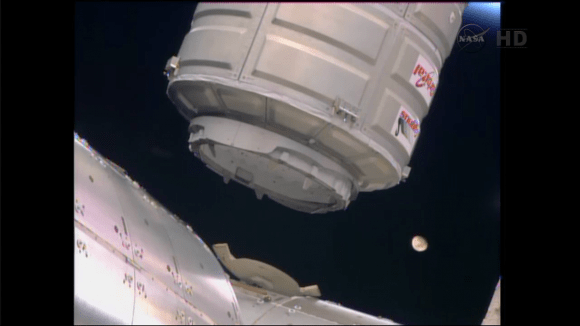
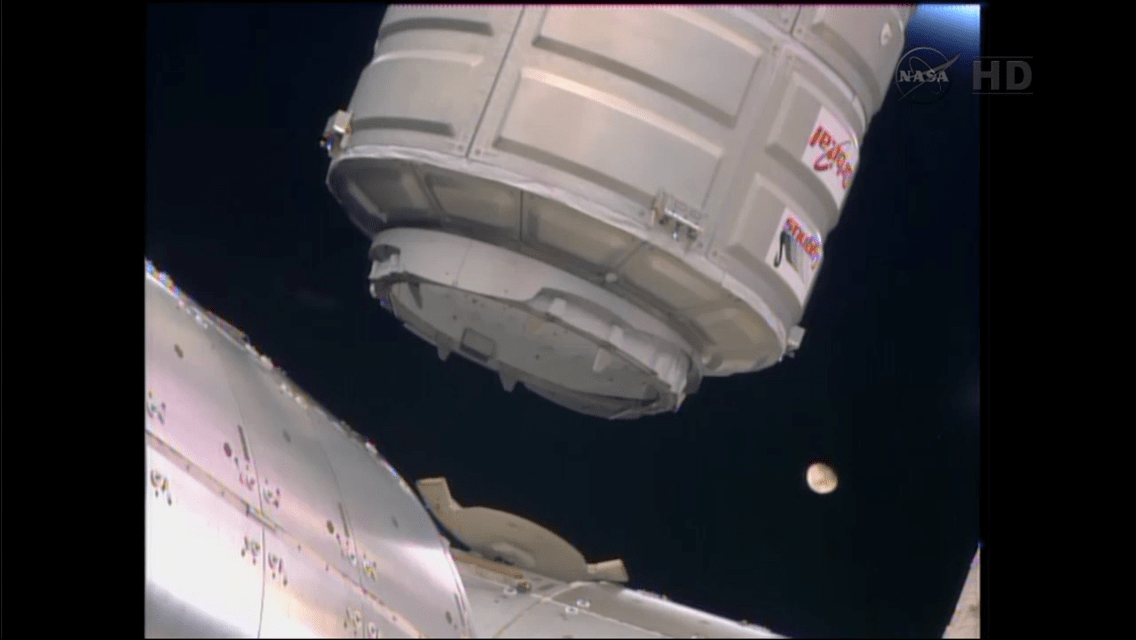
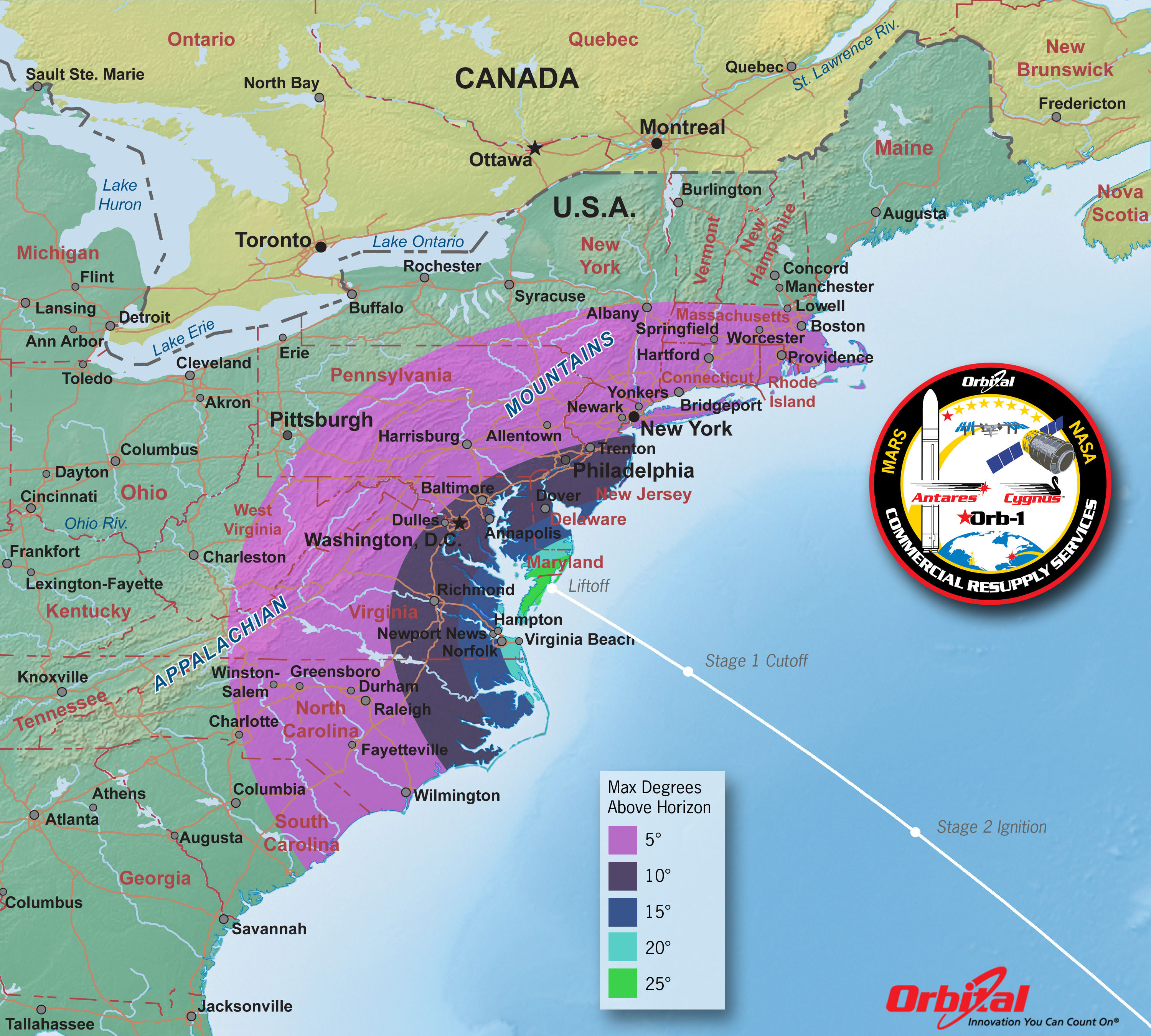
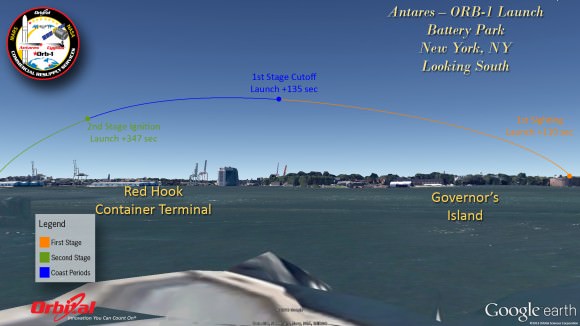
The International Space Station could potentially function far beyond its new extension to 2024. Perhaps out to 2050. The ISS as seen from the crew of STS-119. Credit: NASA
Story updated[/caption]
WALLOPS ISLAND, VA – Just days ago, the Obama Administration approved NASA’s request to extend the lifetime of the International Space Station (ISS) to at least 2024. Ultimately this will serve as a stepping stone to exciting deep space voyages in future decades.
“I think this is a tremendous announcement for us here in the space station world,” said Bill Gerstenmaier, associate administrator for NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate, at a press briefing on Jan. 8.
But there’s really “no reason to stop it there”, said Frank Culbertson, VP at Orbital Sciences and former NASA astronaut and shuttle commander, to Universe Today when I asked him for his response to NASA’s station extension announcement.
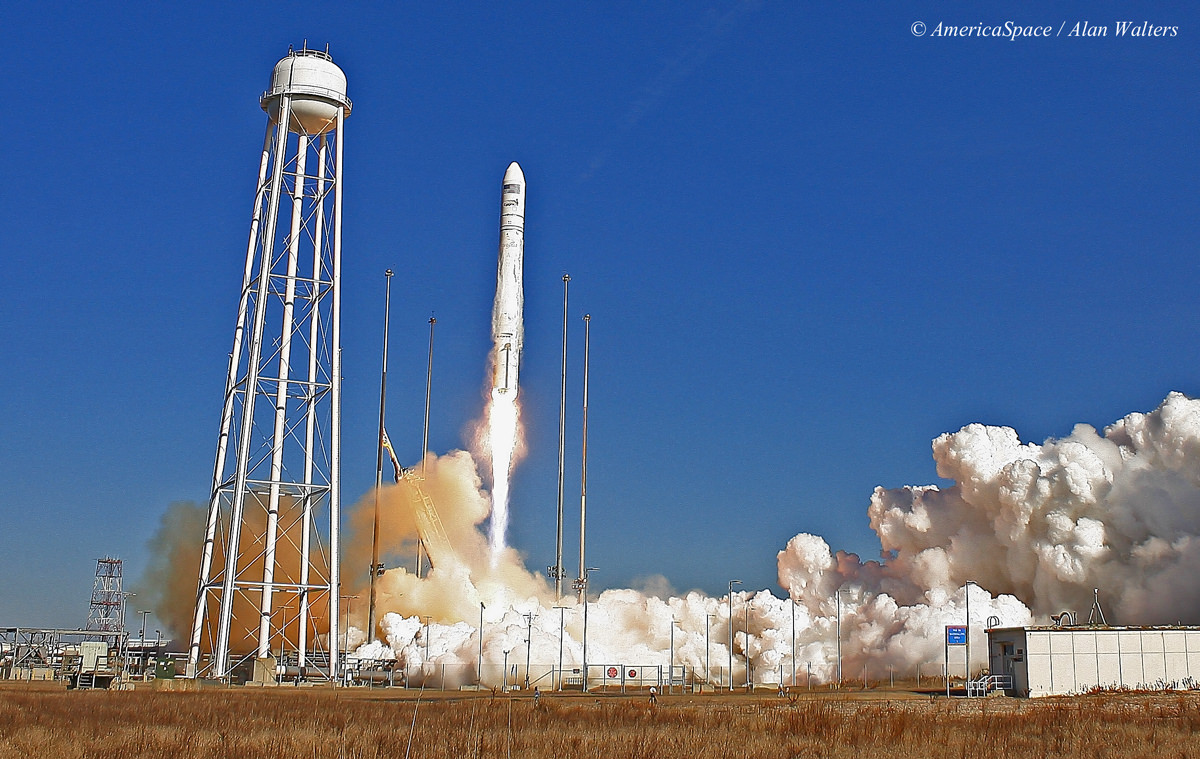
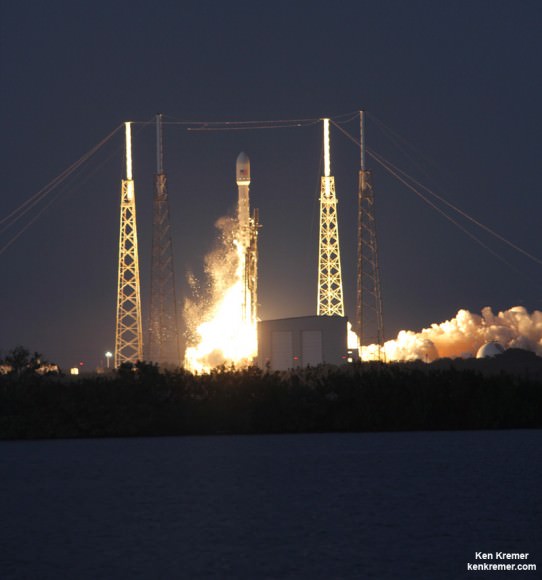
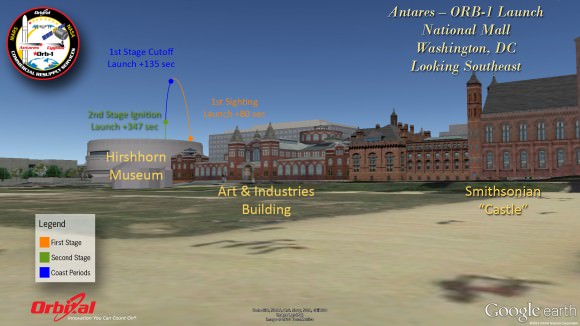
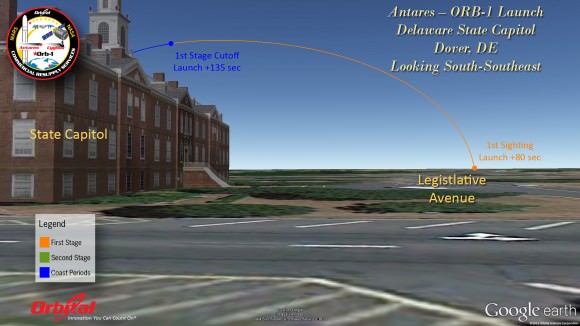
“It’s fantastic!” Culbertson told me, shortly after we witnessed the picture perfect blastoff of Orbital’s Antares/Cygnus rocket on Jan. 9 from NASA’s Wallops launch facility in Virginia, bound for the ISS.
“In my opinion, if it were up to me, we would fly it [the station] to 2050!” Culbertson added with a smile. “Of course, Congress would have to agree to that.”
Gerstenmaier emphasized that the extension will allow both the research and business communities to plan for the longer term and future utilization, be innovative and realize a much greater return on their investments in scientific research and capital outlays.
“The station is really our stepping stone,” Robert Lightfoot, NASA Associate Administrator, told me at Wallops following Antares launch.
The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) – which is searching for elusive dark matter – was one of the key science experiments that Gerstenmaier cited as benefitting greatly from the ISS extension to 2024. The AMS is the largest research instrument on the ISS.
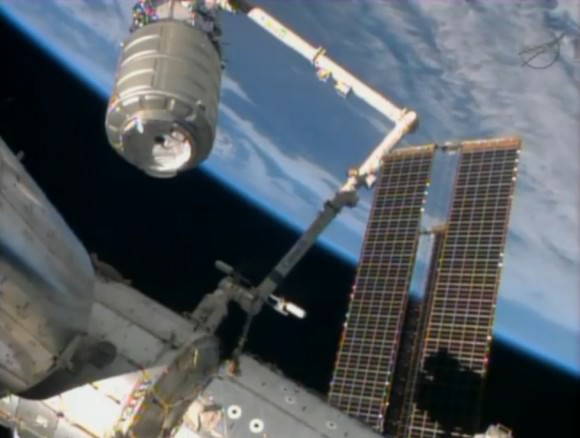

The extension will enable NASA, the academic community and commercial industry to plan much farther in the future and consider ideas not even possible if the station was de-orbited in 2020 according to the existing timetable.
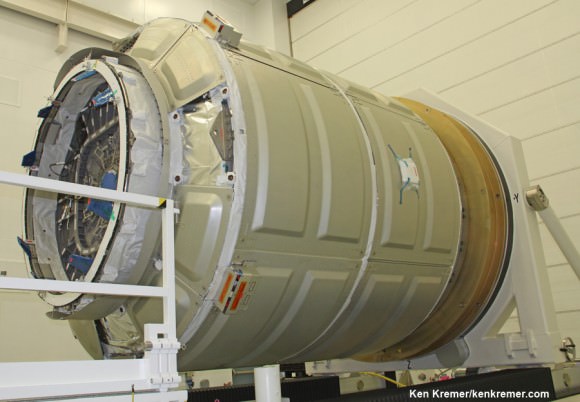
Both the Antares rocket and Cygnus cargo freighter are private space vehicles developed and built by Orbital Sciences with seed money from NASA in a public-private partnership to keep the station stocked with essential supplies and research experiments and to foster commercial spaceflight.
So I asked Culbertson and Lightfoot to elaborate on the benefits of the ISS extension to NASA, scientific researchers and commercial company’s like Orbital Sciences.
“First I think it’s fantastic that the Administration has committed to extending the station, said Culbertson. “They have to work with the ISS partners and there is a lot to be done yet. It’s a move in the right direction.”
“There is really no reason to stop operations on the space station until it is completely no longer usable. And I think it will be usable for a very long time because it is very built and very well maintained.”
“If it were up to me, we would fly it to 2050!”
“NASA and the engineers understand the station very well. I think they are operating it superbly.”

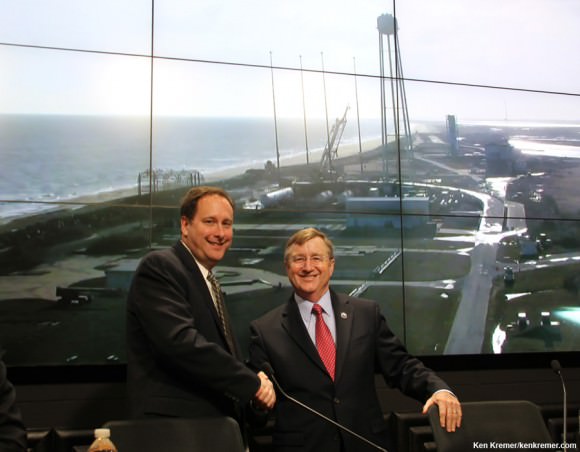
Credit: Ken Kremer – kenkremer
“The best thing about the station is it’s now a research center. And it is really starting to ramp up. It’s not there yet. But it is now finished [the assembly] as a station and a laboratory.”
“The research capability is just starting to move in the right direction.”
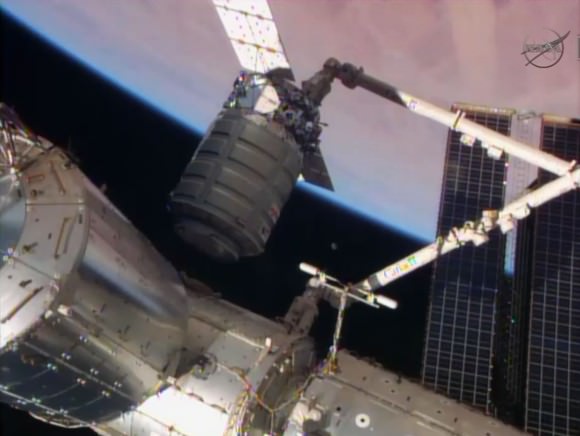
The Cygnus Orbital 1 cargo vehicle launched on Jan. 9 was loaded with approximately 2,780 pounds/1,261 kilograms of cargo for the ISS crew for NASA including vital science experiments, computer supplies, spacewalk tools, food, water, clothing and experimental hardware.
The research investigations alone accounted for over 1/3 of the total cargo mass. It included a batch of 23 student designed experiments representing over 8700 students sponsored by the National Center for Earth and Space Science Education (NCESSE).
“So extending it [ISS] gives not only commercial companies but also researchers the idea that ‘Yes I can do long term research on the station because it will be there for another 10 years. And I can get some significant data.”
“I think that’s really important for them [the researchers] to understand, that it will be backed for that long time and that they won’t be cut off short in the middle of preparing an experiment or flying it.”

“So I think that first of all it demonstrates the commitment of the government to continue with NASA. But also it presents a number of opportunities for a number of people.”
What does the ISS extension mean for Orbital?
The purpose for NASA and Orbital Sciences in building Antares and Cygnus was to restore America’s ability to launch cargo to the ISS – following the shutdown of NASA’s space shuttles – by using commercial companies and their business know how to thereby significantly reduce the cost of launching cargo to low Earth orbit.
“As far as what it [the ISS extension] means for Orbital and other commercial companies – Yes, it does allow us to plan long term for what we might be able to do in providing a service for NASA in the future,” Culbertson replied.
“It also gives us the chance to be innovative and maybe invest in some improvements in how we can do this [cargo service] – to make it more cost effective, more efficient, turnaround time quicker, go more often, go a lot more often!”
“So it allows us the chance to think long term and make sure we can get a return on our investment.”
What does the ISS extension mean for NASA?
“The station is really our stepping stone,” Robert Lightfoot, NASA Associate Administrator, told Universe Today. “If you use that analogy of stepping stones and the next stone. We need to use this stone to know what the next stone looks like. So we can get ready. Whether that’s research or whether that things about the human body. You don’t want to jump off that platform before you are ready.”
“We are learning every day how to live and operate in space. Fortunately on the ISS we are close to home. So if something comes up we can get [the astronauts] home.”
The ISS extension is also the pathway to future exciting journey’s beyond Earth and into deep space, Culbertson and Lightfoot told Universe Today.
“It actually also presents a business opportunity that can be expanded not just to the station but to other uses in spaceflight, such as exploration to Asteroids, Mars and wherever we are going,” said Culbertson.
And we hope it will extend to other civilian uses in space also. Maybe other stations in space will follow this one and we’ll be able to participate in that.”
Lightfoot described the benefits for astronaut crews.
“The further out we go, the more we need to know about how to operate in space, what kind of protection we need, what kind of research we need for the astronauts,” said Lightfoot.
“Orbital is putting systems up there that allow us to test more and more. Get more time. Because when we get further away, we can’t get home as quick. So those are the kinds of things we can do.
“So with this extension I can make those investments as an Agency. And not just us, but also our academic research partners, our industry partners, and the launch market too is part of this.”
He emphasized the benefits for students, like those who flew experiments on Cygnus, and how that would inspire the next generation of explorers!
“You saw the excitement we had today with the students at the viewing area. For example with those little cubesats, 4 inches by 4 inches, that they worked on, and got launched today!”
“That’s pretty cool! And that’s exactly what we need to be doing!

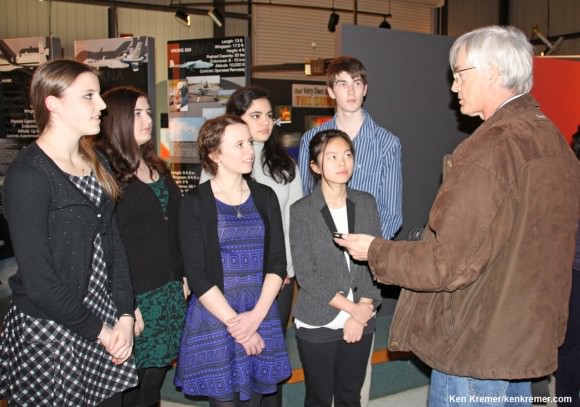
These are among the students benefiting from ISS extension
Science experiments from these students representing six schools across America were selected to fly aboard the Cygnus spacecraft which launched to the ISS from NASA Wallops, VA, on Jan . 9, 2014, as part of the Student Spaceflight Experiments Program (SSEP). Credit: Ken Kremer – kenkremer.com
“So eventually they can take our jobs. And as long as they know that station will be there for awhile, the extension gives them the chance to get the training and learning and do the research we need to take people further out in space.”
“The station is the stepping stone.”
“And it really is important to have this station extension,” Lightfoot explained to me.
The Jan. 9 launch of the Orbital-1 mission is the first of eight operational Antares/Cygnus flights to the space station scheduled through 2016 by Orbital Sciences under its $1.9 Billion Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract with NASA to deliver 20,000 kg of cargo to orbit.
Orbital Sciences and SpaceX – NASA’s other cargo provider – will compete for follow on ISS cargo delivery contracts.
The next Antares/Cygnus flight is slated for about May 1 from NASA Wallops.
In an upcoming story, I’ll describe Orbital Sciences’ plans to upgrade both Antares and Cygnus to meet the challenges of the ISS today and tomorrow.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Orbital Sciences, SpaceX, commercial space, Chang’e-3, LADEE, Mars and more news.