Host: Fraser Cain
Guests: David Dickinson, Amy Shira Teitel, Jason Major, Nicole Gugliucci
Continue reading “Weekly Space Hangout – December 13, 2013 – Europa’s Water Jets and Chinese Lunar Lander”
Upper Stage Engine Restart Essential to High Stakes SpaceX Mission Success for Dec. 3 Launch Attempt
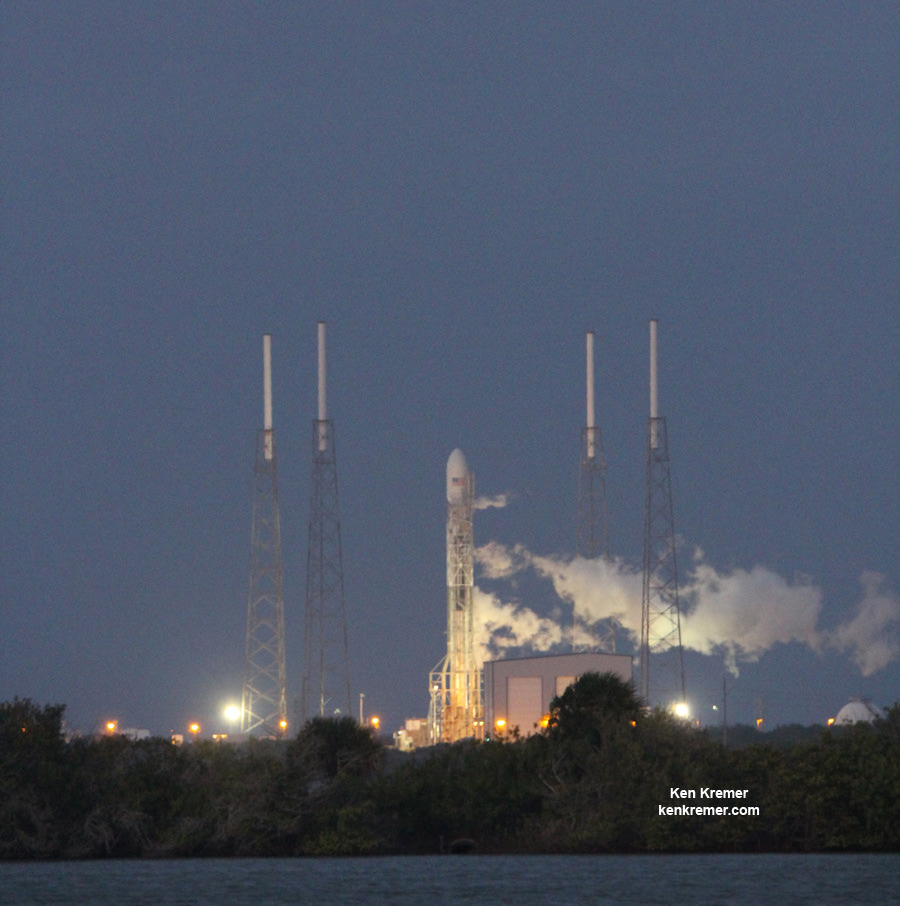

CAPE CANAVERAL, FL – Today (Dec. 3) marks the 3rd attempt by SpaceX to launch the maiden flight of their significantly upgraded Falcon 9 rocket with the SES-8 telecommunications satellite – following the Nov. 28 ‘Thanksgiving = Spacegiving Day’ scrub due to an aborted 1st stage engine firing in progress.
And the stakes could not be higher for the future of SpaceX – with the firms future launch manifest worth billions of dollars riding on the success of today’s liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
In an unprecedented launch event for SpaceX, the upper stage engine on the next generation Falcon 9 booster absolutely must restart in flight for a second time in order for the commercial SES-8 payload to be delivered to geostationary transfer orbit (GTO).
Blastoff from Cape Canaveral’s seaside Space Launch Complex 40 is set for 5:41 p.m. EST (2241 GMT).
The Thanksgiving Day launch was aborted by the computers when the Marlin engines thrust failed to build up as fast as planned.
The weather forecast currently shows a 90% chance of favorable conditions at liftoff time according to Air Force meteorologists. The only concern is for winds.

The launch of SES-8 is a milestone marking the first ever attempt by SpaceX to place a satellite into the geostationary orbit replete with numerous high value commercial satellites. This is the doorway to the future profitability of SpaceX.
“I don’t want to tempt fate, but I think it’s going to have a pretty significant impact on the world launch market and on the launch industry because our prices are the most competitive of any in the world,” said SpaceX CEO and chief designer Elon Musk at a prelaunch briefing for media including Universe Today in Cocoa Beach, FL.
For the mission to be declared a success, the upper stage engine must reignite precisely as planned about 27 minutes after liftoff and burn for approximately 1 minute to successfully propel SES-8 into the propel orbit about 33 minutes after launch.

“Whether or not this launch is successful, I’m confident we will certainly make it on some subsequent launch,” said Musk.
“This is really rocking the industry. Everybody has to look out,” said Martin Halliwell, SES chief technical officer, who joined Musk at the prelaunch meeting.
The upgraded Falcon 9 will also be the launcher utilized for the manned SpaceX Dragon capsules launching to the ISS sometime later this decade!
And the very next satellite set for launch by SpaceX later in December – Thaicom 6- is essentially already waiting at the door to the onramp to space.
SpaceX plans a live broadcast of the Falcon 9 liftoff from pad 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, FL beginning at 5 p.m. EST.
It can be viewed here: www.spacex.com/webcast
The show will feature commentary about the Falcon 9 rocket and launch sequences and the SES-8 commercial satellite from SpaceX corporate headquarters in Hawthorne, CA.
The Falcon 9/SES-8 launch window extends for 86 minutes until 7:07 p.m. EST.
The 3,138 kg (6,918 lbs) SES-8 satellite is a hybrid Ku- and Ka-band spacecraft that will provide TV and communications coverage for the South Asia and Asia Pacific regions.
This mighty new version of the Falcon 9 dubbed v1.1 is powered by a cluster of nine of SpaceX’s new Merlin 1D engines that are about 50% more powerful compared to the standard Merlin 1C engines. The nine Merlin 1D engines 1.3 million pounds of thrust at sea level that rises to 1.5 million pounds as the rocket climbs to orbit
The Merlin 1-D engines are arrayed in an octaweb layout for improved efficiency.
Therefore the upgraded Falcon 9 can boost a much heavier cargo load to the ISS, low Earth orbit, geostationary orbit and beyond.
The next generation Falcon 9 is a monster. It measures 224 feet tall and is 12 feet in diameter. That compares to 13 stories for the original Falcon 9.
Stay tuned here for continuing SpaceX & MAVEN news and Ken’s SpaceX launch reports from on site at Cape Canaveral & the Kennedy Space Center press site.
Chris Hadfield Tells Conan O’Brien What Happens to Underwear in Space
Canadian astronaut Chris Hadfield appeared on Conan last night, and if you missed it here’s a clip in which Conan O’Brien asks Chris to answer one of his most nagging questions about life in orbit: “Do you guys do laundry in space? How do you take care of that issue?”
Like Conan, you might be surprised at his response! (Seen any “shooting stars” recently?)
See this and more videos from Conan on the TeamCoco YouTube page.
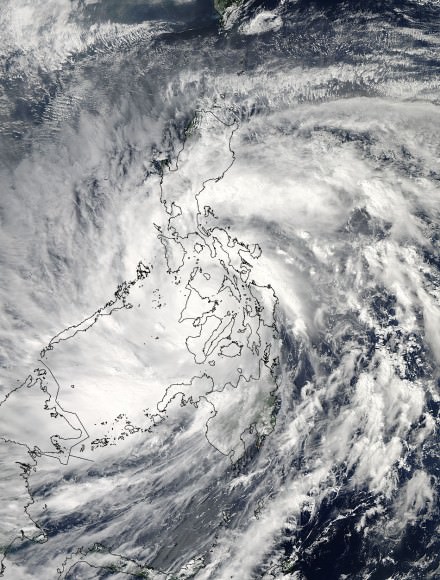
Super-Typhoon Haiyan Causes Catastrophic Death & Destruction – Space Images from NASA, ISRO, Roscosmos & ISS
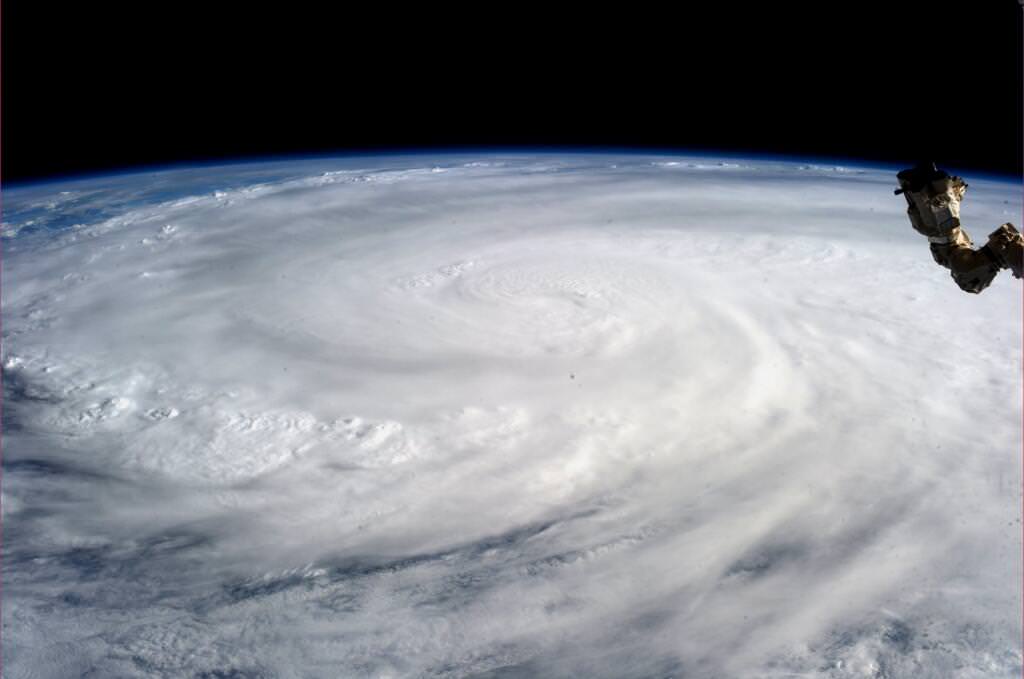

Super Typhoon Haiyan over the Philippines on November 9, 2013 as imaged from Earth orbit by NASA Astronaut Karen Nyberg aboard the International Space Station.Category 5 killer storm Haiyan stretches across the entire photo from about 250 miles (400 kilometer) altitude. Credit: NASA/Karen Nyberg
See more Super Typhoon Haiyan imagery and video below
[/caption]
NASA GODDARD SPACE FLIGHT CENTER, MARYLAND – Super Typhoon Haiyan smashed into the island nation of the Philippines, Friday, Nov. 8, with maximum sustained winds estimated at exceeding 195 MPH (315 kilometer per hour) by the U.S. Navy Joint Typhoon Warning Center – leaving an enormous region of catastrophic death and destruction in its terrible wake.
The Red Cross estimates over 1200 deaths so far. The final toll could be significantly higher. Local media reports today say bodies of men, women and children are now washing on shore.
The enormous scale of Super Typhoon Haiyan can be vividly seen in space imagery captured by NASA, ISRO and Russian satellites – as well as astronaut Karen Nyberg flying overhead on board the International Space Station (ISS); collected here.

Super Typhoon Haiyan is reported to be the largest and most powerful storm ever to make landfall in recorded human history.
Haiyan is classified as a Category 5 monster storm on the U.S. Saffir-Simpson scale.
It struck the central Philippines municipality of Guiuan at the southern tip of the province of Eastern Samar early Friday morning Nov. 8 at 20:45 UTC (4:45 am local time).
As Haiyan hit the central Philippines, NASA says wind gusts exceeded 235 mph (379 kilometers per hour).
The high resolution imagery and precise measurements provided by the worlds constellation of Earth observing space satellites (including NASA, Roscosmos, ISRO, ESA, JAXA) are absolutely essential to tracking killer storms and providing significant advance warning to evacuate residents in affected areas to help minimize the death toll and damage.
More than 800,000 people were evacuated. The storm surge caused waves exceeding 30 feet (10 meters), mudslides and flash flooding.
NASA’s Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite captured visible, microwave and infrared data on the storm just as it was crossing the island of Leyte in the central Philippines, reports NASA – see image below.
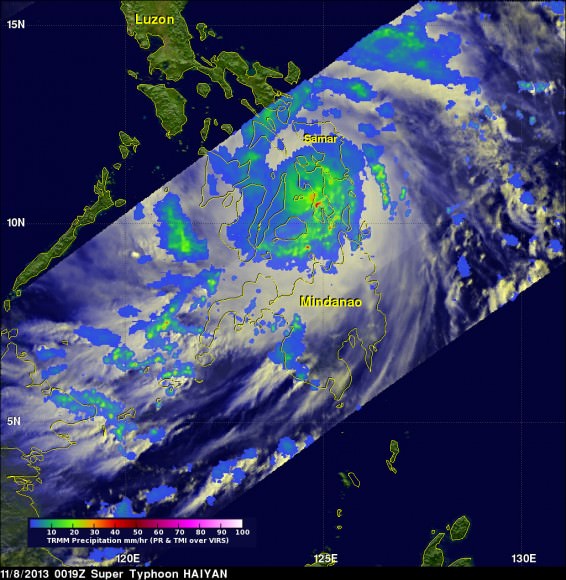
TRMM data from rain rates are measured by the TRMM Precipitation Radar (PR) and TRMM Microwave Imager (TMI) and combined with infrared (IR) data from the TRMM Visible Infrared Scanner (VIRS) by science teams working at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
Coincidentally NASA Goddard has just completed assembly of the next generation weather satellite Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) observatory that replaces TRMM – and where I inspected the GPM satellite inside the Goddard clean room on Friday.
“GPM is a direct follow-up to NASA’s currently orbiting TRMM satellite,” Art Azarbarzin, GPM project manager, told Universe Today during my exclusive clean room inspection of the huge GPM satellite.

Credit: Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com
“TRMM is reaching the end of its usable lifetime. GPM launches in February 2014 and we hope it has some overlap with observations from TRMM.”
“The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) observatory will provide high resolution global measurements of rain and snow every 3 hours,” Dalia Kirschbaum, GPM research scientist, told me at Goddard.
GPM is equipped with advanced, higher resolution radar instruments. It is vital to continuing the TRMM measurements and will help provide improved forecasts and advance warning of extreme super storms like Hurricane Sandy and Super Typhoon Haiyan, Azarbarzin and Kirschbaum explained.
Video Caption: Super Typhoon Haiyan imaged on Nov 6 – 8, 2013 by the Russian Elektro-L satellite operating in geostationary orbit. Credit: Roscosmos via Vitaliy Egorov
The full magnitude of Haiyan’s destruction is just starting to be assessed as rescue teams reach the devastated areas where winds wantonly ripped apart homes, farms, factories, buildings and structures of every imaginable type vital to everyday human existence.
Typhoon Haiyan is moving westward and is expected to forcefully strike central Vietnam in a day or two. Mass evacuations are underway at this time

Orion Service Module Comes Together and Testing Affirms Flight Design for 2014 Blastoff
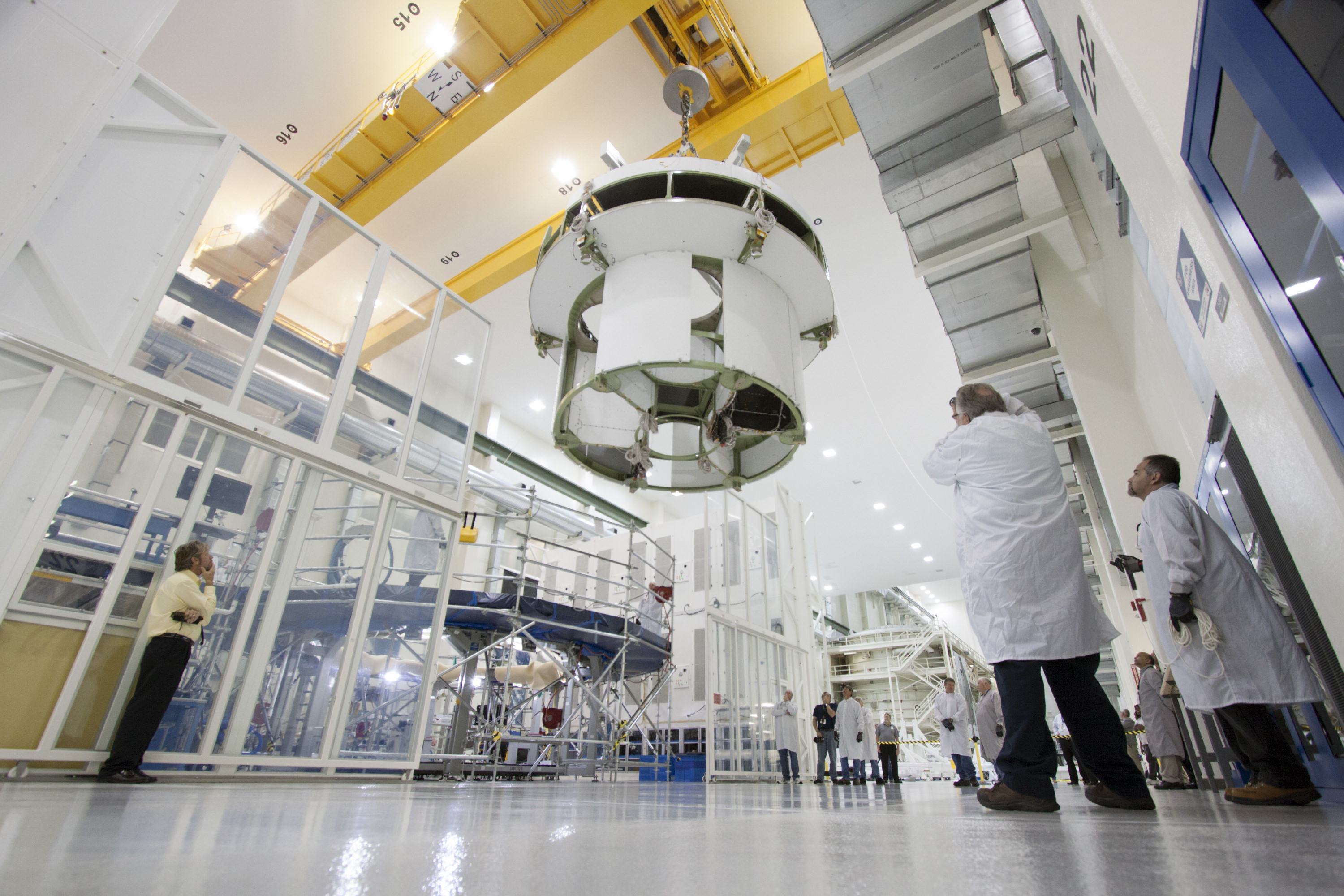

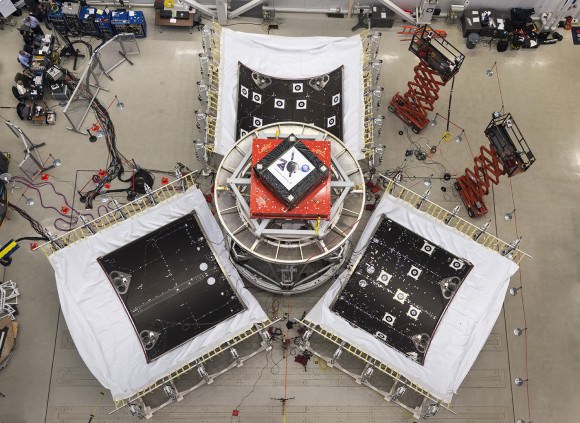
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – All of the key hardware elements being assembled for NASA’s new Orion spacecraft launching just under one year from now are nearing completion at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) – at the same time as a crucial and successful hardware test in California this week helps ensure that the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) vehicle will be ready for an on-time liftoff.
Orion is NASA’s first spaceship designed to carry human crews on long duration flights to deep space destinations beyond low Earth orbit, such as asteroids, the moon, Mars and beyond.
In a major construction milestone, Orion’s massive Service Module (SM) was hoisted out from the tooling stand where it was manufactured at the Operations and Checkout Building (O & C) at KSC and moved to the next assembly station where it will soon be mated to the spacecraft adapter cone.
The SM should be mated to the crew module (CM) by year’s end, Orion managers told Universe Today during my recent inspection tour of significant Orion hardware at KSC.
“We are working 24 hours a day, 7 days a week,” said Jules Schneider, Orion Project manager for Lockheed Martin at KSC, during an exclusive interview with Universe Today inside the Orion clean room at KSC. “We are moving fast!”

The Orion CM recently passed a significant milestone when it was “powered on” for the first time at KSC.
“We are bringing Orion to life. Lots of flight hardware has now been installed.”
And on the other side of the country, the Service Module design passed a key hurdle on Wednesday (Nov. 6) when the trio of large spacecraft panels that surround the SM were successfully jettisoned from the spacecraft during a systems test by Lockheed Martin that simulates what would happen during an actual flight several minutes after liftoff.
“Hardware separation events like this are absolutely critical to the mission and some of the more complicated things we do,” said Mark Geyer, Orion program manager at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. “We want to know we’ve got the design exactly right and that it can be counted on in space before we ever launch.”

Lockheed Martin is the prime contractor for Orion and responsible for assembly, testing and delivery of the Orion EFT-1 spacecraft to NASA that’s slated for an unmanned test flight targeted to lift off from Cape Canaveral, Florida in September 2014.
The CM rests atop the SM similar to the Apollo Moon landing program architecture.
However in a significant difference from Apollo, the Orion fairings support half the weight of the crew module and the launch abort system during launch and ascent. The purpose is to improve performance by saving weight thus maximizing the vehicles size and capability.
The SM also provides in-space power, propulsion capability, attitude control, thermal control, water and air for the astronauts.
At Lockheed Martin’s Sunnyvale, California facility a team of engineers used a series of precisely-timed, explosive charges and mechanisms attached to the Orion’s protective fairing panels in a flight-like test to verify that the spacecraft can successfully and confidently jettison them as required during the ascent to orbit.
The trio of fairing panels protect the SM radiators and solar arrays from heat, wind and acoustics during ascent.

“This successful test provides the Orion team with the needed data to certify this new fairing design for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) next year. The test also provides significant risk reduction for the fairing separation on future Orion manned missions,” said Lance Lininger, engineering lead for Lockheed Martin’s Orion mechanism systems in a statement.
This was the 2nd test of the fairing jettison system. During the first test in June, one of the three fairing panels did not completely detach due to an interference “when the top edge of the fairing came into contact with the adapter ring and kept it from rotating away and releasing from the spacecraft,” said NASA.

2013 has been an extremely busy and productive year for the Orion EFT-1 team.
“There are many significant Orion assembly events ongoing this year,” said Larry Price, Orion deputy program manager at Lockheed Martin, in an interview with Universe Today at Lockheed Space Systems in Denver.
“This includes the heat shield construction and attachment, power on, installing the plumbing for the environmental and reaction control system, completely outfitting the crew module, attached the tiles, building the service module and finally mating the crew and service modules (CM & SM),” Price told me.

Credit: Lockheed Martin
The two-orbit, four- hour flight will lift the Orion spacecraft and its attached second stage to an orbital altitude of 3,600 miles, about 15 times higher than the International Space Station (ISS) – and farther than any human spacecraft has journeyed in 40 years.
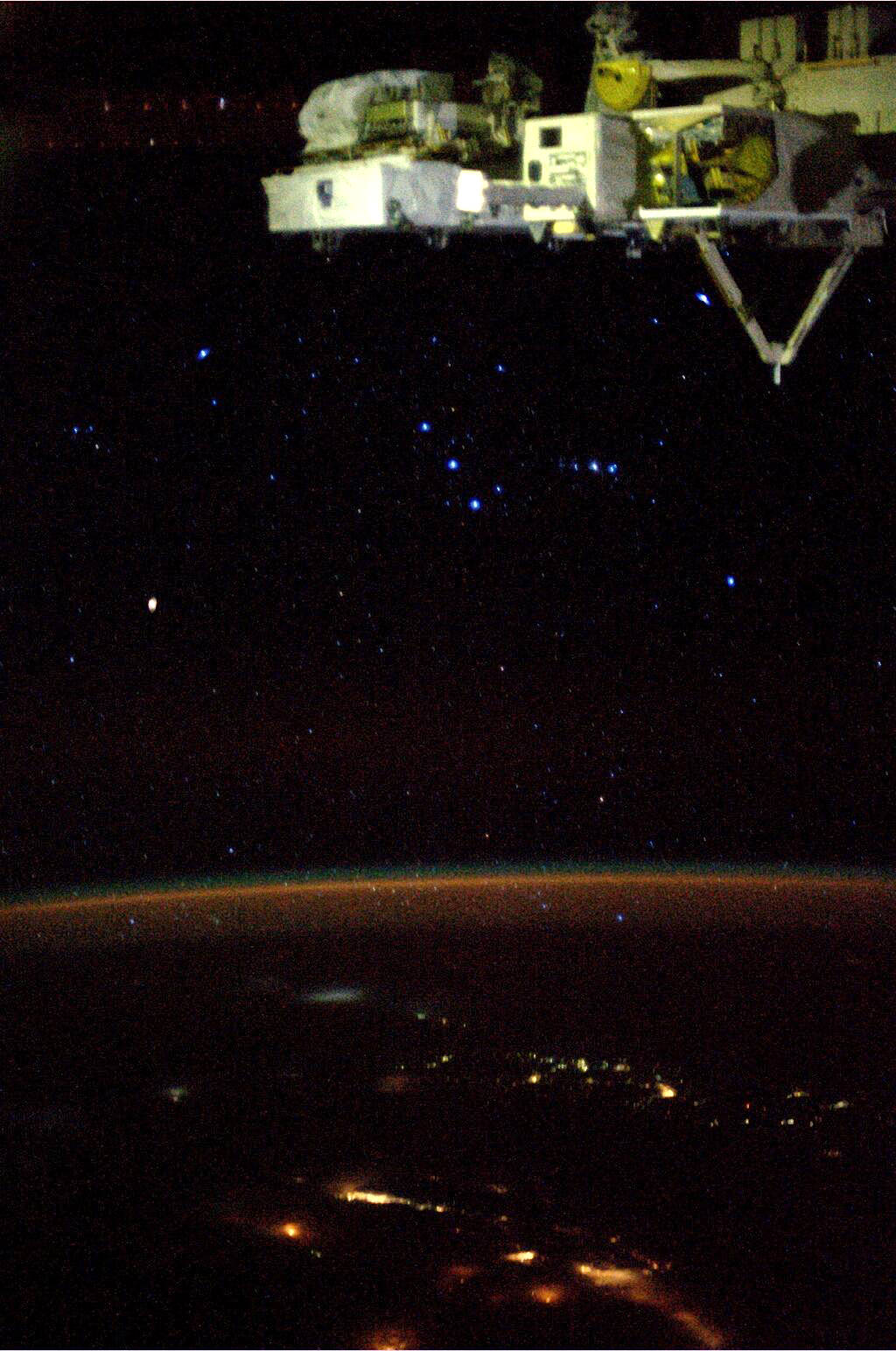
The Stars of Orion Seen Blazing From Orbit
The mighty hunter soars above the atmosphere in this photo, taken by NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg currently living and working in space aboard the ISS. One of the most recognizable constellations in night skies all across the Earth, Orion also puts on an impressive display for those well above the Earth!
Appearing here to be lying on his right side, the three stars of Orion’s famous belt — Mintaka, Alnilam, and Alnitak, top to bottom — are center frame, while his sword is nearly horizontal just to the right (the blurry center star of which isn’t a star at all, of course, but rather the enormous star-forming Orion nebula.)

At Orion’s right shoulder is Betelgeuse, a huge red giant 20 times more massive than our Sun. Its fiery color is obvious in Karen’s photo, mirroring many of the much-closer human-made city lights visible on the ground.
In addition to featuring my favorite constellation, this photo that Karen recently shared on Twitter also serves to prove (to those few who still require evidence of such) that yes, astronauts can see stars from space. Very nicely too, I may add. The only reason they are not visible in all images is purely photographic — cameras exposing for a bright scene, like a daylit Earth (or Moon) won’t be able to capture the relatively much dimmer light of stars in the same shot, making it look like space is empty of them. Even here we can see a bit of noise in the glowing line of Earth’s atmosphere and a little blurring of edges — that’s a result of a high ISO setting to increase camera sensitivity along with a slightly longer shutter speed than your hand can easily keep stable… again, all to better capture the faint streams of photons from distant stars.
Blaze on, mighty Hunter! See this and more views from the ISS on Karen’s Twitter page here.
Orion Crew Module Comes Alive at T Minus 1 Year to Maiden Blastoff
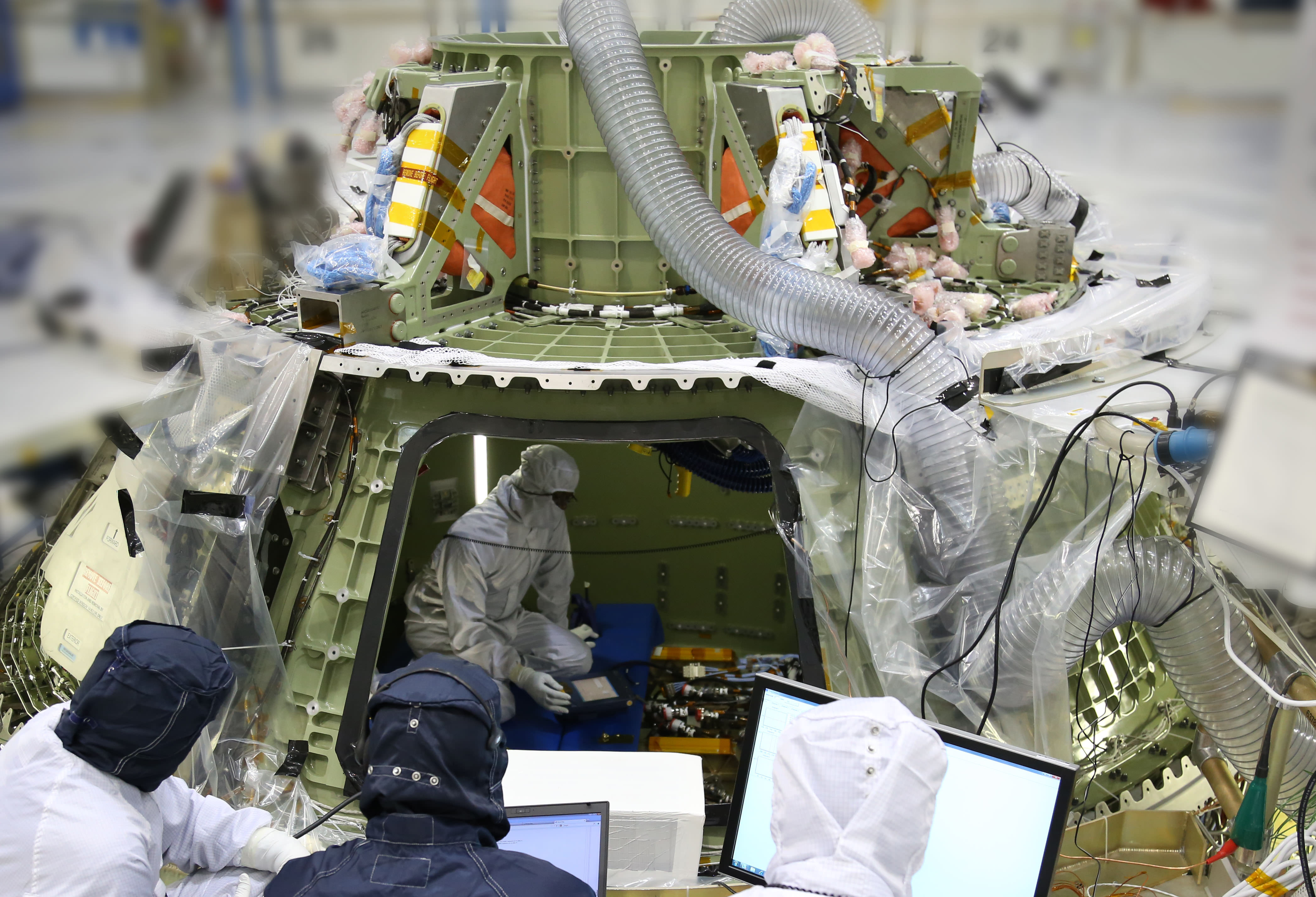

Technicians work inside the Orion crew module being built at Kennedy Space Center to prepare it for its first power on. Turning the avionics system inside the capsule on for the first time marks a major milestone in Orion’s final year of preparations before its first mission, Exploration Flight Test 1. Credit: Lockheed Martin
Story and imagery updated[/caption]
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – Orion, the first NASA spaceship that will ever carry Earthlings to deep space destinations, has at last been “powered on” for the first time at the manufacturing facility at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) where it’s the centerpiece of a beehive humming 24/7 with hi tech processing activities in all directions.
“Power On” marks a major milestone ahead of the maiden space bound Orion test flight dubbed “EFT-1” – now at T-Minus 1 year and counting!
NASA and prime contractor Lockheed Martin recently granted Universe Today an exclusive in depth inspection tour of the impressive Orion EFT-1 crew module, service module and associated hardware destined for the crucial unmanned test flight slated for liftoff from Cape Canaveral in September 2014.
“We are moving fast!” said Jules Schneider, Orion Project manager for Lockheed Martin at KSC, during an exclusive interview with Universe Today as we spoke beside the Orion EFT-1 spacecraft inside the clean room.
“We are bringing Orion to life. Lots of flight hardware has now been installed.”

“We are working 24 hours a day, 7 days a week,” Schneider told me.
Some 200 people are actively employed on building Orion by Lockheed Martin at the Kennedy Space Center.
“There are many significant Orion assembly events ongoing this year,” said Larry Price, Orion deputy program manager at Lockheed Martin, in an interview with Universe Today at Lockheed Space Systems in Denver.
“This includes the heat shield construction and attachment, power on, installing the plumbing for the environmental and reaction control system, completely outfitting the crew module, attached the tiles, building the service module and finally mating the crew and service modules (CM & SM),” Price told me.
Orion is a state of the art crew capsule that will ultimately enable astronauts to fly to deep space destinations including the Moon, Asteroids, Mars and beyond – throughout our solar system.
And Universe Today has had a front row seat.
I have been very fortunate to periodically visit Orion up close over the past year and half to evaluate the testing and assembly progress inside the Operations and Checkout Building at KSC where the vehicle is now rapidly coming together, since the bare bones pressure vessel arrived to great fanfare in June 2012.
For the first time Orion looked to my eyes like a real spaceship, rather than the backbone shell outfitted with hundreds of important test harnesses, strain gauges and wiring to evaluate its physical and structural integrity.

Engineers and technicians at KSC have removed the initial pressure testing gear and are now installing all the flight systems and equipment – such as avionics, instrumentation, flight computers, thrusters, wiring, plumbing, heat shield and much more – required to transform the initial empty shell into a fully functioning spacecraft.
“The Orion skeleton was here before. Now we are putting in all of the other systems,” Schneider explained to me.
“We are really busy.”
“So far over 66,000 Orion parts have been shipped to KSC from over 40 US states,” Price explained.
The heat shield was due to arrive soon and technicians were drilling its attachment ring holes as I observed the work in progress.
“The propulsion, environmental control and life support systems are now about 90% in. The ammonia and propylene glycol loops for the thermal control system are in. Many of the flight harnesses are installed.”
“All of the reaction control thrusters are in – fueled by hydrazine – as well as the two hydrazine tanks and a helium tank. Altogether there are 12 hydrazine pods with two thrusters each,” Schneider elaborated.
The power distribution unit (PDU) – which basically functions as Orion’s computer brains – was installed just prior to my visit. All four PDU’s – which issue commands to the vehicle – were built by Honeywell.
Technicians were actively installing fiber optic and coaxial cables as I watched. They also were conducting leak tests on the environmental control coolant (ECLS) systems which had to be completed before the ‘power on’ testing could begin – in order to cool the avionics systems.
Thermal protection system (TPS) tiles were being bonded to the back panels which ring Orion. The TPS panels get attached early in 2014.
“This is real stuff,” said Schneider gleefully.

NASA says that “the preliminary data indicate Orion’s vehicle management computer, as well as its innovative power and data distribution system — which use state-of-the-art networking capabilities — performed as expected” during the initial crew module power on.
About two months or so of power on functional testing of various systems will follow.
Just like the configuration used in the Apollo era, the Orion crew module will sit atop a service module – and that work is likewise moving along at a rapid clip.
“The Orion service module (SM) is also almost complete,” Schneider said as he showed me the service module structure.
“Structurally the SM is 90% done. The active thermal control system is in and all the fluid systems are welded in and pressure tested.”
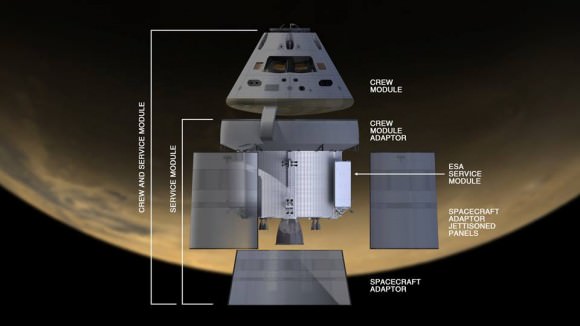
Orion EFT-1 will blastoff atop a mammoth United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket – the most powerful booster in America’s arsenal since the shuttle’s retirement in 2011.
The crew module and service module (CM/SM) will be mated inside the O&C and then be placed onto a mission adapter that eventually attaches to the top of the Delta IV Heavy booster.
They will be mated at the exact same spot in the O&C Building where the Apollo era command and service modules were stacked four decades ago.
Currently, the schedule calls for the Orion CM/SM stack to roll out to Kennedy’s Payload Hazardous Services Facility (PHSF) for servicing and fueling late this year, said Larry Price.
After that the CM/SM stack is transported to the nearby Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) for mating to the emergency Launch Abort System (LAS).
All that work could be done around March 2014 so that ground operations preparing for launch can commence, according to Price.
“In March 2014 we’ll be ready for ground ops. The normal launch processing flow starts in June 2014 leading to Orion’s launch from pad 37 in September 2014.”
“It’s very exciting and a tribute to the NASA and contractor teams,” Price said.
The 2014 uncrewed flight will be loaded with a wide variety of instruments to evaluate how the spacecraft behaves during launch, in space and then through the searing heat of reentry.
The two-orbit, four- hour flight will lift the Orion spacecraft and its attached second stage to an orbital altitude of 3,600 miles, about 15 times higher than the International Space Station (ISS) – and farther than any human spacecraft has journeyed in 40 years.
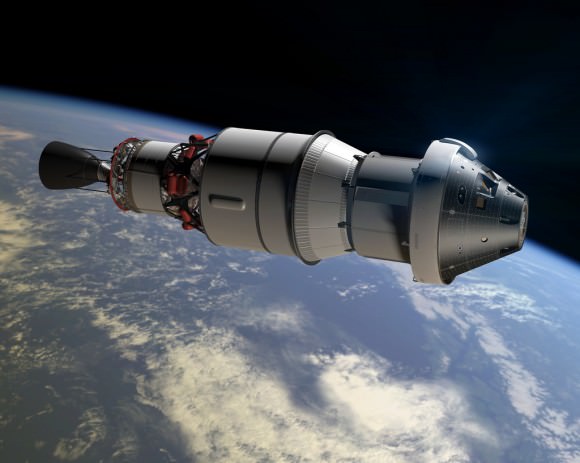

Although the mission will only last a few hours it will be high enough to send the vehicle plunging back into the atmosphere and a Pacific Ocean splashdown to test the craft and its heat shield at deep-space reentry speeds of 20,000 mph and endure temperatures of 4,000 degrees Fahrenheit – like those of the Apollo moon landing missions.

The EFT-1 mission will provide engineers with critical data about Orion’s heat shield, flight systems and capabilities to validate designs of the spacecraft, inform design decisions, validate existing computer models and guide new approaches to space systems development. All these measurements will aid in reducing the risks and costs of subsequent Orion flights before it begins carrying humans to new destinations in the solar system.
“The Orion hardware and the Delta IV Heavy booster for the EFT-1 launch are on target for launch in 2014,” Scott Wilson, NASA’s Orion Manager of Production Operations, told Universe Today in an interview.
…………….
Learn more about Orion, MAVEN, Mars rovers and more at Ken’s upcoming presentations
Nov 14-19: “MAVEN Mars Launch and Curiosity Explores Mars, Orion and NASA’s Future”, Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, 8 PM
Dec 11: “Curiosity, MAVEN and the Search for Life on Mars”, “LADEE & Antares ISS Launches from Virginia”, Rittenhouse Astronomical Society, Franklin Institute, Phila, PA, 8 PM

Damaged Dream Chaser Can be Fixed and Program to Move Forward with Flight Tests – Video
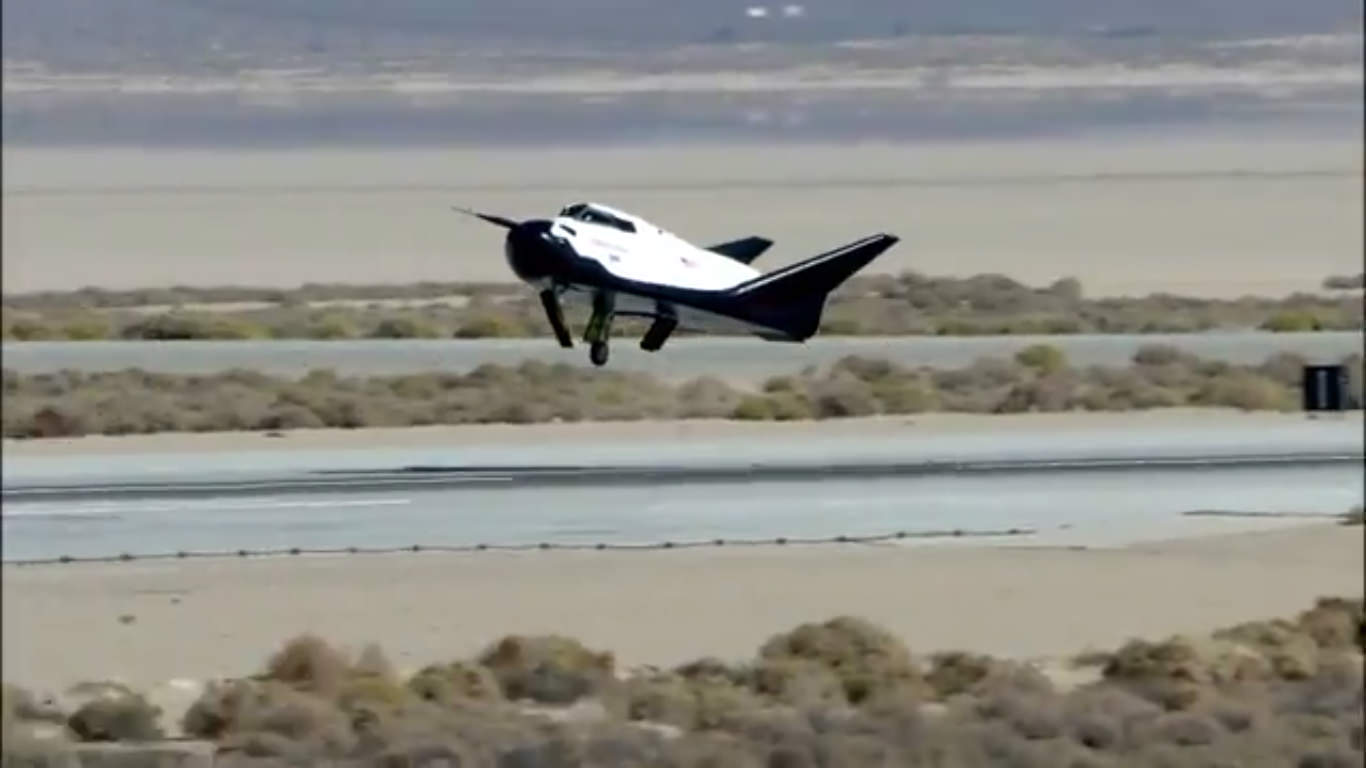

Left landing gear tire visibly failed to deploy as private Dream Chaser spaceplane approaches runway at Edwards Air Force Base, Ca. during first free flight landing test on Oct. 26, 2013 – in this screenshot. Credit: Sierra Nevada Corp.
Watch approach and landing test video below[/caption]
The privately built Dream Chaser ‘space taxi’ that was damaged after landing during its otherwise successful first ever free-flight glide test on Saturday, Oct 26, is repairable and the program will live on to see another day, says the developer Sierra Nevada Corp., (SNC).
The Dream Chaser engineering test vehicle skidded off the runway and landed sideways when its left landing gear failed to deploy at the last second during touchdown on runway 22L at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., said Mark Sirangelo, corporate vice president for SNC Space Systems, at a media teleconference.
The primary goal of the Oct. 26 drop test was to see whether the Dream Chaser mini-shuttle would successfully fly free after being released by an Erickson Air-Crane from an altitude of over 12,000 feet and glide autonomously for about a minute to a touchdown on the Mojave desert landing strip.
“We had a very successful day with an unfortunate anomaly at the end of the day on one of the landing gears,” said Sirangelo.
Dream Chaser is one of three private sector manned spaceships being developed with funding from NASA’s commercial crew program known as Commercial Crew Integrated Capability (CCiCap) initiative to develop a next-generation crew transportation vehicle to ferry astronauts to and from the International Space Station – totally lost following the space shuttle retirement.

The unmanned approach and landing test (ALT) accomplished 99% of its objectives and was only marred by the mechanical failure of the left tire to drop down and deploy for a safe and smooth rollout.
SNC released a short 1 minute video of the test flight – see below – showing the helicopter drop, dive, glide and flare to touchdown. The failure of the landing gear to drop is clearly seen. But the video cuts away just prior to touchdown and does not show the aftermath of the skid or damage to the vehicle.
“The Dream Chaser spacecraft automated flight control system gently steered the vehicle to its intended glide slope. The vehicle adhered to the design flight trajectory throughout the flight profile. Less than a minute later, Dream Chaser smoothly flared and touched down on Edwards Air Force Base’s Runway 22L right on centerline,” said SNC in a statement with the video.
The vehicle is “repairable and flyable again,” Sirangelo noted.
More good news is that the ships interior was not damaged and the exterior can be fixed.
Dream Chaser measures about 29 feet long with a 23 foot wide wing span and is about one third the size of NASA’s space shuttle orbiters.

Since there was no pilot in the cockpit no one was injured. That also meant that no evasive action could be taken to drop the gear.
“We don’t think it’s actually going to set us back,” Sirangelo noted. “In some interesting way, it might actually accelerate it.
NASA’s commercial crew initiative aims at restoring America’s manned spaceflight access to low Earth orbit and the International Space Station (ISS) – perhaps by 2017 – following the forced shutdown of the Space Shuttle program in 2011.
Until an American commercial space taxi is ready for liftoff, NASA is completely dependent on the Russian Soyuz capsule for astronaut rides to the ISS at a cost of roughly $70 million per seat.
Because Congress continues to significantly cut NASA’s budget further delays can be expected – inevitably meaning more payments to Russia and no savings for the American tax payer.
SNC was awarded $227.5 million in the current round of NASA funding and must successfully complete specified milestones, including up to five ALT drop tests to check the aerodynamic handling in order to receive payment.

This particular vehicle had been intended to fly two test flights. Further drop tests were planned with a new test vehicle to be constructed.
The way forward is being evaluated.
“We don’t think there is going to be any significant delay to the program as a result of this. This was meant to be a test vehicle with a limited number of flights,” Sirangelo said.
SNC and NASA have assembled a team to investigate the cause of the anomaly.
“SNC cannot release any further video at this time,” said SNC.
Dream Chaser is a reusable mini shuttle that launches from the Florida Space Coast atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket and lands on the shuttle landing facility (SLF) runway at the Kennedy Space Center, like the space shuttle.
Dream Chaser spaceship test article damaged during 1st Free-Flight Drop Test
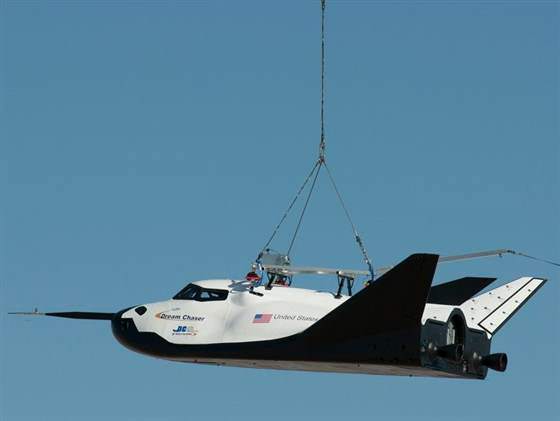

The engineering test article of the commercial Dream Chaser spaceship being developed by Sierra Nevada Corp (SNC) suffered some significant damage during its critical 1st ever approach-and-landing (ALT) drop test on Saturday, Oct. 26, in California due to an unspecified type of malfunction with the deployment of the left landing gear.
The Dream Chaser mini-shuttle suffered “an anomaly as it touched down on the Runway 22L at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif.,” according to a post-test statement from NASA.
A report at NASA Spaceflight.com indicated that the Dream Chaser “flipped over on the runway” after touchdown.
The full extent of damage to the winged vehicle or whether it can be repaired and reflown is not known at this time. No photos or details explaining the damage have yet emerged – beyond brief press releases issued by SNC and NASA.
The performance of the vehicles’ nose skid, brakes, tires and other flight systems is being tested to prove that it can safely land an astronaut crew returning from the space station after surviving the searing heat of re-entry from Earth orbit.
This initial atmospheric drop test was conducted in an automated mode. There was no pilot on board and no one was hurt on the ground.
“No personnel were injured. Damage to property is being assessed,” said NASA. “Edwards Air Force Base emergency personnel responded to scene as a precaution.
“Support personnel are preparing the vehicle for transport to a hangar.”
Dream Chaser is one of three private sector manned spaceships being developed with funding from NASA’s commercial crew program known as Commercial Crew Integrated Capability (CCiCap) initiative to develop a next-generation crew transportation vehicle.

The NASA seed money aims at restoring America’s manned spaceflight access to low Earth orbit and the International Space Station (ISS) – perhaps by 2017 – following the forced shutdown of the Space Shuttle program in 2011.
Until one of the American commercial space taxis is ready for liftoff, NASA is completely dependent on the Russian Soyuz capsule for astronaut rides to the ISS at a cost of roughly $70 million per seat.
SNC was awarded $227.5 million in the current round of NASA funding and must complete specified milestones including up to five ALT drop tests to check the aerodynamic handling.
To date this test vehicle has successfully accomplished a series of runway tow and airborne captive carry tests.
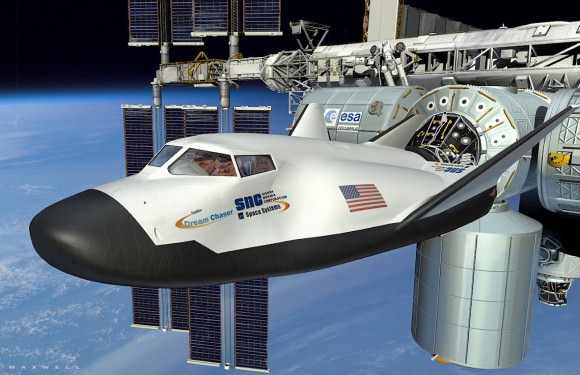
Development of crew versions of the SpaceX Dragon and Boeing CST-100 capsules are also being funded by NASA’s commercial crew program office.
Dream Chaser can carry a crew of up to seven and is the only reusable, lifting body shuttle type vehicle with runway landing capability among the three competitors.

Credit: Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com
During Saturday’s test, SNC was performing the first in a series of free-flight approach-and-landing tests with the Dream Chaser prototype test vehicle known as the ETA.
The prototype spaceship was released as planned from its carrier aircraft, an Erickson Air-Crane helicopter, at approximately 11:10 a.m. Pacific Standard Time (2:10 p.m. EDT), said SNC in a statement.

“Following release, the Dream Chaser spacecraft automated flight control system gently steered the vehicle to its intended glide slope. The vehicle adhered to the design flight trajectory throughout the flight profile. Less than a minute later, Dream Chaser smoothly flared and touched down on Edwards Air Force Base’s Runway 22L right on centerline,” according to the SNC press release.
SNC went on to say that reviews are in progress to determine the cause of the landing gear failure.
“While there was an anomaly with the left landing gear deployment, the high-quality flight and telemetry data throughout all phases of the approach-and-landing test will allow SNC teams to continue to refine their spacecraft design. SNC and NASA Dryden are currently reviewing the data. As with any space flight test program, there will be anomalies that we can learn from, allowing us to improve our vehicle and accelerate our rate of progress.”
The engineering test article (ETA) is a full sized vehicle.
Dream Chaser is a reusable mini shuttle that launches from the Florida Space Coast atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket and lands on the shuttle landing facility (SLF) runway at the Kennedy Space Center, like the space shuttle.
“It’s not outfitted for orbital flight. It is outfitted for atmospheric flight tests,” said Marc Sirangelo, Sierra Nevada Corp. vice president and SNC Space Systems chairman told Universe Today previously.
“The best analogy is it’s very similar to what NASA did in the shuttle program with the Enterprise, creating a vehicle that would allow it to do significant flights whose design then would filter into the final vehicle for orbital flight,” Sirangelo told me.
We’ll provide further details as they become known.
Cygnus Commercial Cargo Craft Completes Historic First Flight to Space Station

Commercial space took another major leap forward this morning, Oct 22., when the privately developed Cygnus cargo vehicle undocked from the International Space Station on its historic maiden flight and successfully completed a highly productive month long stay during its demonstration mission – mostly amidst the US government shutdown.
The Cygnus was maneuvered about 10 meters (30 feet) away from the station and held in the steady grip of the stations fully extended robotic arm when astronauts Karen Nyberg and Luca Parmitano unlatched the arm and released the ship into free space at 7:31 a.m. EDT today – signifying an end to joint flight operations.
The next Cygnus resupply vessel is due to blast off in mid-December and is already loaded with new science experiments for microgravity research and assorted gear and provisions.
After the Expedition 37 crew members quickly pulled the arm back to a distance 1.5 meters away from Cygnus, ground controllers issued a planned “abort” command to fire the ships thrusters and safely depart from the massive orbiting lab complex.

“It’s been a great mission. Nice work today!” radioed Houston Mission Control at NASA’s Johnson Space Center.
The vehicles were flying over the Atlantic Ocean and off the east coast of Argentina as Cygnus left the station some 250 miles (400 km) overhead in low Earth orbit.
The event was carried live on NASA TV and Cygnus was seen moving rapidly away.
Barely five minutes later Cygnus was already 200 meters away, appeared very small in the cameras view and exited the imaginary “Keep Out Sphere” – a strictly designated safety zone around the million pound station.

The Cygnus resupply ship delivered about 1,300 pounds (589 kilograms) of cargo, including food, clothing, water, science experiments, spare parts and gear to the six person Expedition 37 crew.
After the crew unloaded all that cargo, they packed the ship with 2,850 pounds of no longer needed trash.
On Wednesday (Oct. 23), a pair of deorbit burns with target Cygnus for a destructive reentry back into the Earth’s atmosphere at 2:18 p.m. EDT, to plummet harmlessly into the Pacific Ocean.
Cygnus was developed by Orbital Sciences Corp. with seed money from NASA in a public-private partnership between NASA and Orbital Sciences under NASA’s COTS commercial transportation initiative.
SpaceX Corp. was also awarded a COTS contract to develop the Dragon cargo carrier so that NASA would have a dual capability to stock up the station.
COTS was aimed at fostering the development of America’s commercial space industry to deliver critical and essential supplies to the ISS following the retirement of the Space Shuttle program.
“Congratulations to the teams at Orbital Sciences and NASA who worked hard to make this demonstration mission to the International Space Station an overwhelming success,” NASA Administrator Charles Bolden said in a statement.

“We are delighted to now have two American companies able to resupply the station. U.S. innovation and inspiration have once again shown their great strength in the design and operation of a new generation of vehicles to carry cargo to our laboratory in space. Orbital’s success today is helping make NASA’s future exploration to farther destinations possible.”
America completely lost its capability to send humans and cargo to the ISS when NASA’s space shuttles were forcibly retired in 2011. Orbital Sciences and SpaceX were awarded NASA contracts worth over $3 Billion to restore the unmanned cargo resupply capability over 20 flights totally.
Cygnus was launched to orbit on its inaugural flight on Sept. 18 atop Orbital’s commercial Antares rocket from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility on the Eastern shore of Virginia.
The initially planned Sept. 22 berthing of the spacecraft at a port on the Earth facing Harmony node was delayed a week to Sept. 29 due to an easily fixed communications glitch. It was no worse for the wear and performed admirably.
“Antares next flight is scheduled for mid December,” according to Frank Culbertson, former astronaut and now Orbital’s executive Vice President responsible for the Antares and Cygnus programs.


