[/caption]
The historic flight of the first private spaceship to ever connect to the International Space Station (ISS) has entered its waning hours and by all accounts it’s been a resounding success thus far ahead of the imminent return trip to Earth.
All objectives have been fully accomplished and all that remains is for the unmanned Dragon cargo capsule to be detached from the huge outpost early Thursday morning, May 31, following by a mission ending splashdown and ocean recovery off the coast of California some 6 hours later.
Astronauts living aboard the huge Earth orbiting lab closed the hatches to the SpaceX Dragon capsule earlier today (May 30) and will finish their activities to seal the capsule for a safe departure before going to sleep later today ahead of tomorrow’s momentous final feats on this landmark mission.
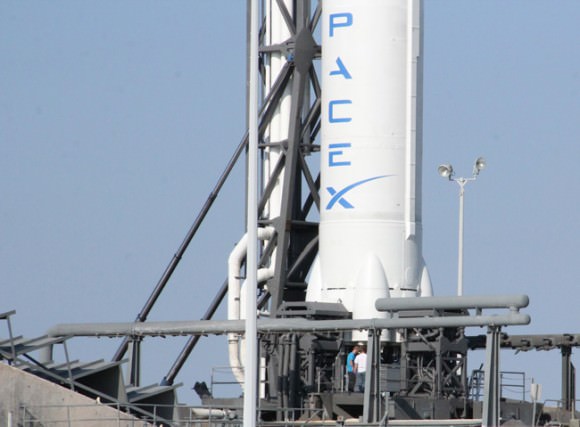
Dragon is the world’s first commercial spacecraft and was built by Hawthorne, Calif., based SpaceX Corporation, founded in 2002 by CEO and Chief Designer Elon Musk.

NASA and SpaceX described the Dragon’s upcoming unberthing and return to Earth activities at a news media briefing today.
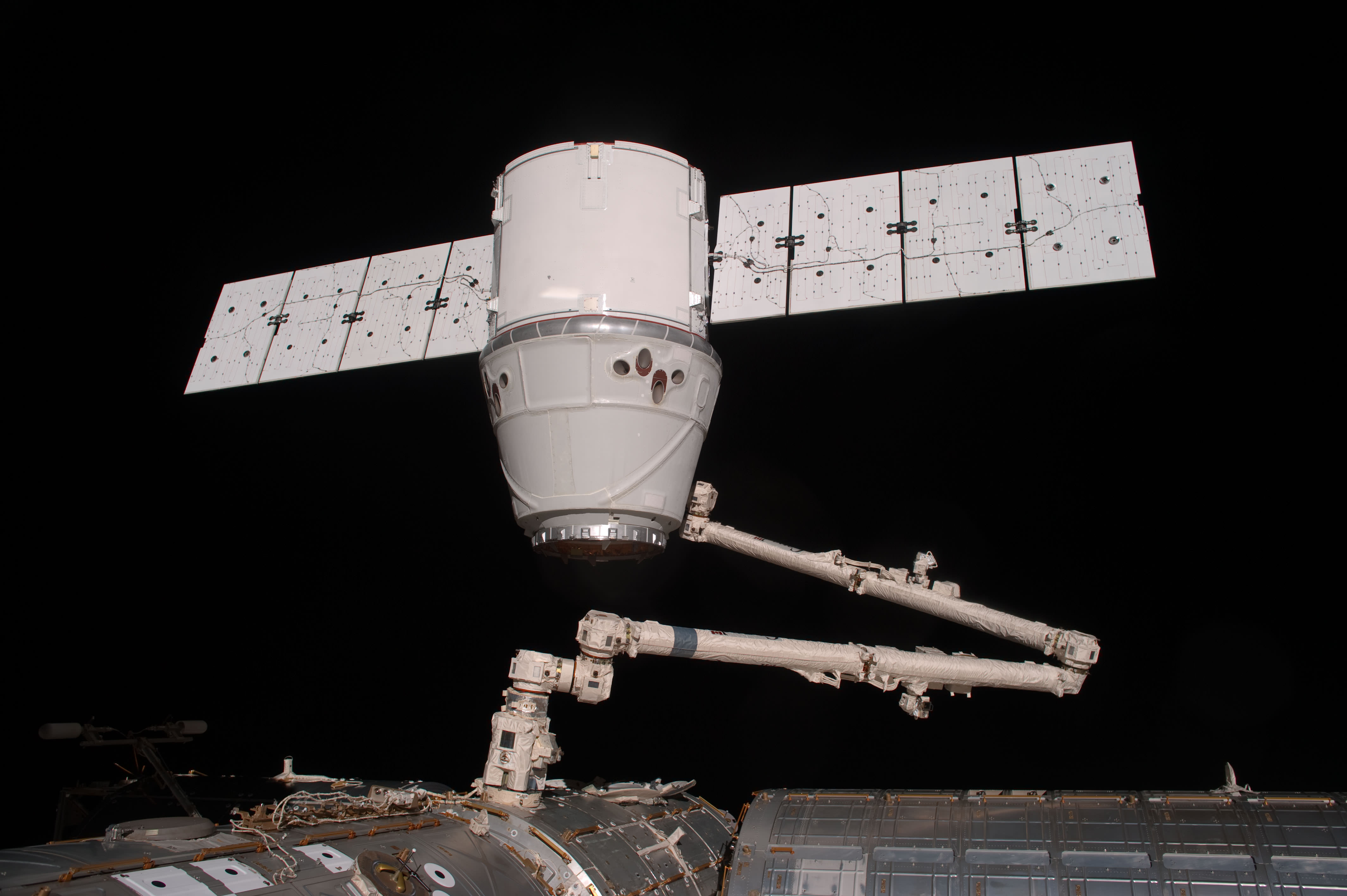
The ISS crew is scheduled to disconnect the Dragon from the Earth-facing Harmony node using the station’s robotic arm at 4:05 a.m. EDT (0805 GMT), said NASA flight director Holly Ridings. They will release the Dragon from the arm’s grip into space at 5:35 a.m. EDT (0935 GMT).
“The Dragon really looks great,” Ridings told Universe Today.
Ridings said that the crew completed virtually “all the cargo [unloading and refilling] operations in a single day on Monday”.
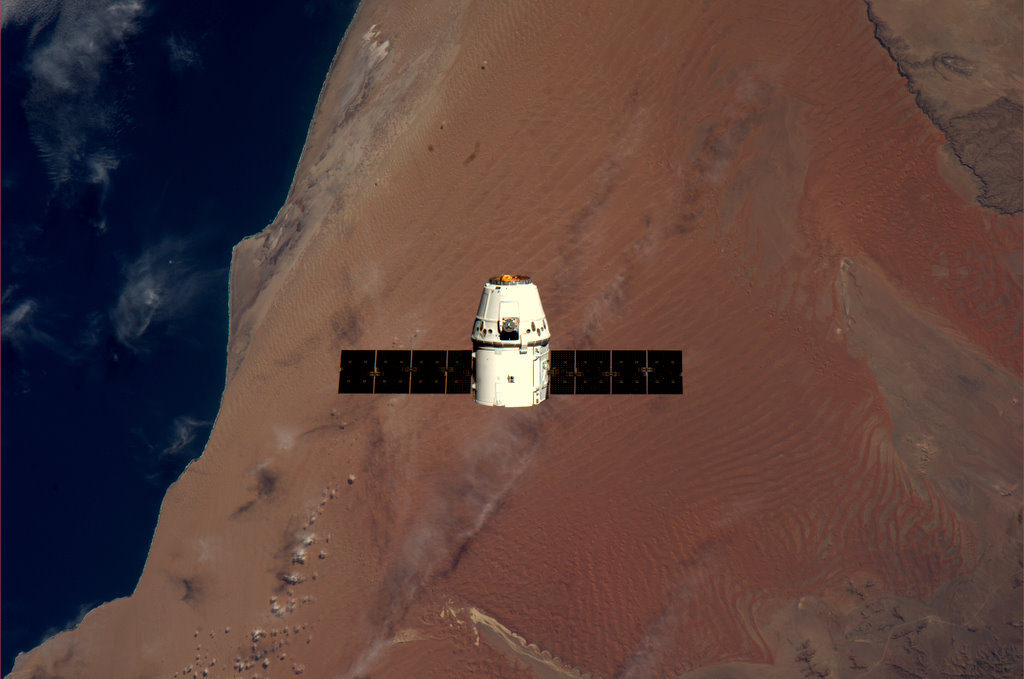
Dragon will fire the first of a series of three small orbit transfer burns starting at 5:36 a.m. EDT (0936 GMT) to back it away from the orbiting lab complex. The big de-orbit burn lasting about 7 minutes is set for 10:51 am, the Dragon trunk will be jettisoned at 11:09 a.m., main chutes deploy at 11:36 a.m. and the splashdown in the Pacific Ocean is due at 11:44 a.m. (1544 GMT) some 490 nautical miles southwest of Los Angeles off the West Coast of California using a flotilla of recovery vessels rented by SpaceX for the ocean retrieval process.
Although SpaceX has demonstrated the capability to safely return Dragon to Earth once before in December 2010, the firm is taking nothing for granted.
“It’s still a very challenging phase of flight,” said SpaceX Dragon Mission Manager John Couluris at the briefing. “Only a few countries have done this so far, so we’re not taking this lightly.”
“It will take about 2 to 3 days to return the capsule to the port of Los Angeles and then to the SpaceX facility in Texas for cargo unloading.”
Unlike the other Russian, European and Japanese cargo freighters that service the ISS and then disintegrate on reentry, the SpaceX Dragon is uniquely equipped with a heat shield (made of PICA-X) that allows it to plunge safely through the Earth’s atmosphere and survive the fiery temperatures exceeding more than 3000 degrees F (1600 degrees C).
The down mass capability restores another critical capability lost with the forced retirement of NASA’s Space Shuttle orbiters in July 2011. The astronauts filled Dragon with about 620 kilograms (1367 pounds) of science experiments, trash and non-critical items on this historic test flight.
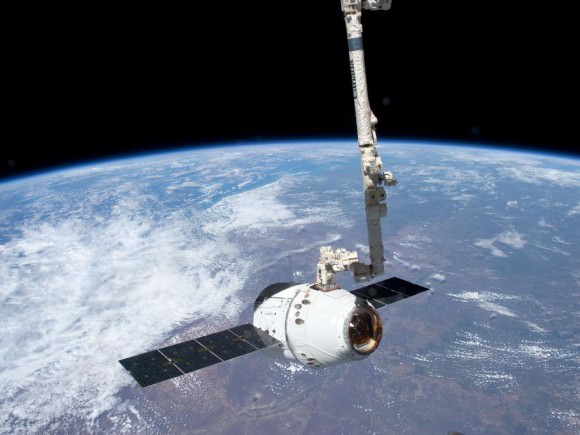
The Dragon arrived at the million pound orbiting space lab on May 25. On May 26, the crew opened the hatches and ‘Entered the Dragon’ for the first time.
Look here for a collection of incredible images snapped by European ISS astronaut Andre Kuipers who berthed Dragon at an open parking port on the ISS after it was snared with the 18 m (58 ft) Canadian robot arm by NASA astronaut Don Pettit.
Ridings said the astronauts used the robot arm to thoroughly inspect the Dragon’s exterior, trunk space and solar arrays.
“The results were very positive and our models were very accurate and match the on orbit Dragon configuration and clearances. On downstream flights we’ll be using Dextre on the end of the robot arm to reach around into the Dragon’s truck and grab payloads out,” Ridings told Universe Today.

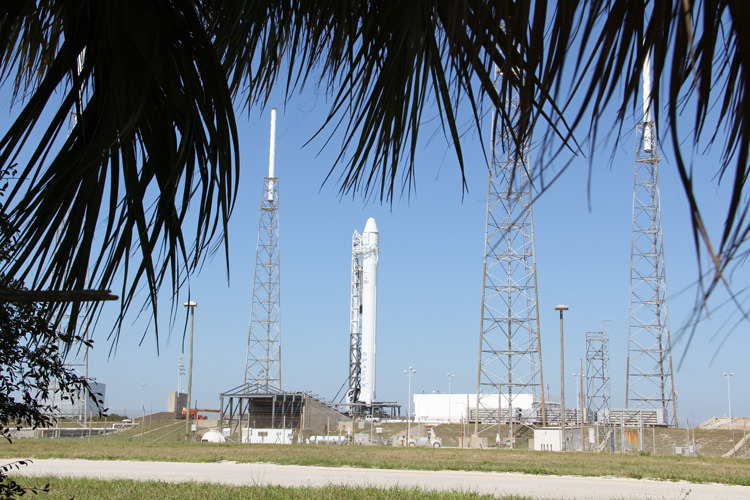
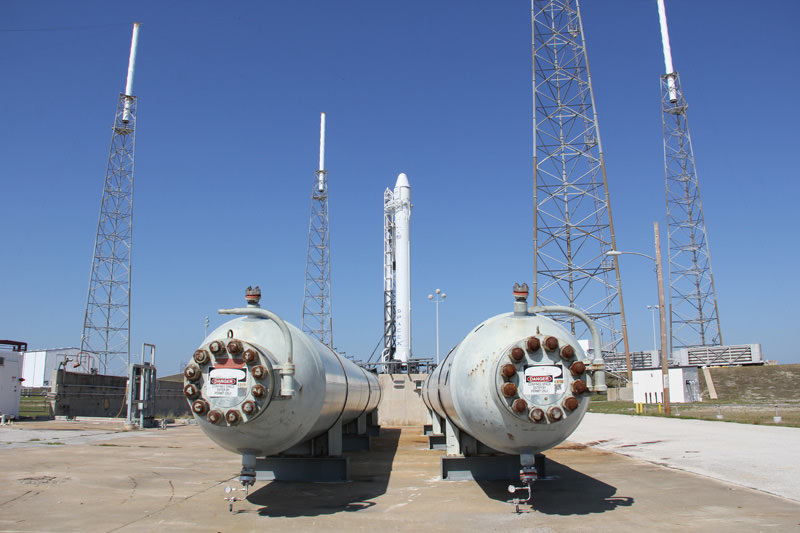
Dragon is the world’s first commercial resupply vehicle. It was launched atop a SpaceX built Falcon 9 booster on May 22 from Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
SpaceX signed a contract with NASA in 2006 to conduct twelve Falcon 9/Dragon resupply missions to carry about 44,000 pounds of cargo to the ISS at a cost of some $1.6 Billion over the next several years.
NASA TV will provide live coverage of Dragon’s return to Earth and ocean splash down starting at 2:30 a.m. EDT.
…………………….
Dragon Return Timeline from SpaceX – (times are approximate and subject to change)
5/31/12
Time (Pacific) — Event
01:05 — Dragon uninstalled using station’s robotic arm
02:35 — Dragon released by the station’s robotic arm
03:11 — Dragon’s Draco thrusters fire departure burns
04:07 — Unlatch/close/latch GNC door holding sensors
07:51 — Dragon’s Draco thrusters fire deorbit burn
08:09 — Dragon’s trunk is jettisoned
08:35 — Dragon’s drogue parachutes are deployed
08:36 — Dragon’s main parachutes are deployed
08:44 — Dragon lands in the Pacific