A number of missions are destined for the Moon before this decade is over. In addition to the Artemis Program, the European Space Agency (ESA), the China National Space Agency (CNSA), Roscosmos, and other space agencies have some ambitious plans of their own. These include sending robotic missions to characterize the local environment, scout out resources, and pave the way for permanent human outposts.
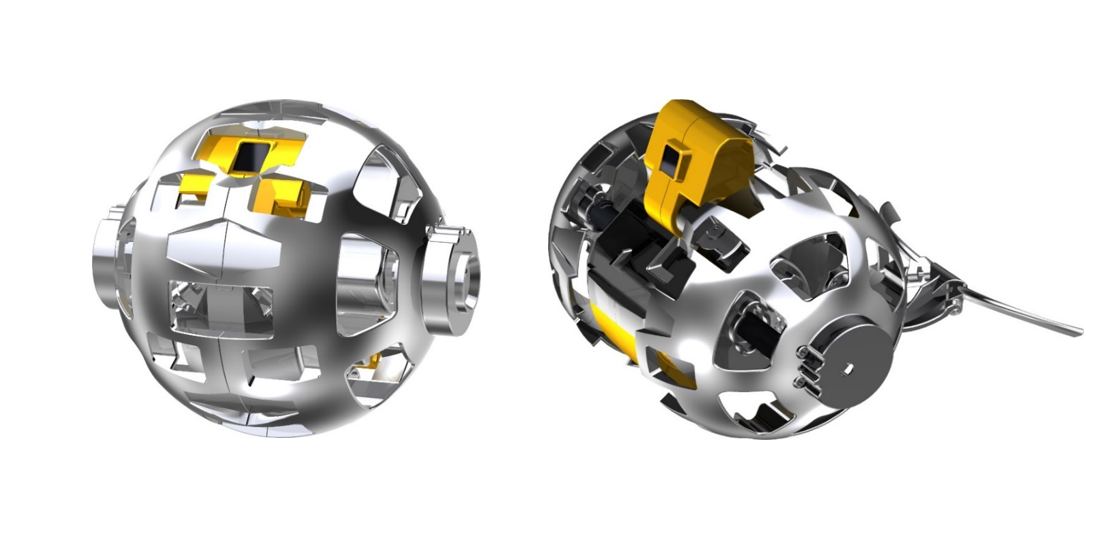
The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) also some very interesting lunar missions in mind. In addition to partnering with NASA on the Artemis Program and helping to create the Lunar Gateway, JAXA has the radical idea to send a transforming rover to the Moon. The data this rover collects will be used to inform the design of a pressurized rover that will allow for a sustained human presence on the Moon.
Continue reading “Lunar Rovers! Transform and Roll Out!”