The ‘Return to Flight’ launch of Orbital ATK’s re-engined Antares rocket on a cargo resupply launch for NASA bound for the space station has been postponed for at least another month into September due to the need for further analysis of the revamped booster and other factors.
Today’s announcement by Orbital ATK of a launch delay to mid-September comes barely two weeks before the long hoped for liftoff – which had been scheduled for late afternoon on August 22 from Orbital ATK’s launch base on Virginia’s picturesque eastern shore.
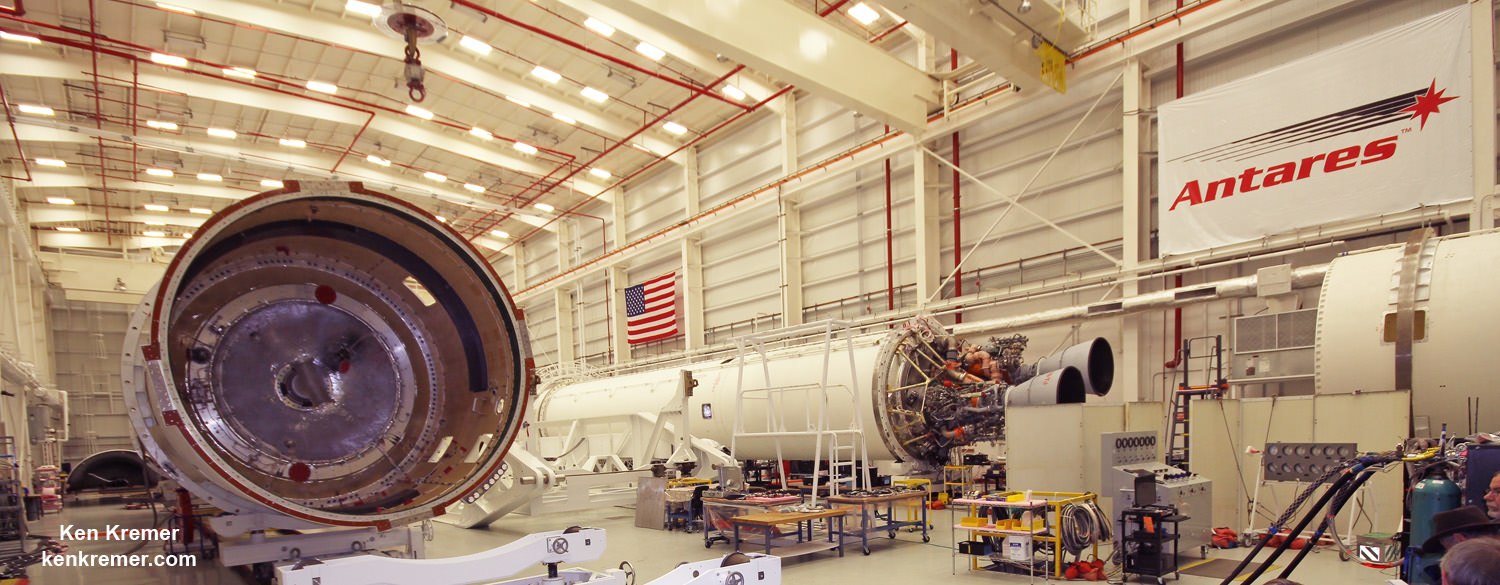
The Antares 230 medium-class commercial launch vehicle rocket has been upgraded with new first stage Russian-built RD-181 engines that must be fully validated before launching NASA’s precious cargo to the International Space Station (ISS).
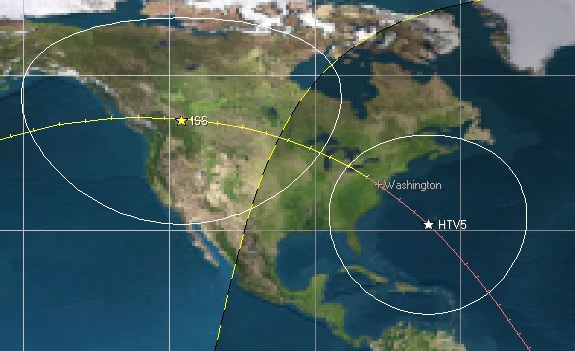
Almost simultaneously, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) decided to postpone the upcoming launch of their next HTV H-11 Transfer Vehicle “KOUNOTORI6” (HTV6) which had been slated for October 1 from the Tanegashima Space Center.
JAXA said a leak was detected during pressure testing which must be fixed before any launch attempt.
Antares could potentially take the launch slot vacated by JAXA.
Orbital ATK cited multiple factors for the launch postponement from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in a short statement released today, August 10.
“Due to a variety of interrelated factors, including the company’s continuing processing, inspection and testing of the flight vehicle at Wallops Island, and NASA’s scheduling of crew activities on the International Space Station in preparation for upcoming cargo and crew launches, Orbital ATK is currently working with NASA to target a window in the second half of September for the launch of the OA-5 mission,” Orbital ATK announced.
Also there are reports that the re-engined Antares experience some form of unexpected ‘vibrations’ during the recent static fire test conducted in May.
This is the latest in a string of Antares launch delays, running back to the start of 2016.
Furthermore, a new launch date won’t be announced for at least several more weeks.
“A more specific launch date will be identified in the coming weeks,” said Orbital ATK.

Orbital ATK’s Antares commercial rocket had to be overhauled with completely new first stage engines following the catastrophic launch failure nearly two years ago on October 28, 2014 just seconds after blastoff that doomed the Orb-3 resupply mission to the space station.

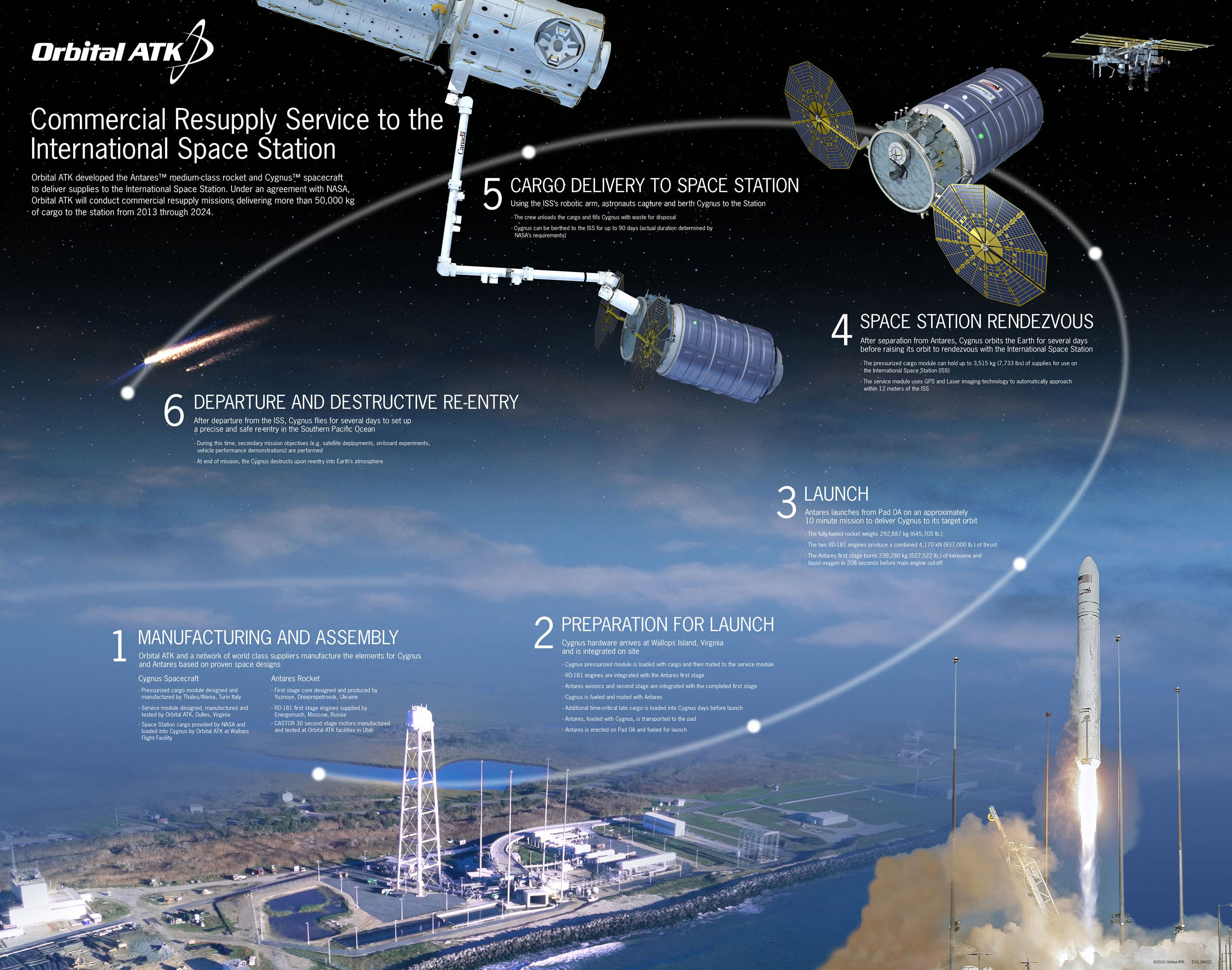
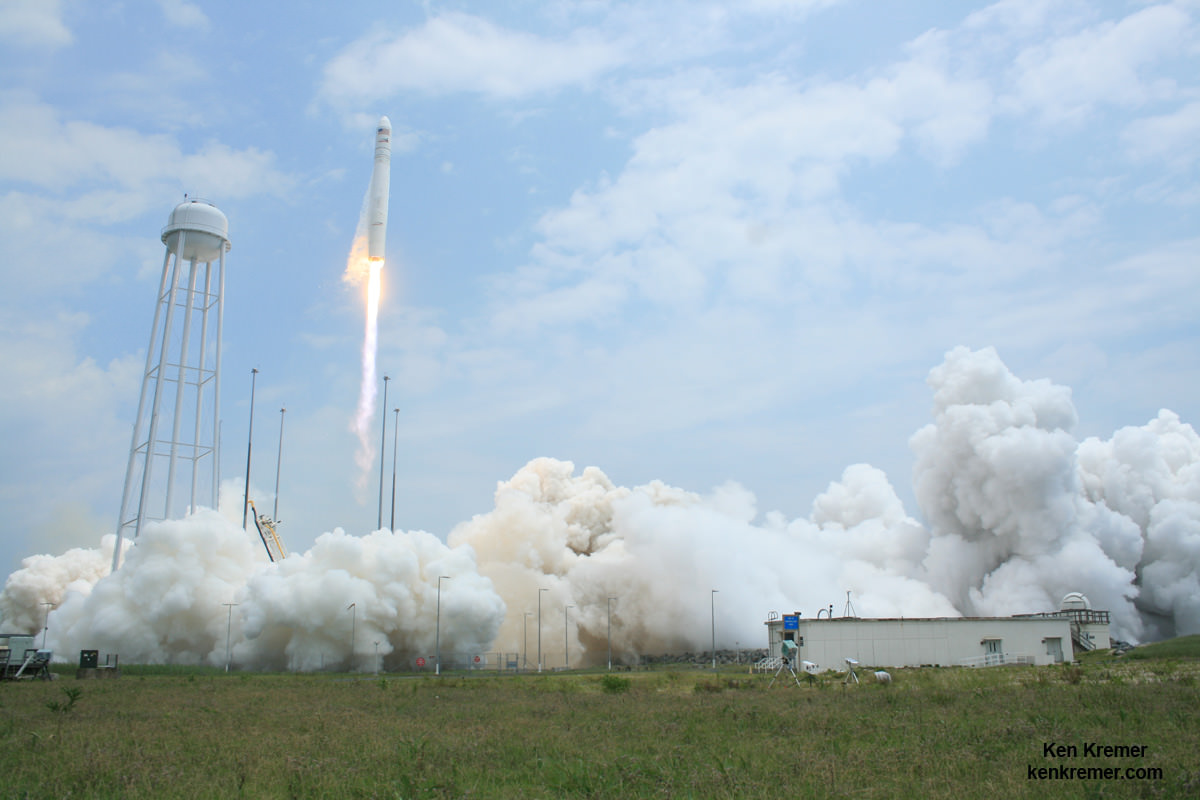
The goal of the Antares ‘Return to Flight’ mission is to launch Orbital ATK’s Cygnus cargo freighter on the OA-5 resupply mission for NASA to the International Space Station (ISS).
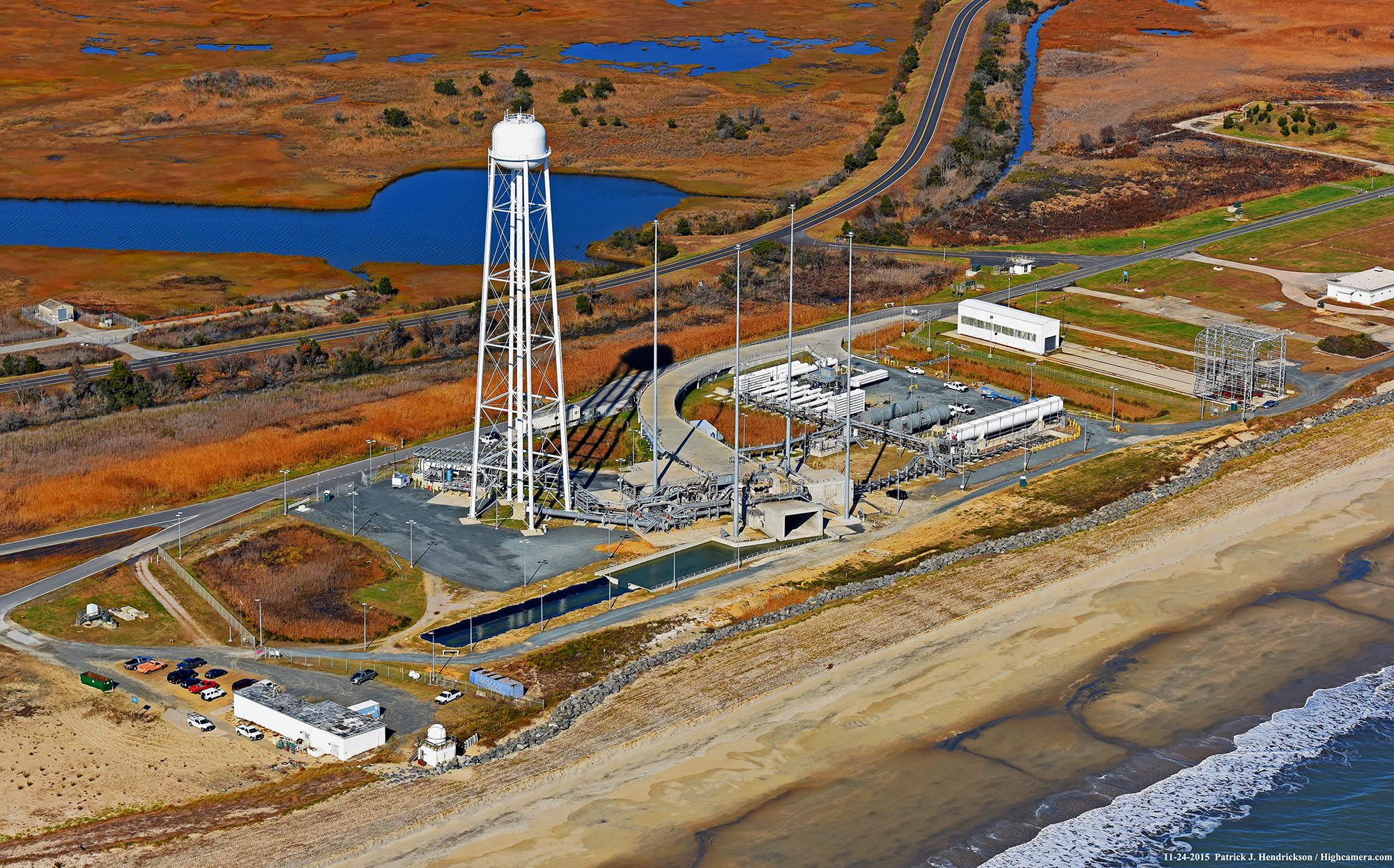
To that end the aerospace firm recently completed a successful 30 second long test firing of the re-engined first stage on May 31 at Virginia Space’s Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) Launch Pad 0A – as I reported here earlier.
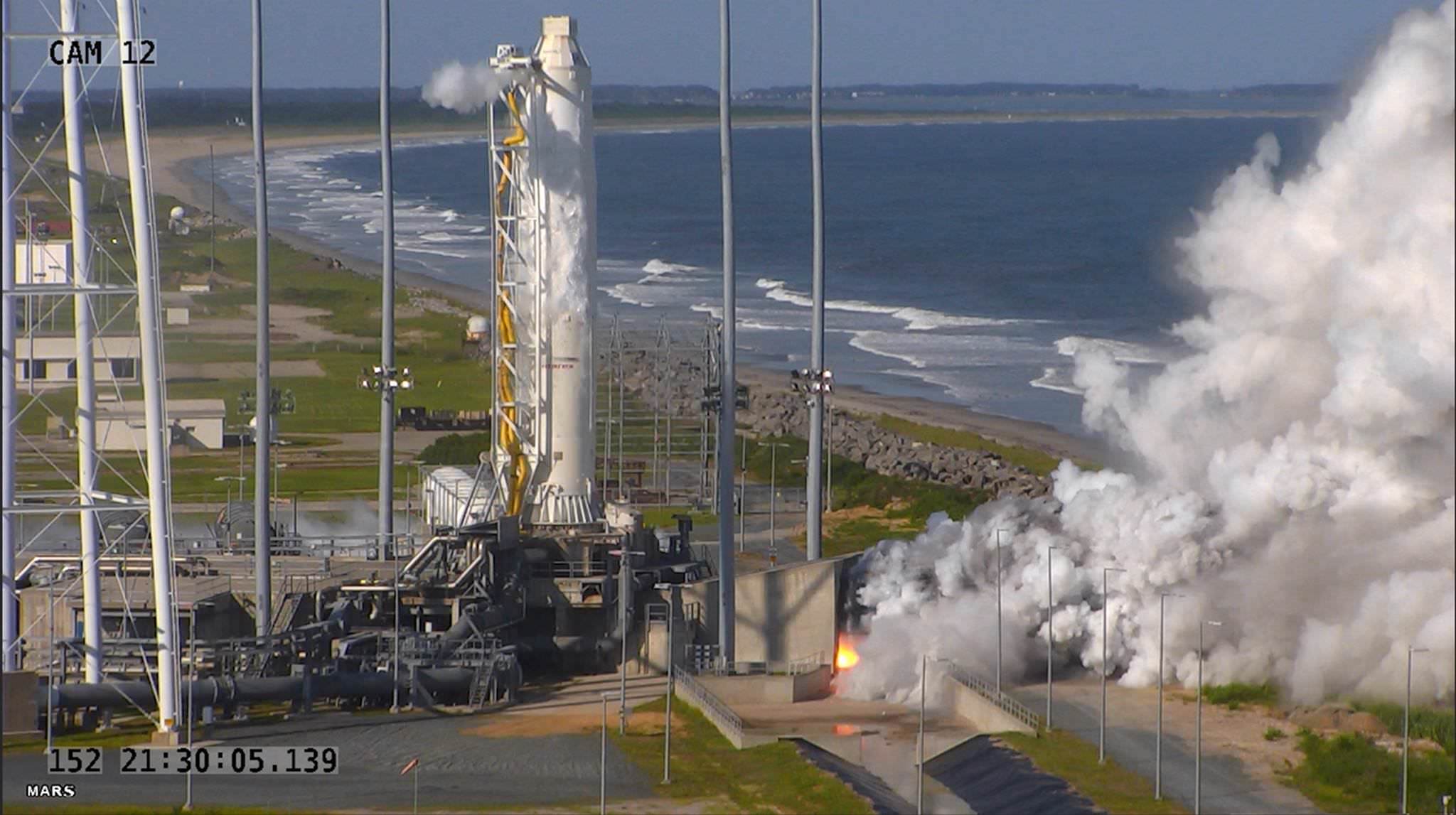

Teams from Orbital ATK and NASA have been scrutinizing the data in great detail ever since then to ensure the rocket is really ready before committing to the high stakes launch.
“Orbital ATK completed a stage test at the end of May and final data review has confirmed the test was successful, clearing the way for the Antares return to flight,” said the company.
“Simultaneously, the company has been conducting final integration and check out of the flight vehicle that will launch the OA-5 mission to ensure that all technical, quality and safety standards are met or exceeded.”

Antares launches had immediately ground to a halt following the devastating launch failure 22 months ago which destroyed the rocket and its critical payload of space station science and supplies for NASA in a huge fireball just seconds after blastoff – as witnessed by this author.
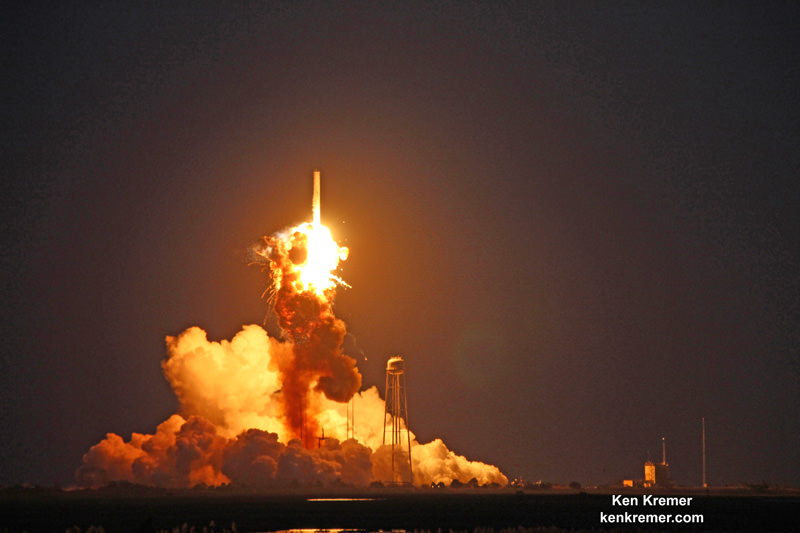

As a direct consequence of the catastrophic launch disaster, Orbital ATK managers decided to outfit the Antares medium-class rocket with new first stage RD-181 engines built in Russia.
The RD-181 replaces the previously used AJ26 engines which failed moments after liftoff during the last launch on Oct. 28, 2014 resulting in a catastrophic loss of the rocket and Cygnus cargo freighter.
The RD-181 flight engines are built by Energomash in Russia and had to be successfully tested via the static hot fire test to ensure their readiness.
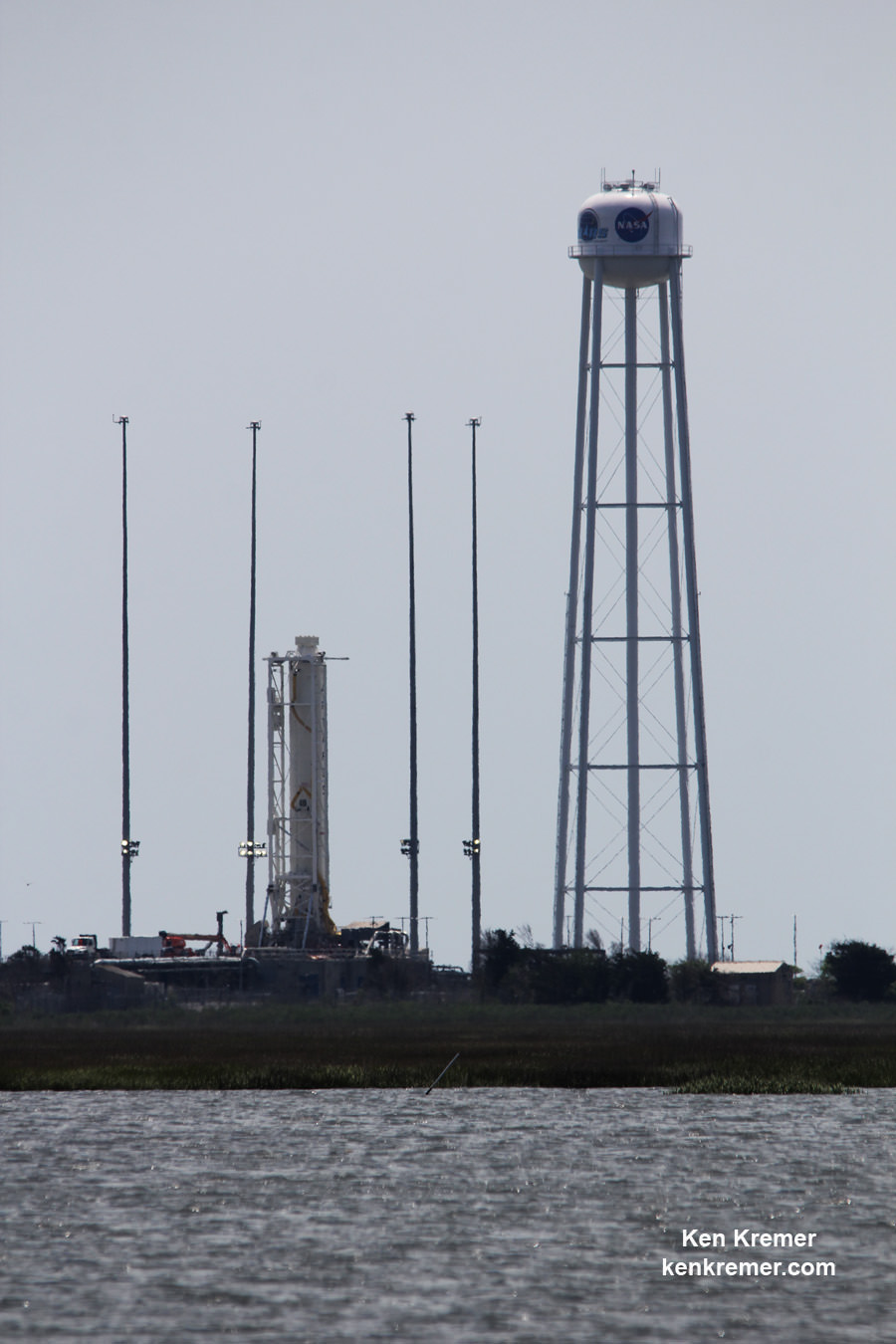

Whenever it does fly on the OA-5 mission, Orbital ATK’s Cygnus cargo craft will be loaded with approximately 2,400 kg (5,290 lbs.) of supplies and science experiments for space station and its six person crews.
Under the Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract with NASA, Orbital ATK will deliver approximately 28,700 kilograms of cargo to the space station. OA-5 is the sixth of these missions.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.