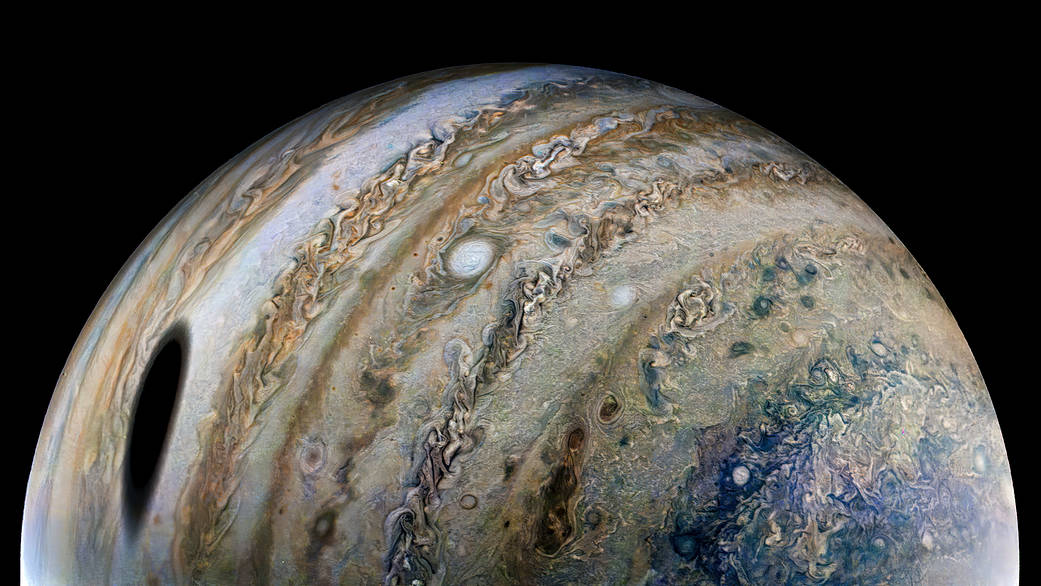
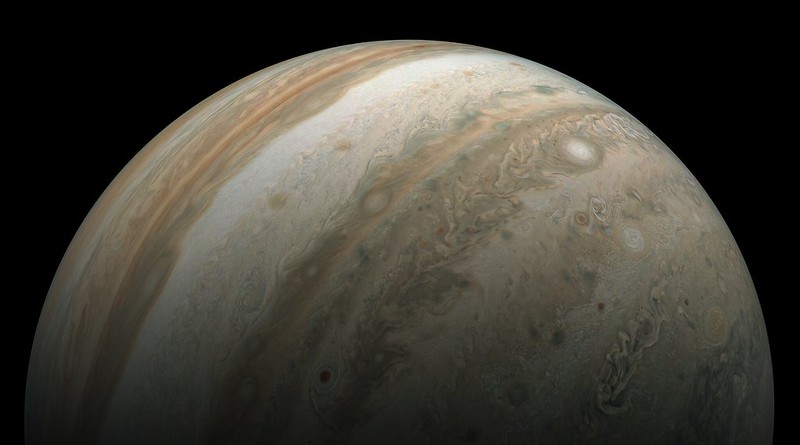
What is that large dark smudge on Jupiter’s side? It may remind you of a certain scene from the sci-fi film “2010: The Year We Make Contact,” where a growing black spot appears in Jupiter’s atmosphere.
But this is a real photo, and the dark spot is just an elongated shadow of Ganymede, Jupiter’s largest moon. Just like when Earth’s Moon crosses between our planet and the Sun creating an eclipse for lucky Earthlings, when Jupiter’s moons cross between the gas giant and the Sun, they create shadows too.
Continue reading “Ganymede Casts a Long Shadow Across the Surface of Jupiter”