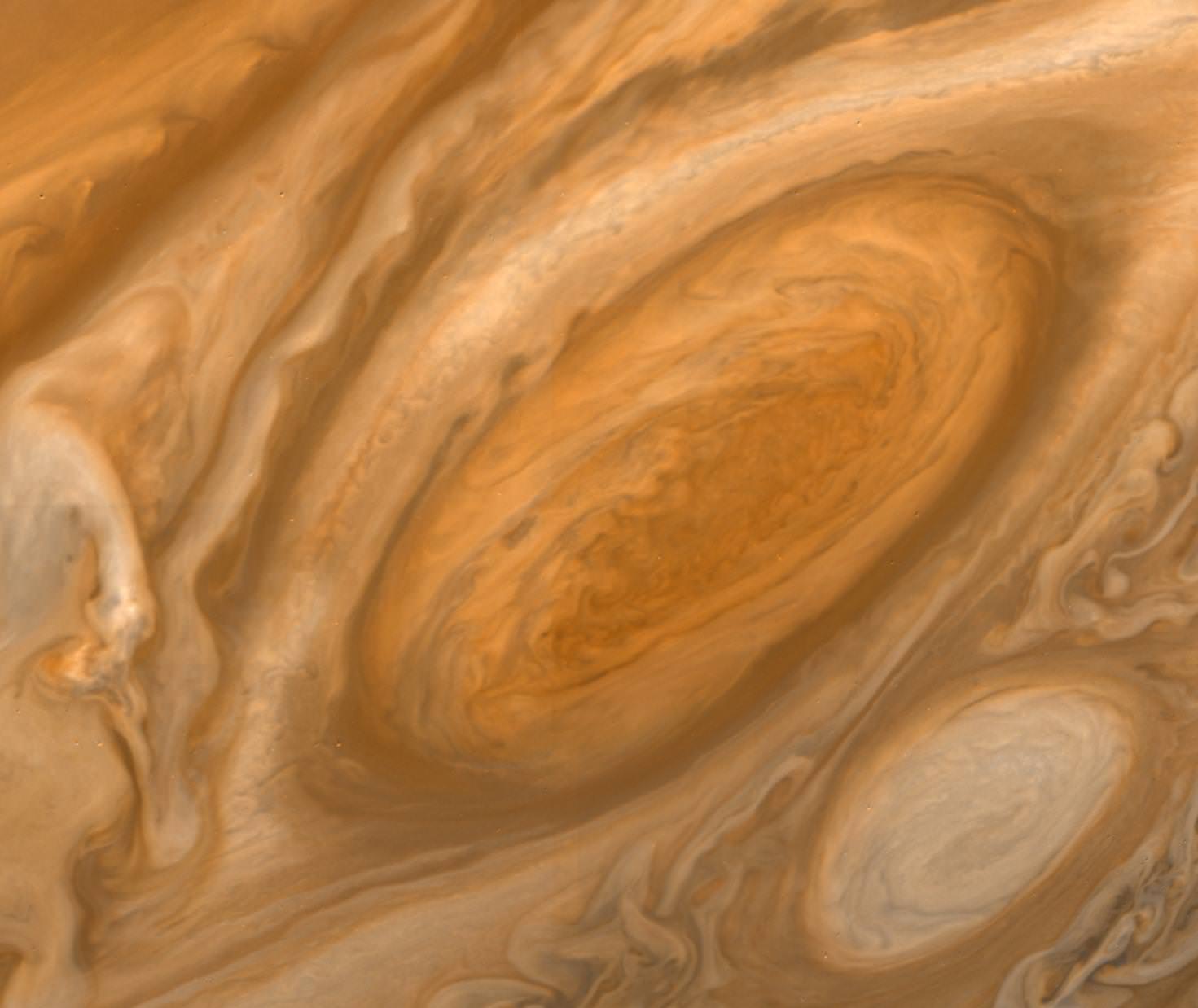
The Great Red Spot of Jupiter – the largest storm in the solar system – has been raging for centuries. Over the past 100 years however, the cyclone has been dwindling, but recent observations with Hubble show that the wind speeds may be picking up again. Is this just temporary, or will the storm return to its former glory?
Continue reading “Wind Speeds in Jupiter’s Great Red Spot are Picking up”NASA Spacecraft Takes a Picture of Jupiter … From the Moon

You know the feeling …. seeing Jupiter through your own telescope. If it gives you the chills — like it does for me — then you’ll know how the team for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter felt when they turned their spacecraft around – yes, the orbiter that’s been faithfully circling and looking down at the Moon since 2008 – and saw the giant planet Jupiter with their camera. If you zoom in on the picture, you can even see Jupiter’s Galilean moons.
Continue reading “NASA Spacecraft Takes a Picture of Jupiter … From the Moon”Giant Balls of Mush Made From Ammonia and Water Form in the Atmospheres of Uranus and Neptune
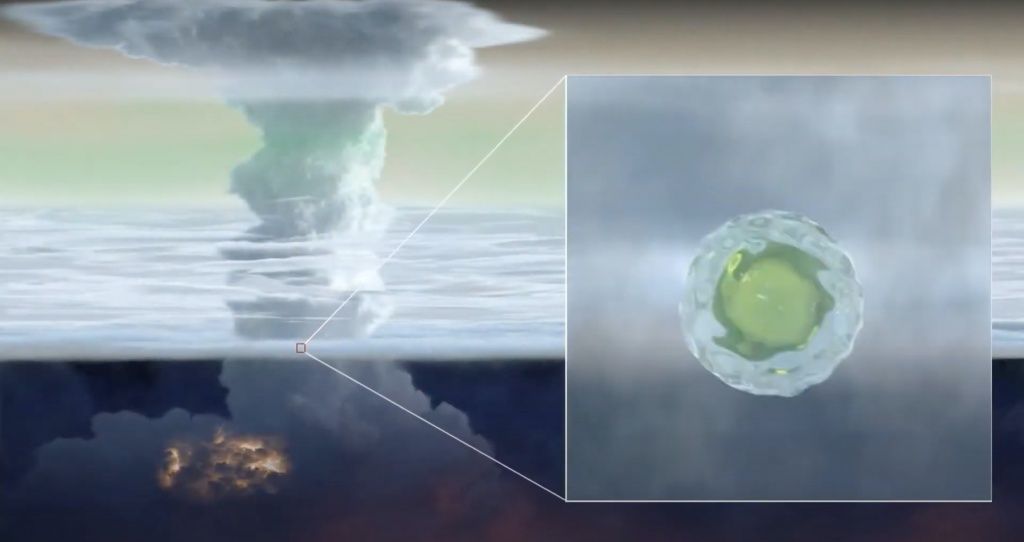
One advantage to planetary science is that insights from one planet could explain phenomena on another. We understand Venus’ greenhouse gas effect from our own experience on the Earth, and Jupiter and Saturn share some characteristics. But Jupiter also provides insight into other, farther out systems, such as Uranus and Neptune. Now, a discovery from a spacecraft orbiting Jupiter might have solved a long-standing mystery about Uranus and Neptune – where has all the ammonia gone?
Continue reading “Giant Balls of Mush Made From Ammonia and Water Form in the Atmospheres of Uranus and Neptune”Here’s What it Would Be Like to Fly Low Over Jupiter’s Cloudtops
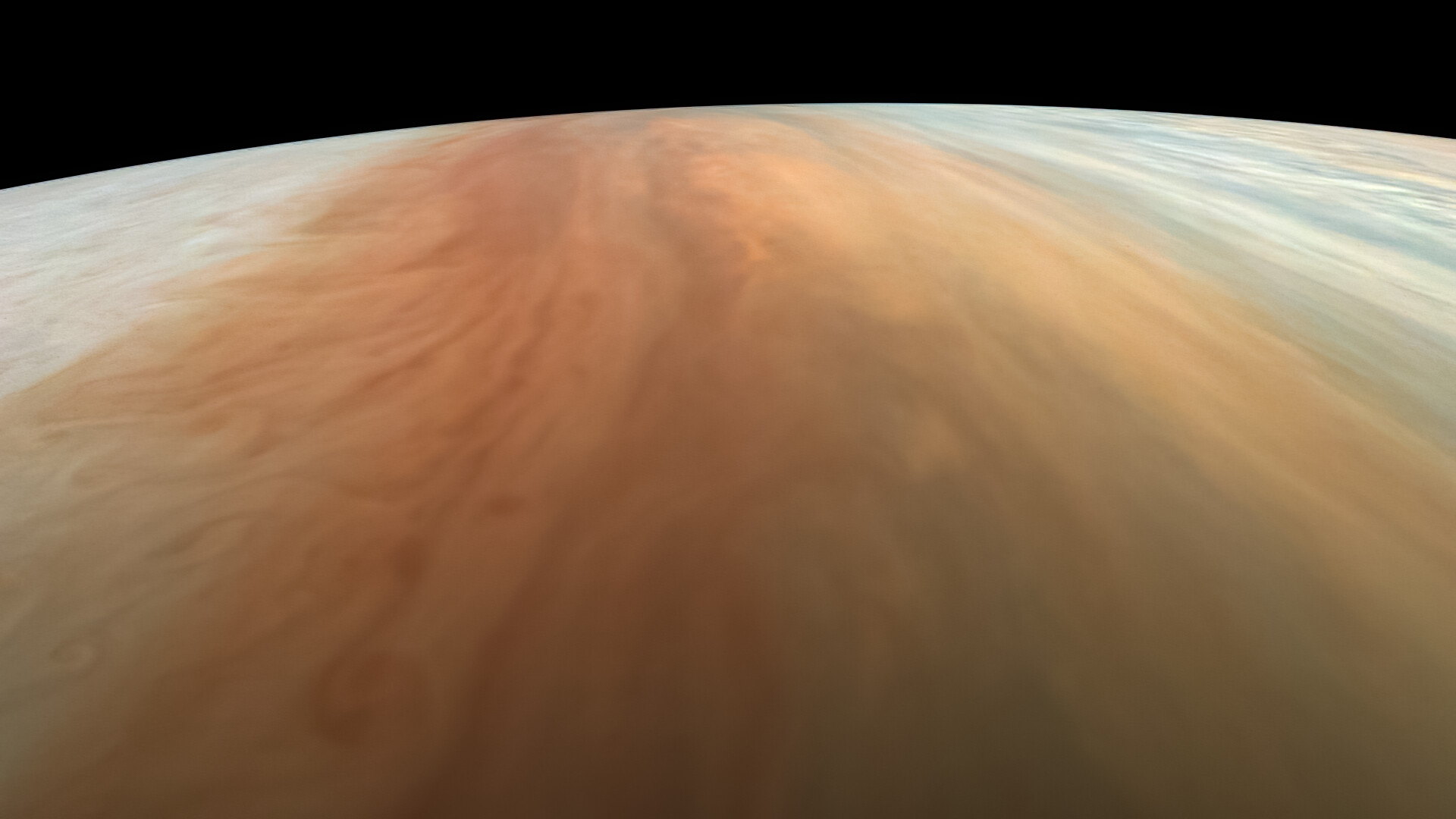
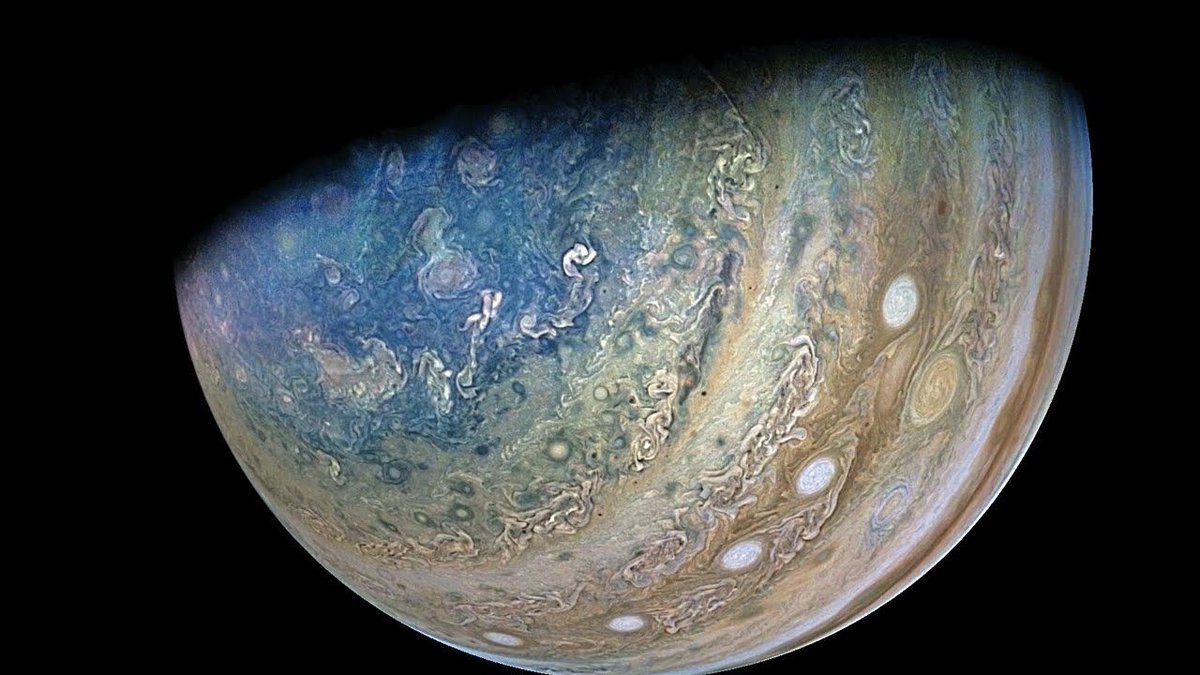
During Juno’s extended mission, every orbit is like a new adventure. Each orbit is a little different, and NASA says the natural evolution of Juno’s orbit around Jupiter provides a wealth of new science opportunities.
But for most of us, what we look forward to on every perijove – the point in each orbit where the Juno spacecraft comes closest to the gas giant – are the incredible images taken by the camera on board, JunoCam. As Juno’s “eyes,” the camera provides a unique vantage point no other spacecraft has been able to give us.
Continue reading “Here’s What it Would Be Like to Fly Low Over Jupiter’s Cloudtops”Ganymede in Infrared Taken During Juno’s Most Recent Flyby
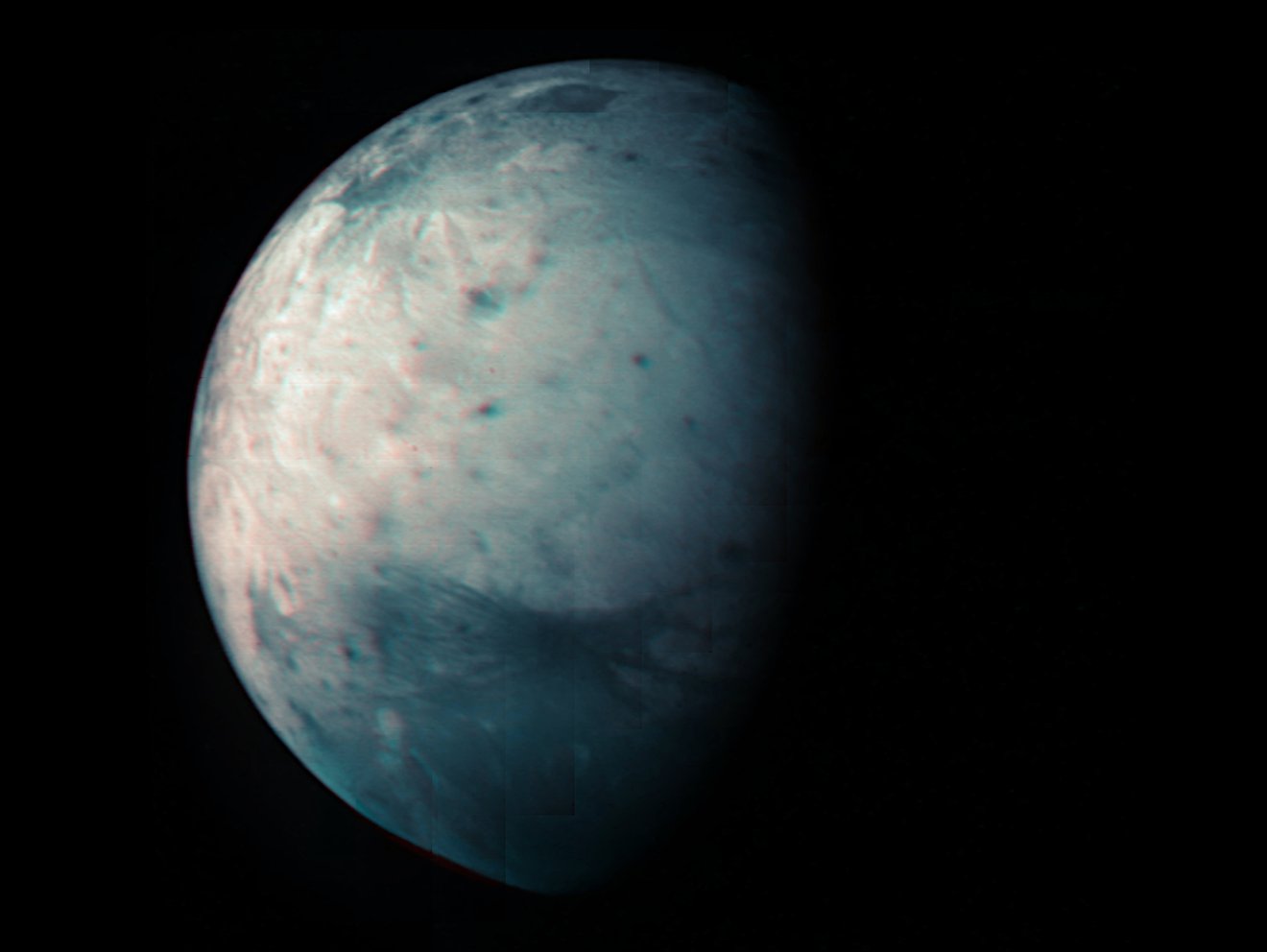
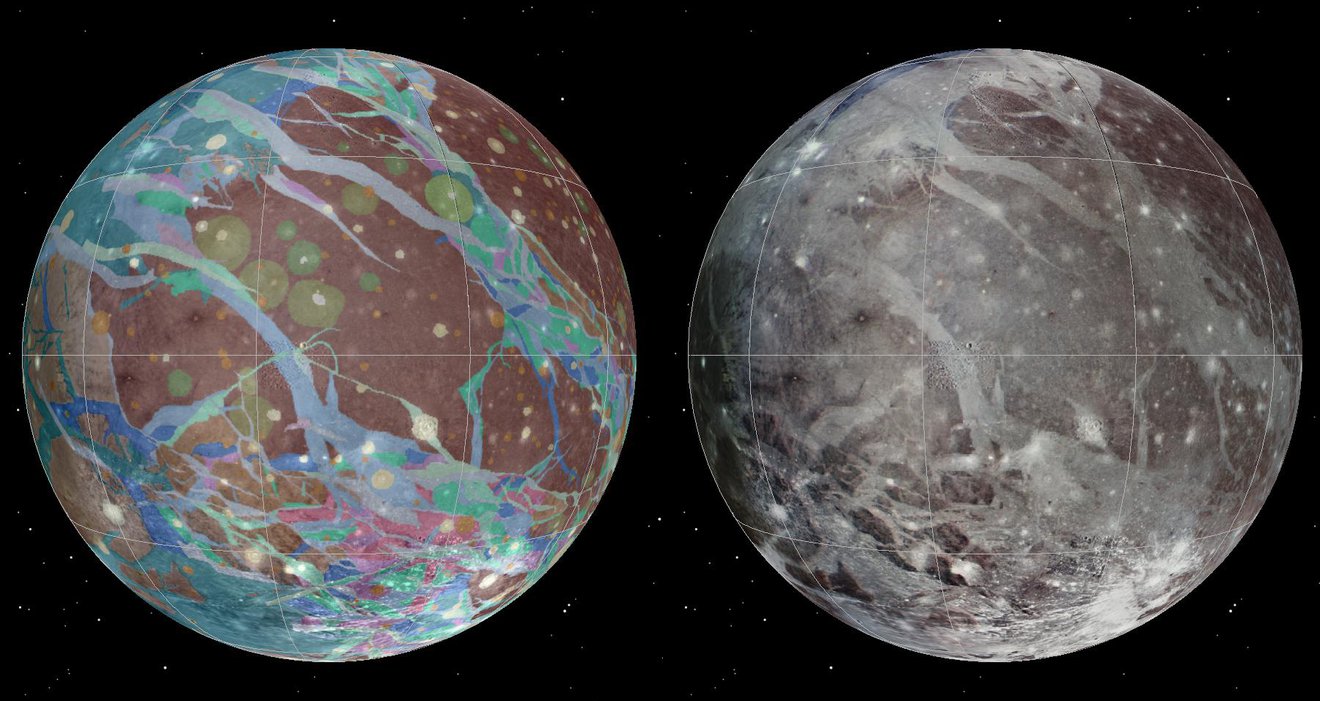
On July 20th, 2021, NASA’s Juno spacecraft conducted a flyby of Jupiter’s (and the Solar System’s) largest moon, Ganymede. This close pass was performed as part of the orbiter’s thirty-fourth orbit of the gas giant (Perijove 34), which saw the probe come within 50,109 km (31,136 mi) of the moon’s surface. The mission team took this opportunity to capture images of Ganymede’s using Juno’s Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper (JIRAM).
These were combined with images acquired during two previous flybys to create a new infrared map of Ganymede’s surface, which was released in honor of the mission’s tenth anniversary (which launched from Earth on Aug. 5th, 2011). This map and the JIRAM instrument could provide new information on Ganymede’s icy shell and the composition of its interior ocean, which could shed led on whether or not it could support life.
Continue reading “Ganymede in Infrared Taken During Juno’s Most Recent Flyby”Water Vapour has Been Discovered at Ganymede
Ganymede has been getting alot of attention lately. It was the co-star of a video from Juno recently, and now scientists found something to make it an even more intriguing place visit – water vapor.
Continue reading “Water Vapour has Been Discovered at Ganymede”Ions Surf Through Jupiter’s Magnetic Field, Triggering its Auroras
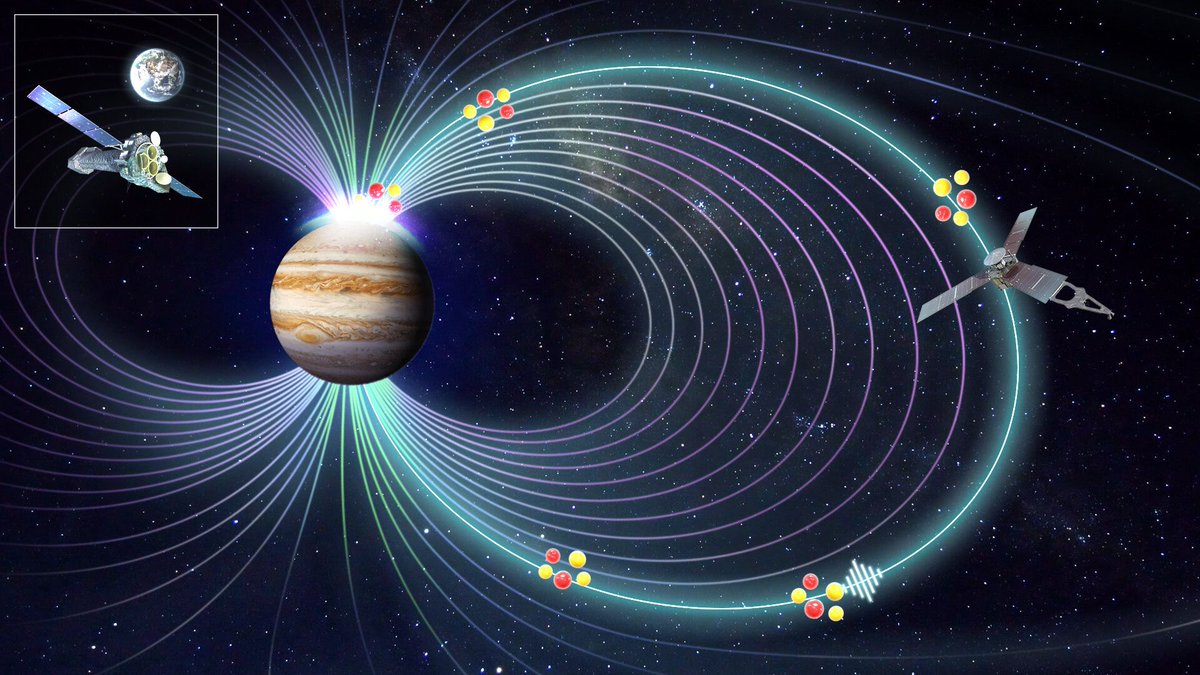
Auroras come in many shapes and sizes. Jupiter is well known for its spectacular complement of bright polar lights, which also have the distinction of appearing in the X-ray band. These auroras are also extreme power sources, emitting almost a gigawatt of energy in a few minutes. But what exactly causes them has been a mystery for the last 40 years. Now, a team used data from a combination of satellites to identify what is causing these powerful emissions. The answer appears to be charged ions surfing on a kind of wave.
Continue reading “Ions Surf Through Jupiter’s Magnetic Field, Triggering its Auroras”This is the View From Juno During its Flyby of Ganymede and Jupiter
Visualizations shape how we perceive space exploration. Whether it’s the Pale Blue Dot, the Hubble Ultra Deep Field, Earthrise, or any other myriad images captured as part of this great endeavor, they all help inspire the next generation of explorers. Now, with advances in image capture and processing technology, we can finally start to take the next step in those visualizations – video. Ingenuity was recently captured on video during its first flight a few months ago. And this week, NASA released a breathtaking video of Juno’s view of Jupiter and Ganymede, one of its moons, as it flew past the gas giant.
Continue reading “This is the View From Juno During its Flyby of Ganymede and Jupiter”Bad News, Life Probably can’t Exist on Venus. Good News, it Could be in Jupiter’s Clouds
For decades, scientists engaged in the search for life in the Universe (aka. astrobiology) have focused on searching for life on other Earth-like planets. These included terrestrial (aka. rocky) planets beyond our Solar System (extrasolar planets) and ones here at home. Beyond Earth, Mars is considered to be the most habitable planet next to Earth, and scientists have also theorized that life could exist (in microbial form) in the cloud tops of Venus.
In all cases, a major focal point is whether or not planets have large bodies of water on their surfaces (or did in the past). However, a new study led by a research team from the UK and German (with support from NASA) has shown that the existence of life may have less to do with the quantity of water and more to with the presence of atmospheric water molecules. As a result, we may have better luck finding life on Jupiter’s turbulent cloud deck than Venus’.
Continue reading “Bad News, Life Probably can’t Exist on Venus. Good News, it Could be in Jupiter’s Clouds”Next up, Juno has Ganymede in its Sights
NASA’s Juno mission is set for a close encounter with the Solar System’s largest moon, Ganymede, on Monday. This will be the first flyby of the icy world since the Galileo and Cassini spacecraft jointly observed the moon in 2000. New Horizons also got a quick snap of Ganymede as it slingshotted around Jupiter on its way out to Pluto in 2007, but from a distance of 3.5 million kilometers away. Juno’s pass on Monday will get much closer, approaching within 1038 kilometers of the surface.
Continue reading “Next up, Juno has Ganymede in its Sights”