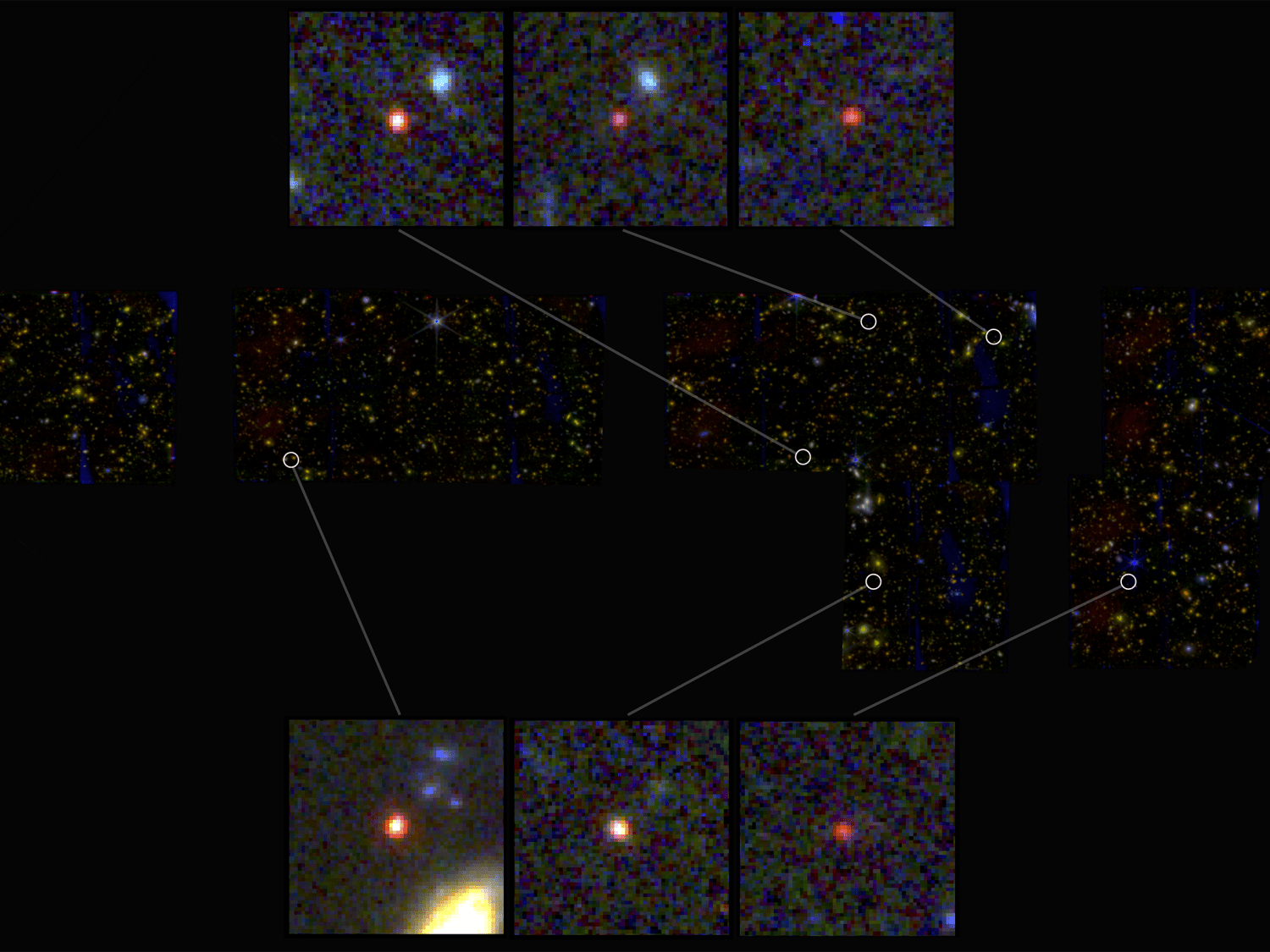
The Milky Way Galaxy contains an estimated one hundred billion stars. Between these lies the Interstellar Medium (ISM), a region permeated by gas and dust grains. This dust is largely composed of heavier elements, including silicate minerals, ice, carbon, and iron compounds. This dust plays a key role in the evolution of galaxies, facilitating the gravitational collapse of gas clouds to form new stars. This galactic dust is measurable by how it attenuates starlight from distant galaxies, causing it to shift from ultraviolet to far-infrared radiation.
However, the origin of various dust grains is still a mystery, especially during the early Universe when heavier elements are thought to have been scarce. Previously, scientists believed that elements like carbon took hundreds of millions of years to form and could not have existed before about 2.5 billion years after the Big Bang. Using data obtained by the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES), an international team of astronomers and astrophysicists report the detection of carbonaceous grains around a galaxy that existed roughly 1 billion years after the Big Bang.
Continue reading “Clouds of Carbon Dust Seen When the Universe was Less Than a Billion Years Old”