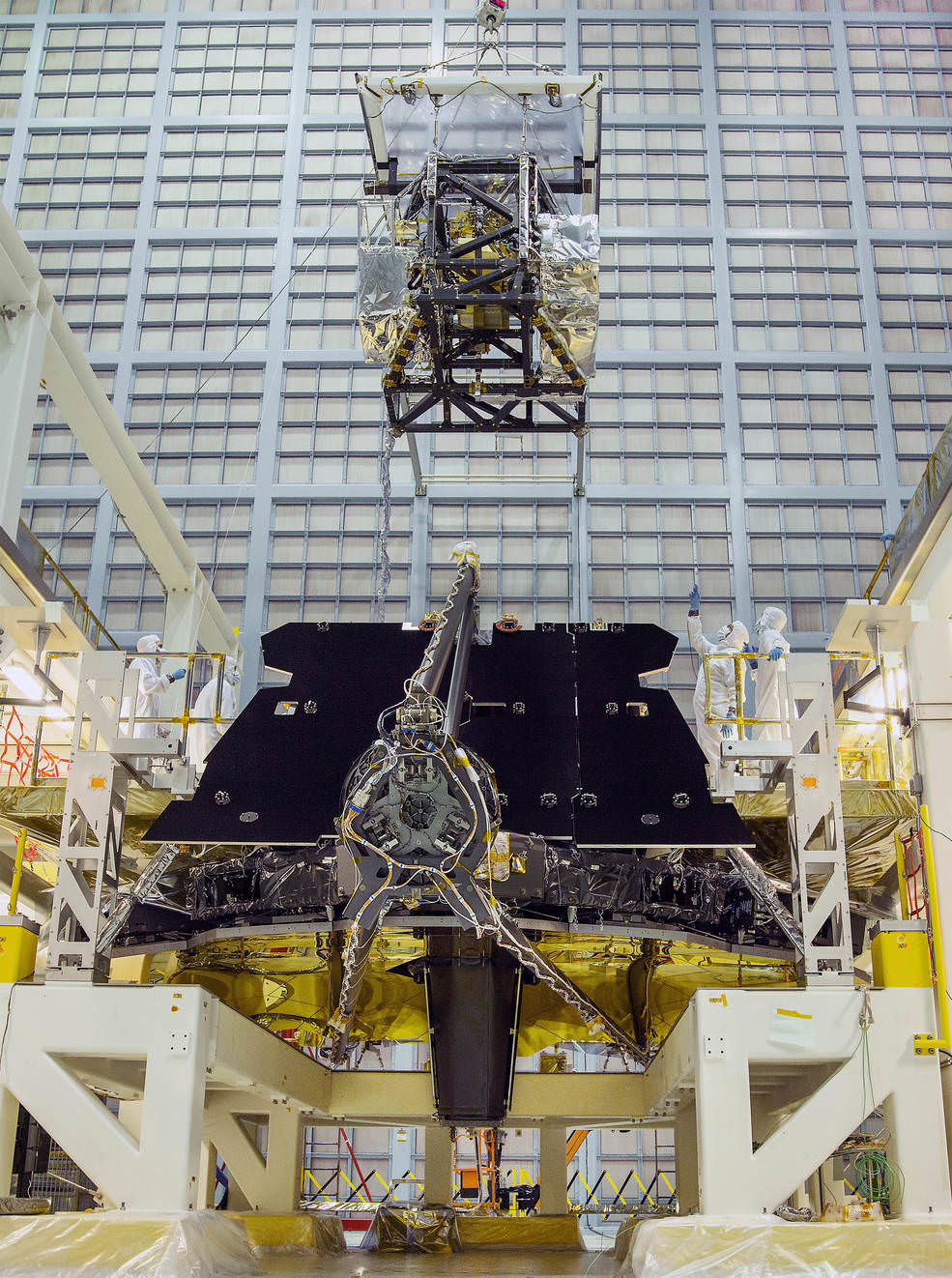
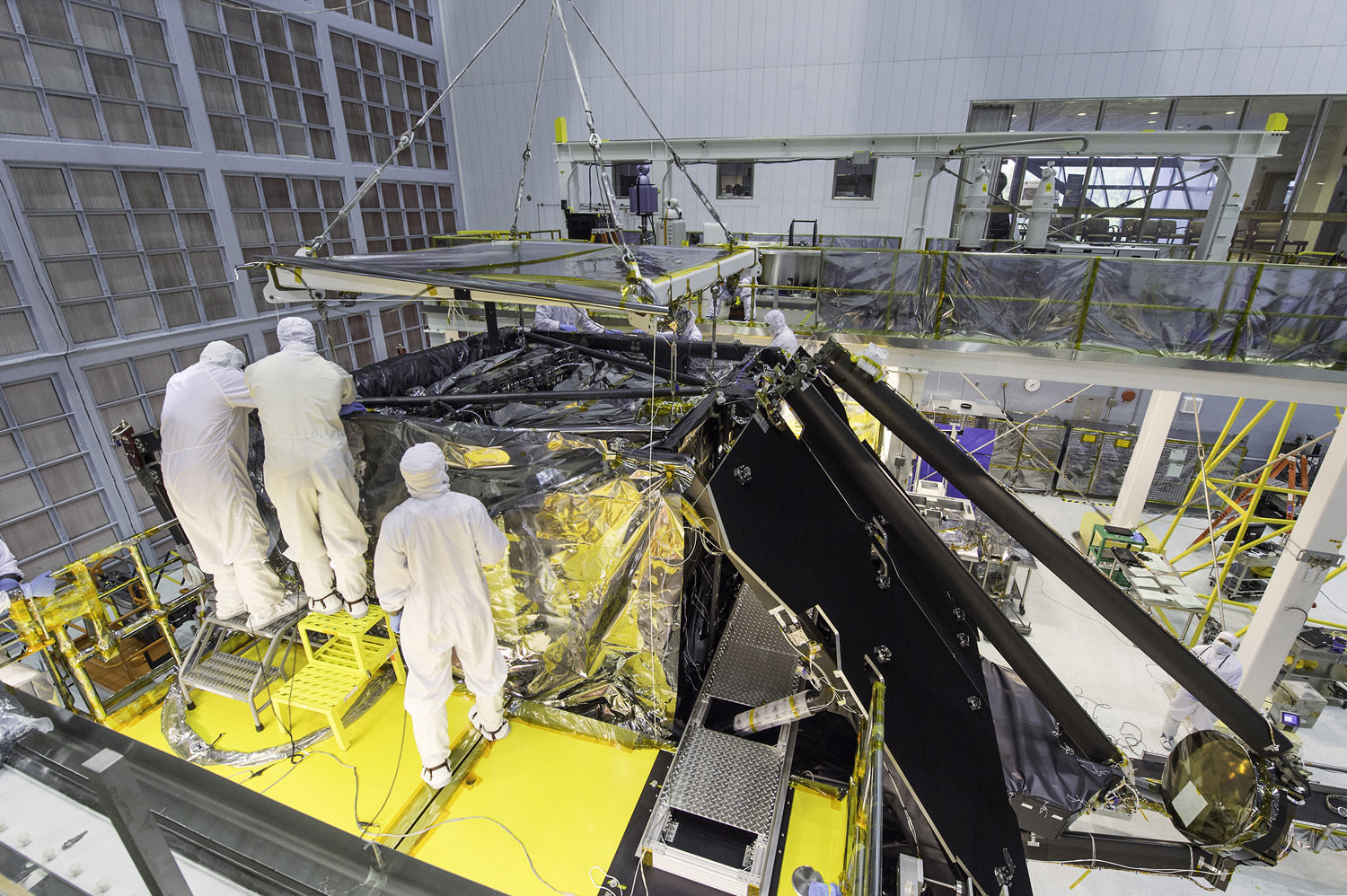
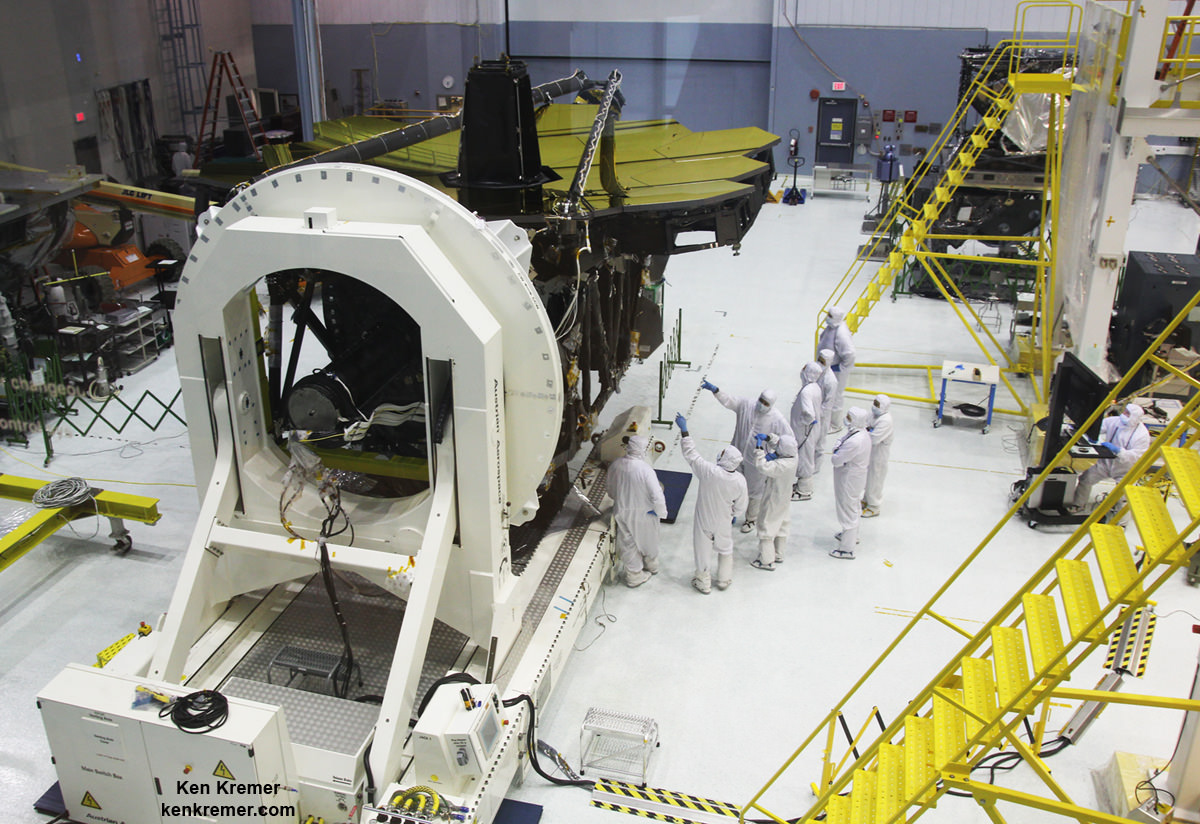
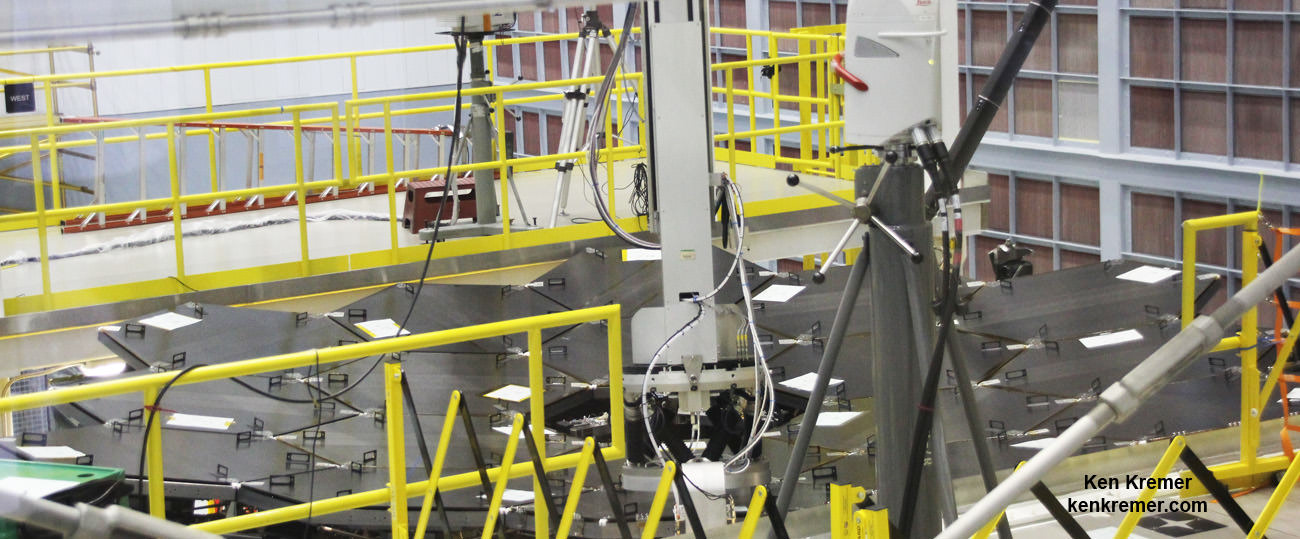
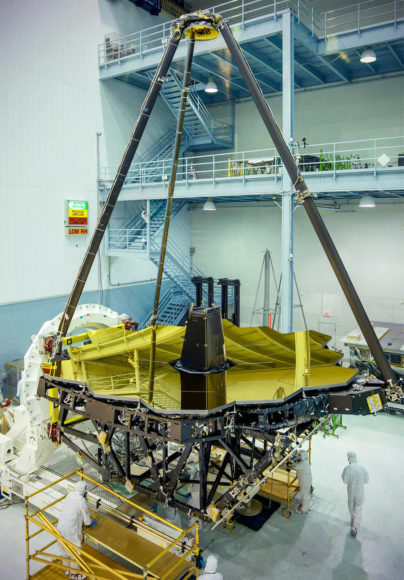
Engineers have resumed a series of critical and rigorous vibration qualification tests on NASA’s mammoth James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, in Greenbelt, Maryland to confirm its safety, integrity and readiness for the unforgiving environment of space flight, after pausing due to a testing ‘anomaly’ detected in early December 2016.
The vibration tests are conducted by the team on a shaker table at Goddard to ensure Webb’s worthiness and that it will survive the rough and rumbling ride experienced during the thunderous rocket launch to the heavens slated for late 2018.
“Testing on the ground is critical to proving a spacecraft is safe to launch,” said Lee Feinberg, an engineer and James Webb Space Telescope Optical Telescope Element Manager at Goddard, in a statement.
“The Webb telescope is the most dynamically complicated article of space hardware that we’ve ever tested.”

Testing of the gargantuan Webb Telescope had ground to a halt after a brief scare in early December when technicians initially detected “anomalous readings” that raised potential concerns about the observatories structural integrity partway through a preplanned series of vibration tests.
“On December 3, 2016, vibration testing automatically shut down early due to some sensor readings that exceeded predicted levels,” officials said.
Thereafter, engineers and technicians carried out a new batch of intensive inspections of the observatory’s structure during December.
Shortly before Christmas, NASA announced on Dec. 23 that JWST was deemed “sound” and apparently unscathed after engineers conducted both “visual and ultrasonic examinations” at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland. Officials said the telescope was found to be safe at this point with “no visible signs of damage.”
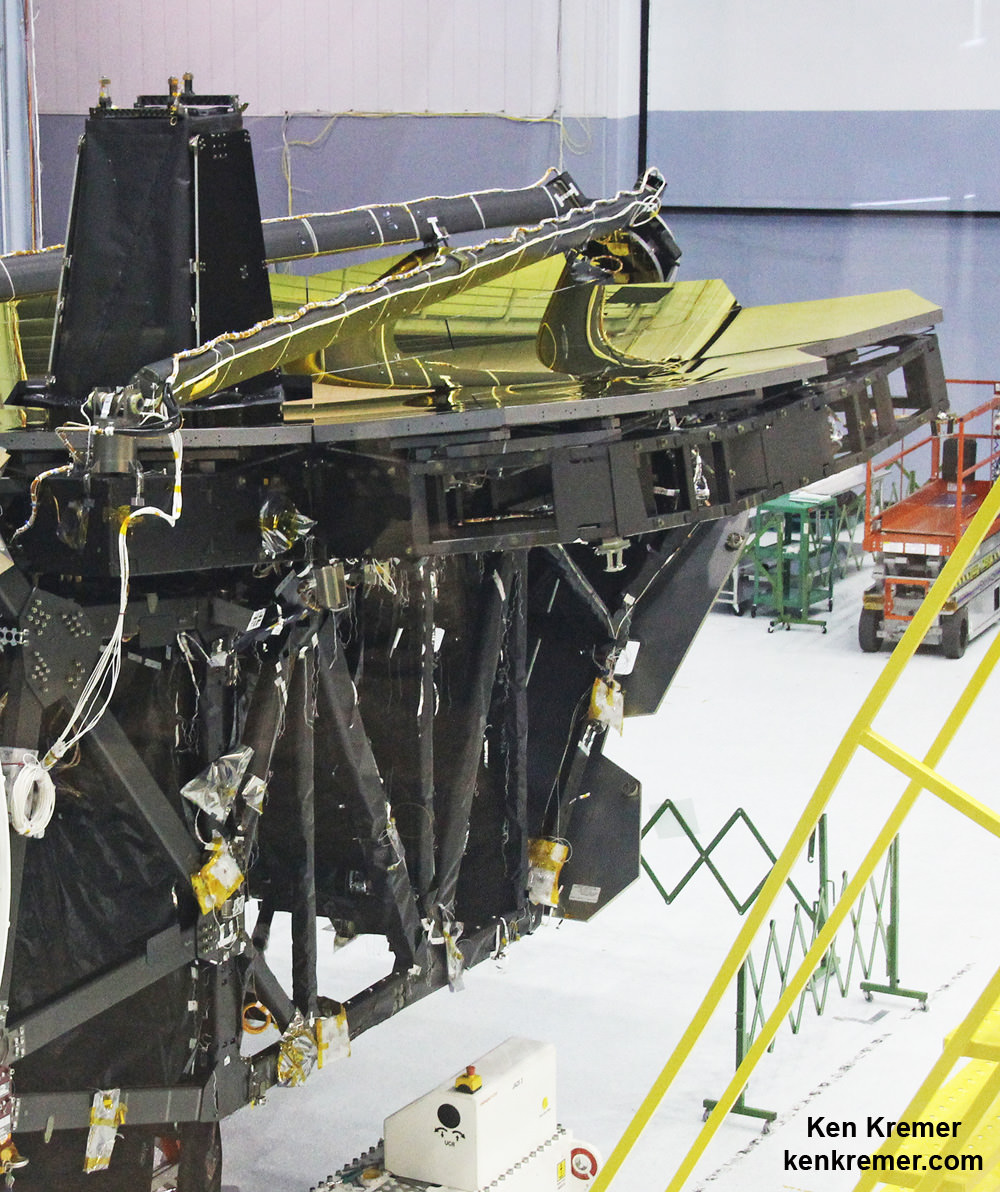
As it turned out the culprit of the sensor anomaly was the many “tie-down … restraint mechanisms ” that hold the telescope in place.
“After a thorough investigation, the James Webb Space Telescope team at NASA Goddard determined that the cause was extremely small motions of the numerous tie-downs or “launch restraint mechanisms” that keep one of the telescope’s mirror wings folded-up for launch,” NASA officials explained in a statement.
Furthermore engineers revealingly discovered that “the ground vibration test itself is more severe than the launch vibration environment.”

NASA reported today (Jan. 25) that the testing resumed last week at the point where it had been paused. Furthermore the testing was completed along the first of three axis.
“In-depth analysis of the test sensor data and detailed computer simulations confirmed that the input vibration was strong enough and the resonance of the telescope high enough at specific vibration frequencies to generate these tiny motions. Now that we understand how it happened, we have implemented changes to the test profile to prevent it from happening again,” explained Feinberg.
“We have learned valuable lessons that will be applied to the final pre-launch tests of Webb at the observatory level once it is fully assembled in 2018. Fortunately, by learning these lessons early, we’ve been able to add diagnostic tests that let us show how the ground vibration test itself is more severe than the launch vibration environment in a way that can give us confidence that the launch itself will be fully successful.”
The next step is to resume and complete shaking the telescope in the other two axis, or “two directions to show that it can withstand vibrations in all three dimensions.”
“This was a great team effort between the NASA Goddard team, Northrop Grumman, Orbital ATK, Ball Aerospace, the European Space Agency, and Arianespace,” Feinberg said. “We can now proceed with the rest of the planned tests of the telescope and instruments.”
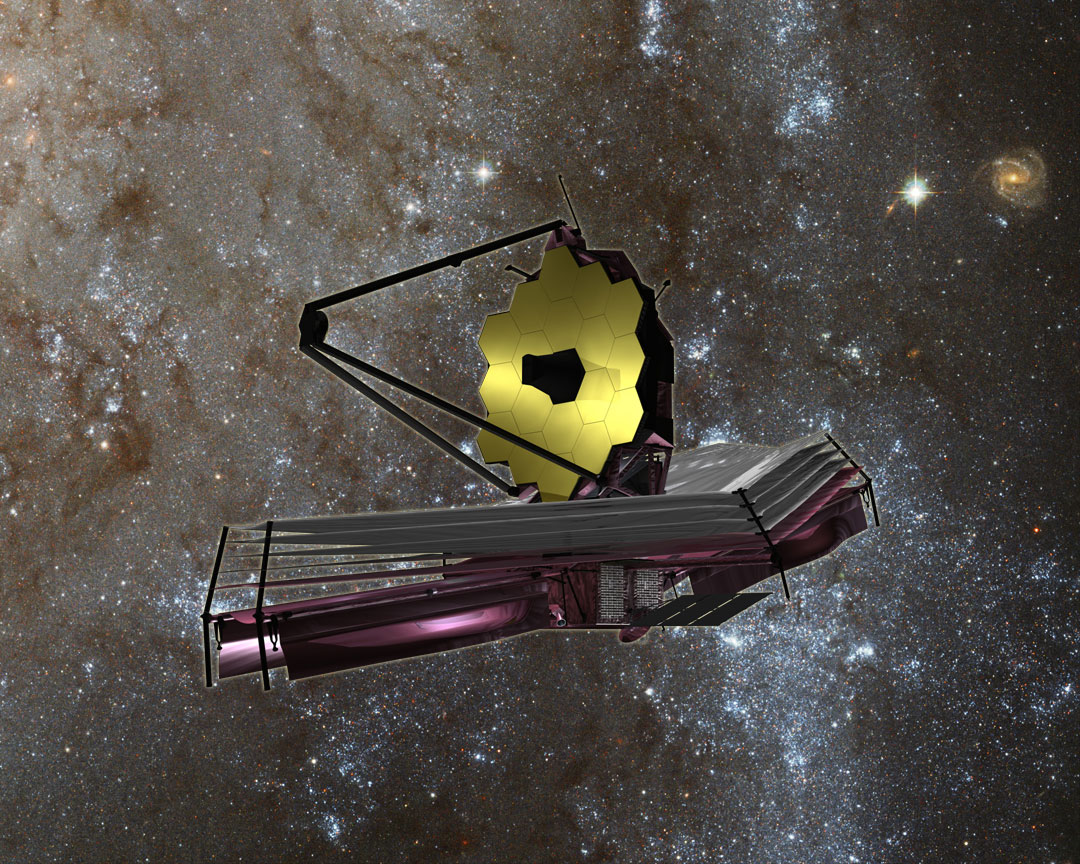
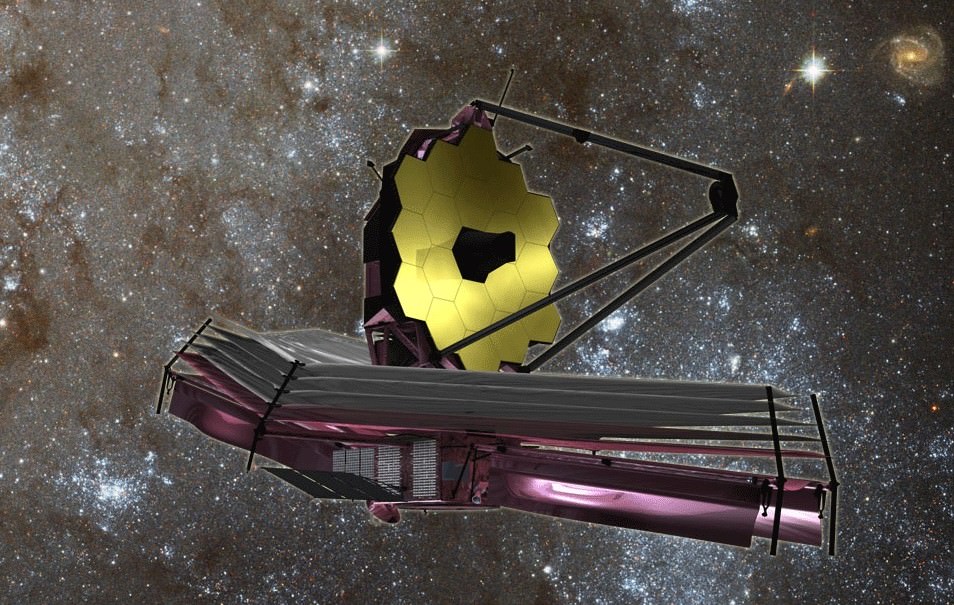
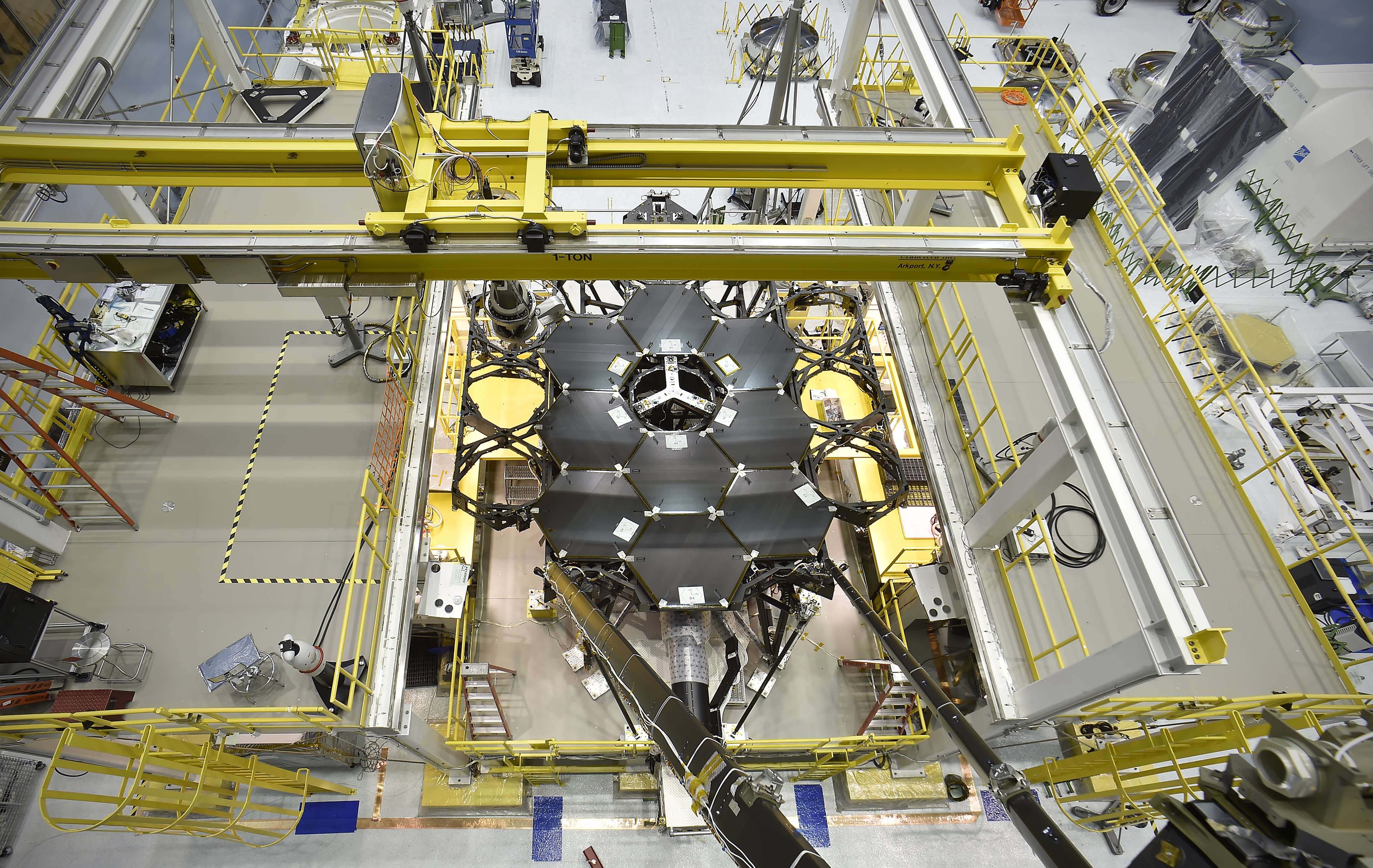
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is the most powerful space telescope ever built and is the scientific successor to the phenomenally successful Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The mammoth 6.5 meter diameter primary mirror has enough light gathering capability to scan back over 13.5 billion years and see the formation of the first stars and galaxies in the early universe.
The Webb telescope will launch on an ESA Ariane V booster from the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana in 2018.
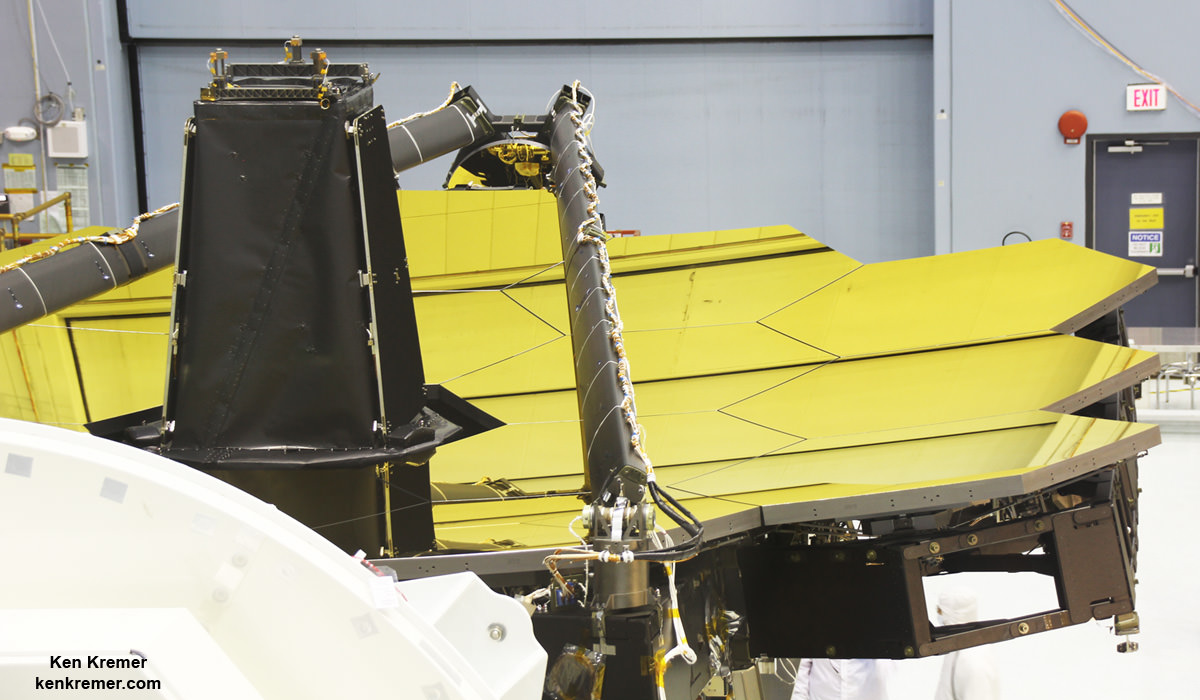
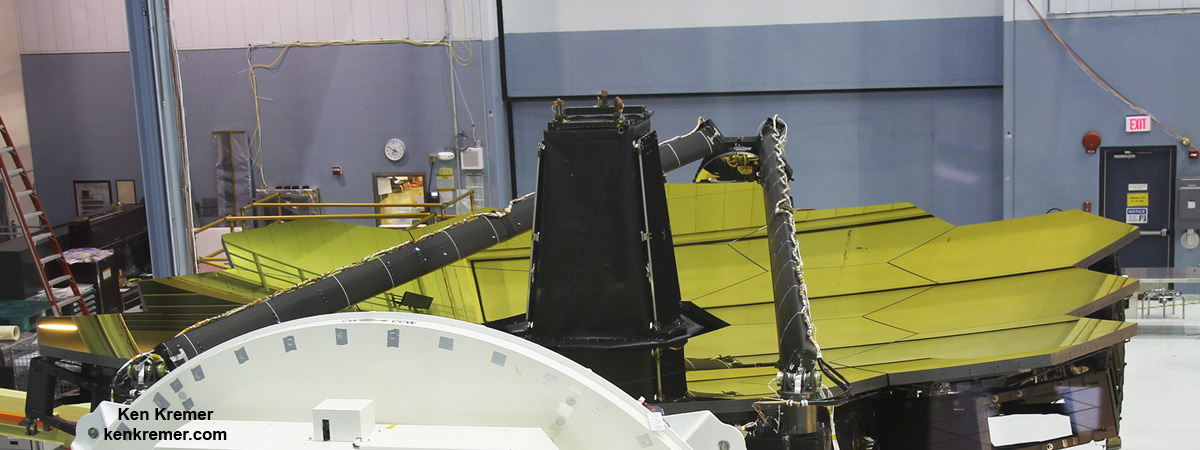
But Webb and its 18 segment “golden” primary mirror have to be carefully folded up to fit inside the nosecone of the Ariane V booster.
“Due to its immense size, Webb has to be folded-up for launch and then unfolded in space. Prior generations of telescopes relied on rigid, non-moving structures for their stability. Because our mirror is larger than the rocket fairing we needed structures folded for launch and moved once we’re out of Earth’s atmosphere. Webb is the first time we’re building for both stability and mobility.” Feinberg said.
“This means that JWST testing is very unique, complex, and challenging.”
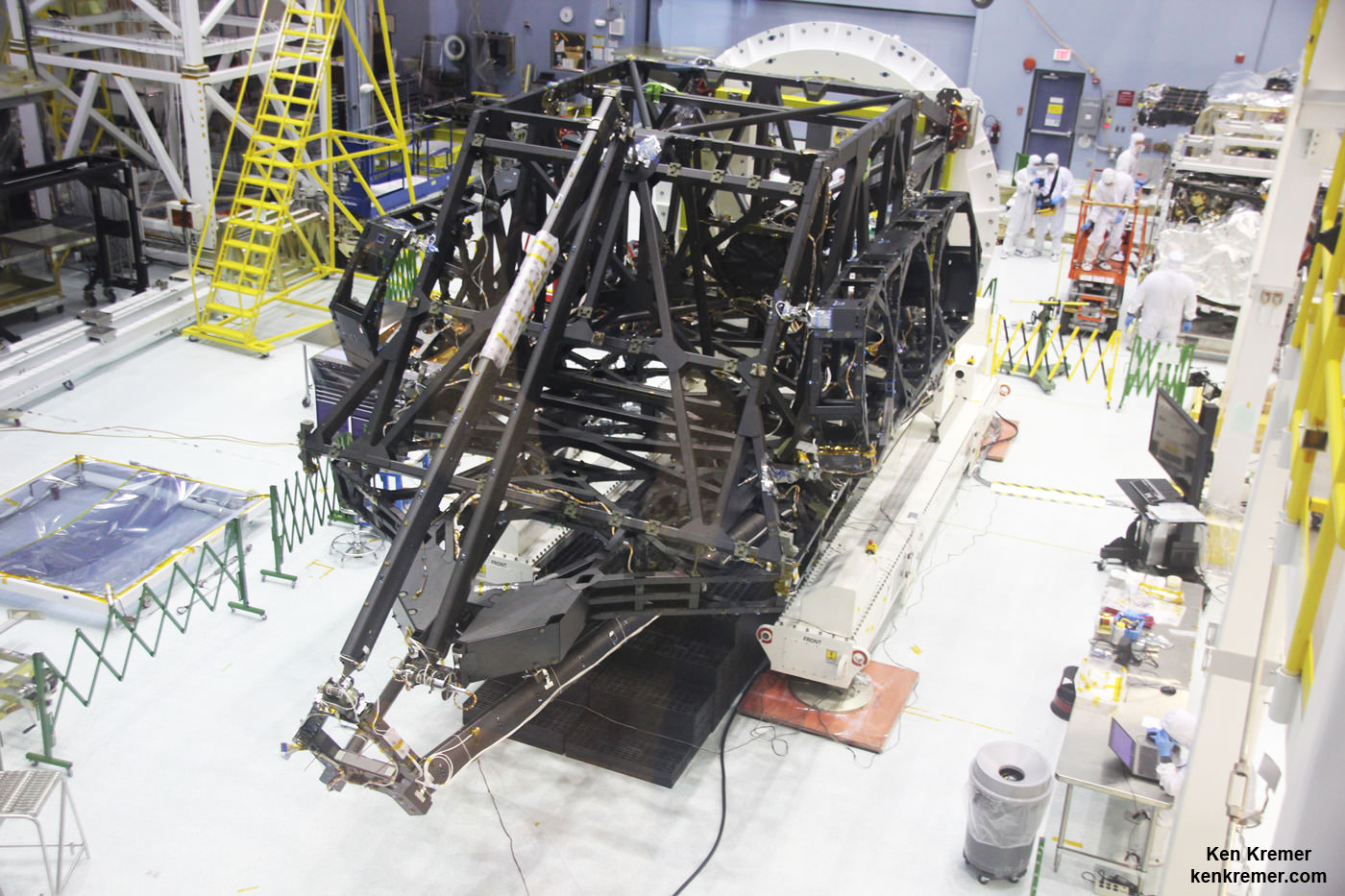

The environmental testing is being done at Goddard before shipping the huge structure to NASA’s Johnson Space Center in February 2017 for further ultra low temperature testing in the cryovac thermal vacuum chamber.
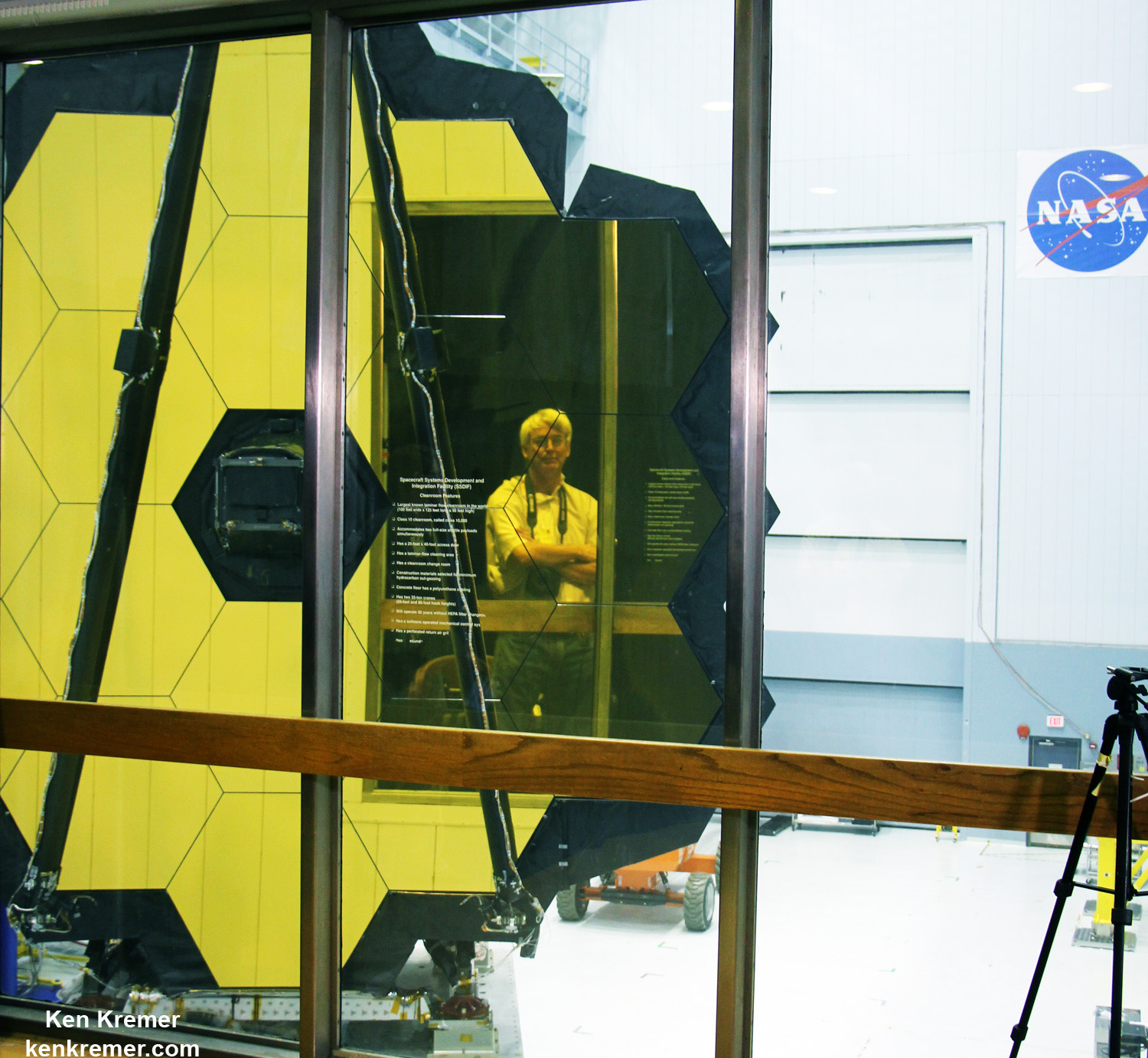
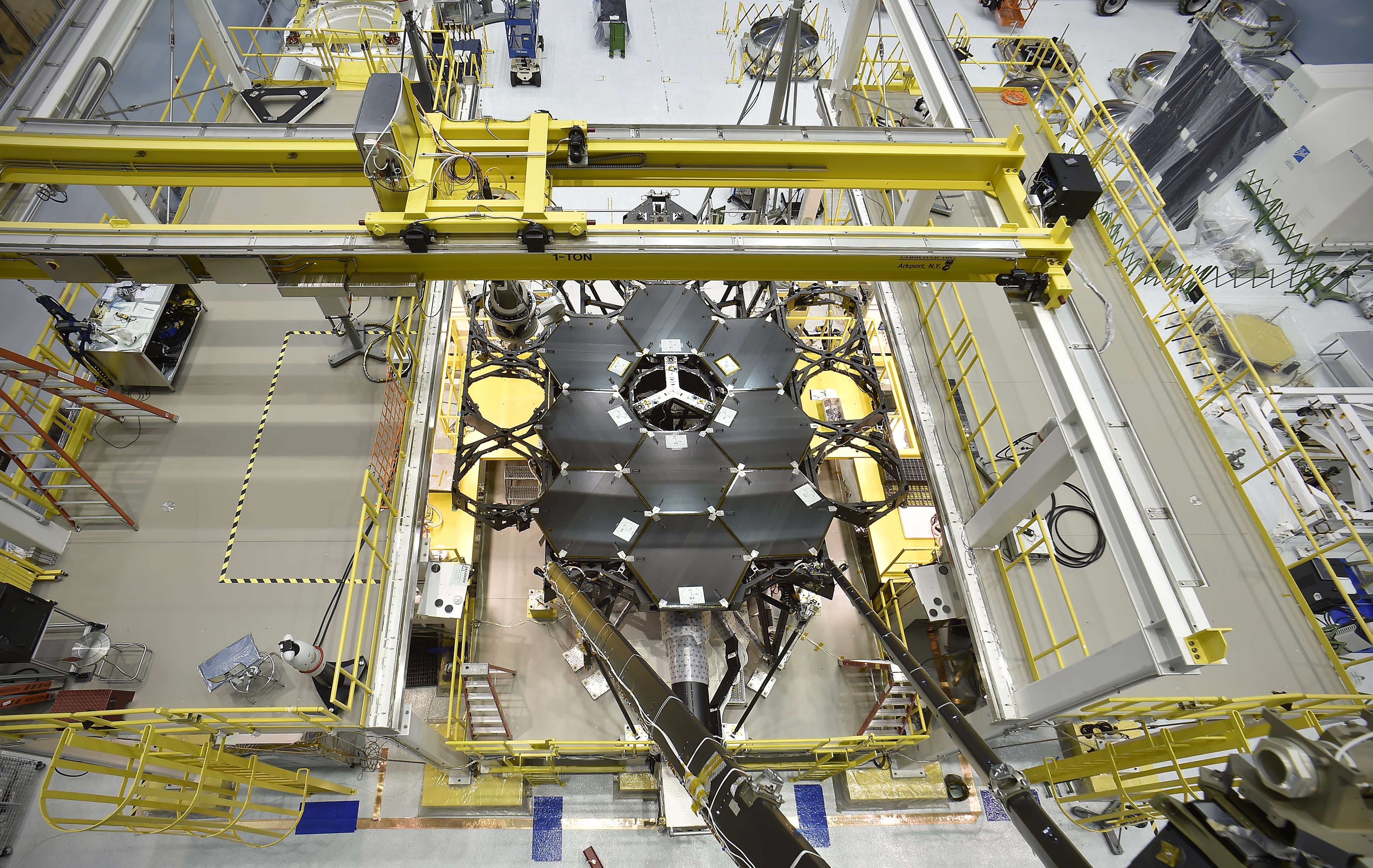
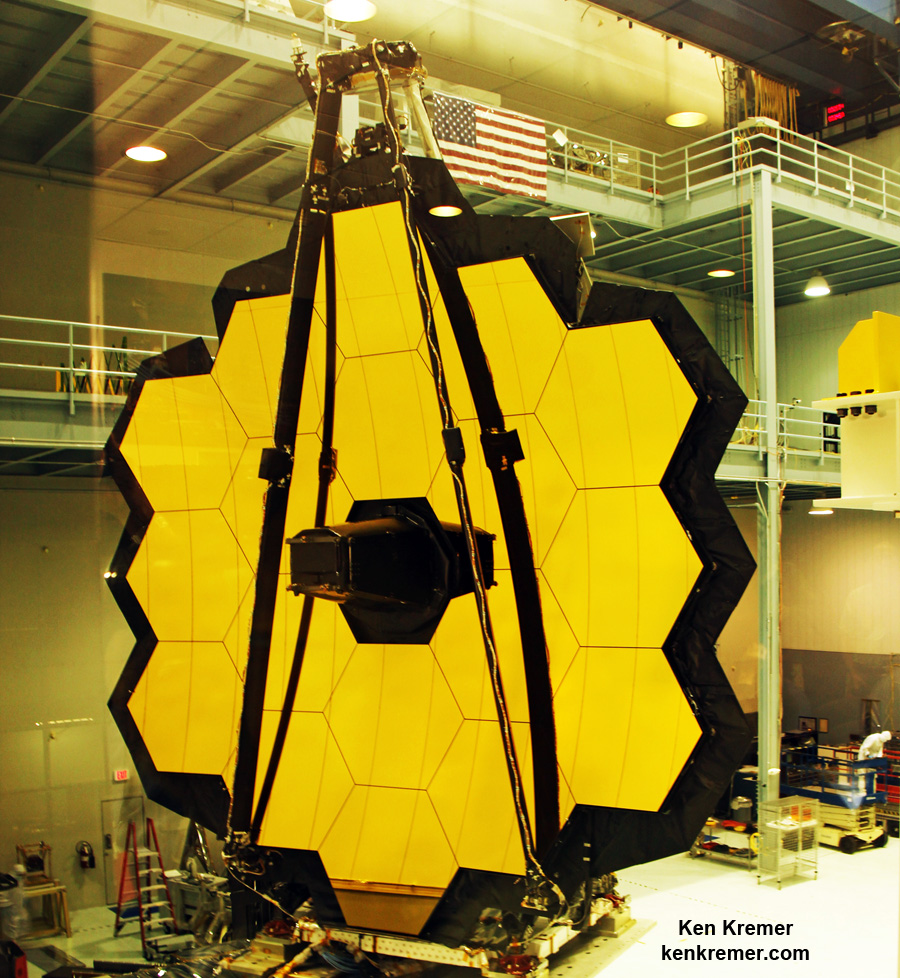
The 6.5 meter diameter ‘golden’ primary mirror is comprised of 18 hexagonal segments – looking honeycomb-like in appearance.
And it’s just mesmerizing to gaze at – as I had the opportunity to do on a few occasions at Goddard this past year – standing vertically in November and seated horizontally in May.
Each of the 18 hexagonal-shaped primary mirror segments measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). They are made of beryllium, gold coated and about the size of a coffee table.
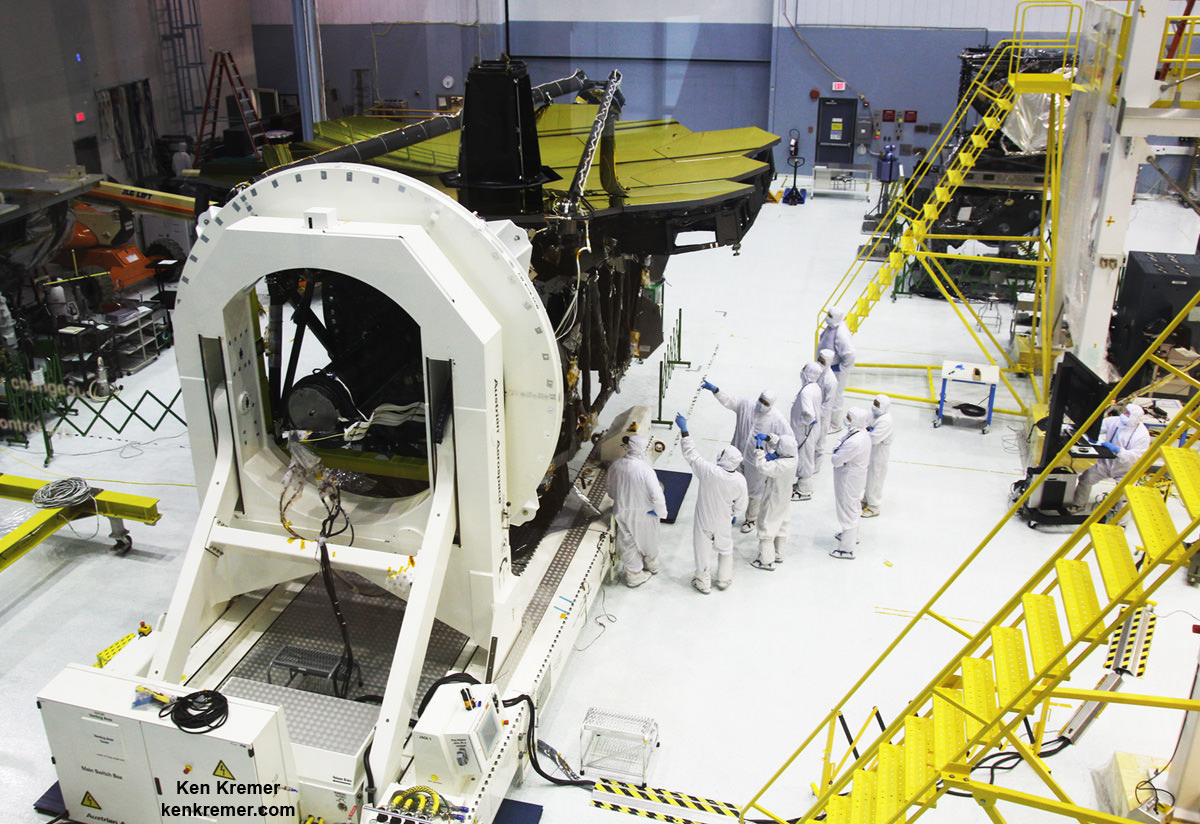

The Webb Telescope is a joint international collaborative project between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
Webb is designed to look at the first light of the Universe and will be able to peer back in time to when the first stars and first galaxies were forming. It will also study the history of our universe and the formation of our solar system as well as other solar systems and exoplanets, some of which may be capable of supporting life on planets similar to Earth.

Watch this space for my ongoing reports on JWST mirrors, science, construction and testing.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.