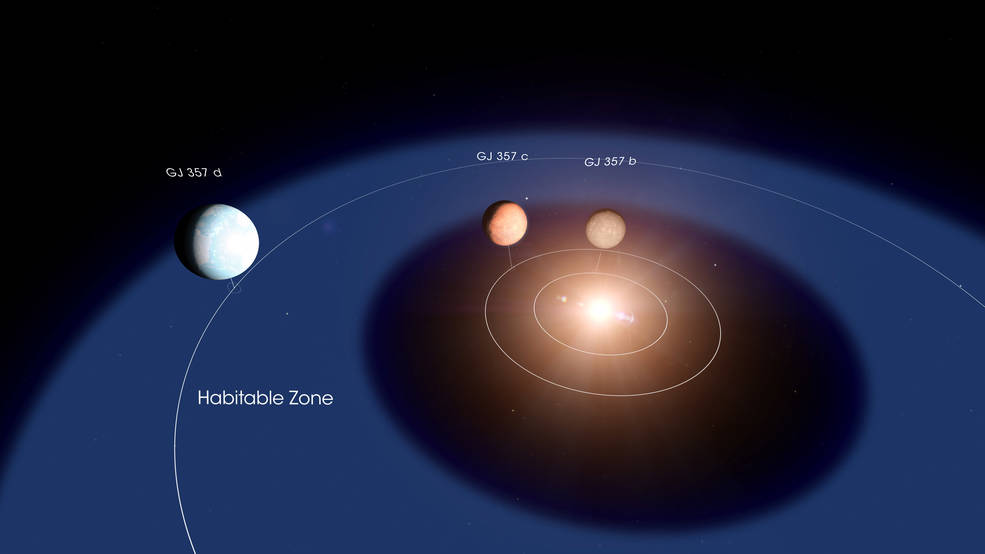
REMINDER: – Universe Today will be hosting an interview with Dr. Dirk Schulze-Makuch, co-author of the research featured in this article, on Thursday October 15th, 2020 at 8:30am PT. Click the video below to watch live or to see the recorded stream afterward
Out Earthing Earth
What planet is this?
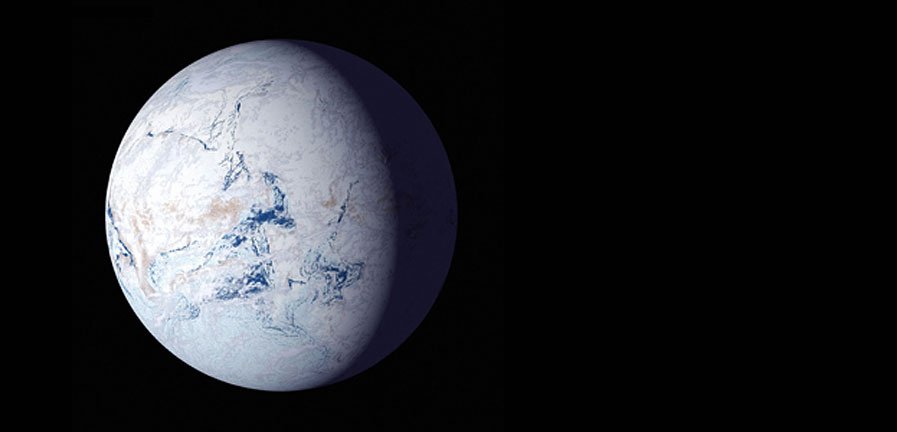
If you said Hoth, that’s a good guess. But, it’s actually Earth depicted in one of two known “snowball” states. The entire planet’s surface was locked beneath glacial ice during the Cryogenian Period 650 million years ago and during the Huronian Glaciation 2 – 2.4 billion years ago.
Continue reading “The Search for Superhabitable Planets. Worlds Even More Habitable Than Earth”