This article was originally published in 2008, but has been updated several times now to keep track with our advancing knowledge of the cosmos!
My six-year old daughter is a question-asking machine. We were driving home from school a couple of days ago, and she was grilling me about the nature of the Universe. One of her zingers was, “What’s the Biggest Star in the Universe”? I had an easy answer. “The Universe is a big place,” I said, “and there’s no way we can possibly know what the biggest star is”. But that’s not a real answer.
So she refined the question. “What’s the biggest star that we know of?” Of course, I was stuck in the car, and without access to the Internet. But once I got back home, and was able to do some research, I learned the answer and thought I’d share it with the rest of you But to answer it fully, some basic background information needs to be covered first. Ready?
Solar Radius and Mass:
When talking about the size of stars, it’s important to first take a look at our own Sun for a sense of scale. Our familiar star is a mighty 1.4 million km across (870,000 miles). That’s such a huge number that it’s hard to get a sense of scale. Speaking of which, the Sun also accounts for 99.9% of all the matter in our Solar System. In fact, you could fit one million planet Earths inside the Sun.
Using these values, astronomers have created the terms “solar radius” and “solar mass”, which they use to compare stars of greater or smaller size and mass to our own. A solar radius is 690,000 km (432,000 miles) and 1 solar mass is 2 x 1030 kilograms (4.3 x 1030 pounds). That’s 2 nonillion kilograms, or 2,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 kg.
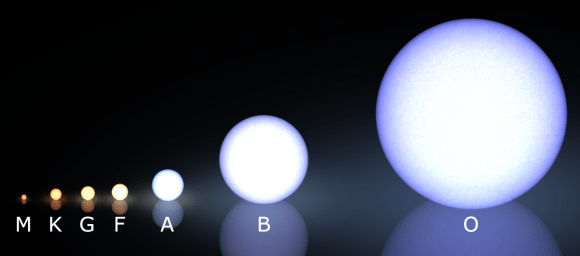
Another thing worth considering is the fact that our Sun is pretty small, as stars go. As a G-type main-sequence star (specifically, a G2V star), which is commonly known as a yellow dwarf, its on the smaller end of the size chart (see above). While it is certainly larger than the most common type of star – M-type, or Red Dwarfs – it is itself dwarfed (no pun!) by the likes of blue giants and other spectral classes.
Classification:
To break it all down, stars are grouped based on their essential characteristics, which can be their spectral class (i.e. color), temperature, size, and brightness. The most common method of classification is known as the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system, which classifies stars based on temperature using the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, and M, – O being the hottest and M the coolest. Each letter class is then subdivided using a numeric digit with 0 being hottest and 9 being coolest (e.g. O1 to M9 are the hottest to coldest stars).
In the MK system, a luminosity class is added using Roman numerals. These are based on the width of certain absorption lines in the star’s spectrum (which vary with the density of the atmosphere), thus distinguishing giant stars from dwarfs. Luminosity classes 0 and I apply to hyper- or supergiants; classes II, III and IV apply to bright, regular giants, and subgiants, respectively; class V is for main-sequence stars; and class VI and VII apply to subdwarfs and dwarf stars.

There is also the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, which relates stellar classification to absolute magnitude (i.e. intrinsic brightness), luminosity, and surface temperature. The same classification for spectral types are used, ranging from blue and white at one end to red at the other, which is then combined with the stars Absolute Visual Magnitude (expressed as Mv) to place them on a 2-dimensional chart (see above).
On average, stars in the O-range are hotter than other classes, reaching effective temperatures of up to 30,000 K. At the same time, they are also larger and more massive, reaching sizes of over 6 and a half solar radii and up to 16 solar masses. At the lower end, K and M type stars (orange and red dwarfs) tend to be cooler (ranging from 2400 to 5700 K), measuring 0.7 to 0.96 times that of our Sun, and being anywhere from 0.08 to 0.8 as massive.
Based on the full of classification of our Sun (G2V), we can therefore say that it a main-sequence star with a temperature around 5,800K. Now consider another famous star system in our galaxy – Eta Carinae, a system containing at least two stars located around 7500 light-years away in the direction of the constellation Carina. The primary of this system is estimated to be 250 times the size of our Sun, a minimum of 120 solar masses, and a million times as bright – making it one of the biggest and brightest stars ever observed.
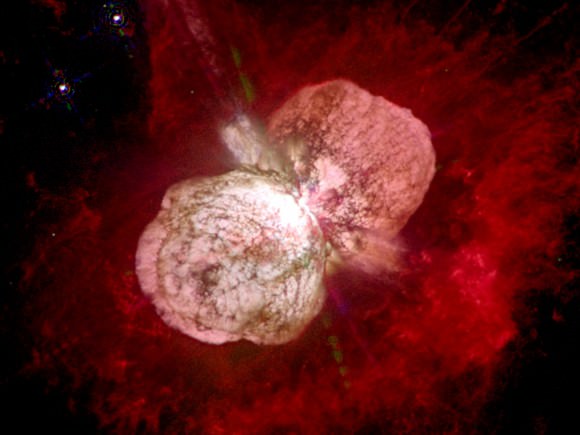

There is some controversy over this world’s size though. Most stars blow with a solar wind, losing mass over time. But Eta Carinae is so large that it casts off 500 times the mass of the Earth every year. With so much mass lost, it’s very difficult for astronomers to accurately measure where the star ends, and its stellar wind begins. Also, it is believed that Eta Carinae will explode in the not-too-distant future, and it will be the most spectacular supernovae humans have ever seen.
In terms of sheer mass, the top spot goes to R136a1, a star located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, some 163,000 light-years away. It is believed that this star may contain as much as 315 times the mass of the Sun, which presents a conundrum to astronomers since it was believed that the largest stars could only contain 150 solar masses. The answer to this is that R136a1 was probably formed when several massive stars merged together. Needless to say, R136a1 is set to detonate as a hypernova, any day now.
In terms of large stars, Betelgeuse serves as a good (and popular) example. Located in the shoulder of Orion, this familiar red supergiant has a radius of 950-1200 times the size of the Sun, and would engulf the orbit of Jupiter if placed in our Solar System. In fact, whenever we want to put our Sun’s size into perspective, we often use Betelgeuse to do it (see below)!
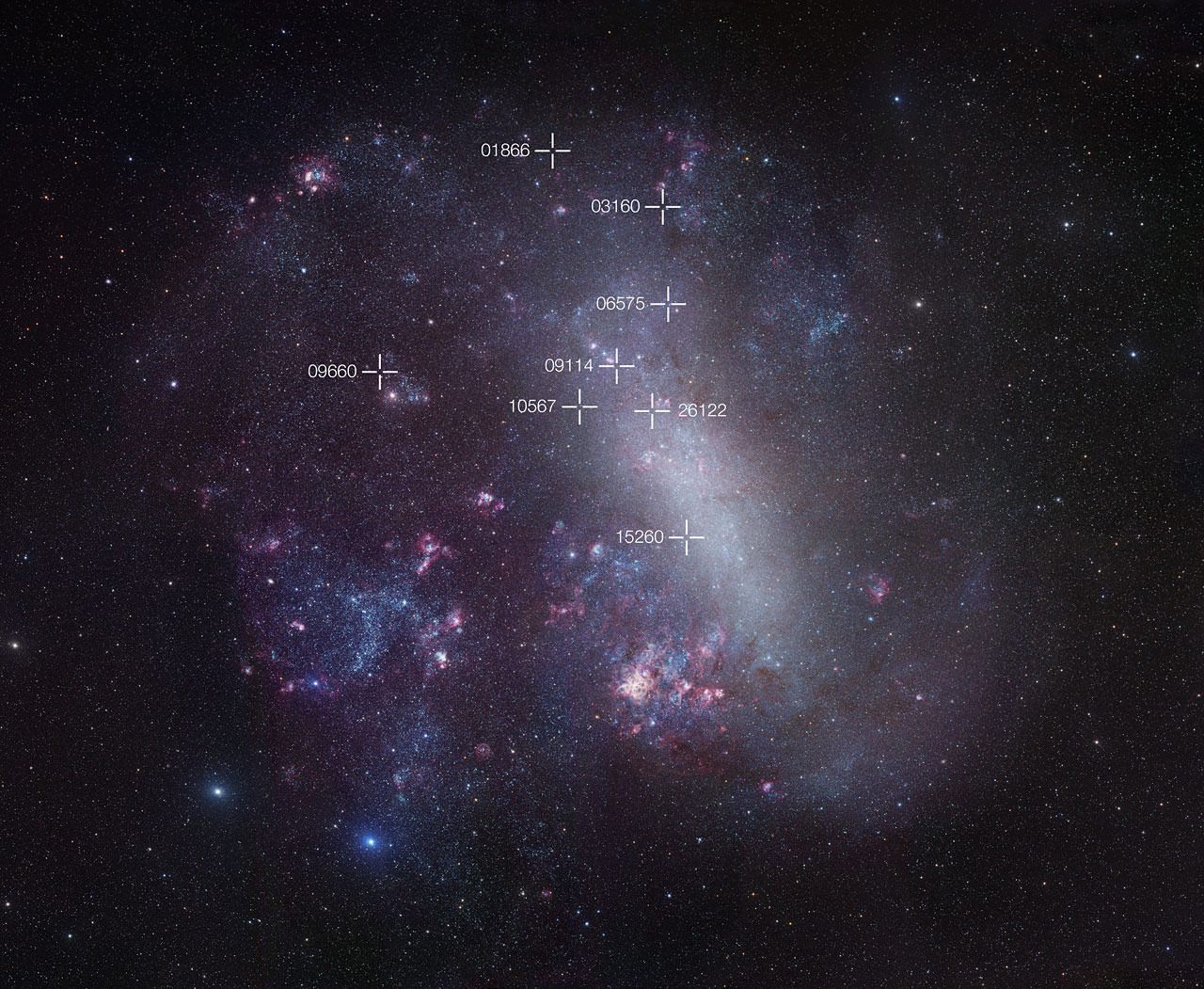
Yet, even after we use this hulking Red Giant to put us in our place, we are still just scratching the surface in the game of “who’s the biggest star”. Consider WOH G64, a red supergiant star located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, approximately 168,000 light years from Earth. At 1.540 solar radii in diameter, this star is currently one of the largest in the known universe.
But there’s also RW Cephei, an orange hypergiant star in the constellation Cepheus, located 3,500 light years from Earth and measuring 1,535 solar radii in diameter. Westerlund 1-26 is also pretty huge, a red supergiant (or hypergiant) located within the Westerlund 1 super star cluster 11,500 light-years away that measures 1,530 solar radii in diameter. Meanwhile, V354 Cephei and VX Sagittarii are tied when it comes to size, with both measuring an estimated 1,520 solar radii in diameter.
The Largest Star: UY Scuti
As it stands, the title of the largest star in the Universe (that we know of) comes down to two contenders. For example, UY Scuti is currently at the top of the list. Located 9.500 light years away in the constellation Scutum, this bright red supergiant and pulsating variable star has an estimated average median radius of 1,708 solar radii – or 2.4 billion km (1.5 billion mi; 15.9 AU), thus giving it a volume 5 billion times that of the Sun.
However, this average estimate includes a margin of error of ± 192 solar radii, which means that it could be as large as 1900 solar radii or as small as 1516. This lower estimate places it beneath stars like as V354 Cephei and VX Sagittarii. Meanwhile, the second star on the list of the largest possible stars is NML Cygni, a semiregular variable red hypergiant located in the Cygnus constellation some 5,300 light-years from Earth.

Due to the location of this star within a circumstellar nebula, it is heavily obscured by dust extinction. As a result, astronomers estimate that its size could be anywhere from 1,642 to 2,775 solar radii, which means it could either be the largest star in the known Universe (with a margin of 1000 solar radii) or indeed the second largest, ranking not far behind UY Scuti.
And up until a few years ago, the title of biggest star went to VY Canis Majoris; a red hypergiant star in the Canis Major constellation, located about 5,000 light-years from Earth. Back in 2006, professor Roberta Humphrey of the University of Minnesota calculated its upper size and estimated that it could be more than 1,540 times the size of the Sun. Its average estimated mass, however, is 1420, placing it in the no. 8 spot behind V354 Cephei and VX Sagittarii.
These are the biggest star that we know of, but the Milky way probably has dozens of stars that are even larger, obscured by gas and dust so we can’t see them. But even if we cannot find these stars, it is possible to theorize about their likely size and mass. So just how big can stars get? Once again, Professor Roberta Humphreys of the University of Minnesota provided the answer.
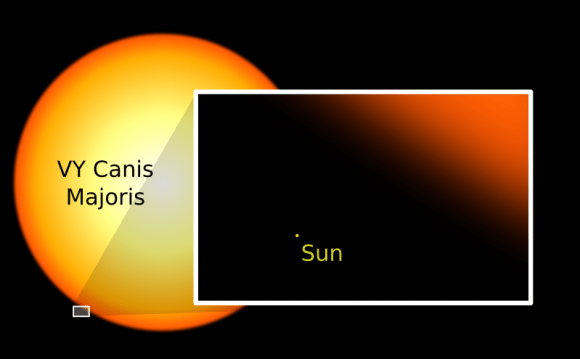
As she explained when contacted, the largest stars in the Universe are the coolest. So even though Eta Carinae is the most luminous star we know of, it’s extremely hot – 25,000 Kelvin – and therefore only 250 solar radii big. The largest stars, in contrast, will be cool supergiants. Case in point, VY Canis Majoris is only 3,500 Kelvin, and a really big star would be even cooler.
At 3,000 Kelvin, Humphreys estimates that cool supergiant would be as big as 2,600 times the size of the Sun. This is below the upper estimates for NML Cygni, but above the average estimates for both it and UY Scutii. Hence, this is the upper limit of a star (at least theoretically and based on all the information we have to date).
But as we continue to peer into the Universe with all of our instruments, and explore it up close through robotic spacecraft and crewed missions, we are sure to find new and exciting things that will confound us further!
And be sure to check out this great animation that shows the size of various objects in space, starting with our Solar System’s tiny planets and finally getting to UY Scuti. Enjoy!
We have written many articles about stars for Universe Today. Here’s The Sun, What’s the Brightest Star in the Sky Past and Future?, and What Is The Smallest Star?
Want to learn more about the birth and death of stars? We did a two part podcast at Astronomy Cast. Here’s part 1, Where Stars Come From, and here’s part 2, How Stars Die.