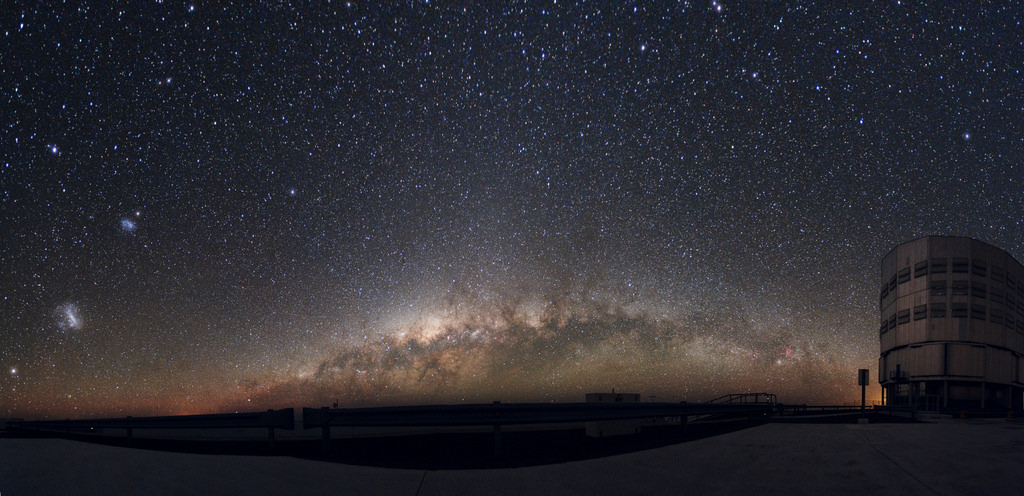
As the Milky Way rises over the horizon at the European Southern Observatory, its companion galaxies also come into view. Credit: ESO/Y. Beletsky
A previously undetected heist of stars was uncovered by astronomers who were actually looking for why an unexpected amount of microlensing events were being seen around the outskirts of the Milky Way. Instead, they found the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) had been stealing stars from its neighbor, the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), leaving behind a trail of stars. Although the crime was likely committed hundreds of milllions of years ago during a collision between the two galaxies, the new information is helping astronomers to understand the history of these two galaxies that are in our neighborhood.
“You could say we discovered a crime of galactic proportions,” said Avi Loeb of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics.
The Large Magellanic Cloud almost got away with it, if it wasn’t for those meddling astronomers….
Astronomers were originally monitoring the LMC to hunt for the reason for the unexpected microlensing events. Their initial hypothesis was that massive compact halo objects, or MACHOs were causing the effect, where a nearby object passes in front of a more distant star. The gravity of the closer object bends light from the star like a lens, magnifying it and causing it to brighten. The MACHOs were thought to be faint objects, roughly the mass of a star, but not much is known about them. Several surveys looked for MACHOs in order to find out if they could be a major component of dark matter – the unseen stuff that holds galaxies together.
In order for MACHOs to make up dark matter, they must be so faint that they can’t be directly detected. So, the team of astronomers hoped to see MACHOs within the Milky Way by lensing distant LMC stars.
“We originally set out to understand the evolution of the interacting LMC and SMC galaxies,” said lead author of a new paper on the results, Gurtina Besla of Columbia University. “We were surprised that, in addition, we could rule out the idea that dark matter is contained in MACHOs.”
“Instead of MACHOs, a trail of stars removed from the SMC is responsible for the microlensing events,” said Loeb.
Only a fast-moving population of stars could yield the observed rate and durations of the microlensing events. The best way to get such a stellar population is a galactic collision, which appears to have occurred in the LMC-SMC system.
“By reconstructing the scene, we found that the LMC and SMC collided violently hundreds of millions of years ago. That’s when the LMC stripped out the lensed stars,” said Loeb.
Their research also supports recent findings suggesting that both Magellanic Clouds are on their first pass by the Milky Way.
However, this isn’t a closed case. The evidence for the trail of lensed stars is persuasive, but they haven’t been directly observed yet. A number of teams are searching for the signatures of these stars within a bridge of gas that connects the Magellanic Clouds.
The simulation results will be published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Read the team’s paper: The Origin of the Microlensing Events Observed Towards the LMC and the Stellar Counterpart of the Magellanic Stream
Source: CfA