Uranus is a most unusual planet. Aside from being the seventh planet of our Solar System and the third gas giant, it is also classified sometimes as an “ice giant” (along with Neptune). This is because of its peculiar chemical composition, where water and other volatiles (i.e. ammonia, methane, and other hydrocarbons) in its atmosphere are compressed to the point where they become solid.
In addition to that, it also has a very long orbital period. Basically, it takes Uranus a little over 84 Earth years to complete a single orbit of the Sun. What this means is that a single year on Uranus lasts almost as long as a century here on Earth. On top of that, because of it axial tilt, the planet also experiences extremes of night and day during the course of a year, and some pretty interesting seasonal changes.
Orbital Period:
Uranus orbits the Sun at an average distance (semi-major axis) of 2.875 billion km (1.786 billion mi), ranging from 2.742 billion km (1.7 mi) at perihelion to 3 billion km (1.86 billion mi) at aphelion. Another way to look at it would be to say that it orbits the Sun at an average distance of 19.2184 AU (over 19 times the distance between the Earth and the Sun), and ranges from 18.33 AU to 20.11 AU.
The difference between its minimum and maximum distance from the Sun is 269.3 million km (167.335 mi) or 1.8 AU, which is the most pronounced of any of the Solar Planets (with the possible exception of Pluto). And with an average orbital speed of 6.8 km/s (4.225 mi/s), Uranus has an orbital period equivalent to 84.0205 Earth years. This means that a single year on Uranus lasts as long as 30,688.5 Earth days.
However, since it takes 17 hours 14 minutes 24 seconds for Uranus to rotate once on its axis (a sidereal day). And because of its immense distance from the Sun, a single solar day on Uranus is about the same. This means that a single year on Uranus lasts 42,718 Uranian solar days. And like Venus, Uranus’ rotates in the direction opposite of its orbit around the Sun (a phenomena known as retrograde rotation).
Axial Tilt:
Another interesting thing about Uranus is the extreme inclination of its axis (97.7°). Whereas all of the Solar Planets are tilted on their axes to some degree, Uranus’s extreme tilt means that the planet’s axis of rotation is approximately parallel with the plane of the Solar System. The reason for this is unknown, but it has been theorized that during the formation of the Solar System, an Earth-sized protoplanet collided with Uranus and tilted it onto its side.
A consequence of this is that when Uranus is nearing its solstice, one pole faces the Sun continuously while the other faces away – leading to a very unusual day-night cycle across the planet. At the poles, one will experience 42 Earth years of day followed by 42 years of night.
This is similar to what is experienced in the Arctic Circle and Antarctica. During the winter season near the poles, a single night will last for more than 24 hours (aka. a “Polar Night”) while during the summer, a single day will last longer than 24 hours (a “Polar Day”, or “Midnight Sun”).
Meanwhile, near the time of the equinoxes, the Sun faces Uranus’ equator and gives it a period of day-night cycles that are similar to those seen on most of the other planets. Uranus reached its most recent equinox on December 7th, 2007. During the Voyager 2 probe’s historic flyby in 1986, Uranus’s south pole was pointed almost directly at the Sun.
Seasonal Change:
Uranus’ long orbital period and extreme axial tilt also lead to some extreme seasonal variations in terms of its weather. Determining the full extent of these changes is difficult because astronomers have yet to observe Uranus for a full Uranian year. However, data obtained from the mid-20th century onward has showed regular changes in terms of brightness, temperature and microwave radiation between the solstices and equinoxes.
These changes are believed to be related to visibility in the atmosphere, where the sunlit hemisphere is thought to experience a local thickening of methane clouds which produce strong hazes. Increases in cloud formation have also been observed, with very bright cloud features being spotted in 1999, 2004, and 2005. Changes in wind speed have also been noted that appeared to be related to seasonal increases in temperature.
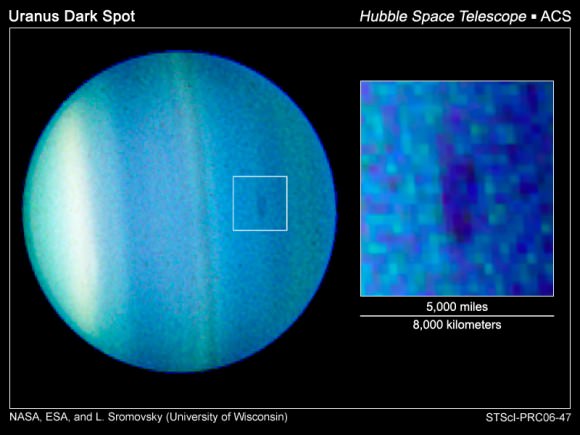

Uranus’ “Great Dark Spot” and its smaller dark spot are also thought to be related to seasonal changes. Much like Jupiter’s Great Red Spot, this feature is a giant cloud vortex that is created by winds – which in this case are estimated to reach speeds of up to 900 km/h (560 mph). In 2006, researchers at the Space Science Institute and the University of Wisconsin observed a storm that measured 1,700 by 3,000 kilometers (1,100 miles by 1,900 miles).
Interestingly enough, while Uranus’ polar regions receive more energy on average over the course of a year than the equatorial regions, the equatorial regions have been found to be hotter than the poles. The exact cause of this remains unknown, but is certainly believed to be due to something endogenic.
Yep, Uranus is a pretty weird place! On this planet, a single year lasts almost a century, and the seasons are characterized by extreme versions of Polar Nights and Midnight Suns. And of course, an average year brings all kinds of seasonal changes, complete with extreme winds, massive storms, and thickening methane clouds.
We have written many articles about the length of a year on other planets here at Universe Today. Here’s How Long is a Year on the Other Planets?, How Long is a Year on Mercury?, How Long is a Year on Venus?, How Long is a Year on Earth?, How Long is a Year on Mars?, How Long is a Year on Jupiter?, How Long is a Year on Saturn?, How Long is a Year on Neptune? and How Long is a Year on Pluto?
If you’d like more info on Uranus, check out Hubblesite’s News Releases about Uranus. And here’s a link to the NASA’s Solar System Exploration Guide to Uranus.
We have recorded an episode of Astronomy Cast just about Uranus. You can access it here: Episode 62: Uranus.
Sources:




