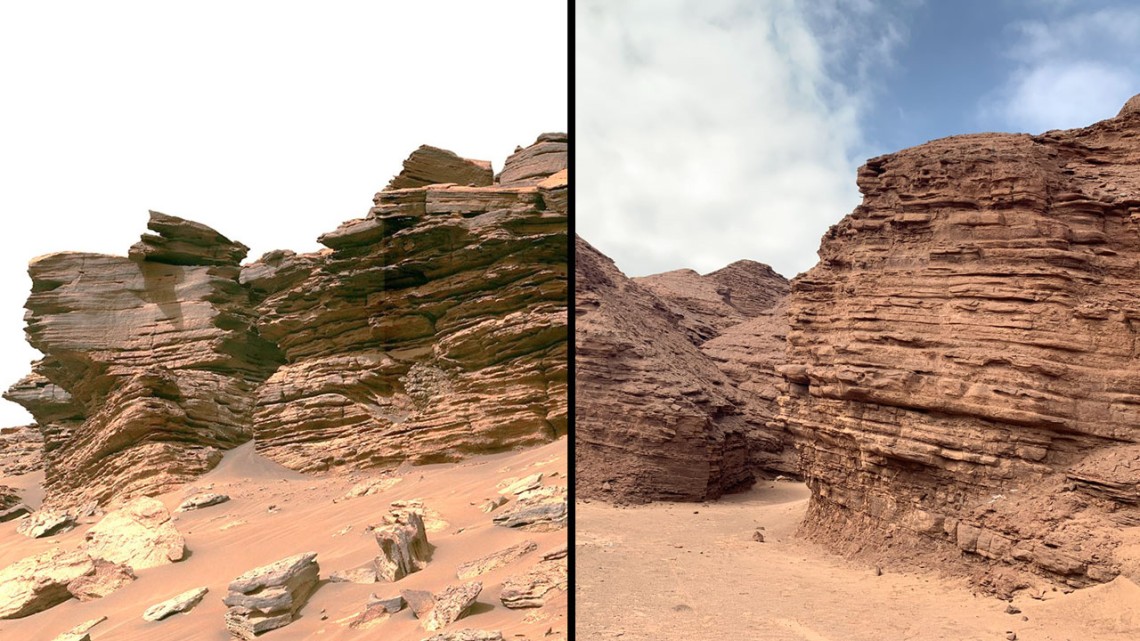
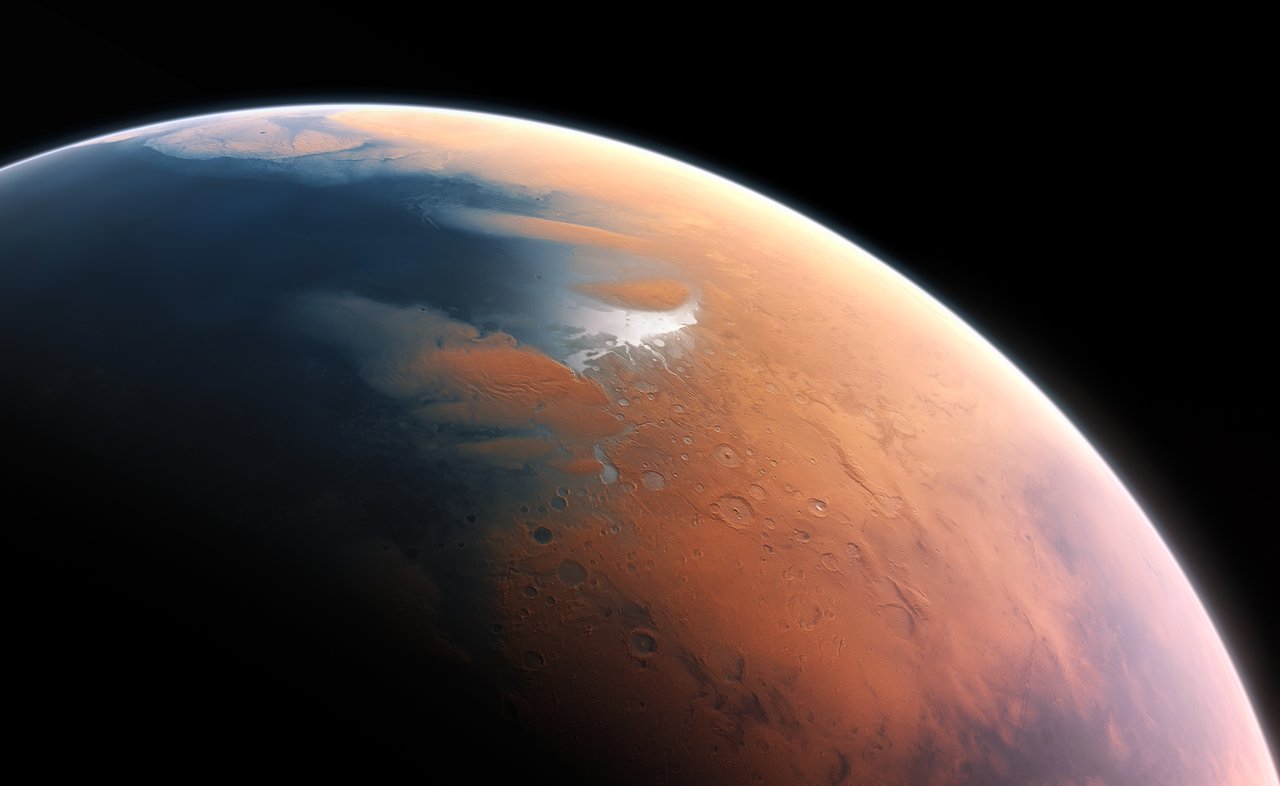
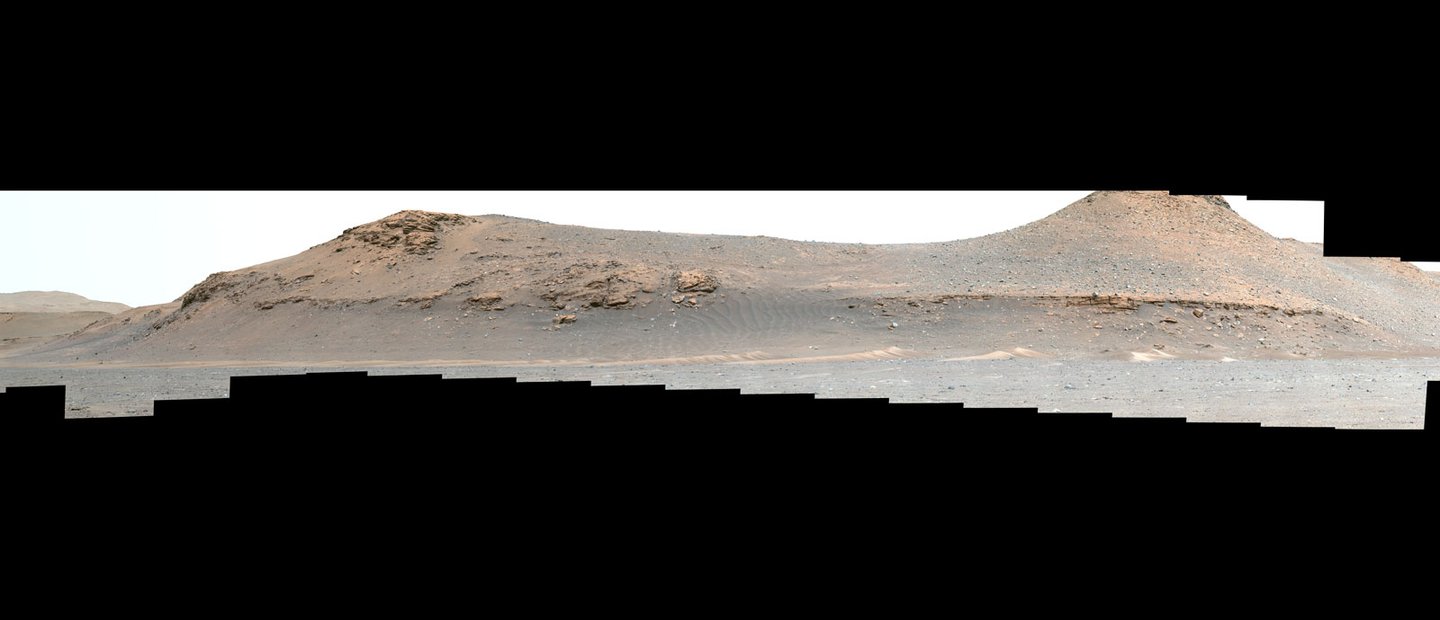
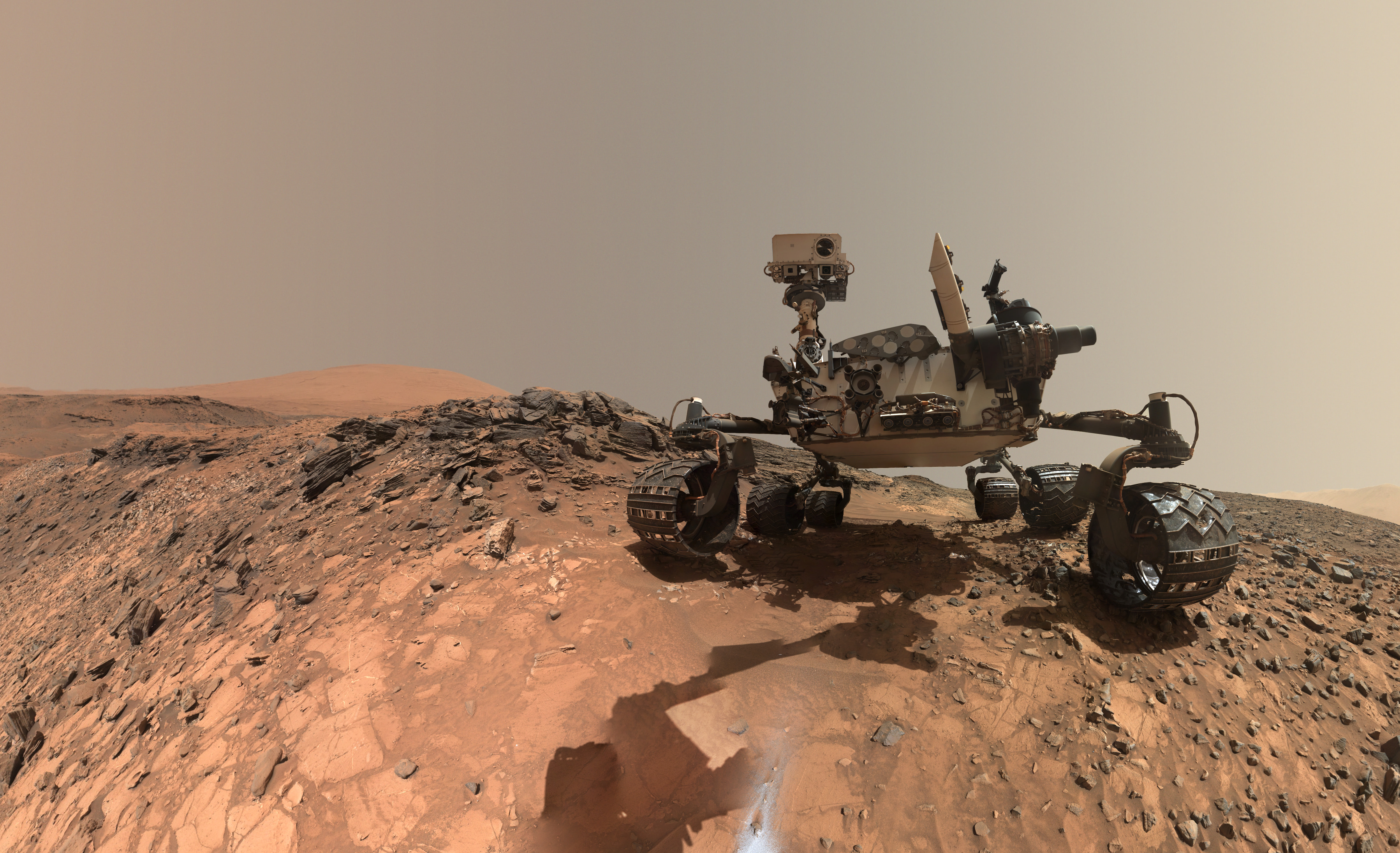
At this very moment, eleven robotic missions are exploring Mars, a combination of orbiters, landers, rovers, and one aerial vehicle (the Ingenuity helicopter). Like their predecessors, these missions are studying Mars’ atmosphere, surface, and subsurface to learn more about its past and evolution, including how it went from a once warmer and wetter environment to the freezing, dusty, and extremely dry planet we see today. In addition, these missions are looking for evidence of past life on Mars and perhaps learning if and where it might still exist today.
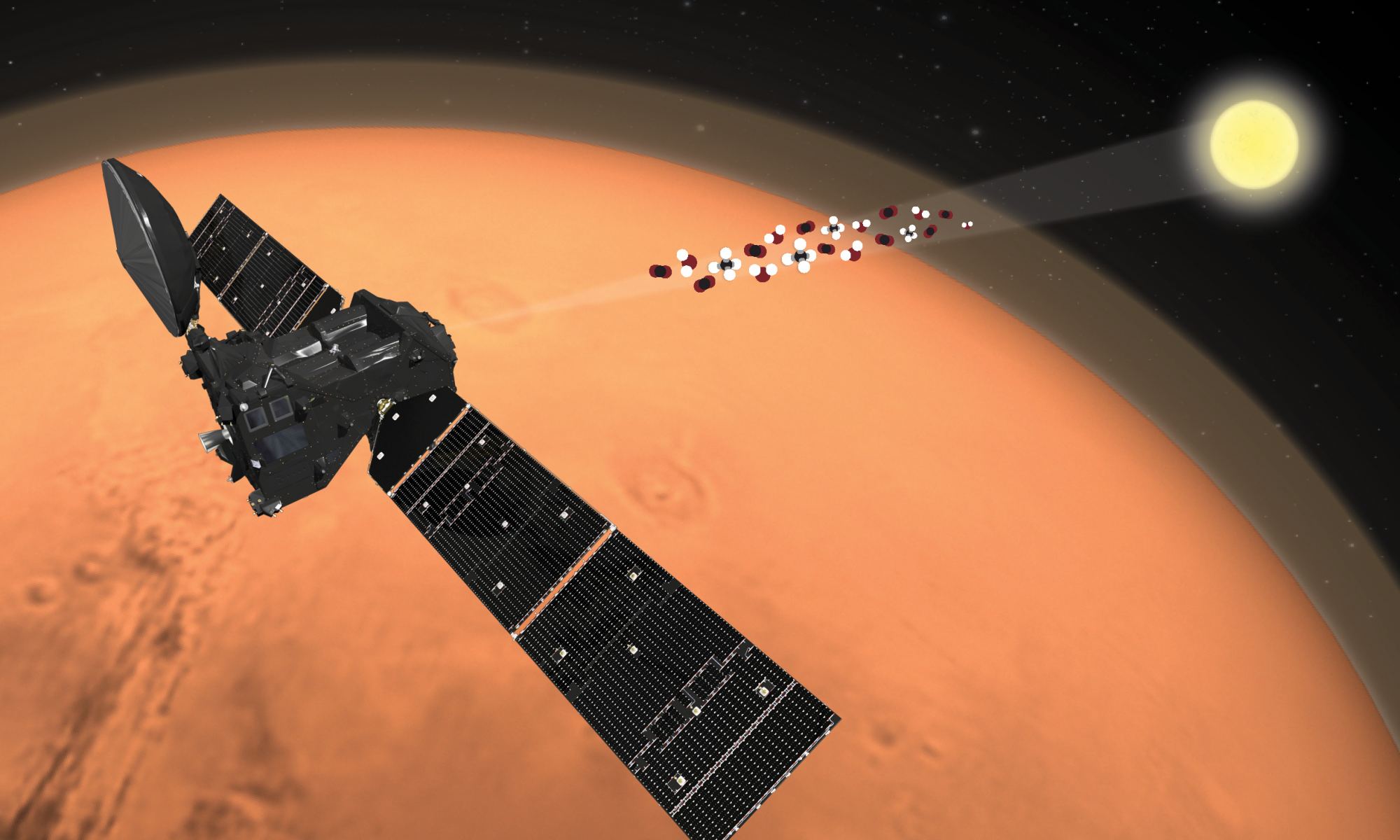
One particularly interesting issue is how the atmosphere of Mars – primarily composed of carbon dioxide (CO2) – is relatively enriched with Carbon-13 (13C), aka. “heavy carbon.” For years, scientists have speculated that the ratio of this isotope to “light carbon” (12C) might be responsible for organics found on the surface (a sign of biological processes!). But after analyzing data from the ESA’s ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) mission, an international team led by The Open University determined that these organics may be “abiotic” in origin (i.e., not biological).
Continue reading “Life Probably Didn't Have a Hand in Creating Organic Deposits on the Surface of Mars”