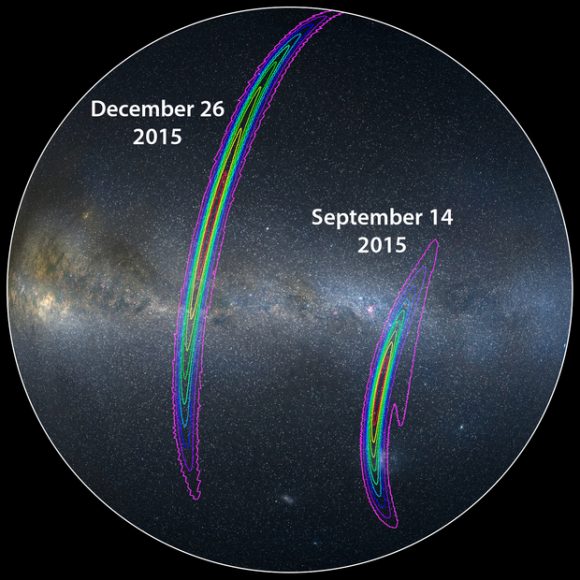
“This is quite literally a physics gold mine!” said Masao Sako, with the University of Pennsylvania.
For over a week now, the astronomy and astrophysics communities have been buzzing with the news of the latest gravitational wave discovery. And this discovery has been big.
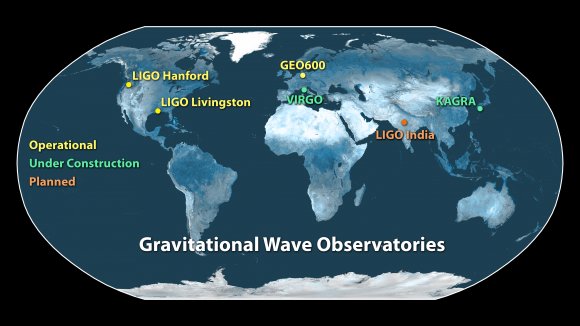
Four days before the Great American Solar Eclipse on August 21, a newly discovered gravitational wave caused more astronomers (8,223+), using more telescopes (70), to publish more papers (100 — see the list below) in less time than for any other astronomical event in history. The sixth gravitational wave (GW) to be discovered by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO) and Virgo GW observatories, which occurred on August 17, 2017 at 12:41:04 UTC, was surprising in two ways already reported.
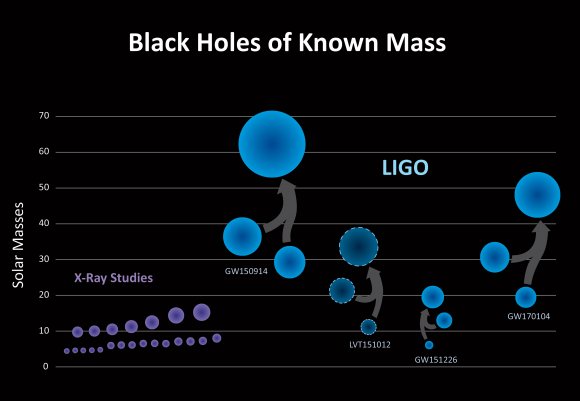
GW event six, designated GW170817, did not result from the collision and subsequent explosion of two black holes. All previous GW events, including the first ever discovered in 2015, had involved the collision of black holes with typically 40 times the mass of the Sun between them. Here however, the GW was evidently triggered by the collision and explosion of two neutron stars, having only 3 times the Sun’s mass in total.

Crucially, GW170817 occurred ten times closer to Earth than all earlier GW events. Earlier GWs involved black hole collisions at more than 1.3 billion light-years (400 million parsecs or Mpc). GW170817, in comparison, was known within hours of its discovery to lie within only 130 million light-years (40 Mpc). That vastly improved astronomer’s odds of detecting the event independently, because in cosmological terms, it occurred within less than 1% of the universe’s Hubble length of 14 billion light-years (4,300 Mpc).
Not widely reported is that our current astronomical theory regarding GW170817 still depends significantly on observations yet to be made. In brief, astronomers currently believe that GW170817 was triggered by the merger of two neutron stars, which triggered the explosion of a Short Gamma-Ray Burst (SGRB), which emitted only a fraction of the gamma-ray energy in our direction normally associated with SGRBs, because it was the first SGRB observed at such a large angle away from the direction of its focused jets of gamma-rays. The SGRB associated with GW170817 emitted its jet at roughly 30 degrees away from our line-of-sight. All other SGRBs have been observed at only a few degrees from alignment with their jets. The exact angle of the newly discovered SGRB’s jet is important in understanding how its afterglow compares with other SGRB afterglows. Significant properties reported for the GW, including its distance, depend on the angle at which the two neutron stars collided relative to Earth.
The collision angle determined roughly based on the GW itself is probably OK. Only radio maps of the SGRB region at 100 days however, will provide astronomers with the most precise measurements of the resulting explosion’s velocities and directions over time to date. Only then will astronomers learn more about the exact angle of the SGRB’s jet, providing potentially a more accurate estimate of the angle at which the neutron stars collided. More surprises could be in store as a result, including refinements of the properties reported.

Unlike previous events, GW170817 was close enough that within 1.74 seconds of its initial detection by LIGO, it’s gamma radiation was detected by the Fermi Gamma-Ray space telescope. The INTEGRAL Gamma-Ray space observatory detected it too, and it was later designated SGRB 170817A. As an SGRB alone, the event would have triggered alerts to observatories worldwide and aloft, each aiming to detect the explosion’s faint optical afterglow. SGRB optical afterglows have been used to pinpoint the exact positions of SGRBs, not only on the sky, but also in terms of their distance from Earth.
Astronomers in this case had the first GW ever to coincide with, and be independently corroborated by, any observable counterpart, and alerts became a call to astronomical arms. Even though its exact position on the sky was uncertain by many degrees, GW170817 was so close that astronomers were able to quickly narrow down its exact location.
“With a previously-compiled list of nearby galaxies having positions and distances culled from the massive on-line archive of the NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED), our team rapidly zeroed in on the host galaxy of the event,” said Barry Madore, of Carnegie Observatories.
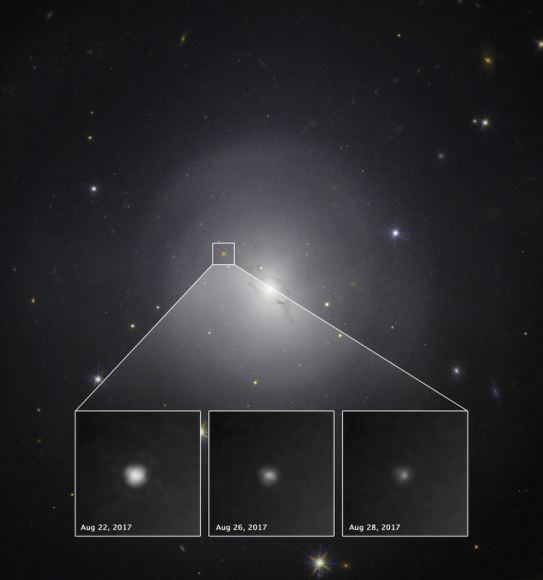
Precisely because GW170817 occurred at only 130 million light-years, the number of candidate galaxies to observe was only several dozen. In contrast, for previous GW discoveries occurring at billions of light-years, thousands of galaxies would have to be observed. Within 11 hours of the explosion, its afterglow was discovered in the lenticular galaxy NGC 4993, by the Swope 1-m telescope in Chile. They obtained the first-ever visual image of an event associated with a GW.
“Where observation is concerned, chance favors only the prepared mind,” added Madore, quoting Louis Pasteur from 150 years ago. Madore is also a researcher with the Swope team and a co-author on six papers reporting Swope’s discovery of the afterglow and some of its implications. “When alerts were sent out to the LIGO/VIRGO gravity wave detection consortium on the night of August 17, 2017, our team of astronomers was indeed prepared.”
New images of the afterglow of GW170817, aka SGRB 170817A, initially designated as Swope Supernova Survey SSS17a, revealed a bright blue astronomical transient, later designated as AT2017gfo by the International Astronomical Union (IAU).
“There will be more such events, no doubt; but this image taken at the Henrietta Swope 1m telescope at the Las Campanas Observatory in Chile was the first in history, and it truly ushered in the Era of Multi-Messenger Astronomy,” said Madore.
Radio observatories joined the hunt, including the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA), the Australia Telescope Compact Array (ATCA) and the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT). So did the Swift ultraviolet and Chandra X-ray space observatory satellites. By day one after the explosion, all frequencies of the electromagnetic spectrum were being observed in the direction of NGC 4993. On multiple wavelengths, multiple “messengers” of GW170817’s existence began to reveal more than the sum of their parts.
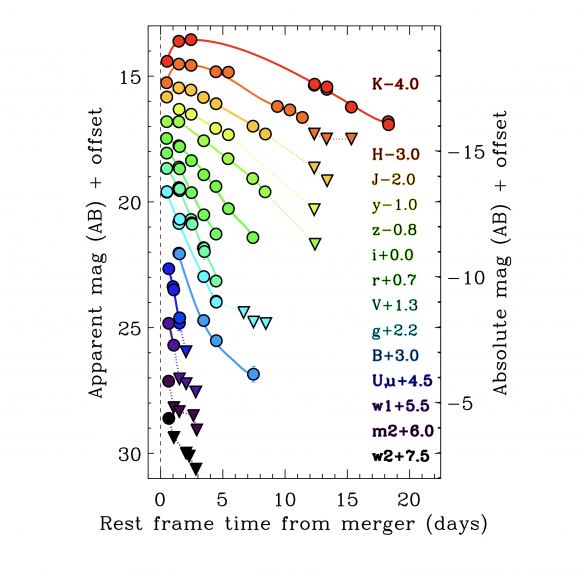
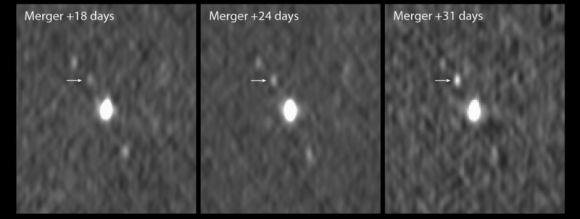
AT2017gfo brightened over the next few days after explosion, in near infrared observations continued by Swope. Their light-curves show the changes in the afterglow’s brightness over time. At three days post explosion, the near-infrared afterglow stops brightening and begins to fade. As with other SGRB afterglows, AT2017gfo faded completely from visual observation over the course of days to weeks, but observations in X-rays and radio continue. Radio observations at 100 days post explosion, which will not occur until November 25, are crucial as said. Although a month away, planned radio observations will determine more than just the long-term evolution of the afterglow over 3 months. Indeed, our astronomical theory accounting for the event’s first three weeks, as already observed, analyzed, and reported, still depends to a surprising degree on an exact number of degrees. The number of degrees relative to Earth for this SGRB based on radio data however, will not be known for at least a month.
“With GW170817 we have for the first time truly independent verification of a gravitational wave source,” said Robert Quimby, of the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe at the University of Tokyo, and coauthor of a paper regarding the event’s implications. “The electromagnetic signature of this event can be uniquely matched to the predictions of binary neutron star mergers, and it is actually quite amazing how well the theory matches the data considering how few observational constraints were available to guide the model.”
“With GW170817, we can learn about nuclear physics, relativity, stellar evolution, and cosmology all in one shot,” added Sako, who is also a co-author on ten papers regarding the event. “Plus we now know how all of the heaviest elements in the Universe are created.”
EVENT CHRONOLOGY
T = 0 sec.: GW170817 detected by LIGO/VIRGO [1, 82]
T = 1.74 sec.: SGRB 170817A detected by Fermi Gamma-Ray Burst Monitor satellite immediately after GW170817 [52]
T = 28 min.: Gamma-ray Coordinates Network (GCN) Notice [53]
T = 40 min.: GCN Circular [53]
T = 5.63 hr.: First sky map locating GW170817 to within several degrees [53]
T = 10.9 hr.: Swope 1-m observatory discovers explosion’s afterglow, AT 2017gfo, in galaxy NGC 4993 [18, 24, 64, 75, 77]
T = 11.09 hr.: PROMPT 0.4m observatory detects AT 2017gfo [88]
T = 11.3 hr.: Hubble Space Telescope images AT 2017gfo [20]
T = 12-24 hr.: Magellan; Las Campanas Observatory; W. M. Keck Observatory; Blanco 4-m Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory; Gemini South; European Southern Observatory VISTA; Subaru among 6 Japanese telescopes; Pan-STARRS1; Very Large Telescope; 14 Australian telescopes; and Antarctic Survey Telescope optical observatories, and VLA, VLITE, ATCA, GMRT, and ALMA radio observatories, as well as Swift and NuSTAR ultraviolet satellite observatories
PROPERTIES
Position: Right Ascension 13h09m48.085s ± 0.018s; Declination -23d22m53.343s ± 0.218s (J2000 equinox); 10.6s or 7,000 light-years (2.0 kiloparsecs or kpc) from the nucleus of lenticular galaxy NGC 4993 [18]
Distance: 140 ± 40 million light-years (41 ± 13 Mpc), with 30% scatter based on 3 GW-based estimates [1, 25, 82], and 131 ± 9 million light-years (39.3 ± 2.7 Mpc), with 7% scatter based on 3 distance indicators, including GW-based as well as new Fundamental Plane relation-based distances for NGC 4993 [41, 43], and Tully-Fisher relation-based distances for galaxies in the group of galaxies including NGC 4993 from the NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED)
Mass: Neutron stars total 2.82 +0.47 -0.09 Sun’s mass [82]; mass ejected in elements heavier than iron is 0.03 ± 0.01 Sun’s mass or 10,000 Earth masses, based on 4 estimates [24, 59, 82, 93], including gold amounting to 150 ± 50 Earth masses [60]
Luminosity: Peaks at 0.5 days after explosion, at ~1042 erg/s, equivalent to 260 million Suns [24]
SGRB jet angle: 31 ± 3 degrees away from line-of-sight to Earth, based on 9 estimates [2, 25, 34, 35, 36, 44, 58, 62, 82]
SGRB jet speed: 30% speed of light, based on 4 estimates [20, 42, 59, 75]
Names: GW170817, SGRB 170817A, AT 2017gfo = IAU designation for SGRB afterglow, aka SSS17a, DLT17ck, J-GEM17btc, and MASTER OTJ130948.10-232253.3
IMPLICATIONS
Astronomy (1): Confirms binary neutron star collisions as a source for GW and SGRB events [1, 82]
Astronomy (2): GWs provide a new way of measuring neutron star diameters [8]
Astronomy (3): Gives universal expansion rate, or Hubble constant, as H0 = 71 ± 10 km -1 Mpc-1, with 14% accuracy, based on 6 GW-based estimates for GW170817 ranging from 69 to 74 km -1 Mpc-1, bridging current estimates [1, 22, 36, 60, 74, 82]; accuracy will improve to 4% with future similar events [74]
General Relativity (1): Confirms GW velocity equals speed of light to within 1 part per 1,000,000,000,000,000 or 1/1015 [7, 21, 70, 91]
General Relativity (2): Confirms equivalence of gravitational energy and inertial energy, or Weak Equivalence Principle, to within 1 part per 1,000,000,000 or 1/109 [7, 11, 91, 92]
Physics: Confirms binary neutron star collisions are significant production sites for elements heavier than iron, including gold, platinum, and uranium [17, 69]
Life on Earth: Indicates a higher deadly rate of gamma-rays for extraterrestrial life [15]
GW170817 (1): Predicted one binary neutron star collision per year similar to GW170817 within a distance from Earth of 130 million light-years [40 Mpc] [24]
GW170817 (2): Predicted to produce a 10 Giga-Hertz afterglow that peaks at ~100 days with a radio magnitude of ~10 milli-Janskys [24]
GW170817 (3): Predicted to remain visible in radio for 5-10 years, and for decades with next-generation radio observatories [2]
BIBLIOGRAPHY
96 papers on GW170817 released on arXiv during week of October 16-20
1. Abbott, B. P. et al., A gravitational-wave standard siren measurement of the Hubble constant, Nature, arXiv:1710.05835
2. Alexander, K. D. et al., The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/VIRGO GW170817. VI. Radio Constraints on a Relativistic Jet and Predictions for Late-Time Emission from the Kilonova Ejecta, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05457
3. Andreoni, I. et al., Follow up of GW170817 and its electromagnetic counterpart by Australian-led observing programs, PASA, arXiv:1710.05846
4. ANTARES, IceCube, Pierre Auger, LIGO Scientific, Virgo Collaborations, Search for High-energy Neutrinos from Binary Neutron Star Merger GW170817 with ANTARES, IceCube, and the Pierre Auger Observatory, na, arXiv:1710.05839
5. Arcavi, I. et al., Optical emission from a kilonova following a gravitational-wave-detected neutron-star merger, Nature, arXiv:1710.05843
6. Arcavi, I. et al., Optical Follow-up of Gravitational-wave Events with Las Cumbres Observatory, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05842
7. Baker, T. et al., Strong constraints on cosmological gravity from GW170817 and GRB 170817A, na, arXiv:1710.06394
8. Bauswein, A. et al., Neutron-star radius constraints from GW170817 and future detections, ApJL, submitted, arXiv:1710.06843
9. Belczynski, K. et al., GW170104 and the origin of heavy, low-spin binary black holes via classical isolated binary evolution, A&A, arXiv:1706.07053
10. Blanchard, P. K. et al., The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/VIRGO GW170817. VII. Properties of the Host Galaxy and Constraints on the Merger Timescale, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05458
11. Boran, S. et al., GW170817 Falsifies Dark Matter Emulators, na, arXiv:1710.06168
12. Brocato, E. et al., GRAWITA: VLT Survey Telescope observations of the gravitational wave sources GW150914 and GW151226, MNRAS, submitted, arXiv:1710.05915
13. Bromberg, O. et al., The gamma-rays that accompanied GW170817 and the observational signature of a magnetic jet breaking out of NS merger ejecta, MNRAS, arXiv:1710.05897
14. Buckley, D. A. H. et al., A comparison between SALT/SAAO observations and kilonova models for AT 2017gfo: the first electromagnetic counterpart of a gravitational wave transient – GW170817, MNRAS, arXiv:1710.05855
15. Burgess, J. M. et al., Viewing short Gamma-ray Bursts from a different angle, na, arXiv:1710.05823
16. Chang, P.; & Murray, N., GW170817: A Neutron Star Merger in a Mass-Transferring Triple System, MNRAS Letters, arXiv:1710.05939
17. Chornock, R. et al., The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/VIRGO GW170817. IV. Detection of Near-infrared Signatures of r-process Nucleosynthesis with Gemini-South, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05454
18. Coulter, D. A. et al., Swope Supernova Survey 2017a (SSS17a), the Optical Counterpart to a Gravitational Wave Source, Science, arXiv:1710.05452
19. Covino, S. et al., The unpolarized macronova associated with the gravitational wave event GW170817, Nature Astronomy, arXiv:1710.05849
20. Cowperthwaite, P. S. et al., The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/VIRGO GW170817. II. UV, Optical, and Near-IR Light Curves and Comparison to Kilonova Models, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05840
21. Creminelli, P.; & Vernizzi, F., Dark Energy after GW170817, na, arXiv:1710.05877
22. Di Valentino, E.; & Melchiorri, A., Cosmological constraints combining Planck with the recent gravitational-wave standard siren measurement of the Hubble constant, na, arXiv:1710.06370
23. Diaz, M.C. et al., Observations of the first electromagnetic counterpart to a gravitational wave source by the TOROS collaboration, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05844
24. Drout, M. R. et al., Light Curves of the Neutron Star Merger GW170817/SSS17a: Implications for R-Process Nucleosynthesis, Science, arXiv:1710.05443
25. Evans, P.A. et al., Swift and NuSTAR observations of GW170817: detection of a blue kilonova, Science, arXiv:1710.05437
26. Ezquiaga, J. M.; & Zumalacarregui, M., Dark Energy after GW170817, na, arXiv:1710.05901
27. Fargion, D.; Khlopov, M.; & Oliva, P., Could GRB170817A be really correlated to a NS-NS merging?, Research in Astron. Astrophys. , arXiv:1710.05909
28. Fermi-LAT Collaboration, Fermi-LAT observations of the LIGO/Virgo event GW170817, na, arXiv:1710.05450
29. Fong, W. et al., The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/VIRGO GW170817. VIII. A Comparison to Cosmological Short-duration Gamma-ray Bursts, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05438
30. Gall, C. et al., Lanthanides or dust in kilonovae: lessons learned from GW170817, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05863
31. Goldstein, A. et al., An Ordinary Short Gamma-Ray Burst with Extraordinary Implications: Fermi-GBM Detection of GRB 170817A, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05446
32. Gompertz, B. P. et al., The Diversity of Kilonova Emission in Short Gamma-Ray Bursts, ApJ, submitted, arXiv:1710.05442
33. Gottlieb, O. et al., A cocoon shock breakout as the origin of the ?-ray emission in GW170817, MNRAS, arXiv:1710.05896
34. Granot, J.; Guetta, D.; & Gill, R., Lessons from the short GRB170817A — the First Gravitational Wave Detection of a Binary Neutron Star Merger, na, arXiv:1710.06407
35. Granot, J. et al., Off-Axis Emission of Short GRB Jets from Double Neutron St.r Mergers and GRB 170817A, MNRAS, arXiv:1710.06421
36. Guidorzi, C. et al., Improved Constraints on H0 from a combined analysis of gravitational-wave and electromagnetic emission from GW170817, ApJL, submitted, arXiv:1710.06426
37. H.E.S.S. Collaboration et al., TeV gamma-ray observations of the binary neutron star merger GW170817 with H.E.S.S, ApJL, submitted, arXiv:1710.05862
38. Haggard, D. et al., A Deep Chandra X-ray Study of Neutron Star Coalescence GW170817, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05852
39. Hallinan, G. et al., A Radio Counterpart to a Neutron Star Merger, Science, arXiv:1710.05435
40. He, X.-B.; Tam, P-H. T.; & Shen, R. F.), GRB 170817A: a short GRB seen off-axis, MNRAS, arXiv:1710.05869
41. Hjorth, J. et al., The Distance to NGC 4993: The Host Galaxy of the Gravitational-wave Event GW170817, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05856
42. Hu, L. et al., Optical Observations of LIGO Source GW 170817 by the Antarctic Survey Telescopes at Dome A, Antarctica, Science Direct, arXiv:1710.05462
43. Im, M. et al., Distance and properties of NGC 4993 as the host galaxy of a gravitational wave source, GW170817, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05861
44. Ioka, K.; & Nakamura, T., Can an Off-axis Gamma-Ray Burst Jet in GW170817 Explain All the Electromagnetic Counterparts?, Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. , arXiv:1710.05905
45. Kasen, D. et al., Origin of the heavy elements in binary neutron-star mergers from a gravitational wave event, Nature, arXiv:1710.05463
46. Kasliwal, M. M. et al., Illuminating Gravitational Waves: A Concordant Picture of Photons from a Neutron Star Merger, Science, arXiv:1710.05436
47. Kilpatrick, C. D. et al., Electromagnetic Evidence that SSS17a is the Result of a Binary Neutron Star Merger, Science, arXiv:1710.05434
48. Kim, S. et al., ALMA and GMRT constraints on the off-axis gamma-ray burst 170817A from the binary neutron star merger GW170817, na, arXiv:1710.05847
49. Lamb, G. P.; & Shiho Kobayashi, GRB 170817A as a jet counterpart to gravitational wave trigger GW 170817, MNRAS, arXiv:1710.05857
50. Levan, A. J. et al., The environment of the binary neutron star merger GW170817, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05444
51. Li, T.-P. et al., Insight-HXMT observations of the first binary neutron star merger GW170817, Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. , arXiv:1710.06065
52. LIGO Scientific Collaboration, Virgo Collaboration, Fermi Gamma-Ray Burst Monitor, INTEGRAL, Gravitational Waves and Gamma-rays from a Binary Neutron Star Merger: GW170817 and GRB 170817A, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05834
53. LIGO Scientific Collaboration, Virgo Collaboration, et al., Multi-messenger Observations of a Binary Neutron Star Merger, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05833
54. Lipunov, V. M. et al., MASTER optical detection of the first LIGO/Virgo neutron stars merging GW170817, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05461
55. Lipunov, V. et al., Discovery of the neutron stars merger GW170817/GRB170817A and Binary Stellar Evolution, New Astronomy Review, arXiv:1710.05911
56. Lu, R.-J. et al., {\em Fermi}/GBM Short Gamma-ray Burst Catalog and Case Study for GRB 170817A/GW 170817, na, arXiv:1710.06979
57. Margalit, B.; & Metzger, B., Constraining the Maximum Mass of Neutron Stars From Multi-Messenger Observations of GW170817, ApJL, submitted, arXiv:1710.05938
58. Margutti, R. et al., The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/VIRGO GW170817. V. Rising X-ray Emission from an Off-Axis Jet, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05431
59. McCully, C. et al., The Rapid Reddening and Featureless Optical Spectra of the optical counterpart of GW170817, AT 2017gfo, During the First Four Days, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05853
60. Metzger, B. D. , Welcome to the Multi-Messenger Era! Lessons from a Neutron Star Merger and the Landscape Ahead, na, arXiv:1710.05931
61. Murguia-Berthier, A. et al., A Neutron Star Binary Merger Model for GW170817/GRB170817a/SSS17a, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05453
62. Nicholl, M. et al., The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/VIRGO GW170817. III. Optical and UV Spectra of a Blue Kilonova From Fast Polar Ejecta, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05456
63. Palmese, A. et al., DECam and DES perspective of the GW170817 host, NGC 4993: indication for dynamically-driven formation of binary neutron star in early type galaxies, na, arXiv:1710.06748
64. Pan, Y.-C. et al., The Old Host-Galaxy Environment of SSS17a, the First Electromagnetic Counterpart to a Gravitational Wave Source, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05439
65. Paul, D., Binary neutron star merger rate via the luminosity function of short gamma-ray bursts, MNRAS, arXiv:1710.05620
66. Pian, E. et al., Spectroscopic identification of r-process nucleosynthesis in a double neutron star merger, Nature, arXiv:1710.05858
67. Piro, A. L.; & Kollmeier, J. A., Evidence for Cocoon Emission from the Early Light Curve of SSS17a, na, arXiv:1710.05822
68. Pozanenko, A. et al., GRB170817A associated with GW170817: multifrequency observations and modeling of prompt gamma-ray emission, ApJL, submitted, arXiv:1710.05448
69. Rosswog, S. et al., The first direct double neutron star merger detection: implications for cosmic nucleosynthesis, A&A, accepted?, arXiv:1710.05445
70. Sakstein, J.; & Jain, B., Implications of the Neutron Star Merger GW170817 for Cosmological Scalar-Tensor Theories, na, arXiv:1710.05893
71. Salafia, O. S.; Ghisellini, G.; & Ghirlanda, G., Jet-driven and jet-less fireballs from compact binary mergers, MNRAS Letters, arXiv:1710.05859
72. Savchenko, V. et al., INTEGRAL Detection of the First Prompt Gamma-Ray Signal Coincident with the Gravitational Wave Event GW170817, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05449
73. Scolnic, D. et al., How Many Kilonovae Can Be Found in Past, Present, and Future Survey Datasets?, ApJL, submitted, arXiv:1710.05845
74. Seto, N.; & Kyutoku, K., Prospects of the local Hubble parameter measurement using gravitational waves from double neutron stars, MNRAS, arXiv:1710.06424
75. Shappee, B. J. et al., Early Spectra of the Gravitational Wave Source GW170817: Evolution of a Neutron Star Merger, Science, arXiv:1710.05432
76. Shoemaker, I. M.; & Murase, K., Constraints from the Time Lag between Gravitational Waves and Gamma Rays: Implications of GW 170817 and GRB 170817A, na, arXiv:1710.06427
77. Siebert, M. R. et al., The Unprecedented Properties of the First Electromagnetic Counterpart to a Gravitational Wave Source, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05440
78. Smartt, S. J. et al., A kilonova as the electromagnetic counterpart to a gravitational-wave source, Nature, arXiv:1710.05841
79. Soares-Santos, M. et al., The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. I. Dark Energy Camera Discovery of the Optical Counterpart, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05459
80. Tanaka, M. et al., Kilonova from post-merger ejecta as an optical and near-infrared counterpart of GW170817, PASJ, arXiv:1710.05850
81. Tanvir, N. R. et al., The Emergence of a Lanthanide-Rich Kilonova Following the Merger of Two Neutron Stars, na, arXiv:1710.05455
82. The LIGO Scientific Collaboration, The Virgo Collaboration, GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral, Phys. Rev. Lett., arXiv:1710.05832
83. The LIGO Scientific Collaboration, the Virgo Collaboration, Estimating the Contribution of Dynamical Ejecta in the Kilonova Associated with GW170817, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05836
84. The LIGO Scientific Collaboration, the Virgo Collaboration, On the Progenitor of Binary Neutron Star Merger GW170817, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05838
85. Tominaga, N. et al., Subaru Hyper Suprime-Cam Survey for An Optical Counterpart of GW170817, PASJ, submitted, arXiv:1710.05865
86. Troja, E. et al., The X-ray counterpart to the gravitational wave event GW 170817, Nature, arXiv:1710.05433
87. Utsumi, Y. et al., J-GEM observations of an electromagnetic counterpart to the neutron star merger GW170817, PASJ, arXiv:1710.05848
88. Valenti, S. et al., The discovery of the electromagnetic counterpart of GW170817: kilonova AT 2017gfo/DLT17ck, ApJL, arXiv:1710.05854
89. Verrecchia, F. et al., AGILE Observations of the Gravitational Wave Source GW 170817: Constraining Gamma-Ray Emission from a NS-NS Coalescence, ApJL, submitted, arXiv:1710.05460
90. Wang, F. Y.; & Zou, Y. C., Measuring peculiar velocities from gravitational waves and electromagnetic counterparts, na, arXiv:1710.06113
91. Wang, H. et al., GW170817/GRB 170817A/AT2017gfo association: some implications for physics and astrophysics, na, arXiv:1710.05805
92. Wei, J.-J. et al., Multimessenger tests of the weak equivalence principle from GW170817 and its electromagnetic counterparts, na, arXiv:1710.05860
93. Xiao, D. et al., Afterglows and Macronovae Associated with Nearby Low-Luminosity Short-Duration Gamma-Ray Bursts: Application to GW170817/GRB170817A, na, arXiv:1710.05910
94. Yang, S. et al., An empirical limit on the kilonova rate from the DLT40 one day cadence Supernova Survey, ApJL, submitted, arXiv:1710.05864
95. Yue, C. et al., Is GRB 170817A Alone?, na, arXiv:1710.05942
96. Zhang, B.-B. et al., A peculiar low-luminosity short gamma-ray burst from a double neutron star merger progenitor, na, arXiv:1710.05851