It was 1969 that humans first set foot on the Moon. Now, over 50 years later we are setting sights on building lunar bases. The ability to complete that goal is dependent on either transporting significant amounts of material to the Moon to construct bases or somehow utilising raw lunar materials. A team of Chinese researchers have developed a technique to create bricks from material that is very similar to the soil found on the Moon. The hope is that the lunar soil can in the future, be used to build bricks on the Moon.
Continue reading “Building Bricks out of Lunar Regolith”Plants Could Grow in Lunar Regolith Using Bacteria

In the next decade, NASA, China, and their international and commercial partners plan to establish habitats on the Moon. Through the Artemis Program, NASA will deploy the orbiting Lunar Gateway and the Artemis Base Camp on the lunar surface. Meanwhile, China (and its partner Roscosmos) will deploy the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS), consisting of an orbital and surface element. The creation of this infrastructure will enable a “sustained program of lunar exploration and development” that could lead to a permanent human presence there.
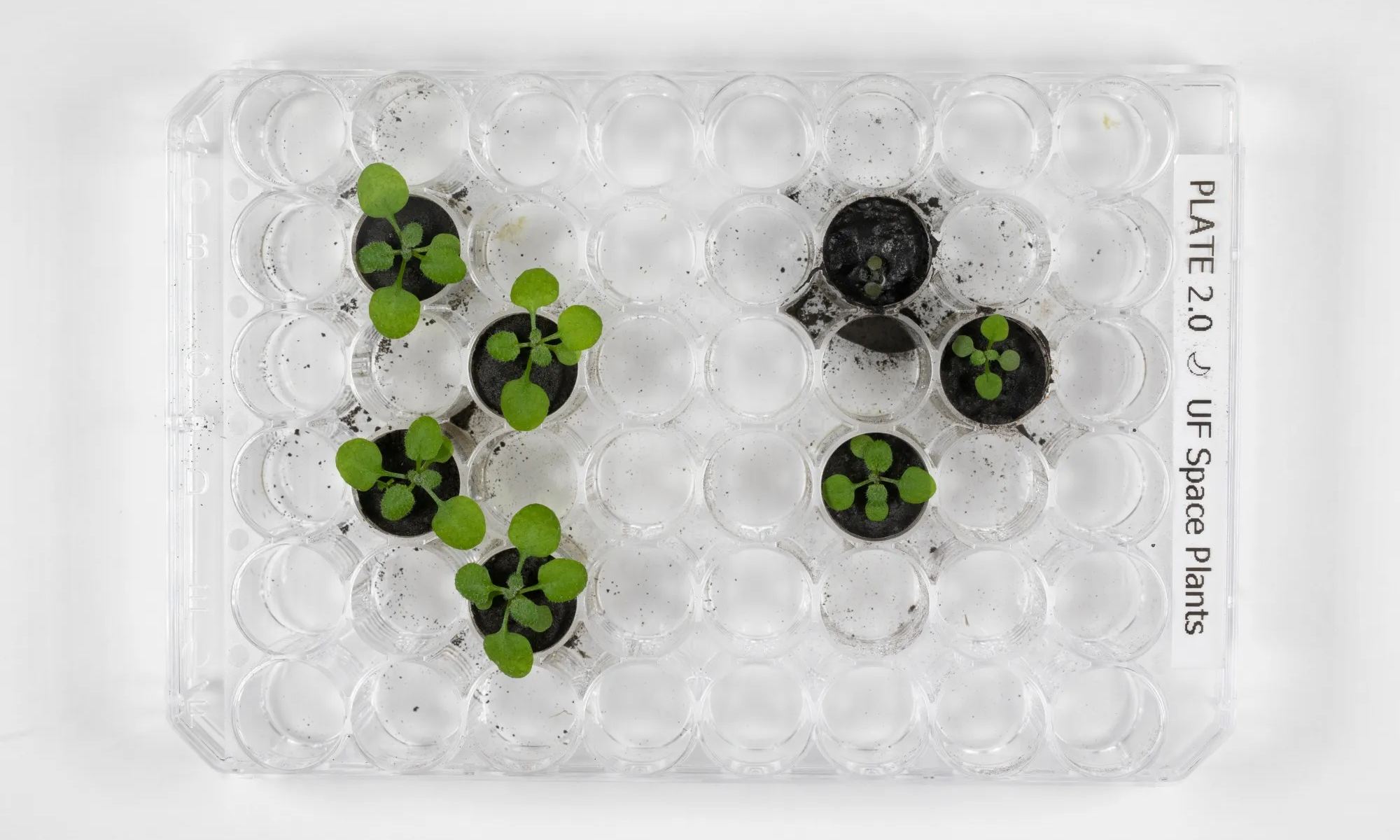
To ensure that humans can work and live sustainably beyond Earth, astronauts and crews will need to be able to harvest local resources to see to their needs – in-situ resource utilization (ISRU). This includes using lunar water ice and regolith to grow plants, providing astronauts with food and an additional source of oxygen and biomass. To test the potential for growing plants on the Moon, a Chinese research team conducted a series of experiments where they grew tobacco plants in simulated lunar soil with the help of bacteria.
Continue reading “Plants Could Grow in Lunar Regolith Using Bacteria”Balloon Animals and Bouncy Castles on the Moon. The Case for Inflatable Habitats
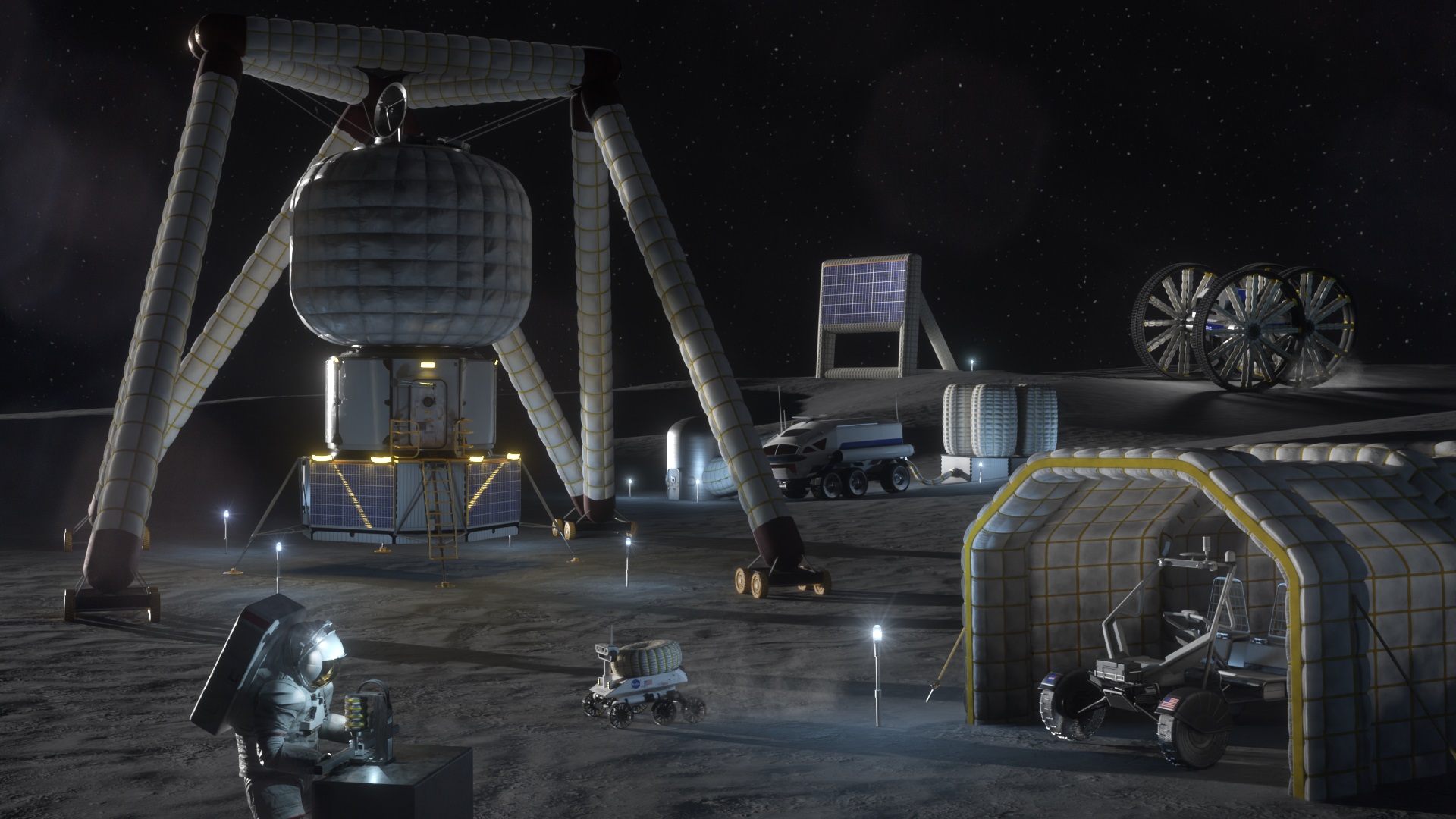

Every year, NASA’s Breakthrough, Innovative, and Game-Changing (BIG) Idea Challenge invites student innovators to build and demonstrate concepts that can benefit future human missions to the Moon and beyond. This year’s theme is “Inflatable Systems for Lunar Operations,” which could greatly reduce the mass and stowed volume of payloads sent to the Moon. This is critical for the Artemis Program as it returns astronauts to the Moon for the first time since the Apollo Era over fifty years ago. It will also reduce the costs of sending payloads to the Moon, Mars, and other deep-space destinations.
Continue reading “Balloon Animals and Bouncy Castles on the Moon. The Case for Inflatable Habitats”Some Lunar Regolith is Better for Living Off the Land on the Moon

Between now and the mid-2030s, multiple space agencies hope to send crewed missions to the Moon. of These plans all involve establishing bases around the Moon’s southern polar region, including the Artemis Base Camp and the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS). These facilities will enable a “sustained program of lunar exploration and development,” according to the NASA Artemis Program mission statement. In all cases, plans for building facilities on the surface call for a process known as In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU), where local resources are used as building materials.
This presents a bit of a problem since not all lunar soil (regolith) is well-suited for construction. Much like engineering and construction projects here on Earth, builders need to know what type of soil they are building on and if it can be used to make concrete. In a recent study, planetary scientist Kevin M. Cannon proposed a lunar soil classification scheme for space resource utilization. This could have significant implications for future missions to the Moon, where it would help inform the construction of bases, habitats, and other facilities based on soil type and location.
Continue reading “Some Lunar Regolith is Better for Living Off the Land on the Moon”This is a 3D-Printed Steel Floor Prototype for a Lunar Habitat
In this decade, multiple space agencies and commercial space entities will be taking us back to the Moon. But unlike the Apollo Era, the goal of these programs is not “footprints and flags,” but to establish the necessary infrastructure to keep going back. In particular, NASA, the ESA, Roscosmos, and China are all planning on establishing outposts that will allow for scientific research and a sustained human presence.
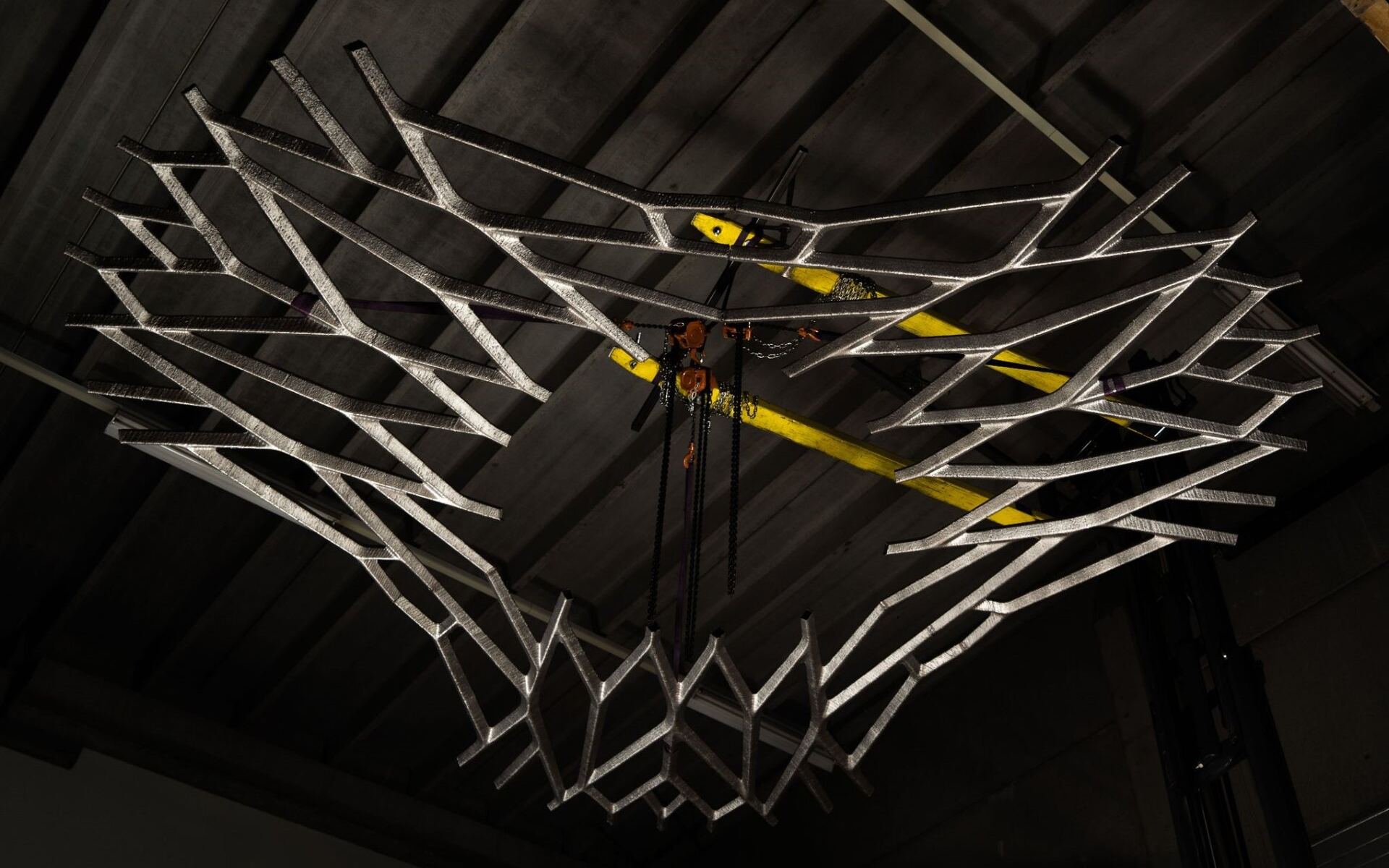
The ESA is currently showcasing what its outpost will look like at the 17th annual Architecture Exhibition at the La Biennale di Venezia museum in Venice. It’s known as the International Moon Village, which was designed by the architecture firm Skidmore, Owings & Merrill (SOM) with technical support from the ESA. This same company recently unveiled a prototype of the skeletal metal component that will one day be part of the Village’s lunar habitats.
Continue reading “This is a 3D-Printed Steel Floor Prototype for a Lunar Habitat”The Lunar Lantern Could be a Beacon for Humanity on the Moon
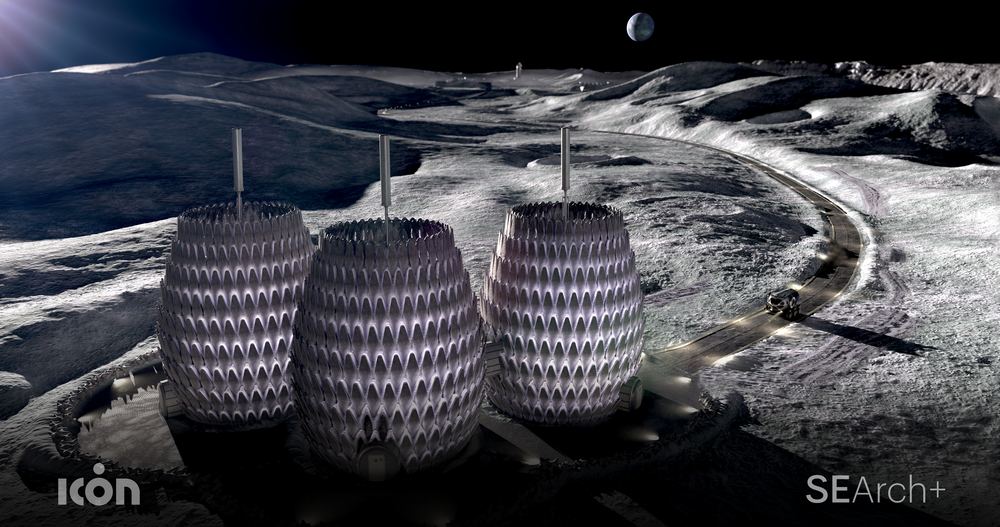
In October of 2024, NASA’s Artemis Program will return astronauts to the surface of the Moon for the first time since the Apollo Era. In the years and decades that follow, multiple space agencies and commercial partners plan to build the infrastructure that will allow for a long-term human presence on the Moon. An important part of these efforts involves building habitats that can ensure the astronauts’ health, safety, and comfort in the extreme lunar environment.
This challenge has inspired architects and designers from all over the world to create innovative and novel ideas for lunar living. One of these is the Lunar Lantern, a base concept developed by ICON (an advanced construction company based in Austin, Texas) as part of a NASA-supported project to build a sustainable outpost on the Moon. This proposal is currently being showcased as part of the 17th International Architecture Exhibition at the La Biennale di Venezia museum in Venice, Italy.
Continue reading “The Lunar Lantern Could be a Beacon for Humanity on the Moon”Orbital ATK Proposes Man-Tended Lunar-Orbit Outpost by 2020 for Link Up with NASA’s Orion
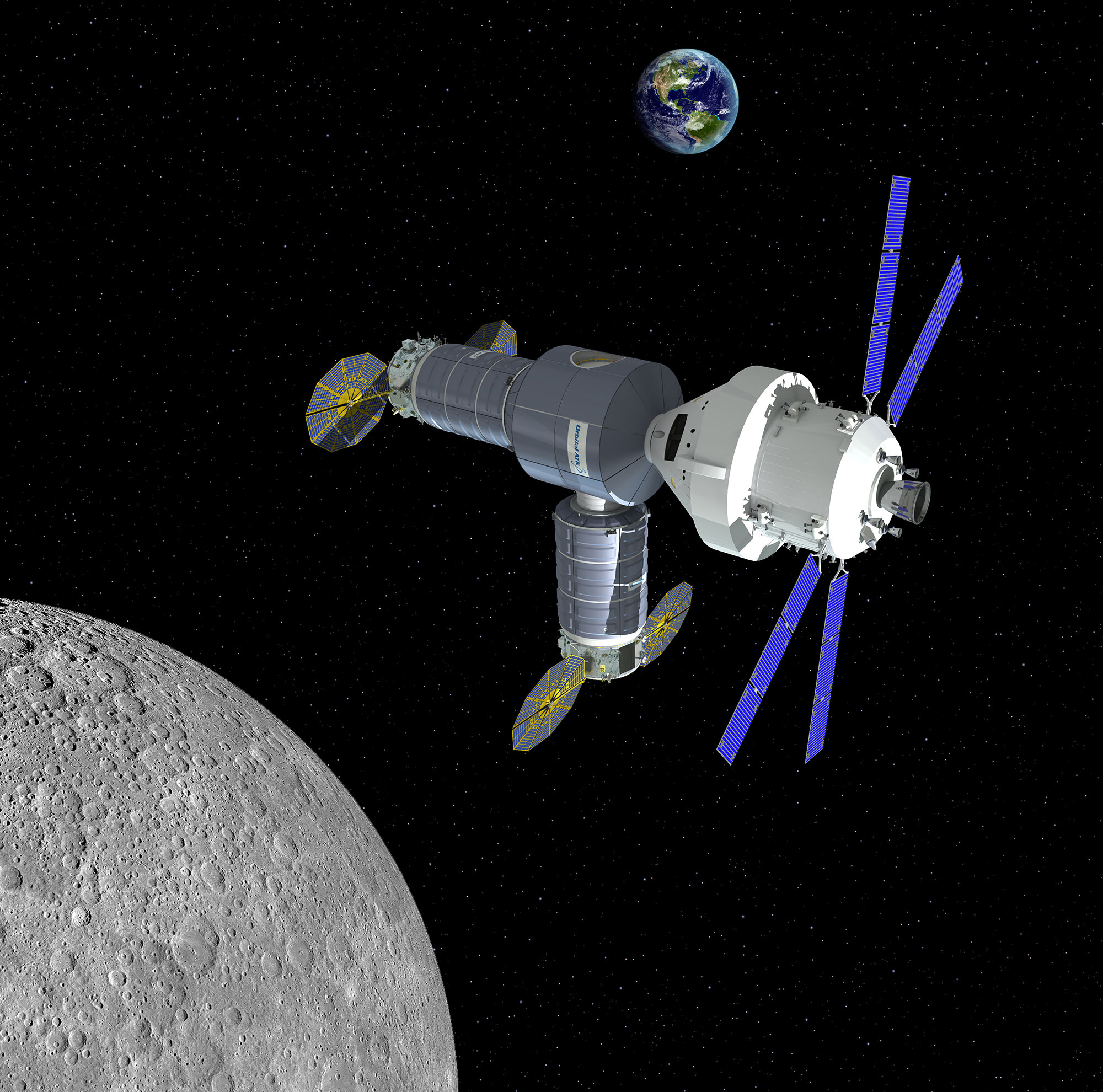

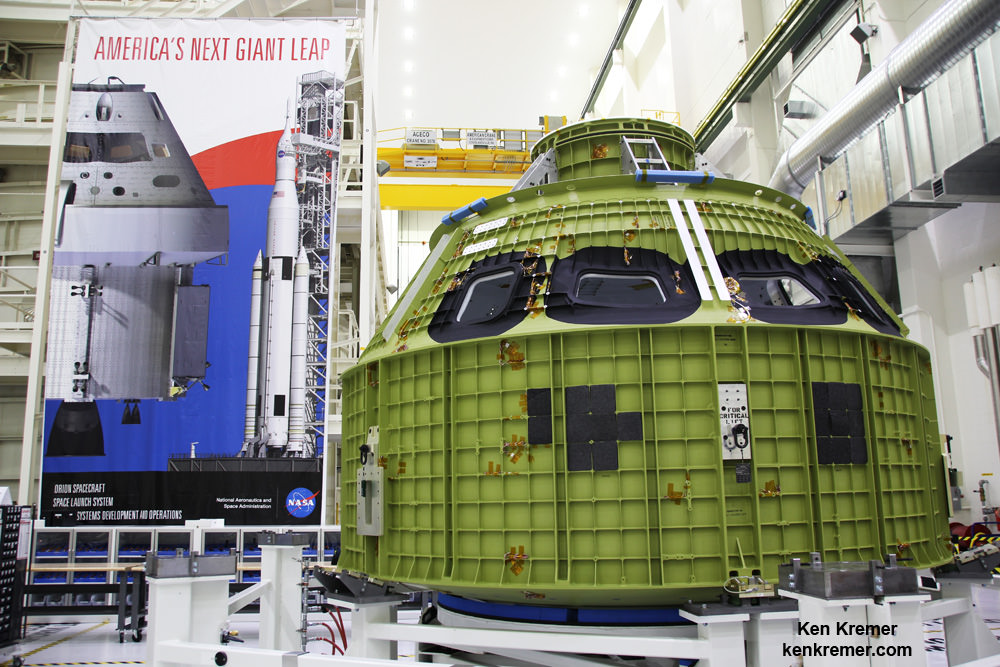
Orbital ATK has unveiled a practical new proposal to build a near term man-tended outpost in lunar orbit that could launch by 2020 and be operational in time for a lunar link-up with NASA’s Orion crew module during its maiden mission, when American astronauts finally return to the Moon’s vicinity in 2021 – thus advancing America’s next giant leap in human exploration of deep space.
The intrepid offer by Orbital could be carried out rather quickly because it utilizes an evolved version of the company’s already proven commercial Cygnus space station resupply freighter as “the building block … in cislunar space,” said Frank DeMauro, Orbital ATK Vice President for Human Spaceflight Systems, in an exclusive interview with Universe Today. See an artist concept in the lead image.
“Our Cygnus spacecraft is the building block to become a vehicle for exploration beyond low Earth orbit,” Orbital ATK’s Frank DeMauro told Universe Today.
“We are all about supporting NASA’s Mission to Mars. We feel that getting experience in cislunar space is critical to the buildup of the capabilities to go to Mars.”
NASA’s agency wide goal is to send astronauts on a ‘Journey to Mars’ in the 2030s – and expeditions to cislunar space in the 2020s serve as the vital ‘proving ground’ to fully develop, test out and validate the robustness of crucial technologies upon which the astronauts lives will depend on later Red Planet missions lasting some 2 to 3 years.
Orbital ATK’s lunar-orbit outpost proposal was announced at an official hearing of the US House of Representatives Subcommittee on Space on Wednesday, May 18, by former NASA Astronaut and Orbital ATK President of the Space Systems Group, Frank Culbertson.
“A lunar-orbit habitat will extend America’s leadership in space to the cislunar domain,” said Orbital ATK President of the Space Systems Group, Frank Culbertson.
“A robust program to build, launch and operate this initial outpost would be built on NASA’s and our international partners’ experience gained in long-duration human space flight on the International Space Station and would make use of the agency’s new Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion deep-space transportation system.”
The idea is to assemble an initial crew-tended habitat with pressurized work and living volume for the astronauts based on a Cygnus derived vehicle, and have it pre-positioned and functioning in lunar-orbit by 2020.
As envisioned by Orbital ATK, the habitat would be visited during NASA’s first manned mission of SLS and Orion to the Moon known as Exploration Mission-2 (EM-2).
The three week long EM-2 lunar test flight could launch as early as August 2021 – if sufficient funding is available.
The goals of EM-2 and following missions could be significantly broadened via docking with a lunar outpost. And Orion mission durations could be extended to 60 days.
NASA hopes to achieve a launch cadence for Orion/SLS of perhaps once per year.
Therefore autonomy and crew tended capability has to be built in to the lunar habitat right from the start – since crew visits would account for only a fraction of its time but enable vastly expanded science and exploration capabilities.
The initial lunar habitat envisioned by Orbital ATK would be comprised of two upgraded Cygnus pressurized vehicles – provisionally dubbed as Exploration Augmentation Modules (EAM). They would be attached to a multi-port docking module very similar in concept and design to the docking Nodes already flying in orbit as integral components of the ISS.

The lunar Cygnus vehicles would be upgraded from the enhanced cargo ships currently being manufactured and launched to the ISS.
“There are additional capabilities that we can put into the Cygnus module. We can make them longer and bigger so they can carry more logistics and carry more science,” DeMauro elaborated.
A variety of supplementary subsystems would also need to be enhanced.
“We looked at what systems we would need to modify to make it a long term habitation module. Since we would not be docked to the ISS, we would need our own Environmental Control and Life Support Systems (ECLSS) out at lunar orbit to support the crew.”
“The service module would also need to be improved due to the high radiation environment and the longer time.”
“We also need to look at the thermal protection subsystem, radiation protection subsystem and power subsystems to support the vehicle for many years as opposed to the short time spent at the ISS. More power is also needed to support more science. We also need a propulsion system to get to the Moon and maintain the vehicle.”
“All that work is getting looked at now – to determine what we need to modify and upgrade and how we would do all that work,” DaMauro told me.
The habitat components would be launched to the Moon on a commercial launch vehicle.
High on the list of candidate launchers would be the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket which recently already successfully delivered two Cygnus cargo ships to the ISS in Dec. 2015 and March 2016.
Other potential boosters include the ULA Delta IV and even ESA’s Ariane V as a way to potentially include international participation.

The habitat components could be manufactured and launched about three years after getting a ‘Go Ahead’ contract from NASA.
Orbital ATK already has an established production line flowing to manufacture a steady stream of Cygnus cargo freighters to fulfill their NASA commercial resupply contract with NASA for the ISS – accumulating know how and cost reduction efficiencies.
“Since many aspects of operations in deep space are as yet untested, confidence must be developed through repeated flights to, and relatively long-duration missions in, cislunar space,” says Culbertson.
“Orbital ATK continues to operate our Cygnus cargo logistics vehicle as a flagship product, so we are ready to quickly and affordably implement an initial Cygnus-derived habitat in cislunar space within three years of a go-ahead.”
Over time, the outpost could be expanded with additional habitat and research modules delivered by Orion/SLS, commercial or international rockets. Perhaps even Bigelow expandable commercial modules could be added later.
Cygnus is suitable for wide ranging science experiments and gear. It could also launch cubesats – like the current Cygnus berthed at the ISS is equipped with a cubesat deployer.
Potential lunar landers developed by international partners could dock at the cislunar habitats open docking ports in between surface science forays.
“We are doing science now on Cygnus and we would expect to carry along science experiments on the new Cygnus vehicle. The vehicle is very attractive to science experiments,” DeMauro explained.
“There really is no limit to what the outpost could become.”
“What we put out is very exciting,” DeMauro noted.
“As a company we are looking forward to working in this arena. Our suggested plans are in line with where NASA wants to go. And we think we are the right company to play a big part in that!”
By incorporating commercial companies and leveraging the considerable technology development lessons learned from Cygnus, NASA should realize significant cost savings in implementing its human exploration strategy. Although Orbital ATK is not divulging a cost estimate for the lunar habitat at this time, the cost savings from a commercial partner should be considerable. And the 3 year time frame to launch is very attractive.
Orion is designed to send astronauts deeper into space than ever before, including missions to the Moon, asteroids and the Red Planet. Cygnus derived modules and/or other augmenting hardware components will be required to carry out any round trip human missions to the Martian surface.
NASA is now building the next Orion capsule at the Kennedy Space Center. It will launch unpiloted atop the first SLS rocket in late 2018 on the EM-1 mission.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.