Hey, how ’bout that annular eclipse last week? Some great images flooded in to Universe Today, as the final solar eclipse for 2016 graced the African continent. This not only marked the start of the second and final eclipse season for 2016, but it also set us up for the final eclipse of the year next week.
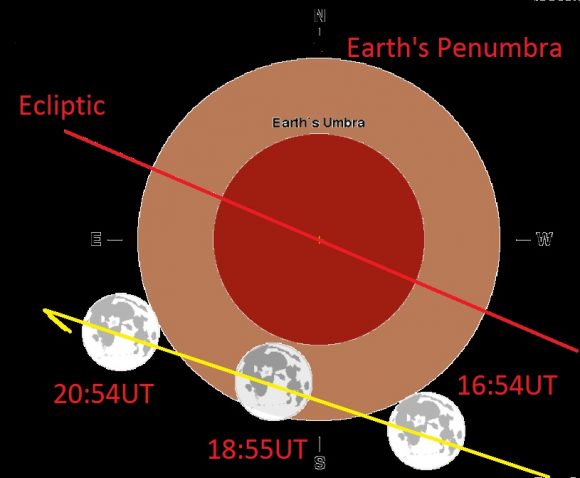
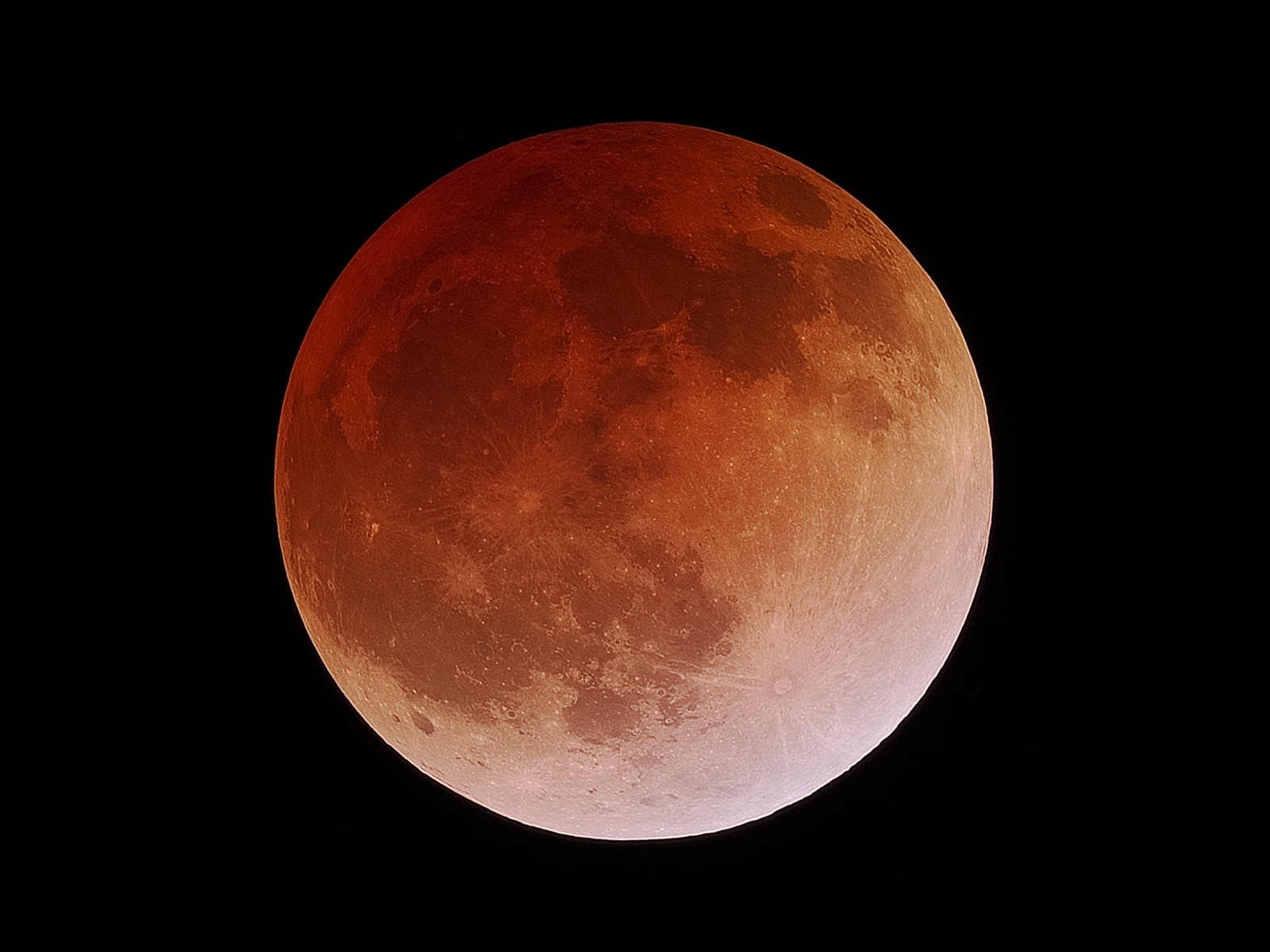
We’re talking about the penumbral lunar eclipse coming up next week on September 16th, 2016. this sort of eclipse occurs when the Moon just misses the dark inner core (umbra) of the Earth’s shadow, and instead, drifts through its relatively bright outer cone, known as the penumbra. Though not the grandest show as eclipses go, astute observers should notice a subtle light tea-colored shading of the Full Moon, and perhaps the ragged dark edge of the umbra on the northwestern limb of the Moon as it brushes by around mid-eclipse.
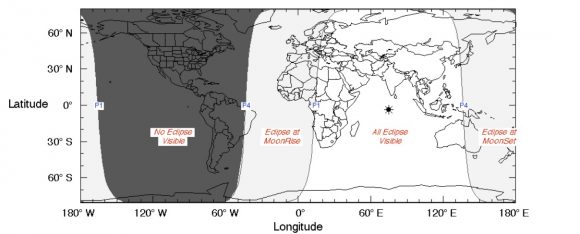
The entirety of the eclipse will be visible from the region surrounding the Indian Ocean on the evening of Friday, September 6th. Viewers in Australia, New Zealand and Japan will see the eclipse transpire at moonset, and the eclipse will get underway at moonrise for observers in western Africa and Europe.
The eclipse runs from first contact at 16:55 Universal Time (UT) to 20:54 UT when the Moon quits the Earth’s shadow almost four hours later. Mid-eclipse occurs at 18:55 UT, with the Moon 91% immersed in the Earth’s outer shadow.
Tales of the Saros
This particular eclipse is member 9 of the 71 lunar eclipses in saros series 147. This saros began on July 2nd 1890 and runs through to the final eclipse in the cycle on May 1st 2990. It will produce its very first partial eclipse next time around on September 28th 2034, and its first total lunar eclipse on June 6th, 2449.
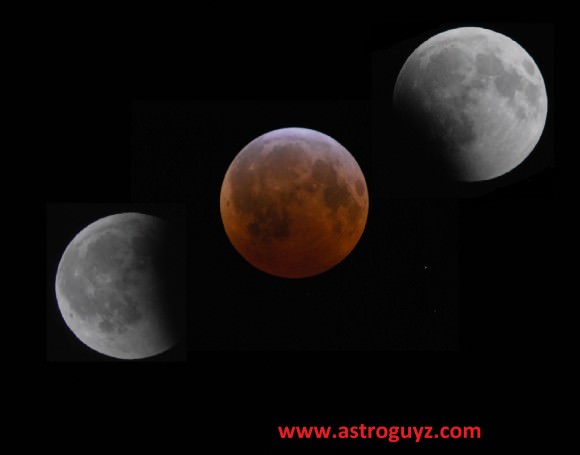
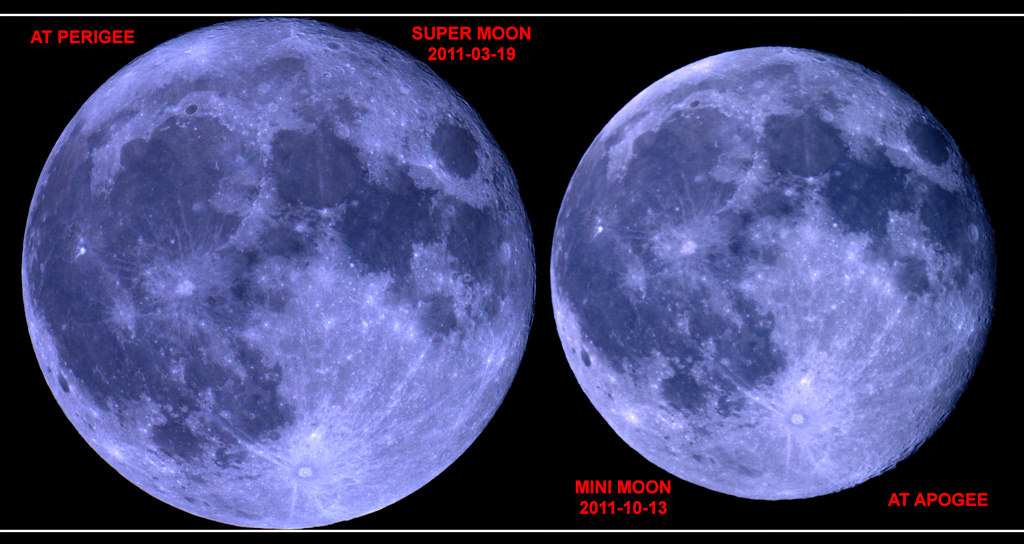
Why penumbrals? Aren’t they the ultimate non-event when it comes to eclipses? Like with much of observational astronomy, a penumbral lunar eclipse pushes our skills as a visual athlete to the limit. Check out the waxing gibbous Moon the night before the eclipse, then the Moon the night of the event. If you didn’t know any better, could you tell the difference from one night to the next? Often, the camera can see what the eye can’t. Photographing the Moon before, during and after a penumbral eclipse will often bring out the subtle shading on post-comparison. You’ll want to photograph the Moon when its high in the sky and free of atmospheric distortion low to the horizon, which tends to discolor the Moon. Such a high-flying Moon during mid-eclipse favors the Indian Subcontinent this time around. We’ve yet to see a good convincing time-lapse documenting a penumbral eclipse, though such a feat is certainly possible.

When is an eclipse… not an eclipse? By some accounts, the Moon underwent a very shallow penumbral one cycle ago on August 18th, 2016, though the brush past the shadow was so slight that many lists, including the NASA’s GSFC eclipse page omitted it. Three eclipses (a lunar partial and a penumbral, or two penumbrals and one solar) can occur in one eclipse season, if the nodes of the Moon’s orbit where it intersects the ecliptic fall just right. This last occurred in 2013, and will happen again in 2020.
And when there’s a lunar eclipse, there’s also a Full Moon. The September Full Moon is the Harvest Moon, providing a few extra hours of illumination to get the crops in. This year, the Harvest Moon falls just six days from the equinox on September 22nd, marking the start of astronomical Fall in the northern hemisphere and Spring in the southern. The relative ecliptic angle also ensures that moonrise only slides back by a slight amount each evening for observers in mid-northern latitudes around the Harvest Moon.
Can’t wait til the next eclipse? Well, 2017 has four of ’em: an annular on February 26th favoring South America, two lunars (another penumbral on February 11th and a partial on August 7th) and oh yeah, there’s a total solar eclipse crossing the United States on August 21st. And the next total lunar eclipse? The dry spell is broken on January 31st, 2018, when a total lunar eclipse favoring the Pacific Rim occurs. Yeah, we got spoiled with four back-to-back lunar eclipses during the Blood Moon tetrad of 2014-2015…
Read Dave Dickinson’s eclipse-fueled sci-fi tales Exeligmos, Shadowfall, The Syzygy Gambit and Peak Season.