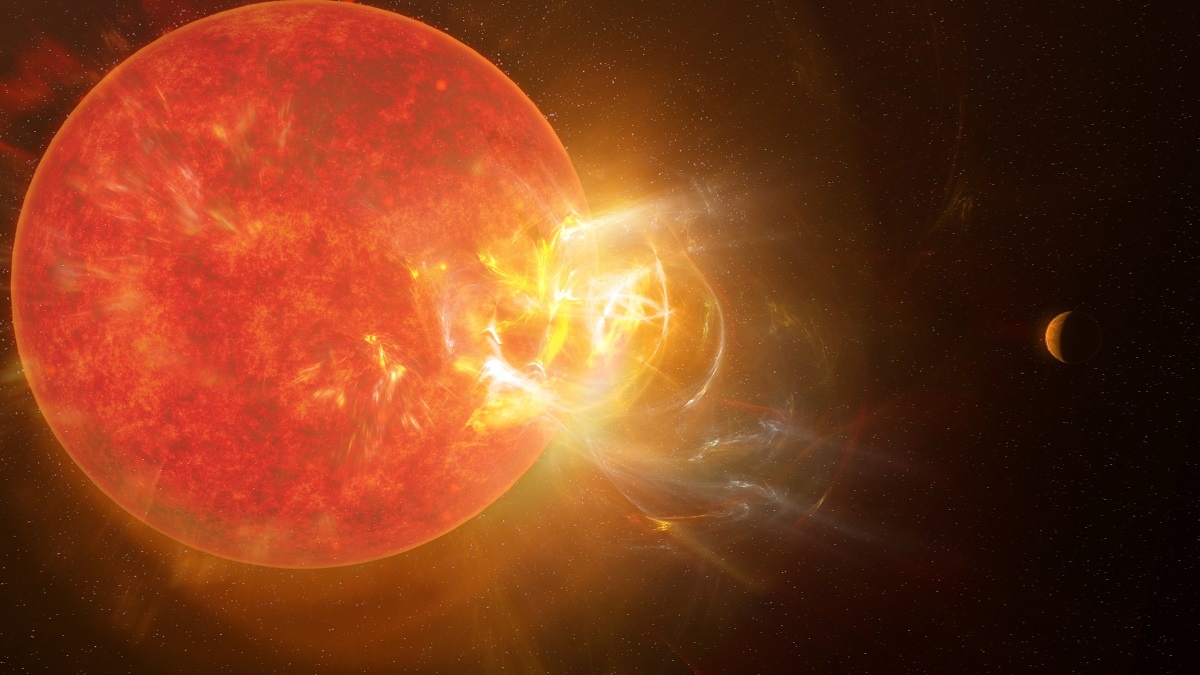
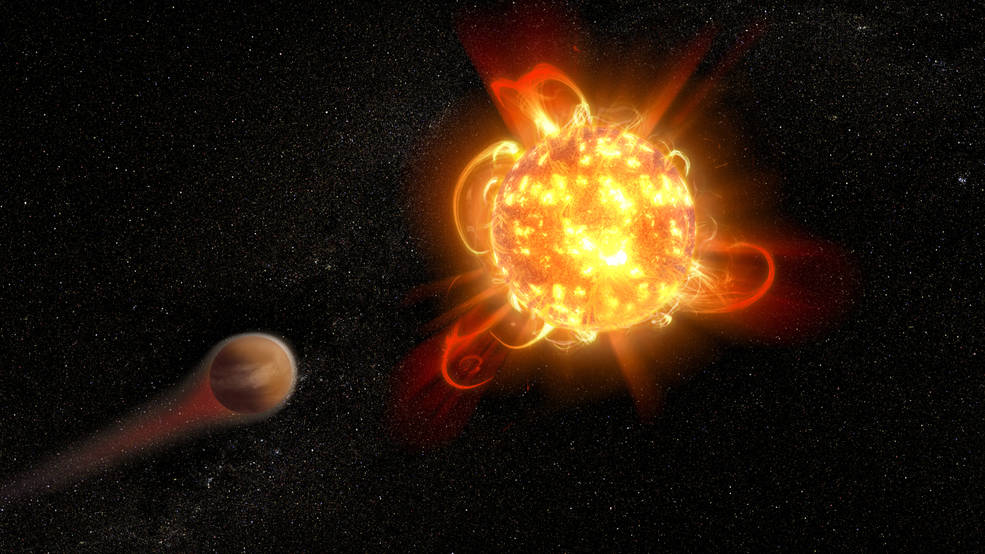
Photosynthesis changed Earth in powerful ways. When photosynthetic organisms appeared, it led to the Great Oxygenation Event. That allowed multicellular life to evolve and resulted in the ozone layer. Life could venture onto land, protected from the Sun’s intense ultraviolet radiation.
But Earth’s photosynthetic organisms evolved under the Sun’s specific illumination. How would plants do under other stars?
Continue reading “Plants Would Still Grow Well Under Alien Skies”