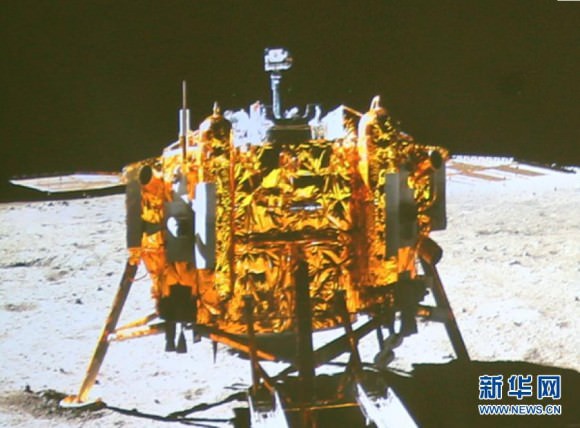
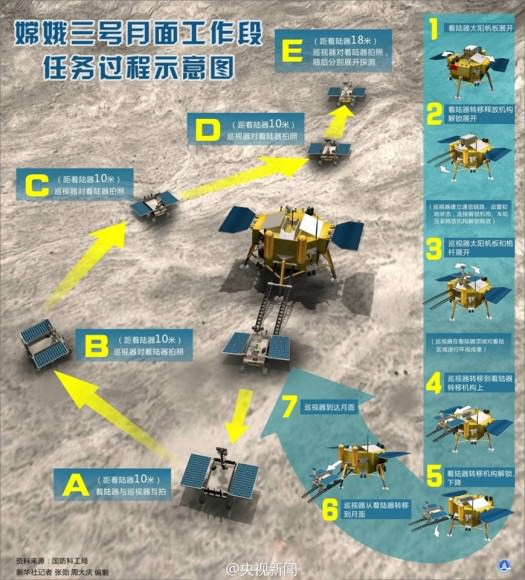
Chang’e-3 lander and Yutu rover – from Above And Below
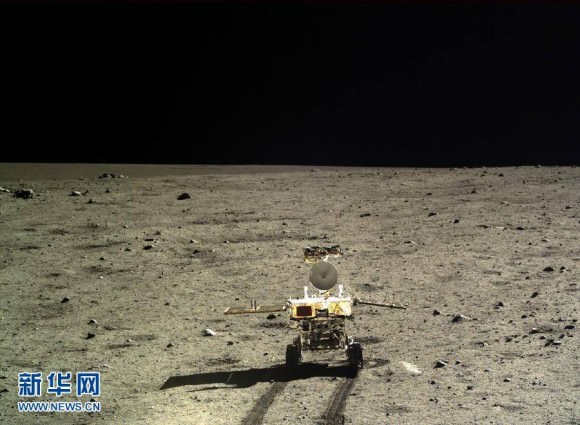
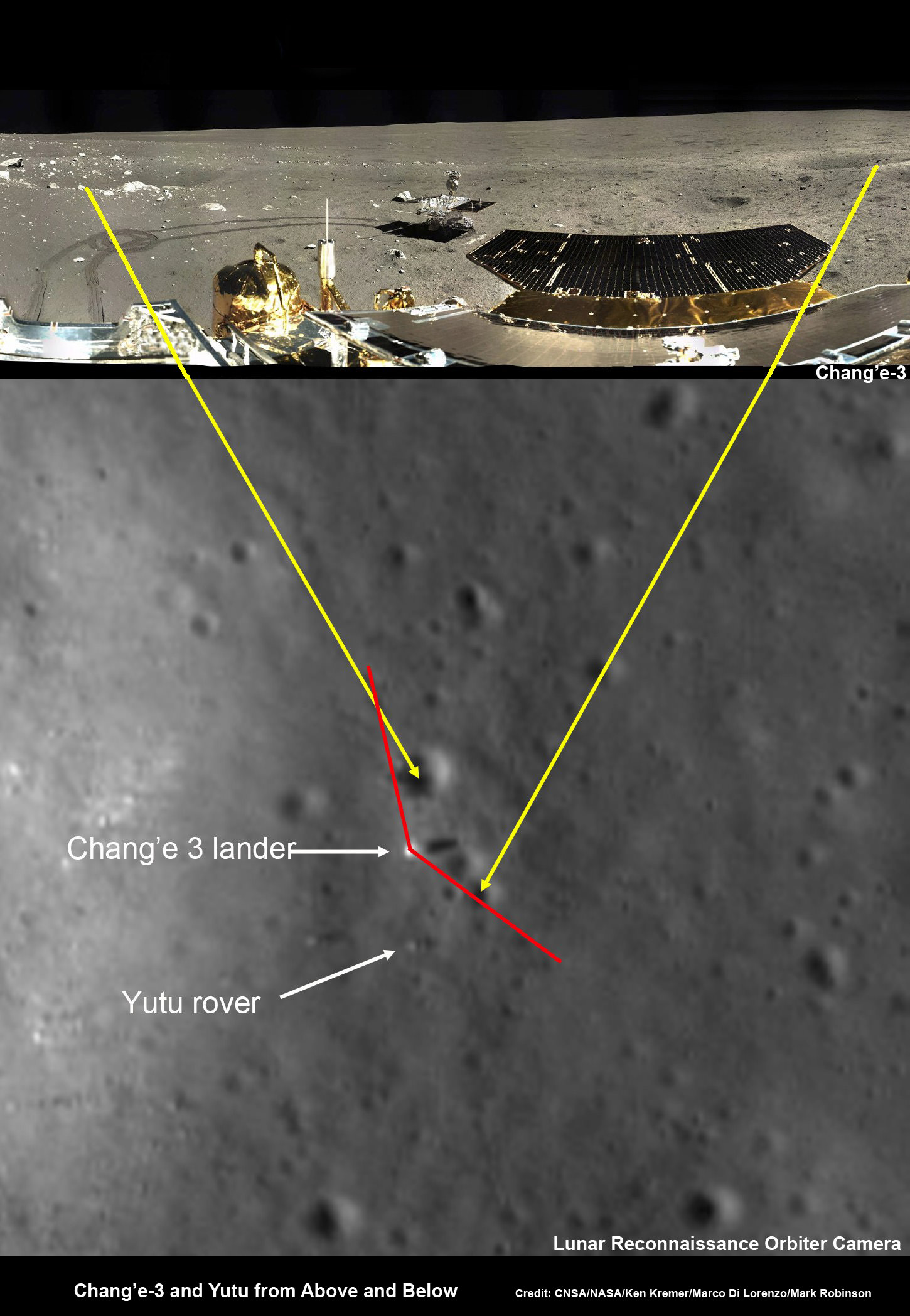
Composite view shows China’s Chang’e-3 lander and Yutu rover from Above And Below (orbit and surface) – lander color panorama (top) and orbital view from NASA’s LRO orbiter (bottom). Chang’e-3 lander color panorama shows Yutu rover after it drove down the ramp to the moon’s surface and began driving around the landers right side to the south. Yellow lines connect craters seen in the lander panorama and the LROC image from LRO (taken at a later date after the rover had moved), red lines indicate approximate field of view of the lander panorama. Credit: CNSA/NASA/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo/Mark Robinson
See further composite and panorama views below
Story updated
See our Yutu timelapse pano at NASA APOD Feb. 3, 2014: http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap140203.html[/caption]
China’s Chang’e-3 lander and Yutu moon rover have been imaged from above and below – in one of those rare, astounding circumstances when space probes from Earth are exploring an extraterrestrial body both from orbit and the surface. And it’s even more amazing when these otherworldly endeavors just happen to overlap and involve actual work in progress to expand human knowledge of the unknown.
And it’s even rarer, when those images stem from active space probes built by two different countries on Earth.
Well by combining imagery from America’s space agency, NASA, and China’s space agency, CNSA, we are pleased to present some breathtaking views of ‘Chang’e-3 and the Yutu rover from Above and Below.’
Check out our composite mosaic (above) combining the view from the Moon’s orbit snapped by the hi res camera aboard NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) with our new color panoramas from the Moon’s surface, compiling imagery from the landing site of China’s Chang’e-3 lander – with Yutu in transit in mid-Dec. 2013 soon after the successful touchdown.
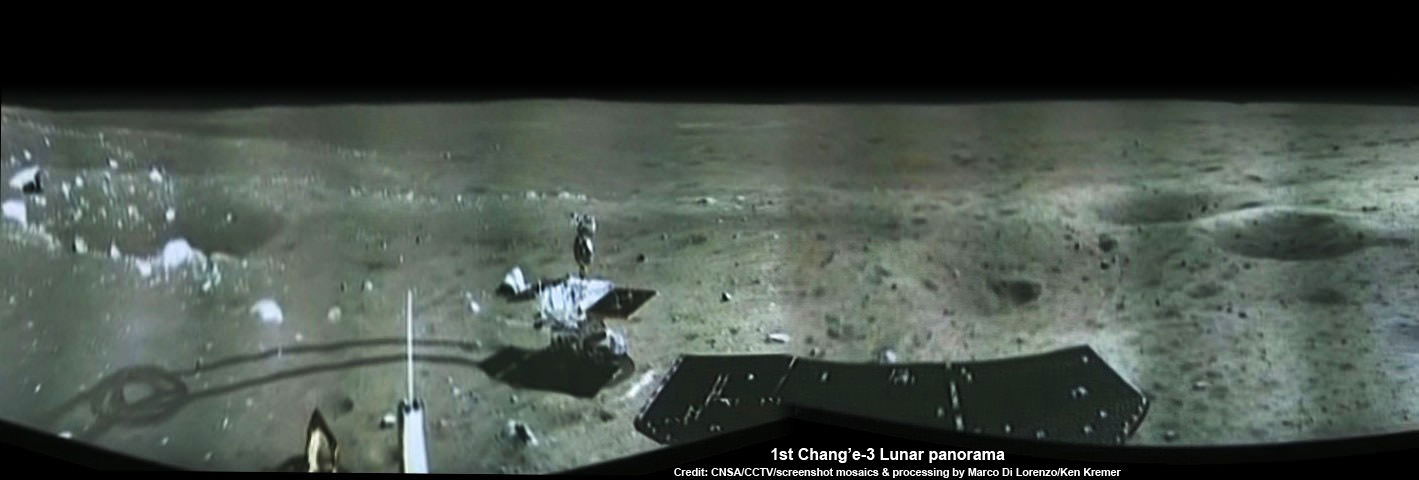
See below an earlier composite mosaic using the first black and white panorama from the Chang’e-3 Moon lander.
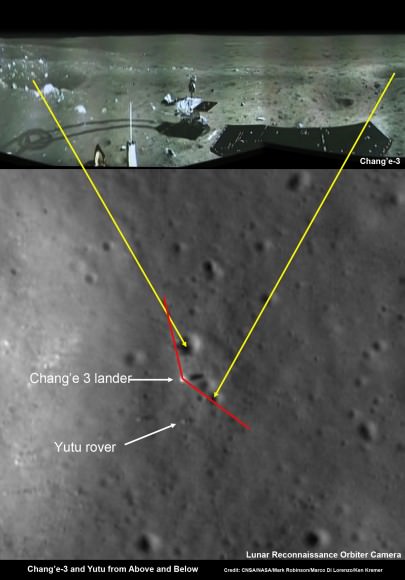
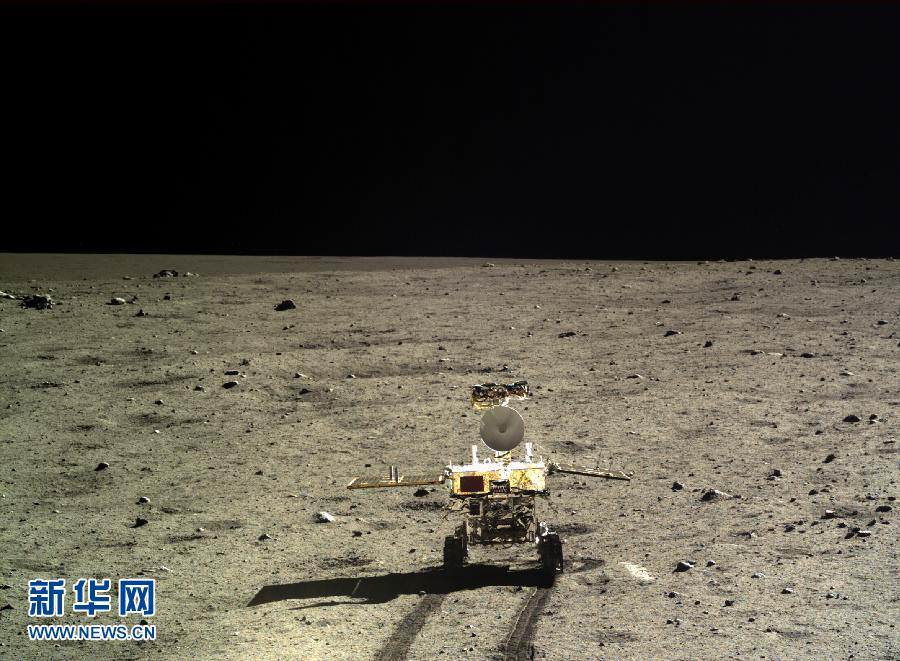
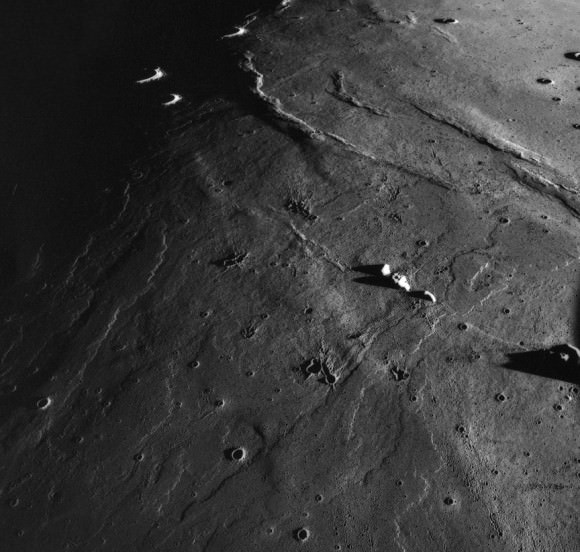
Composite view shows China’s Chang’e-3 lander and Yutu rover from Above And Below (orbit and surface) – lander panorama (top) and orbital view from NASA’s LRO orbiter (bottom). Chang’e-3 lander B/W panorama from camera shows Yutu rover after it drove down the ramp to the moon’s surface and began driving around the landers right side to the south. Yellow lines connect craters seen in the lander panorama and the LROC image from LRO (taken at a later date after the rover had moved), red lines indicate approximate field of view of the lander panorama. Credit: CNSA/NASA/Mark Robinson/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer – kenkremer.com
The composite mosaic combines the efforts of Mark Robinson, Principal Investigator for the LRO camera, and the imaging team of Ken Kremer and Marco Di Lorenzo.
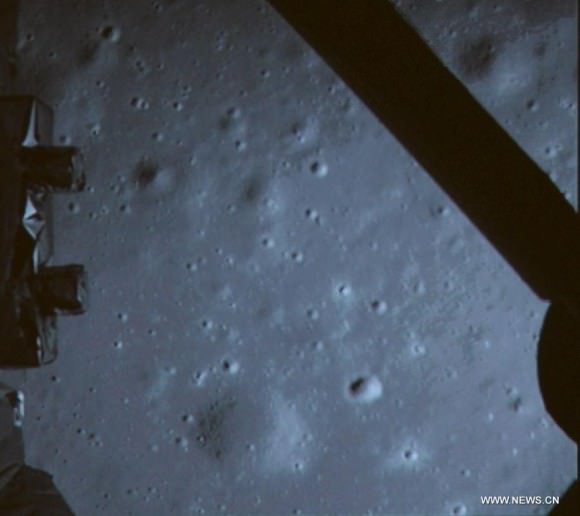
On Christmas eve, Dec. 24, 2013, NASA’s LRO captured it’s first images of China’s Chang’e-3 lander and Yutu moon rover – barely 10 days after the history making touchdown on Mare Imbrium (Sea of Rains) and just 60 meters east of the rim of a 450 meter diameter impact crater.
LRO was orbiting about 150 kilometers above Chang’e-3 and Yutu when the highest resolution orbital image was taken on 24 December 22:52:49 EST (25 December 03:52:49 UT).
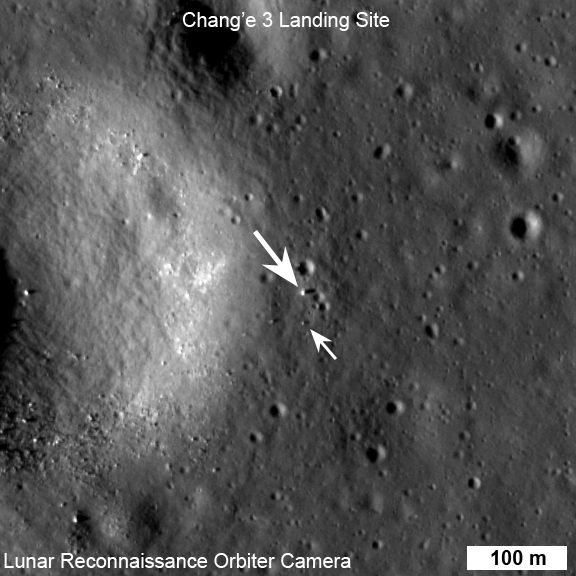

The orbital imagery was taken by the LRO orbiters high resolution Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC) – specifically the narrow angle camera (NAC).
See below my pre-launch cleanroom photo of LRO and the LROC cameras and other science instruments.
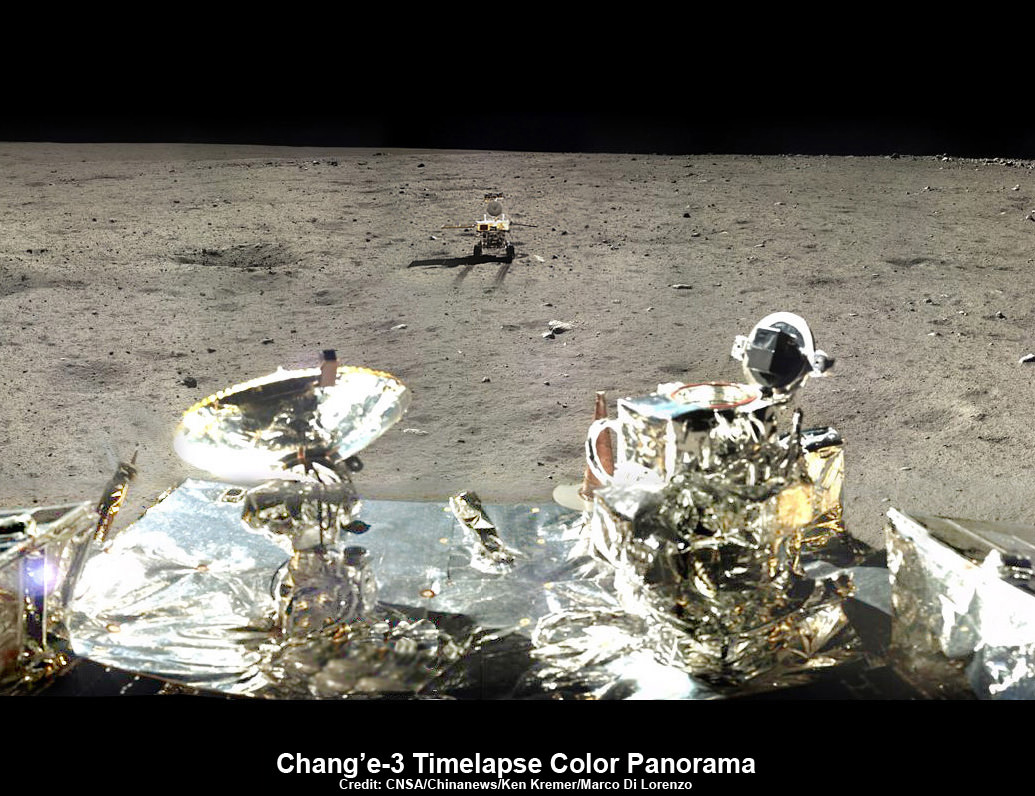
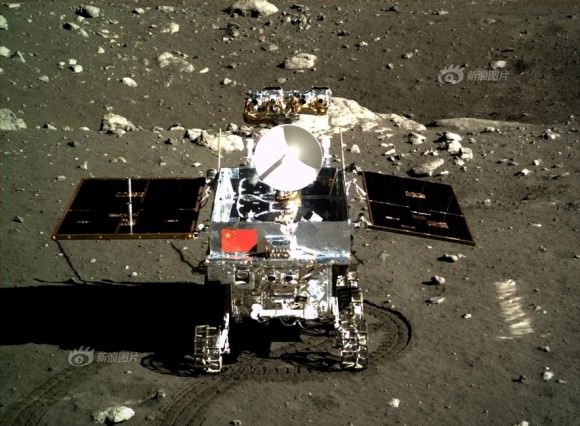
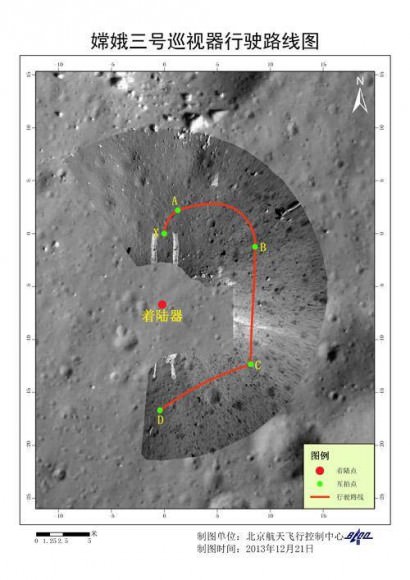
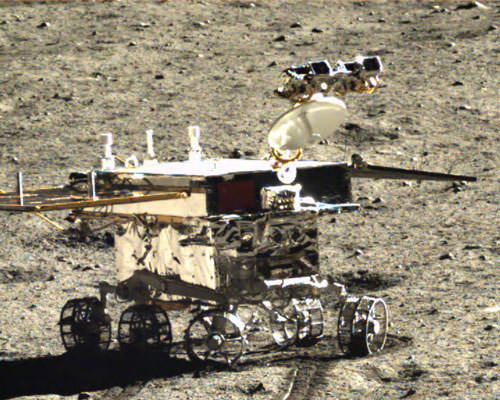
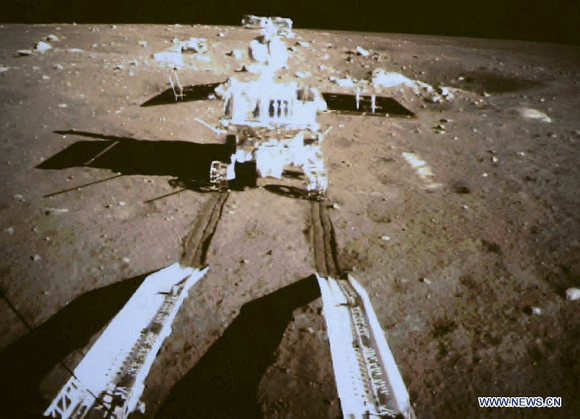
The Chang’e-3 lander color panorama shows the Yutu rover after it drove down the ramp to the moon’s surface and began driving a significant distance around the landers right side on its journey heading southwards.

This 1st color panorama from Chang’e-3 lander shows the view all around the landing site after the ‘Yutu’ lunar rover left impressive tracks behind when it initially rolled all six wheels onto the pockmarked and gray lunar terrain on Dec. 15, 2013. Mosaic Credit: CNSA/Chinanews/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo – kenkremer.com
Yellow lines connect craters seen in the lander panorama to those seen in the LROC hi res NAC image from LRO, in the composite view.
Robinson identified the lunar craters and determined the field of view on the LROC image.
The LRO image was taken at a later date (on Christmas eve) after the rover had already moved. Red lines on the orbital image indicate the approximate field of view of what is seen in the Chang’e-3 lander panorama.
Although Yutu is only about 150 cm wide – which is the same as the pixel size – it shows up in the NAC images for two reasons.
“The solar panels are very effective at reflecting light so the rover shows up as two bright pixels, and the Sun is setting thus the rover casts a distinct shadow (as does the lander),” says NASA in a statement.
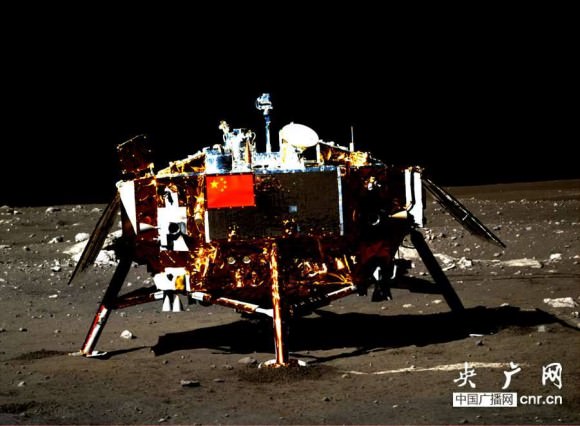
In a historic first for China, the Chang’e-3 spacecraft safely touched down on the Moon at Mare Imbrium near the Bay of Rainbows nearly seven weeks ago on Dec. 14, 2013.
Seven hours later, the piggybacked 140 kg Yutu robot drove off a pair of ramps, onto the Moon and into the history books.
Yutu was about 10 meters away from the 1200 kg stationary lander when the lander panoramic images were taken.
The lander and Yutu were just completing their 1st Lunar Day of explorations when the LROC images were taken, and entered their first period of hibernation soon thereafter on Dec. 25 (Christmas Day) and Dec 26 respectively coinciding with the start of their 1st Lunar Night.
Both spacecraft awoke and functioned well during their 2nd Lunar Day, which just ended.
However, Yutu’s future mission is now in jeopardy following a serious mechanical anomaly this past weekend as both vehicles entered their 2nd hibernation period.
Apparently one of the solar panels did not fold back properly – perhaps due to dust accumulation – and its instruments may not survive.
Read my full story for complete details – here.
Yutu’s fate will remain unknown until the 3rd Lunar Day starts around Feb. 8 or 9.
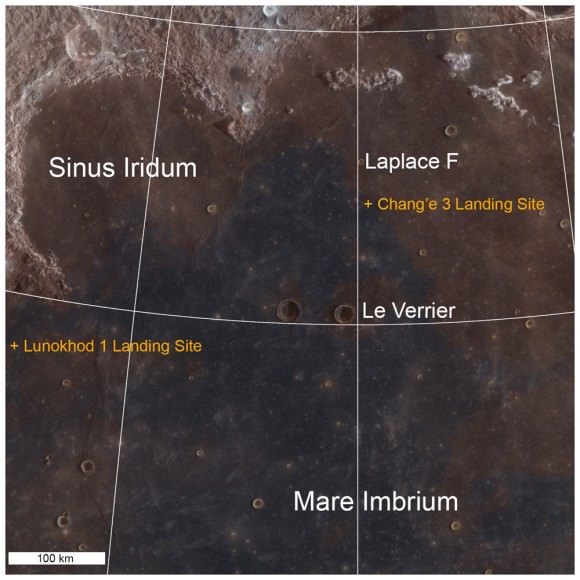
So, What’s the terrain like at the Mare Imbrium landing site?
Chang’e-3 landed on a thick deposit of volcanic material.
“A large scale wrinkle ridge (~100 km long, 10 km wide) cuts across the area and was formed as tectonic stress caused the volcanic layers to buckle and break along faults. Wrinkle ridges are common on the Moon, Mercury and Mars,” says Robinson.
“The landing site is on a blue mare (higher titanium) thought to be about 3.0 billion years old.”
Older red mare about from 3.5 billion years is only 10 km to the north, he notes.
See our Chang’e-3 color panoramas now featured at NBC News and Space.com
China is only the 3rd country in the world to successfully soft land a spacecraft on Earth’s nearest neighbor after the United States and the Soviet Union.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Chang’e-3, Orion, Orbital Sciences, SpaceX, commercial space, LADEE, Mars and more news.