Ever since Musk founded SpaceX is 2002, with the intention of eventually colonizing Mars, every move he has made has been the subject of attention. And for the past two years, a great deal of this attention has been focused specifically on the development of the Falcon Heavy rocket and the Dragon 2 capsule – the components with which Musk hopes to mount a lander mission to Mars in 2018.
Among other things, there is much speculation about how much this is going to cost. Given that one of SpaceX’s guiding principles is making space exploration cost-effective, just how much money is Musk hoping to spend on this important step towards a crewed mission? As it turns out, NASA produced some estimates at a recent meeting, which indicated that SpaceX is spending over $300 million on its proposed Mars mission.
These estimates were given during a NASA Advisory Council meeting, which took place in Cleveland on July 26th between members of the technology committee. During the course of the meeting, James L. Reuter – the Deputy Associate Administrator for Programs at NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate – provided an overview of NASA’s agreement with SpaceX, which was signed in December of 2014 and updated this past April.

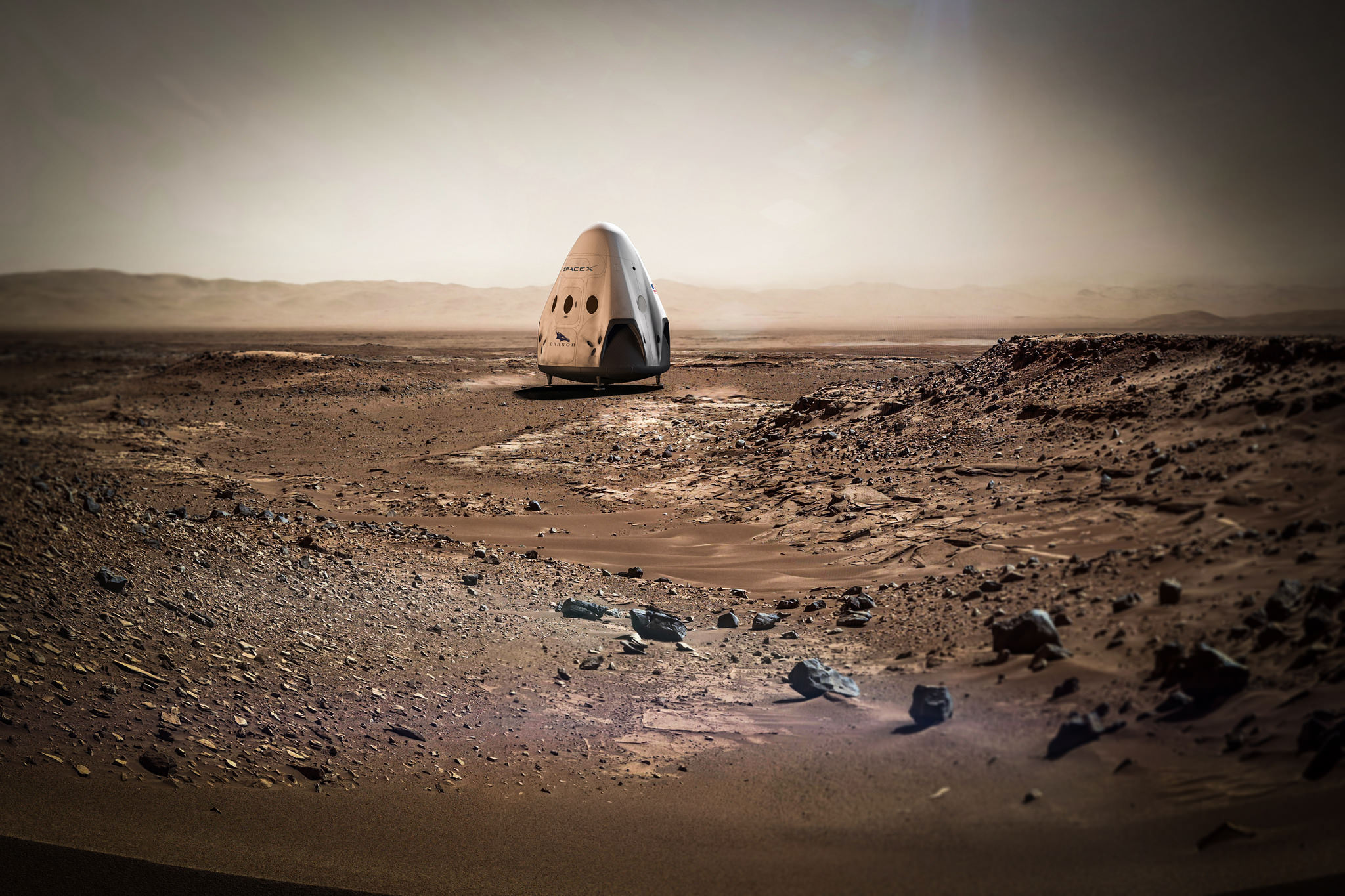
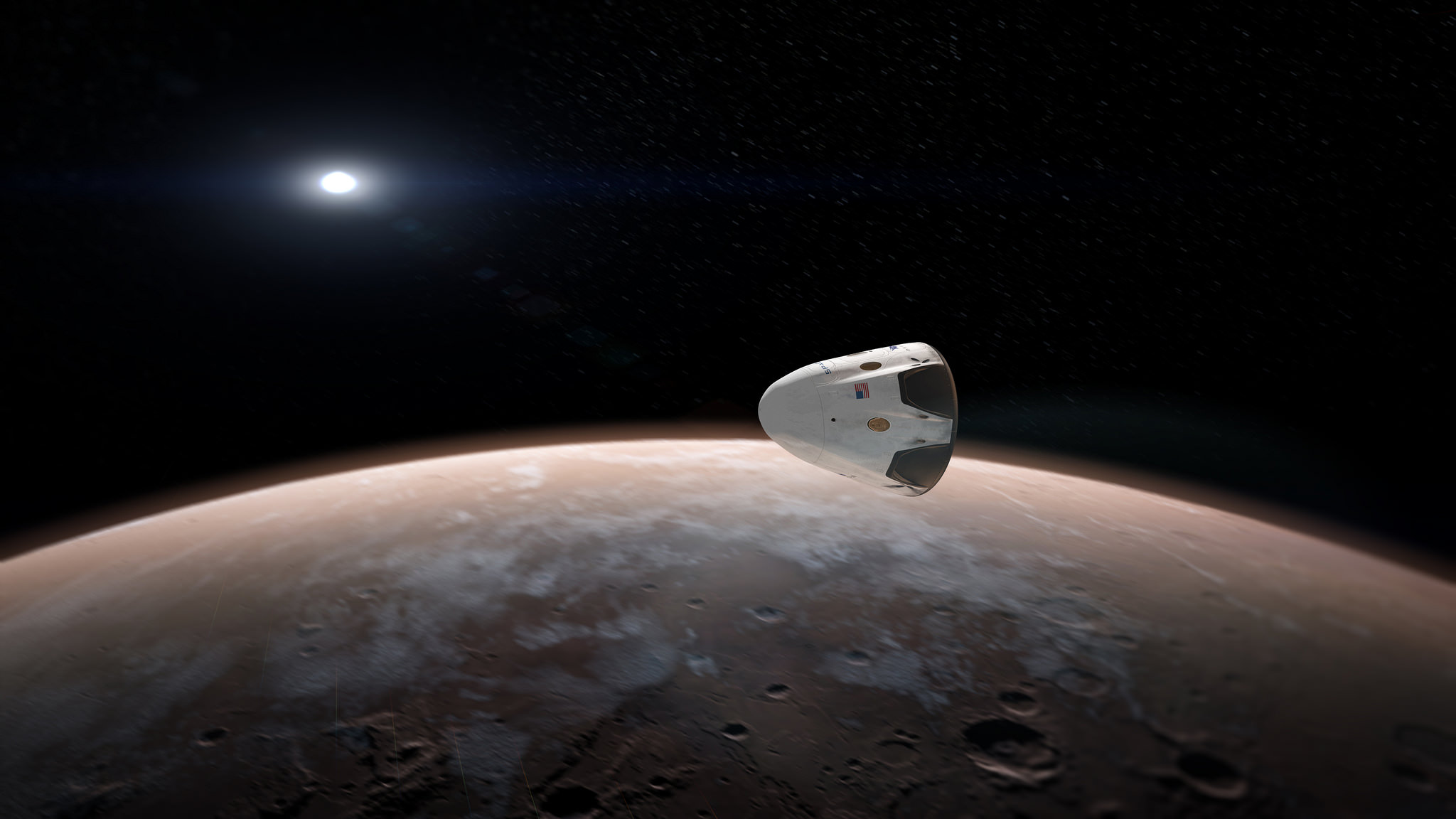
In accordance with this agreement, NASA will be providing support for the company’s plan to send an uncrewed Dragon 2 capsule (named “Red Dragon”) to Mars by May of 2018. Intrinsic to this mission is the plan to conduct a propulsive landing on Mars, which would test the Dragon 2‘s SuperDraco Descent Landing capability. Another key feature of this mission will involve using the Falcon Heavy to deploy the capsule.
The terms of this agreement do not involve the transfer of funds, but entails active collaboration that would be to the benefit parties. As Reuters indicated in his presentation, which NASA’s Office of Communications shared with Universe Today via email (and will be available on the STMD’s NASA page soon):
“Building on an existing no-funds-exchanged collaboration with SpaceX, NASA is providing technical support for the firm’s plan to attempt to land an uncrewed Dragon 2 spacecraft on Mars. This collaboration could provide valuable entry, descent and landing (EDL) data to NASA for our journey to Mars, while providing support to American industry. We have similar agreements with dozens of U.S. commercial, government, and non-profit partners.”
Further to this agreement is NASA’s commitment to a budget of $32 million over the next four years, the timetable of which were partially-illustrated in the presentation: “NASA will contribute existing agency resources already dedicated to [Entry, Descent, Landing] work, with an estimated value of approximately $32M over four years with approximately $6M in [Fiscal Year] 2016.”
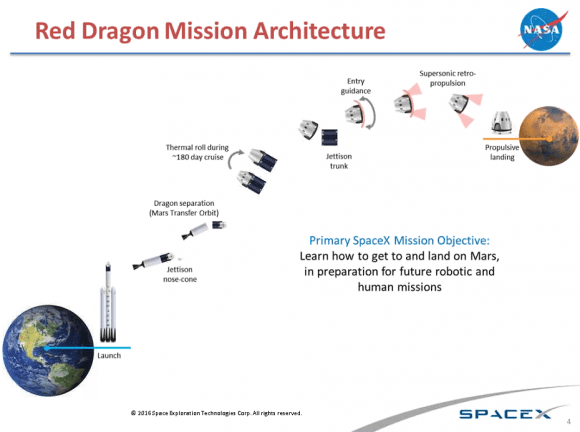
According to Article 21 of the Space Act Agreement between NASA and SpaceX, this will include providing SpaceX with: “Deep space communications and telemetry; Deep space navigation and trajectory design; Entry, descent and landing system analysis and engineering support; Mars entry aerodynamic and aerothermal database development; General interplanetary mission advice and hardware consultation; and planetary protection consultation and advice.”
For their part, SpaceX has not yet disclosed how much their Martian mission plan will cost. But according to Jeff Foust of SpaceNews, Reuter provided a basic estimate of about $300 million based on a 10 to 1 assessment of NASA’s own financial commitment: “They did talk to us about a 10-to-1 arrangement in terms of cost: theirs 10, ours 1,” said Reuter. “I think that’s in the ballpark.”
As for why NASA has chosen to help SpaceX make this mission happen, this was also spelled out in the course of the meeting. According to Reuter’s presentation: “NASA conducted a fairly high-level technical feasibility assessment and determined there is a reasonable likelihood of mission success that would be enhanced with the addition of NASA’s technical expertise.”
Such a mission would provide NASA with valuable landing data, which would prove very useful when mounting its crewed mission in the 2030s. Other items discussed included NASA-SpaceX collaborative activities for the remainder of 2016 – which involved a “[f]ocus on system design, based heavily on Dragon 2 version used for ISS crew and cargo transportation”.

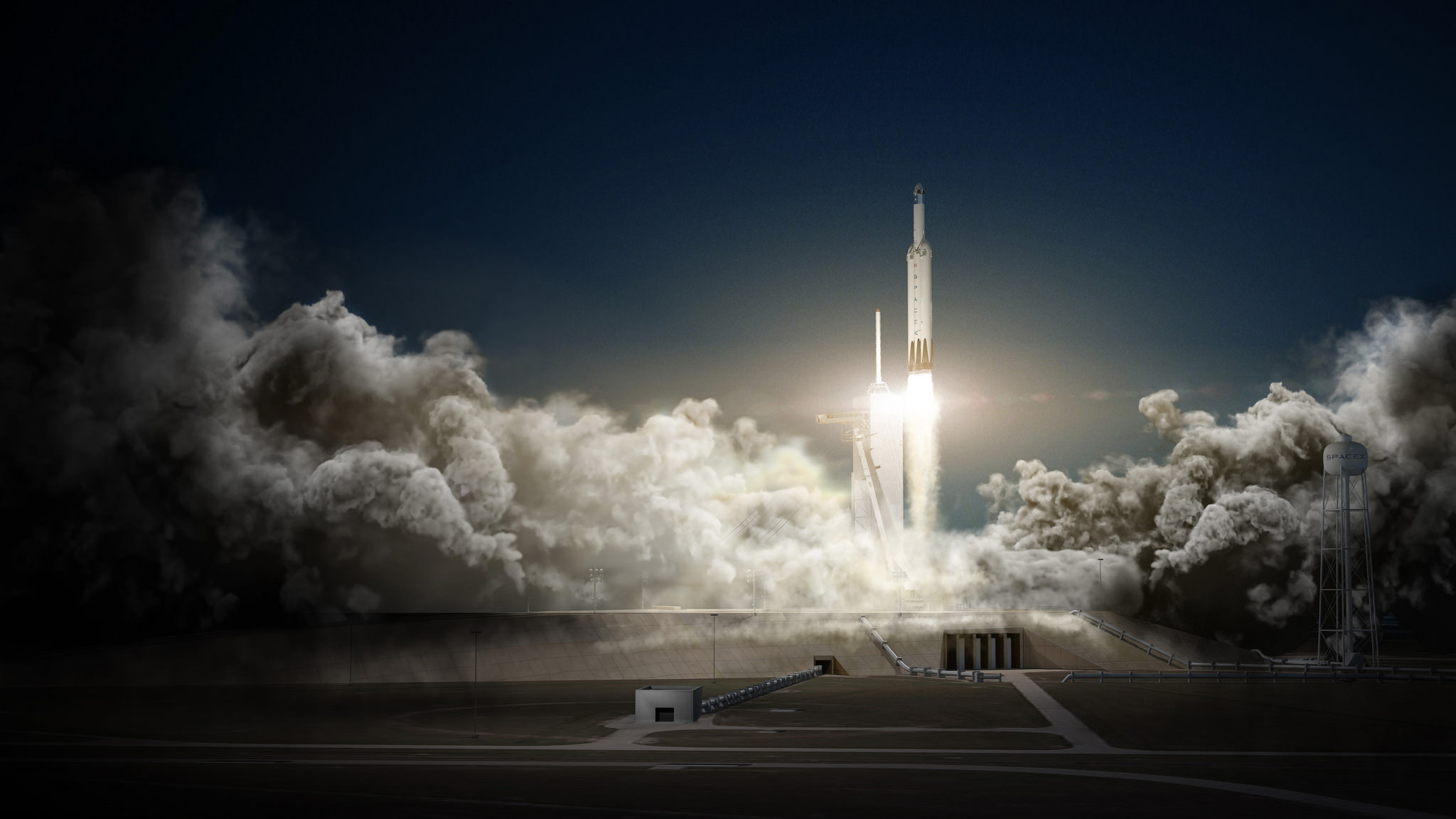
It was also made clear that the Falcon Heavy, which SpaceX is close to completing, will serve as the launch vehicle. SpaceX intends to conduct its first flight test (Falcon Heavy Demo Flight 1) of the heavy-lifter in December of 2016. Three more test flights are scheduled to take place between 2017 and the launch of the Mars lander mission, which is still scheduled for May of 2018.
In addition to helping NASA prepare for its mission to the Red Planet, SpaceX’s progress with both the Falcon Heavy and Dragon 2 are also crucial to Musk’s long-term plan for a crewed mission to Mars – the architecture of which has yet to be announced. They are also extremely important in the development of the Mars Colonial Transporter, which Musk plans to use to create a permanent settlement on Mars.
And while $300 million is just a ballpark estimate at this juncture, it is clear that SpaceX will have to commit considerable resources to the enterprise. What’s more, people must keep in mind that this would be merely the first in a series of major commitments that the company will have to make in order to mount a crewed mission by 2024, to say nothing of building a Martian colony!
In the meantime, be sure to check out this animation of the Crew Dragon in flight:







