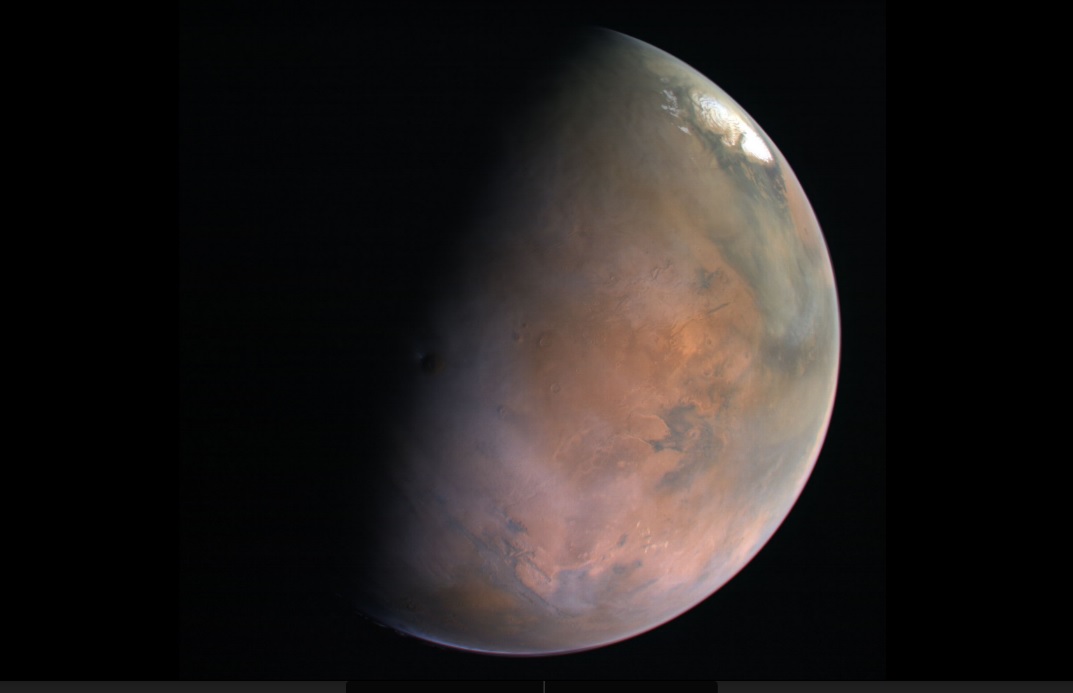
Universe Today has explored the potential for sending humans to Europa, Venus, Titan, and Pluto, all of which possess environmental conditions that are far too harsh for humans to survive. The insight gained from planetary scientists resulted in some informative discussions, and traveling to some of these far-off worlds might be possible, someday. In the final installment of this series, we will explore the potential for sending humans to a destination that has been the focus of scientific exploration and science folklore for more than 100 years: Mars aka the Red Planet.
Continue reading “Should We Send Humans to Mars?”Should We Send Humans to Mars?