WOW MOM !
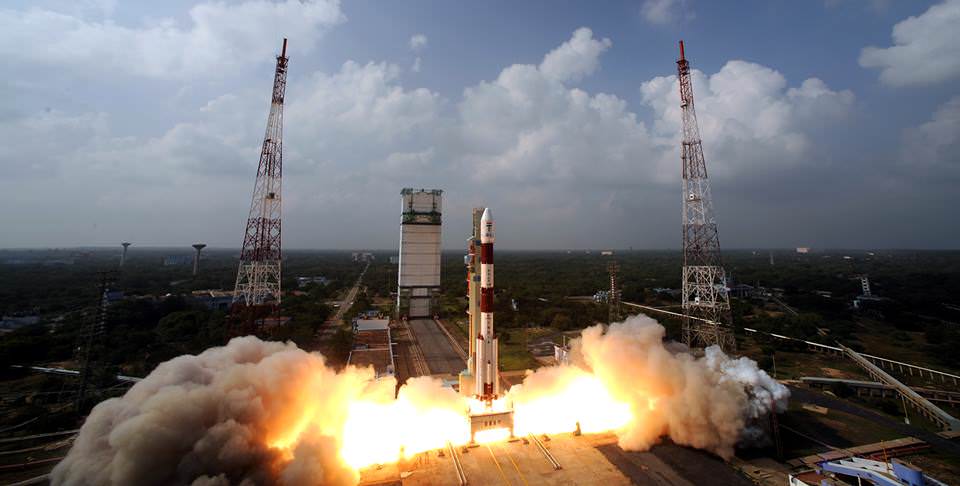
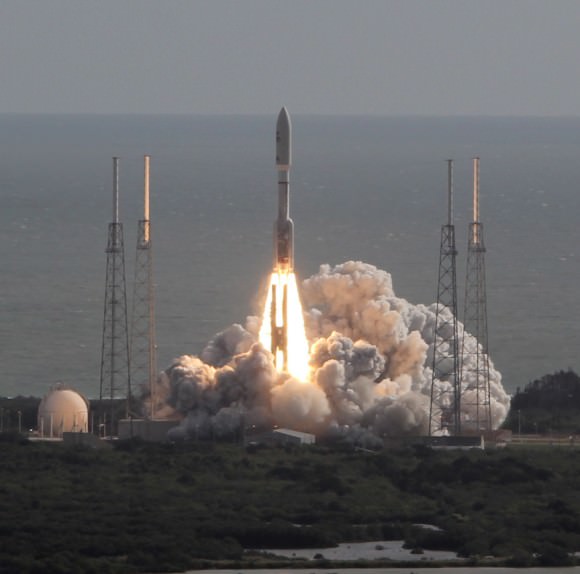
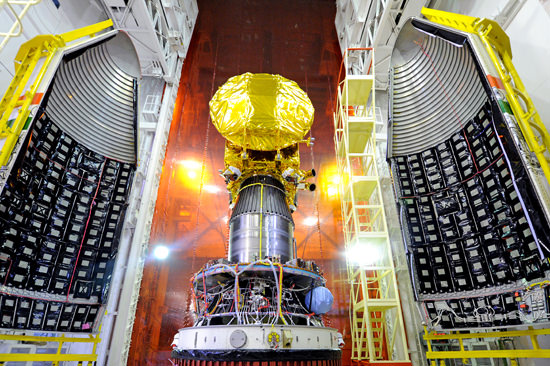
Blastoff of the Indian developed Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) on Nov. 5, 2013 from the Indian Space Research Organization’s (ISRO) Satish Dhawan Space Centre SHAR, Sriharikota. Credit: ISRO[/caption]
India flawlessly launched its first ever mission to Mars today (Nov. 5) to begin a history making ten month long interplanetary voyage to the Red Planet that’s aimed at studying the Martian atmosphere and searching for methane after achieving orbit.
The Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) thundered to space atop the nations four stage Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) precisely on time at 14:38 hrs IST (9:08 UTC, 4:08 a.m. EST) from the Indian Space Research Organization’s (ISRO) Satish Dhawan Space Centre SHAR, Sriharikota, off India’s east coast.
“Our journey to Mars begins now!” announced an elated ISRO Chairman K. Radhakrishnan at the ISRO spaceport during a live broadcast of MOM’s launch from the mission control center. “We achieved orbit and we can all be proud.”
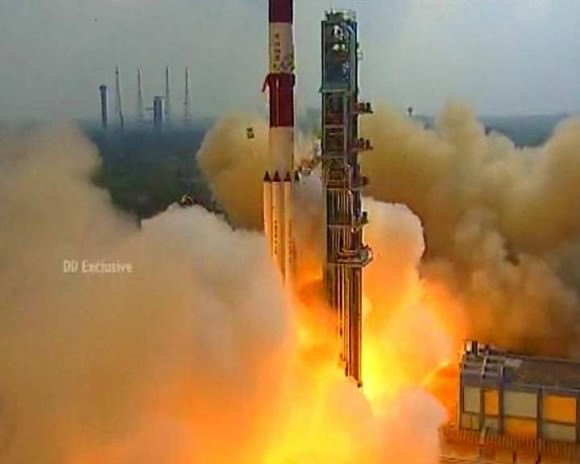

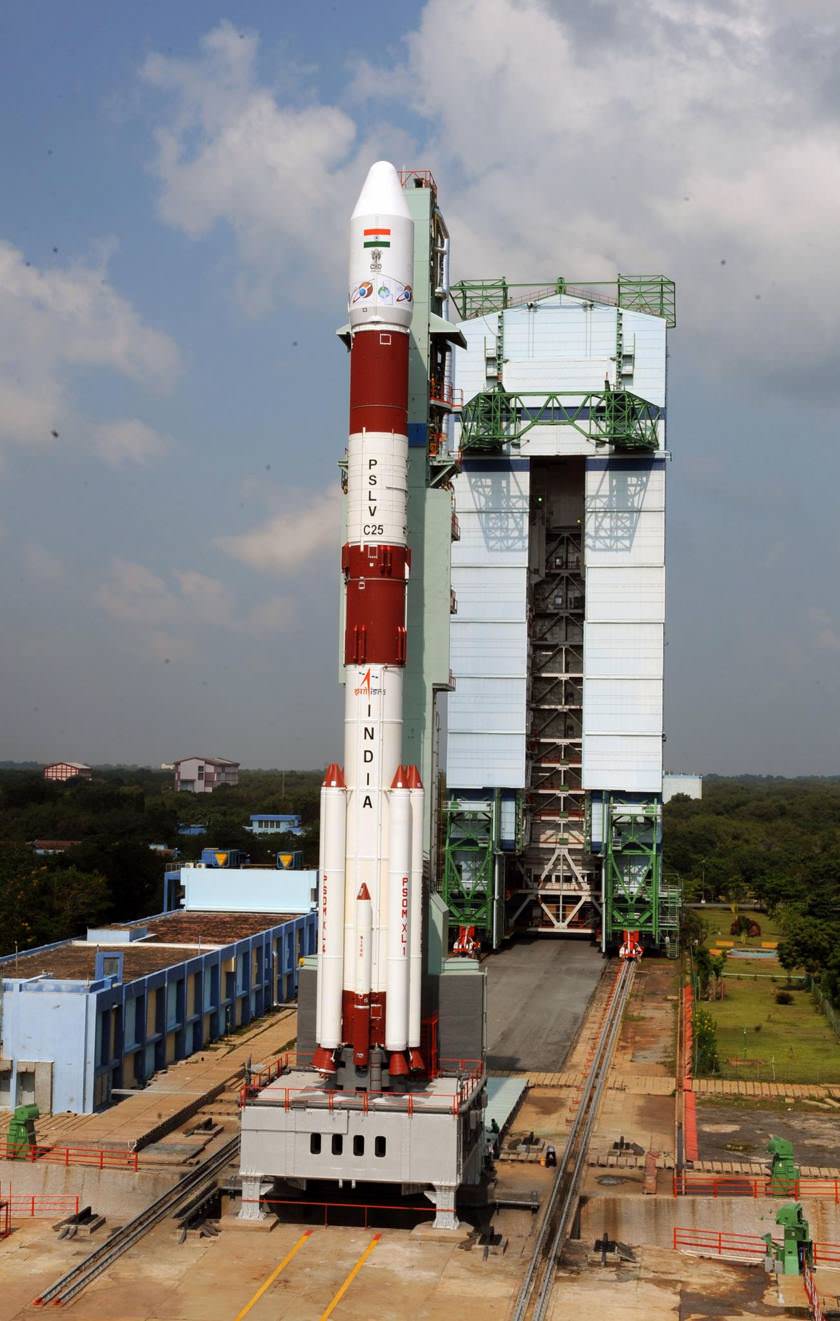
This was the 25th launch of India’s highly reliable 44 meter (144 foot) tall PSLV booster.
The 700,000 pound thrust PSLV rocket launched in its most powerful, extended XL version with six strap on solid rocket motors.

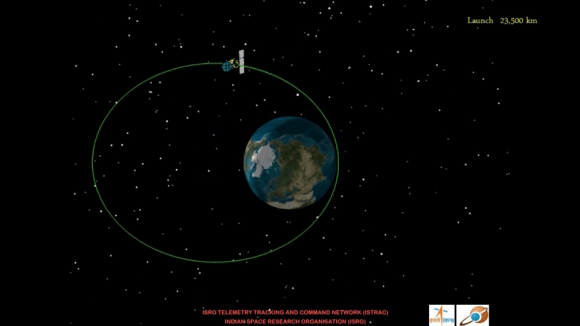
“I’m extremely happy to announce that the PSLV-C25 vehicle has placed the Mars orbiter spacecraft very precisely into an elliptical orbit around Earth of 247 x 23556 kilometers with an inclination of 19.2 degrees,” Radhakrishnan said, after “much meticulous planning and hard work by everyone.”
ISRO announced that MOM separated from the PSLV 4th stage as planned some 44 minutes after liftoff and that the solar panels successfully deployed.
Confirmation of the 4th stage ignition and spacecraft separation was transmitted by ship-borne terminals aboard a pair of specially dispatched tracking ships – SCI Nalanda and SCI Yamuna – stationed by ISRO in the South Pacific Ocean.

MOM was designed and developed by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) in near record time after receiving approval from the Indian Prime Minister Manmohan Singh in August 2012.
“No mission is beyond our capability”, said Radhakrishnan. “MOM is a huge step taking India beyond Earth’s influence for the first time.”
A series of six burns over the next month will raise the apogee and put MOM on a trajectory for Mars around December 1.
Following a 300 day interplanetary cruise phase, the do or die Mars orbital insertion firing by the main engine on September 24, 2014 will place MOM into an 366 km x 80,000 km elliptical orbit.
If all continues to goes well with MOM, India will join an elite club of four who have launched probes that successfully investigated the Red Planet from orbit or the surface – following the Soviet Union, the United States and the European Space Agency (ESA).
MOM is the first of two new Mars orbiter science probes from Earth blasting off for the Red Planet this November. Half a globe away, NASA’s $671 Million MAVEN orbiter remains on target to launch barely two weeks after MOM on Nov. 18 – from Cape Canaveral, Florida.
The 1,350 kilogram (2,980 pound) MOM orbiter is also known as ‘Mangalyaan’ – which in Hindi means ‘Mars craft.’
Although the main objective is a demonstration of technological capabilities, the probe is equipped with five indigenous instruments to conduct meaningful science – including a multi color imager and a methane gas sniffer to study the Red Planet’s atmosphere, morphology, mineralogy and surface features. Methane on Earth originates from both geological and biological sources – and could be a potential marker for the existence of Martian microbes.
MOM’s 15 kg (33 lb) science suite comprises:
MCM: the tri color Mars Color Camera images the planet and its two tiny moons, Phobos and Deimos
LAP: the Lyman Alpha Photometer measures the abundance of hydrogen and deuterium to understand the planets water loss process
TIS: the Thermal Imaging Spectrometer will map surface composition and mineralogy
MENCA: the Mars Exospheric Neutral Composition Analyser is a quadrapole mass spectrometer to analyze atmospheric composition
MSM: the Methane Sensor for Mars measures traces of potential atmospheric methane down to the ppm level.
Scientists will be paying close attention to whether MOM detects any atmospheric methane to compare with measurements from NASA’s Curiosity rover – which found ground level methane to be essentially nonexistent – and Europe’s upcoming 2016 ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter.
MOM and MAVEN will arrive nearly simultaneously in Mars orbit next September – joining Earth’s invasion fleet of five operational orbiters and intrepid surface rovers currently unveiling the mysteries of the Red Planet.
Both MAVEN and MOM’s goal is to study the Martian atmosphere , unlock the mysteries of its current atmosphere and determine how, why and when the atmosphere and liquid water was lost – and how this transformed Mars climate into its cold, desiccated state of today.
Although they were developed independently and have different suites of scientific instruments, the MAVEN and MOM science teams will “work together” to unlock the secrets of Mars atmosphere and climate history, MAVEN’s top scientist told Universe Today.
“We have had some discussions with their science team, and there are some overlapping objectives,” Bruce Jakosky told me. Jakosky is MAVEN’s principal Investigator from the University of Colorado at Boulder.
“At the point where we [MAVEN and MOM] are both in orbit collecting data we do plan to collaborate and work together with the data jointly,” Jakosky said.
The $69 Million ‘Mangalyaan’ mission is expected to continue gathering measurements at the Red Planet for about six to ten months and hopefully much longer.
Stay tuned here for continuing MAVEN and MOM news and my MAVEN launch reports from on site at the Kennedy Space Center press center.

…………….
Learn more about MAVEN, MOM, Mars rovers, Orion and more at Ken’s upcoming presentations
Nov 14-19: “MAVEN Mars Launch and Curiosity Explores Mars, Orion and NASA’s Future”, Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, 8 PM
Dec 11: “Curiosity, MAVEN and the Search for Life on Mars”, “LADEE & Antares ISS Launches from Virginia”, Rittenhouse Astronomical Society, Franklin Institute, Phila, PA, 8 PM