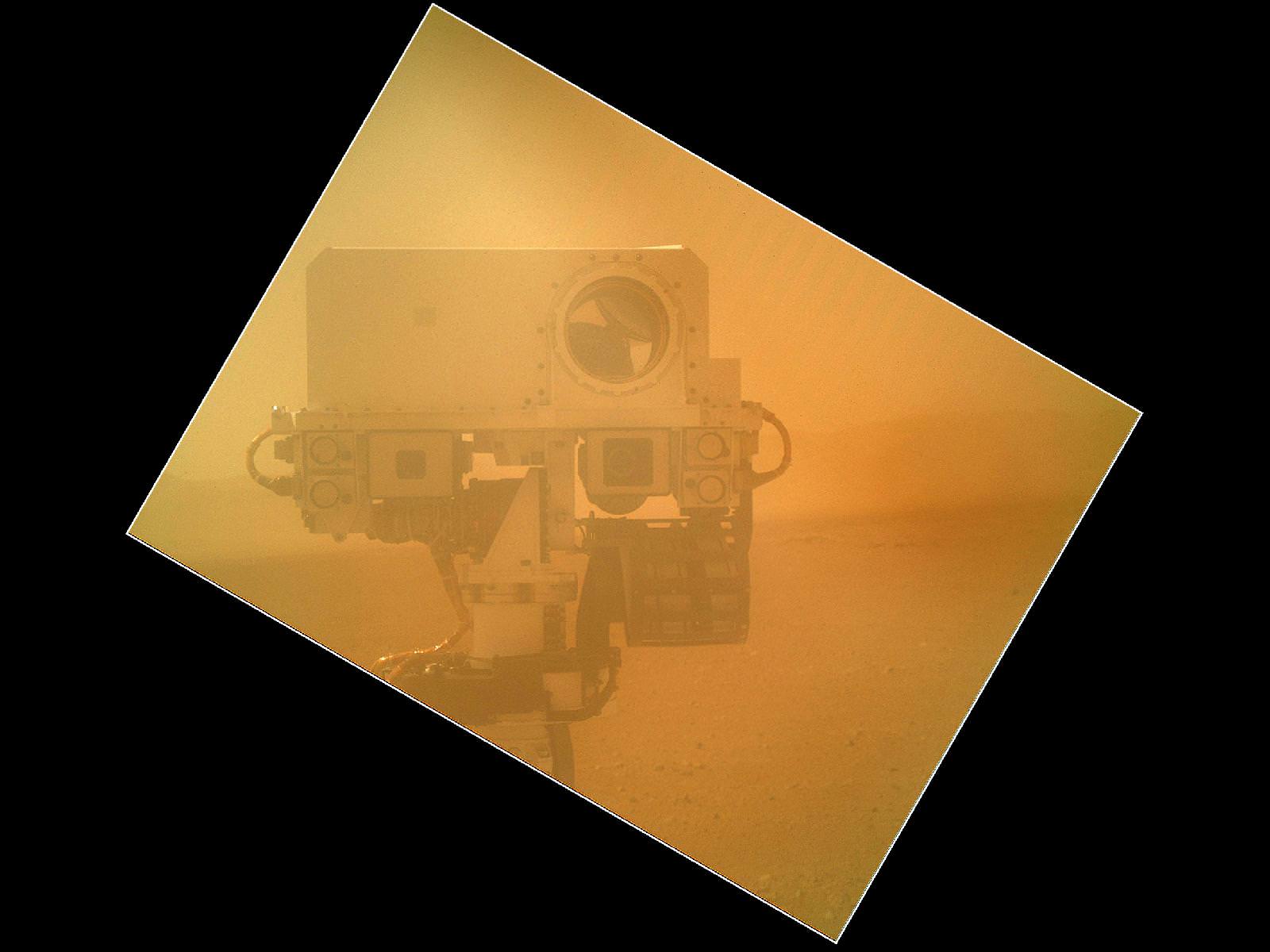
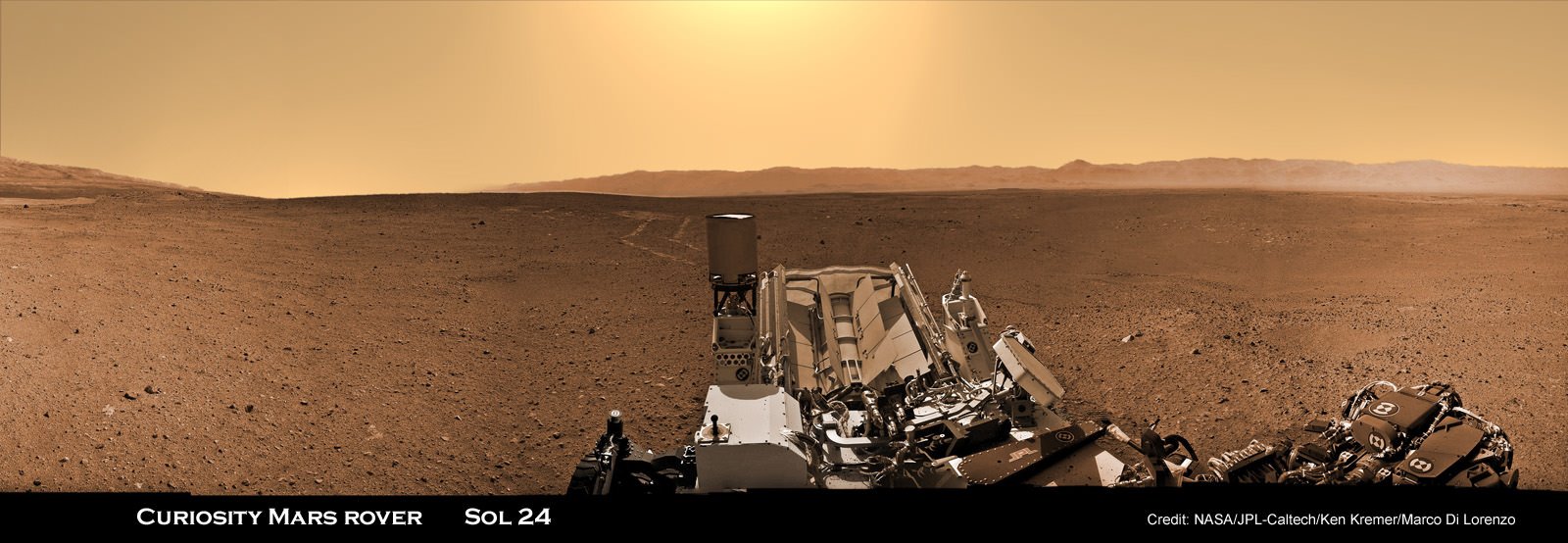
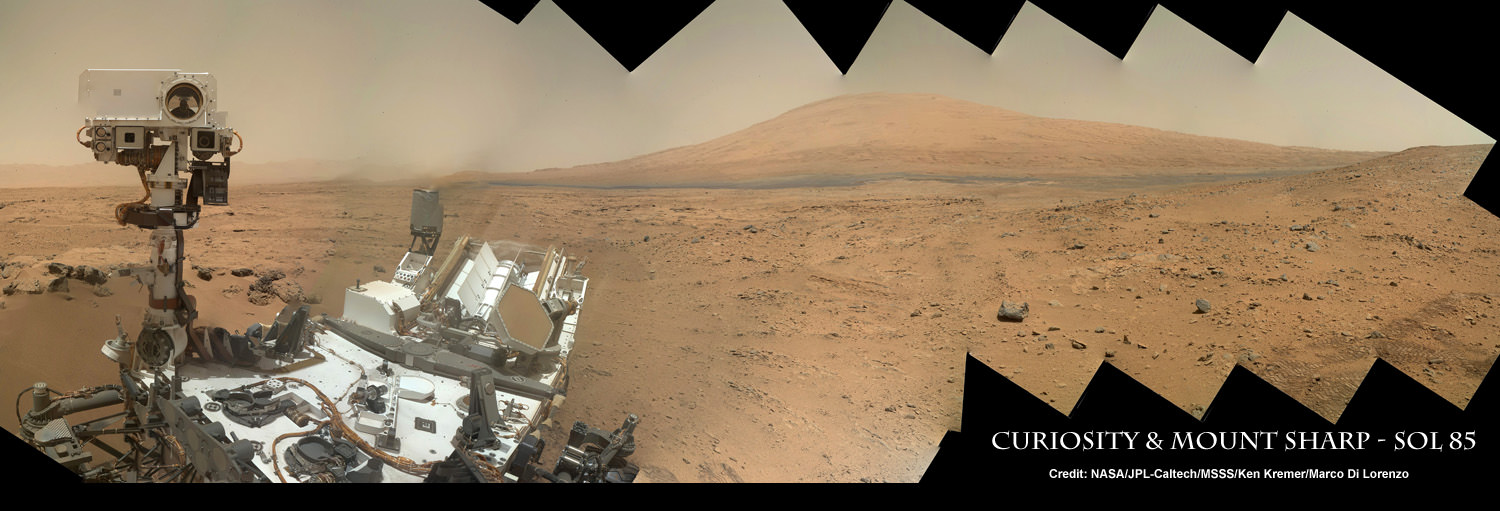
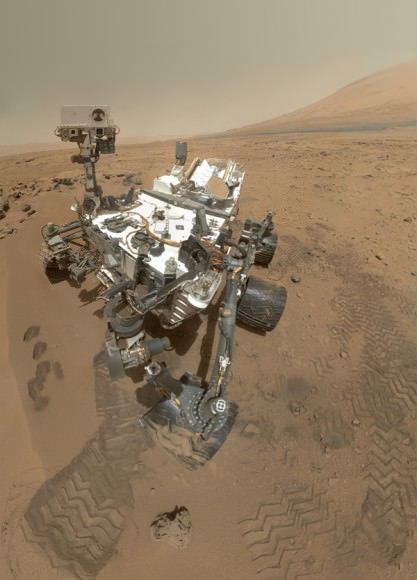
Image Caption: Thanksgiving Greetings from Mars ! Curiosity snaps Head and Shoulders Self-Portrait on Sol 85 while posing at windblown ‘Rocknest’ ripple with eroded rim of Gale Crater in the background. This color mosaic was assembled from Mastcam 34 raw images snapped on Sol 85 (Nov. 1, 2012). See below the utterly cool animation of Curioity’s 1st ever ‘Touch and Go’ maneuver. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
In the days leading up to Thanksgiving, NASA’s Curiosity mega Mars rover completed her first so-called “touch and go” maneuver – whereby she drives to and inspects an interesting rock and then moves on the same day to the next target of interest.
Check out the totally cool action animation below depicting Curiosity’s first ever “touch and go” movement and a subsequent martian drive of 83 feet (25.3 meters) conducted on Nov. 18.
“The ‘touch and go’ on Sol 102 went well, the data arriving in time for planning Sol 104”, says rover team member Ken Herkenhoff, of the US Geological Survey (USGS).
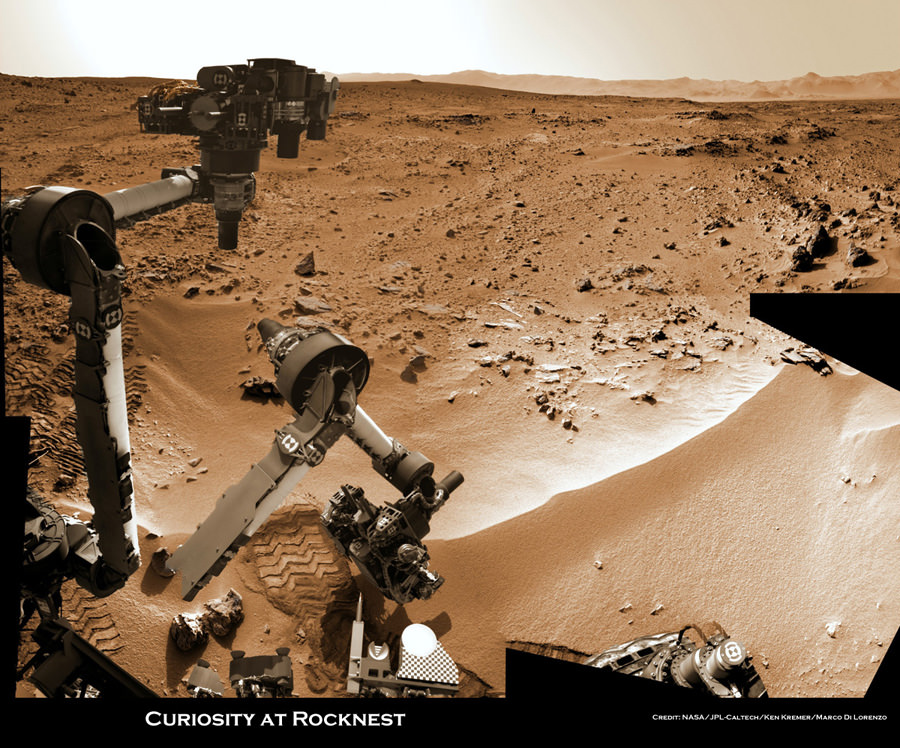
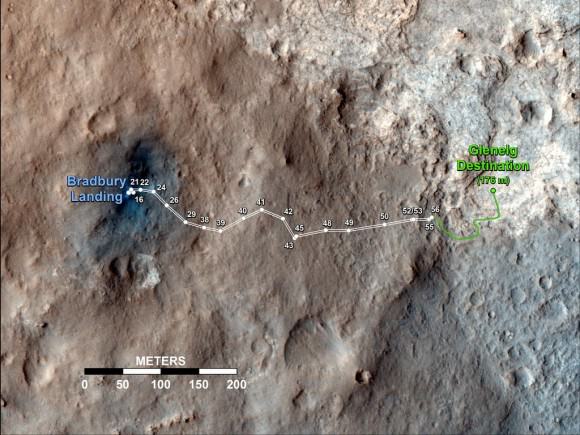
The science and engineering team guiding Curiosity is commanding her to accomplish ever more sophisticated and bold forays across the floor of Gale crater after finishing more than a month of investigations at the windblown ripple named “Rocknest.
On Nov 16, Curiosity drove 6.2 feet (1.9 meters) to get within arm’s reach of a rock called “Rocknest 3”. She deployed the arm and placed the Alpha Particle X-Ray Spectrometer (APXS) instrument onto the rock, and then took two 10-minute APXS readings of data to ascertain the chemical elements in the rock.
Thereafter Curiosity stowed her 7 foot (2.1 m) long arm and drove eastward toward the next target called “Point Lake”.
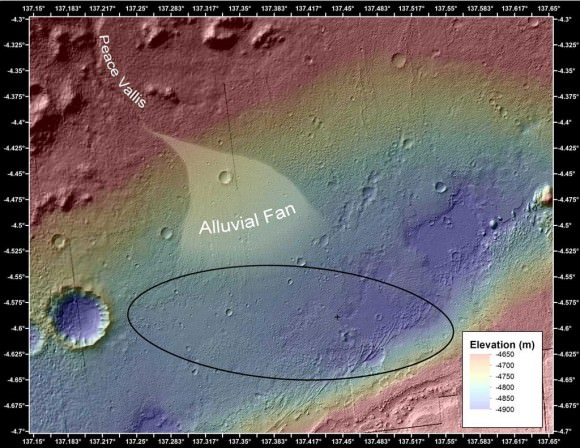
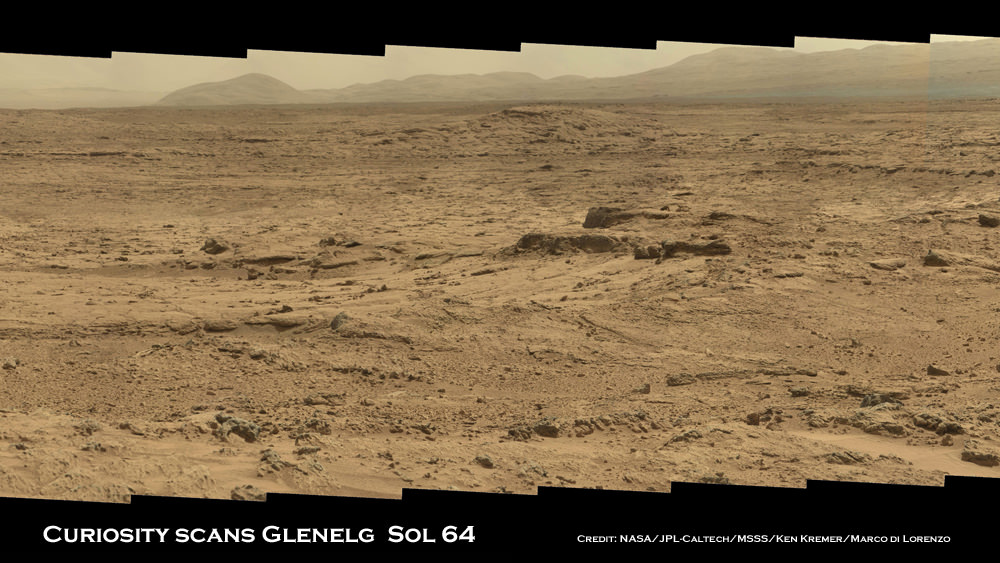
Curiosity is now inside the ‘Glenelg’ geologic formation which the science team selected as the first major science destination because it lies at the intersection of three diverse types of geology areas that will help unlock the secrets of Mars’ ancient watery history and evolution to modern times.
Image Caption: Panoramic mosaic shows gorgeous Glenelg snapped by Curiosity on Sol 64 (Oct. 10) with eroded crater rim and base of Mount Sharp in the distance. Curiosity is now touring inside Glenelg. This is a cropped version of the full mosaic as assembled from 75 images acquired by the Mastcam 100 camera. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
“We have done touches before, and we’ve done goes before, but this is our first ‘touch-and-go’ on the same day,” said Curiosity Mission Manager Michael Watkins of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. “It is a good sign that the rover team is getting comfortable with more complex operational planning, which will serve us well in the weeks ahead.”
During the holiday period, Curiosity is taking high resolution imagery, conducting atmospheric observations and making measurements with the DAN neutron spectrometer and her other state-of-the-art science instruments.
Meanwhile, the Curiosity science team is still ‘chewing over’ the meaning of the results from the first ever scoopful of soil spooned up at ‘Rocknest’ and ingested by the SAM (Sample Analysis at Mars) chemistry instrument on the rover deck that is designed to detect organic molecules – the building blocks of life.
“We’ve got a briefing on Monday [Dec 3] where we’ll discuss our results,” Curiosity project manager John Grotzinger, of Caltech, told me. Those SAM results will be announced to a flurry of interest during the annual meeting of the AGU (American Geophysical Union) being held from Dec 3-7 in San Francisco.
Learn more about Curiosity’s groundbreaking discoveries, SAM and NASA missions at my upcoming pair of free presentations for the general public at two colleges in New Jersey:
-
- on Dec 11 at Princeton University and the Amateur Astronomers Association of Princeton (AAAP) in Princeton, NJ at 8 PM.
-
- and on Dec. 6 at Brookdale Community College, Monmouth Museum, Lincroft, NJ at 8 PM – hosted by STAR astronomy
…..
Dec 6: Free Public lecture titled “Atlantis, The Premature End of America’s Shuttle Program and What’s Beyond for NASA” including Curiosity, Orion, SpaceX and more by Ken Kremer at Brookdale Community College/Monmouth Museum and STAR Astronomy club in Lincroft, NJ at 8 PM
Dec 11: Free Public lecture titled “Curiosity and the Search for Life on Mars (in 3 D)” and more by Ken Kremer at Princeton University and the Amateur Astronomers Association of Princeton (AAAP) in Princeton, NJ at 8 PM – Princeton U Campus at Peyton Hall, Astrophysics Dept.




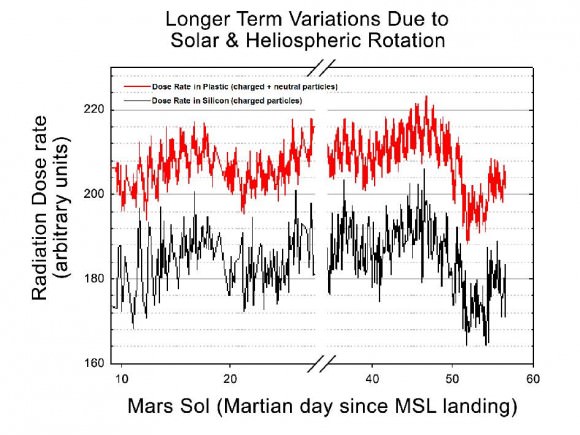

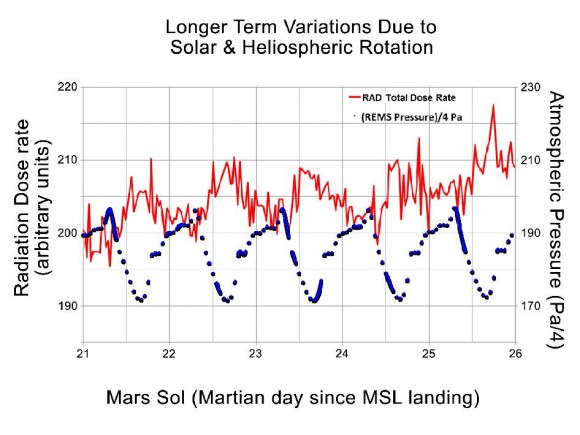










![698428main_Grotzinger-1pia16231-946[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/698428main_Grotzinger-1pia16231-9461-580x435.jpg)

![697173main_pia16229-43_946-710[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/697173main_pia16229-43_946-7101-580x435.jpg)
![697185main_pia16230-43_946-710[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/697185main_pia16230-43_946-7101-580x435.jpg)

![NLA_402906079EDR_F0050104NCAM00326M_[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/NLA_402906079EDR_F0050104NCAM00326M_1-580x580.jpg)
![0061MR0319001000E1_DXXX[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/0061MR0319001000E1_DXXX11-580x435.jpg)




![692089main_Grotzinger-1-pia16156-43_800-600[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/692089main_Grotzinger-1-pia16156-43_800-6001-580x435.jpg)