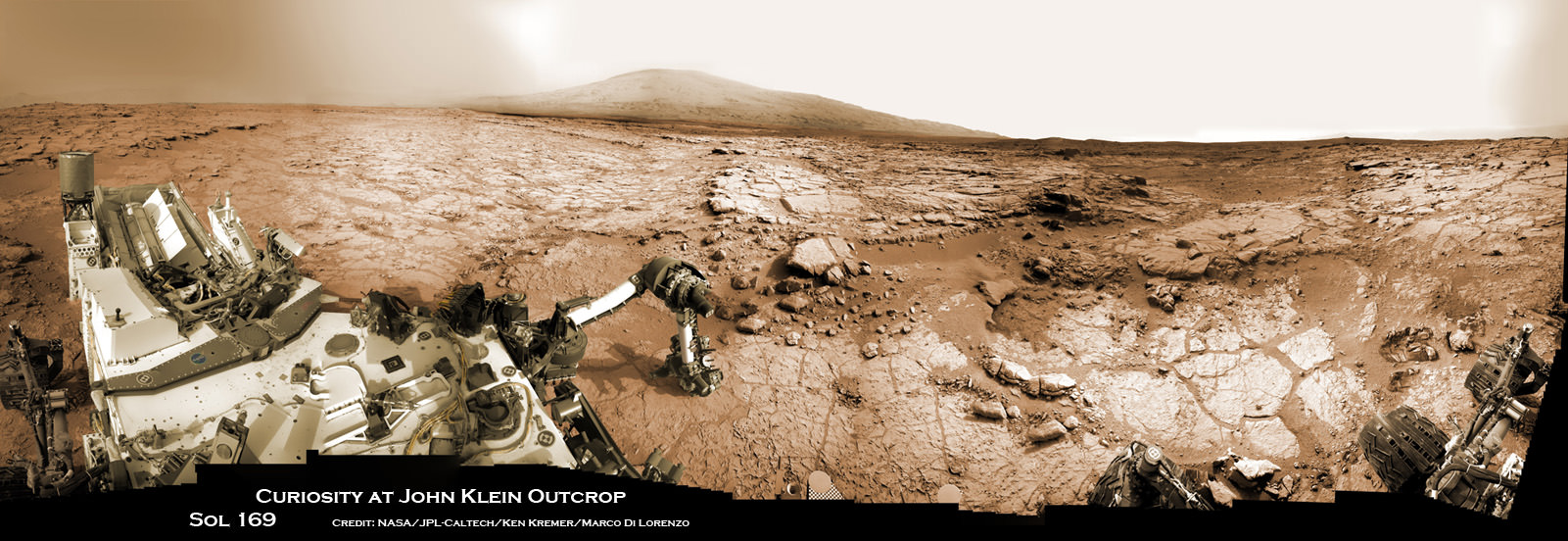
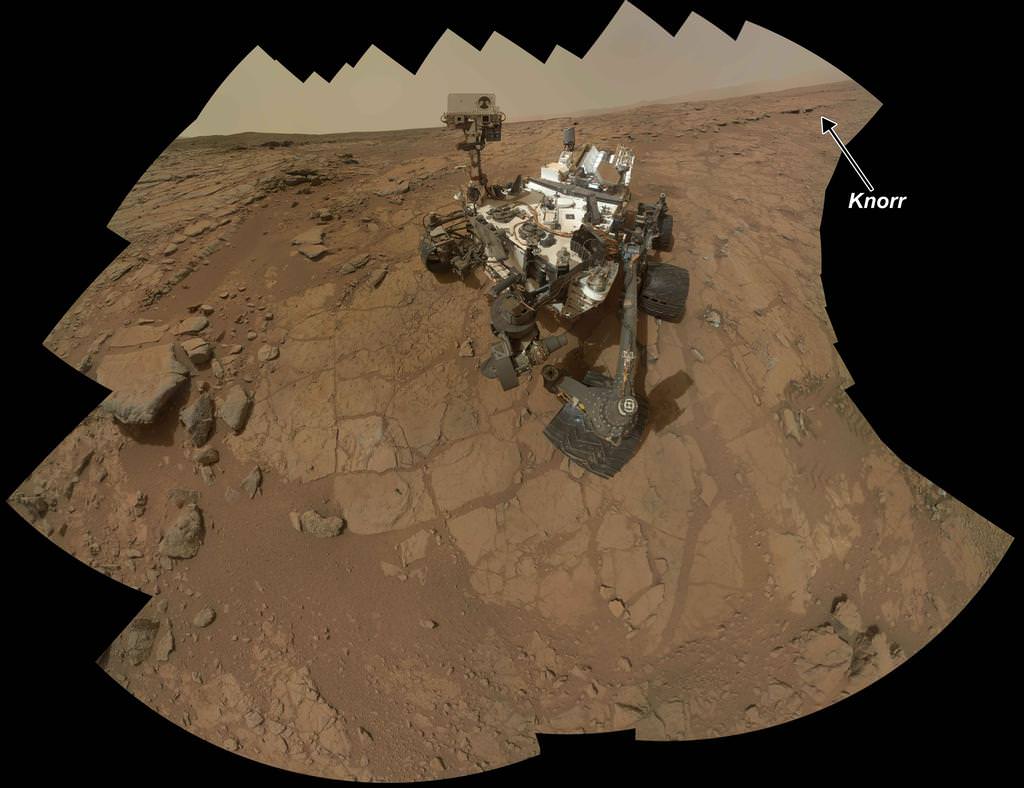
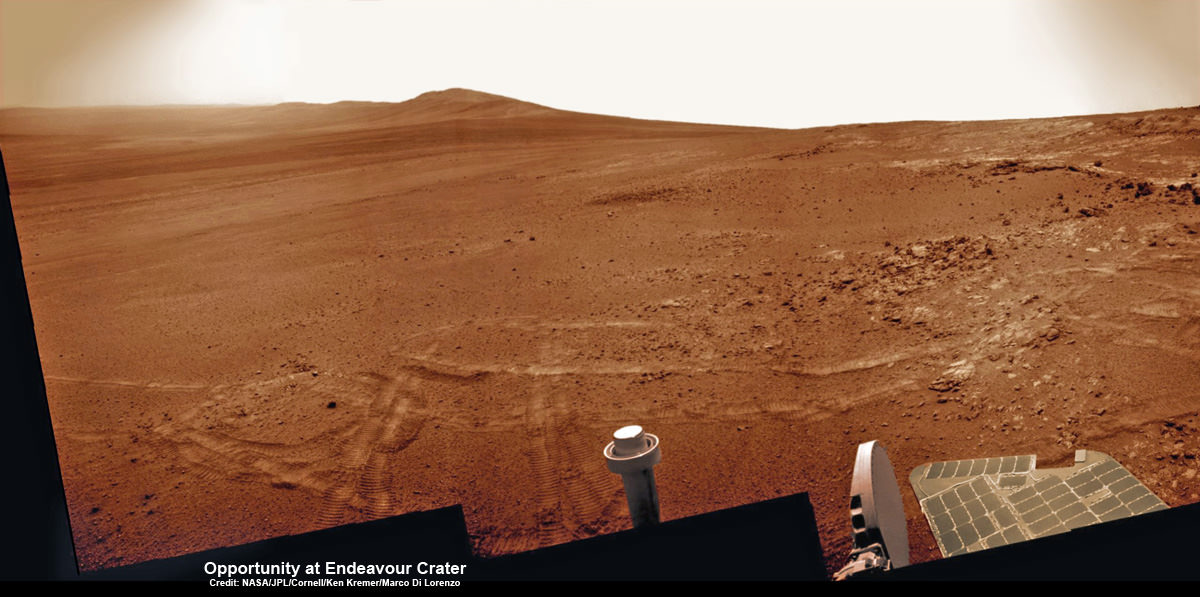
NASA’s Opportunity Mars rover discovered clay minerals at Cape York ridge along the rim of Endeavour crater – seen in this photo mosaic – which stands as the most favorable location for Martian biology discovered during her entire nearly 10 year long mission to Mars. Opportunity also established a new American driving record for a vehicle on another world on May 15, 2013 (Sol 3309) and made history by driving ahead from this point at Cape York. This navcam photo mosaic shows the view forward to her next destinations of Solander Point and Cape Tribulation along the lengthy rim of huge Endeavour crater spanning 14 miles (22 km) in diameter.
Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/Ken Kremer (kenkremer.com)/Marco Di Lorenzo
Updated: Illustrated below with a collection of imagery, mosaics and route maps[/caption]
Now nearly a decade into her planned 3 month only expedition to Mars, NASA’s longest living rover Opportunity, struck gold and has just discovered the strongest evidence to date for an environment favorable to ancient Martian biology – and she has set sail hunting for a motherlode of new clues amongst fabulous looking terrain!!
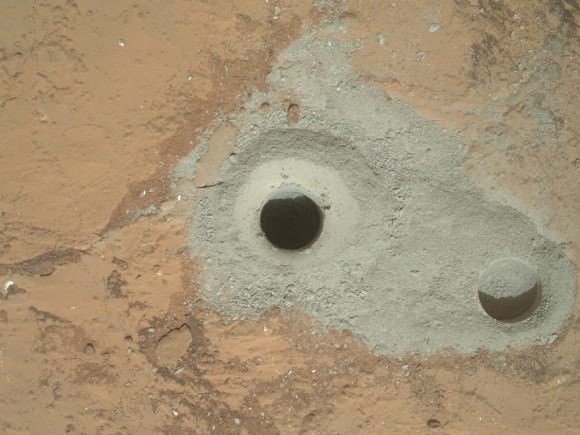
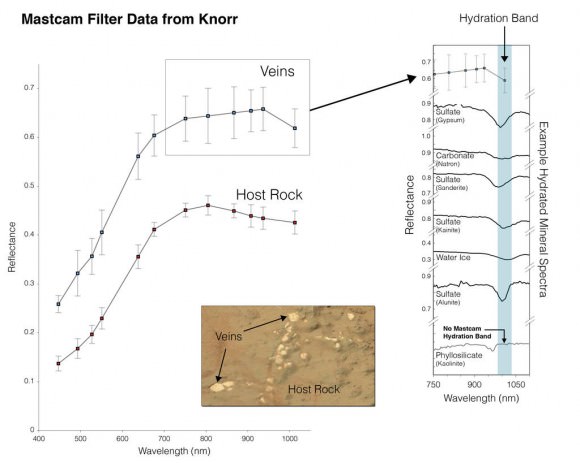
Barely two weeks ago in mid-May 2013, Opportunity’s analysis of a new rock target named “Esperance” confirmed that it is composed of a “clay that had been intensely altered by relatively neutral pH water – representing the most favorable conditions for biology that Opportunity has yet seen in the rock histories it has encountered,” NASA said in a statement.
The finding of a fractured rock loaded with clay minerals and ravaged by flowing liquid water in which life could have thrived amounts to a scientific home run for the golf cart sized rover!
“Water that moved through fractures during this rock’s history would have provided more favorable conditions for biology than any other wet environment recorded in rocks Opportunity has seen,” said the mission’s principal investigator Prof. Steve Squyres of Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y.
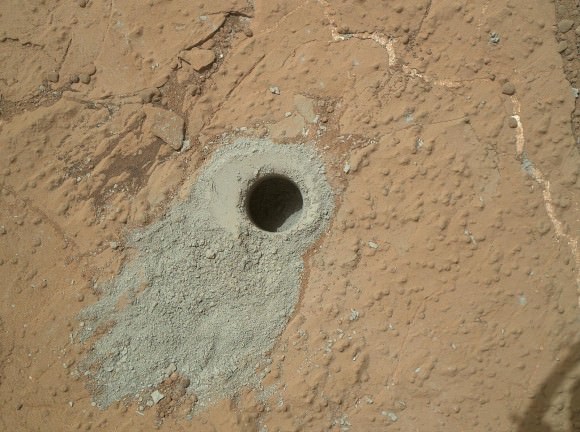
Opportunity accomplished the ground breaking new discovery by exposing the interior of Esperance with her still functioning Rock Abrasion Tool (RAT) and examining a pristine patch using the microscopic camera and X-Ray spectrometer on the end of her 3 foot long robotic arm.
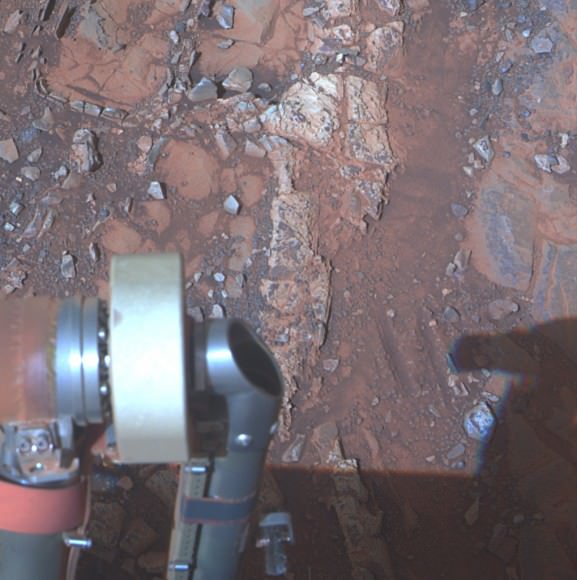

The robot made the discovery at the conclusion of a 20 month long science expedition circling around a low ridge called “Cape York” – which she has just departed on a southerly heading trekking around the eroded rim of the huge crater named “Endeavour.”
“Esperance was so important, we committed several weeks to getting this one measurement of it, even though we knew the clock was ticking.”
Esperance stems from a time when the Red Planet was far warmer and wetter billions of years ago.
“What’s so special about Esperance is that there was enough water not only for reactions that produced clay minerals, but also enough to flush out ions set loose by those reactions, so that Opportunity can clearly see the alteration,” said Scott McLennan of the State University of New York, Stony Brook, a long-term planner for Opportunity’s science team.
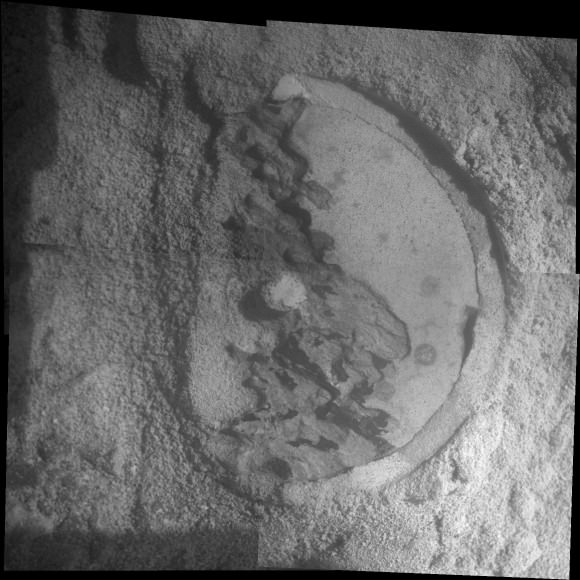

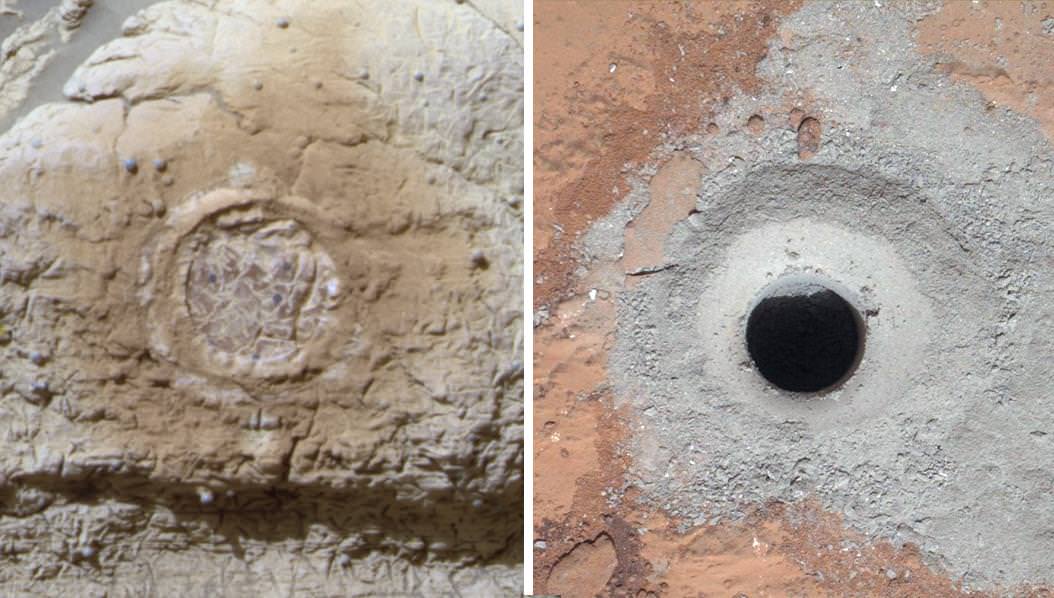
This mosaic of four frames shot by the microscopic imager on the robotic arm of NASA’s Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity shows a rock target called “Esperance” after some of the rock’s surface had been removed by Opportunity’s rock abrasion tool, or RAT. The component images were taken on Sol 3305 on Mars (May 11, 2013). The area shown is about 2.4 inches (6 centimeters) across. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Cornell/USGS
Esperance is unlike any rock previously investigated by Opportunity; containing far more aluminum and silica which is indicative of clay minerals and lower levels of calcium and iron.
Most, but not all of the rocks inspected to date by Opportunity were formed in an environment of highly acidic water that is extremely harsh to most life forms.
Clay minerals typically form in potentially drinkable, neutral water that is not extremely acidic or basic.
Previously at Cape York, Opportunity had found another outcrop containing a small amount of clay minerals formed by exposure to water called “Whitewater Lake.”
“There appears to have been extensive, but weak, alteration of Whitewater Lake, but intense alteration of Esperance along fractures that provided conduits for fluid flow,” said Squyres.

Cape York is a hilly segment of the rim of Endeavour crater which spans 14 miles (22 km) across – where the robot arrived in mid-2011 and will spend her remaining life.
Opportunity has now set sail for her next crater rim destination named “Solander Point”, an area about 1.4 miles (2.2 kilometers) away – due south from “Cape York.”
“Our next destination will be Solander Point,” Squyres told Universe Today.
Along the way, Opportunity will soon cross “Botany Bay” and “Sutherland Point”, last seen when Opportunity first arrived at Cape York.
Eventually she will continue further south to a rim segment named ‘Cape Tribulation’ which holds huge caches of clay minerals.
The rover must arrive at “Solander Point” before the onset of her 6th Martian winter so that she can be advantageously tilted along north facing slopes to soak up the maximum amount of sun by her power generating solar wings. She might pull up around August.
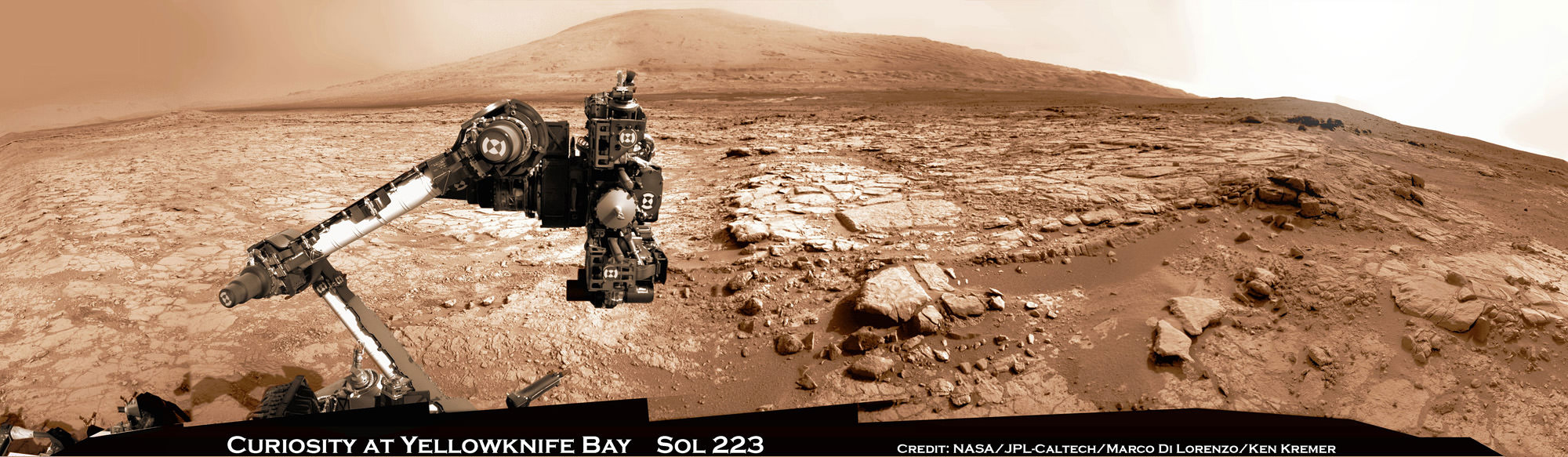
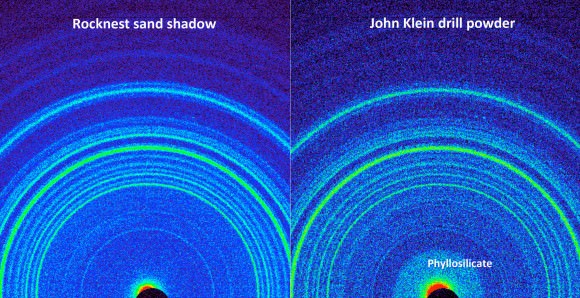
On the other side of Mars, Opportunity’s new sister rover Curiosity also recently discovered clay minerals on the floor of her landing site inside Gale Crater.
Curiosity found the clay minerals – and a habitat that could support life – after analyzing powdery drill tailings from the Yellowknife Bay basin worksite with her on board state-of-the-art chemistry labs.
Just a week ago on May 15 (Sol 3309), Opportunity broke through the 40 year old American distance driving record set back in December 1972 by Apollo 17 astronauts Eugene Cernan and Harrison Schmitt.
But she is not sitting still resting on her laurels!
This past week the robots handlers’ back on Earth put the pedal to the metal and pushed her forward another quarter mile during 5 additional drives over 7 Sols, or Martian days. Thus her total odometry since landing on 24 January 2004 now stands at 22.45 miles (36.14 kilometers).
Opportunity will blast through the world record milestone of 23 miles (37 kilometers) held by the Lunokhod 2 lunar rover (from the Soviet Union), somewhere along the path to “Solander Point” in the coming months.

Endeavour Crater features terrain with older rocks than previously inspected and unlike anything studied before by Opportunity. It’s a place no one ever dared dream of reaching prior to Opportunity’s launch in the summer of 2003 and landing on the Meridiani Planum region in 2004.
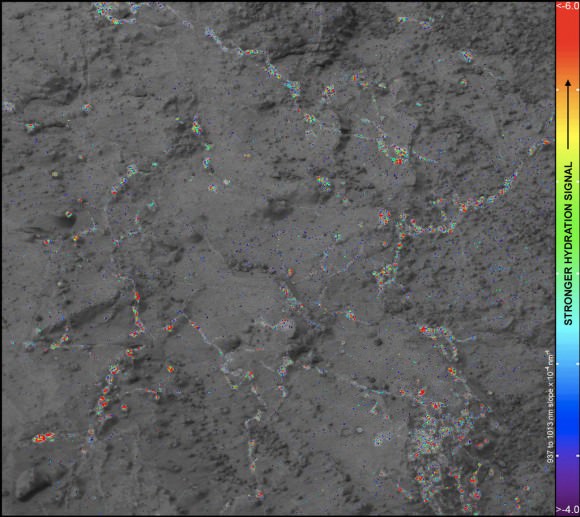
Signatures of clay minerals, or phyllosilicates, were detected at several spots at Endeavour’s western rim by observations from the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) aboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
“The motherlode of clay minerals is on Cape Tribulation. The exposure extends all the way to the top, mainly on the inboard side,” says Ray Arvidson, the rover’s deputy principal investigator at Washington University in St. Louis.
Stay tuned for the continuing breathtaking adventures of NASA’s sister rovers Opportunity and Curiosity!
And don’t forget to “Send Your Name to Mars” aboard NASA’s MAVEN orbiter- details here. Deadline: July 1, 2013
…………….
Learn more about Mars, Curiosity, Opportunity, MAVEN, LADEE and NASA missions at Ken’s upcoming lecture presentations:
June 4: “Send your Name to Mars” and “CIBER Astro Sat, LADEE Lunar & Antares Rocket Launches from Virginia”; Rodeway Inn, Chincoteague, VA, 8:30 PM
June 11: “Send your Name to Mars” and “LADEE Lunar & Antares Rocket Launches from Virginia”; NJ State Museum Planetarium and Amateur Astronomers Association of Princeton (AAAP), Trenton, NJ, 8 PM.
June 12: “Send your Name to Mars” and “LADEE Lunar & Antares Rocket Launches from Virginia”; Franklin Institute and Rittenhouse Astronomical Society, Philadelphia, PA, 8 PM.
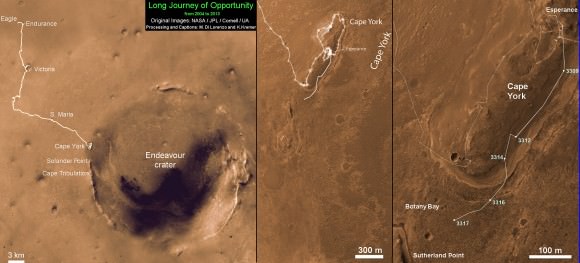

-This map of a portion of the western rim of Endeavour Crater on Mars shows the area where NASA’s Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity worked for 20 months, “Cape York,” in relation to the area where the rover team plans for Opportunity to spend its sixth Martian winter, “Solander Point.” Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona








![470505_10150721848592868_1231281550_o[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/05/470505_10150721848592868_1231281550_o1-580x214.jpg)