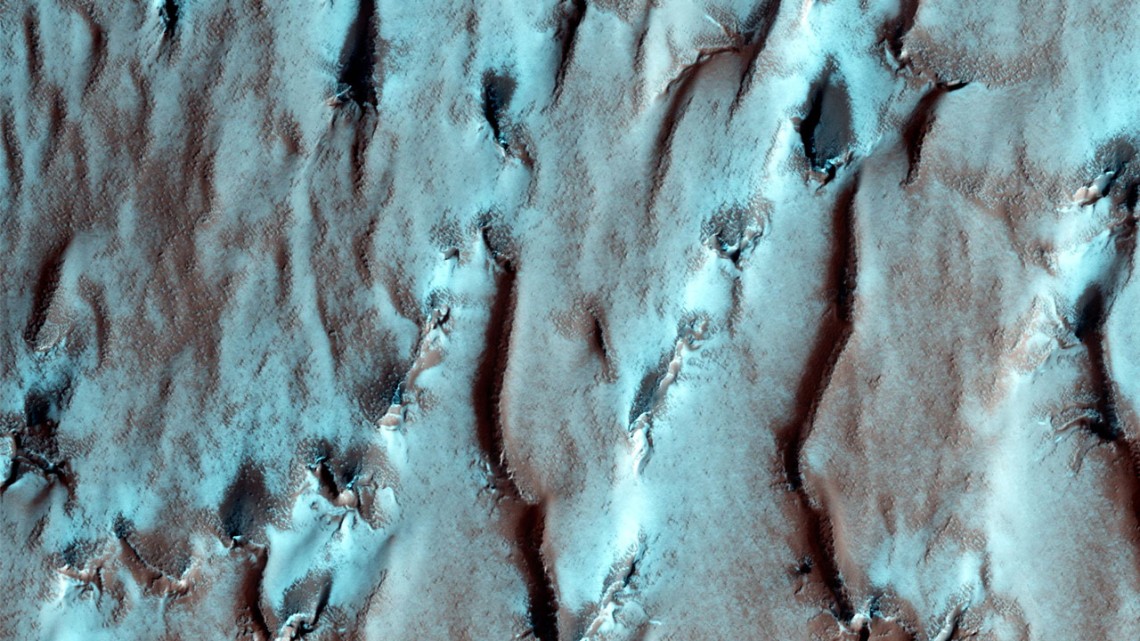
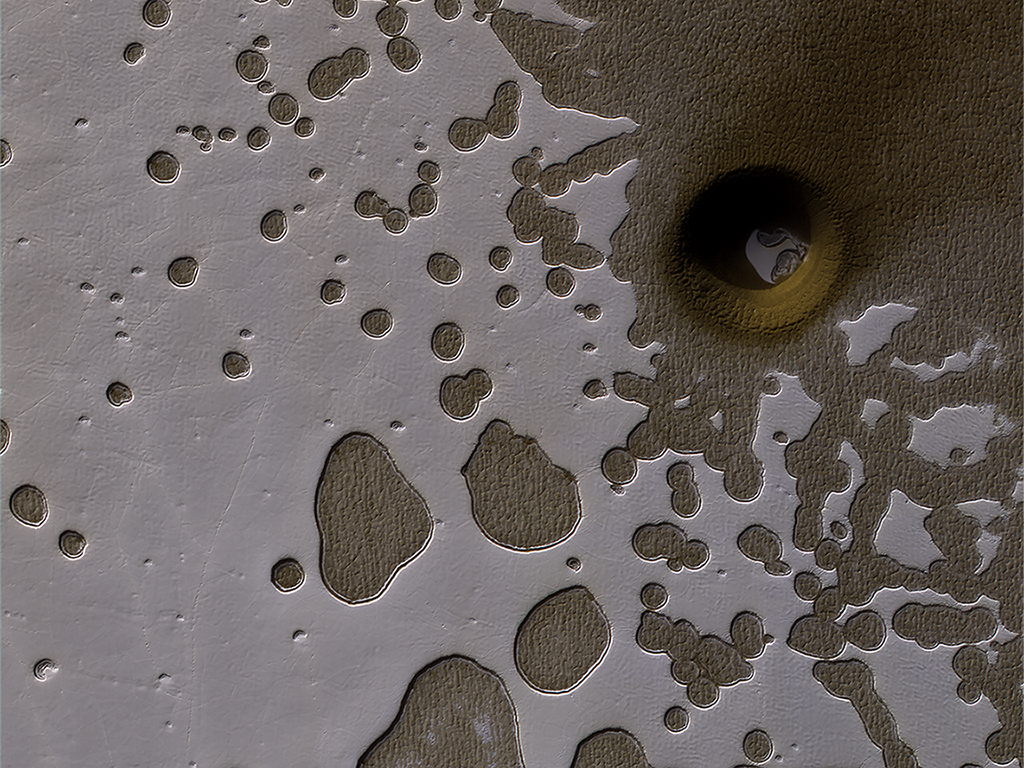
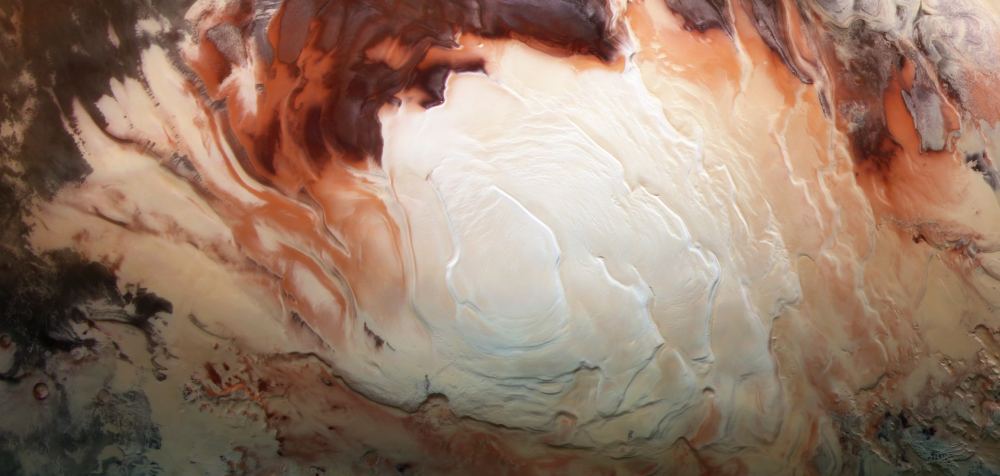
Seen from space, regions of Mars around the south pole have a bizarre, pitted “Swiss cheese” appearance. These formations come from alternating massive deposits of CO2 ice and water ice, similar to different layers of a cake. For decades, planetary scientists wondered how this formation was possible, as it was long believed that this layering would not be stable for long periods of time.
But in 2020, Peter Buhler, a Research Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute, and a team of researchers figured out the dynamics of how the Swiss cheese-like terrain formed: it was due to changes in Mars’ axial tilt that caused changes in the atmospheric pressure, which alternately produced water and CO2 ice. However, they were only able to deduce the rate of CO2 and water deposits over millions of years, which is about ten times longer than Mars’ orbit cycles.
Now, in a follow up study, Buhler was able to model how the frozen carbon dioxide and water deposits grow and shrink over 100,000 year-long cycles of Mars’s polar tilt. The model allowed the researchers to determine how water and carbon dioxide have moved around on Mars over the past 510,000 years.
Continue reading “Mars Has Bizarre “Swiss Cheese” Terrain. You can Thank Water, Carbon Dioxide and 500,000 years of Climate History for That”