Ten months after her breathtaking touchdown on the Red Planet, NASA’s Curiosity rover is nearly set to embark on an epic drive like no other in space history to the slopes of mysterious Mount Sharp – looming supreme inside Gale Crater and the primary mission objective.
But not before the robot completes a few last critical science tasks to more fully illuminate the potential for the origin of Martian microbes in the habitable zone discovered at the work-site of her first penetrations into Mars water altered surface.
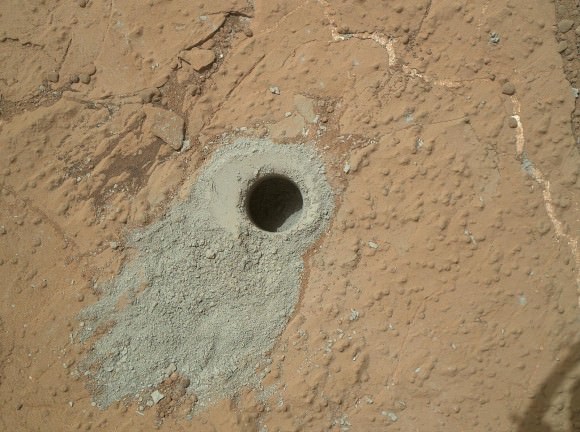
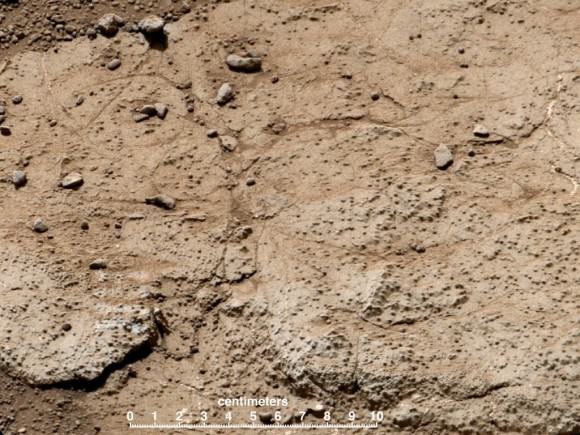
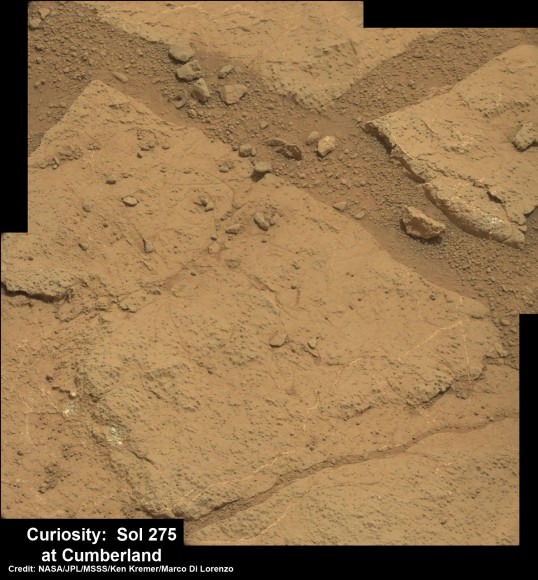
The rover science team has chosen a trio of final targets to investigate around the shallow basin of Yellowknife Bay, that resembles a dried out lakebed, where Curiosity has toiled for the past six months, drilled twice into the mudstone outcrops at ‘John Klein’ and ‘Cumberland’ and repeatedly fired her powerful science laser.
Curiosity will revisit a pair of intriguing outcrops named ‘Point Lake’ and ‘Shaler’ that the rover briefly investigated before arriving at ‘John Klein’, said Joy Crisp of JPL, Curiosity’s deputy project scientist, at a media briefing.
“Shaler might be a river deposit. Point Lake might be volcanic or sedimentary. A closer look at them could give us better understanding of how the rocks we sampled with the drill fit into the history of how the environment changed.”
Curiosity will employ nearly all her science instruments to study the outcrops – except the drill.
“It’s highly unlikely to drill at ‘Point Lake’ and ‘Shaler’ because we want to get driving,” Crisp told Universe Today.
“We might drill somewhere along the way to Mount Sharp depending on whether we find something compelling.”

Researchers will also use the DAN (Dynamic Albedo of Neutrons) instrument to look for traces of mineral bound water – in the form of hydrogen – at the boundary between bedrock areas of mudstone and sandstone.
Thereafter, Curiosity’s handlers will command the 1 ton behemoth to begin the drive to the lower reaches of Mount Sharp which lies about 6 miles (10 kilometers) distant – as the Martian crow flies.
Mount Sharp rises about 3.4 miles (5.5 km) from the center of Gale Crater. It’s taller than Mount Ranier in Washington State.
Billions of years of Mars geologic history are preserved in the sedimentary layers of Mount Sharp – along with potential signatures of the chemical ingredients of life.
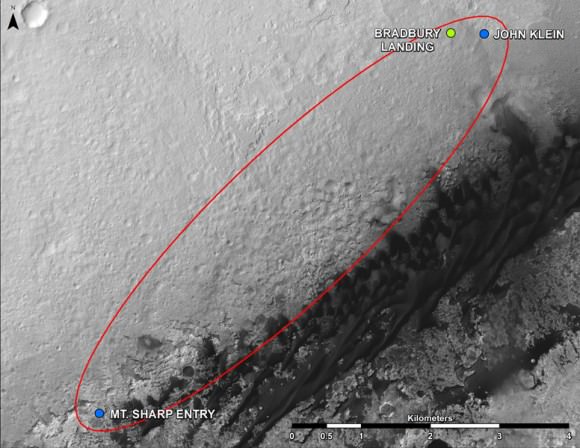

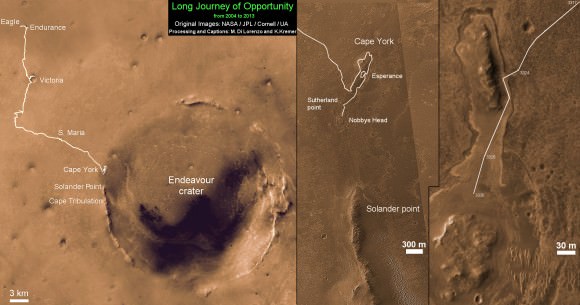
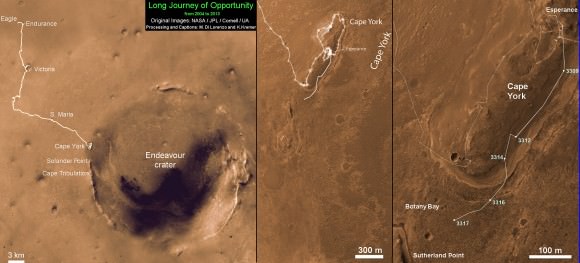
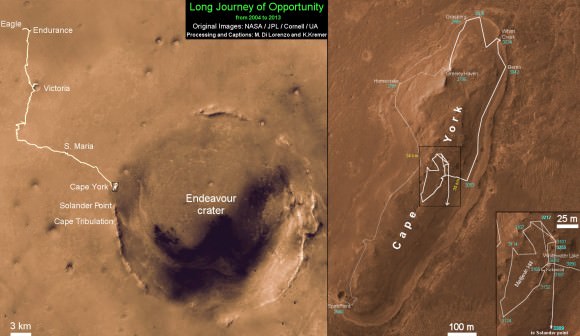
This map shows where NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity landed in August 2012 at “Bradbury Landing”; the area where the rover worked from November 2012 through May 2013 at and near the “John Klein” target rock in the “Glenelg” area; and the mission’s next major destination, the entry point to the base of Mount Sharp. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona
“The drive will start in a few weeks,” said Curiosity Project Manager Jim Erickson of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. at the briefing.
But the team will be on the lookout for targets of opportunity along the way.
“We are on a mission of exploration. If we come across scientifically interesting areas, we are going to stop and examine them before continuing the journey,” Erikson added.
“If we pass something amazing and compelling we might turn around and drive back,” Crisp added.
It could take nearly a year to arrive at Mount Sharp. And Curiosity must pass through a potentially treacherous dune field to get there – see NASA JPL route map above.
“We are looking for the best path though,” said Erickson.
NASA chose Gale as the landing site specifically to dispatch Curiosity to investigate the sedimentary layers of Mount Sharp because it exhibited signatures of clay minerals that form in neutral water and that could possibly support the origin and evolution of simple Martian life forms, past or present.
“We have a real desire to get to Mount Sharp because there we see variations in the mineralogy as we go up from the base to higher levels and a change in the record of the environment,” said Crisp.
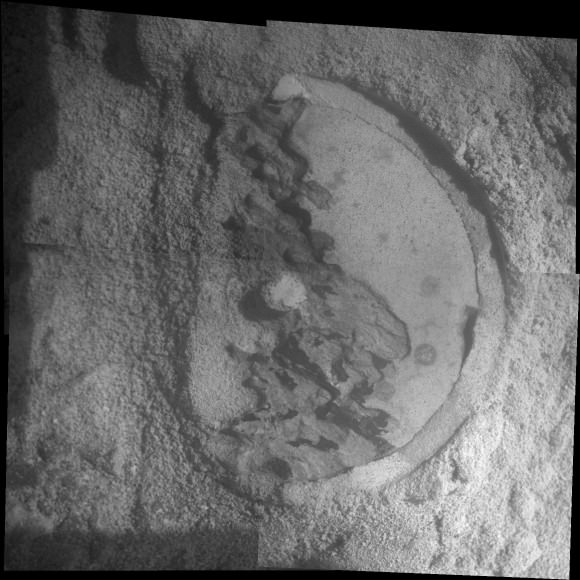
Analysis of the initial gray colored, powdery ‘John Klein’ sample by Curiosity’s pair of onboard chemistry labs – SAM & Chemin – revealed that this location on Mars was habitable in the past and possesses the key chemical ingredients – such as clay minerals – required to support microbial life forms- thereby successfully accomplishing the key science objective of the mission and making a historic discovery long before even arriving at destination Mount Sharp.
Besides the science measurements, researchers also learned lot about how to operate the complex drilling and sample delivery mechanisms much more efficiently for the second drilled rock sample.
The sieved and pulverized Cumberland sample was delivered in about a quarter of the time compared to the John Klein sample – accomplished at a deliberately measured and cautious pace.
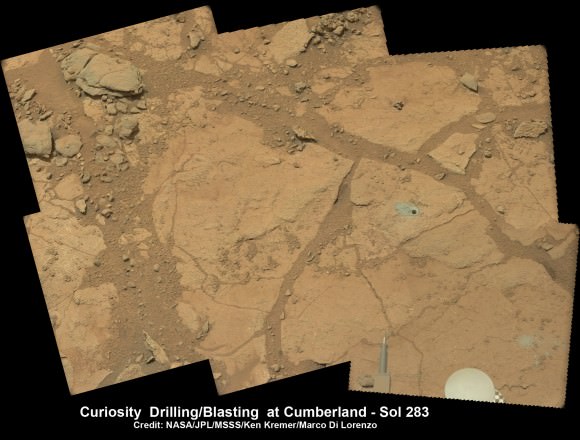

Analysis of the “Cumberland” powder is currently in progress. The goal is to determine how it compares chemically and to confirm the results found at ‘John Klein.’
“No results from Cumberland are available yet,” said Crisp.
The robot used the powerful million watt ChemCam laser to blast into the Cumberland drill hole and gray tailings scattered on the surface to glean as much insight and measurements of the chemical composition and transformation by water as possible before departing.
Curiosity has just arrived at “Point Lake’. Stay tuned for my next Curiosity story.
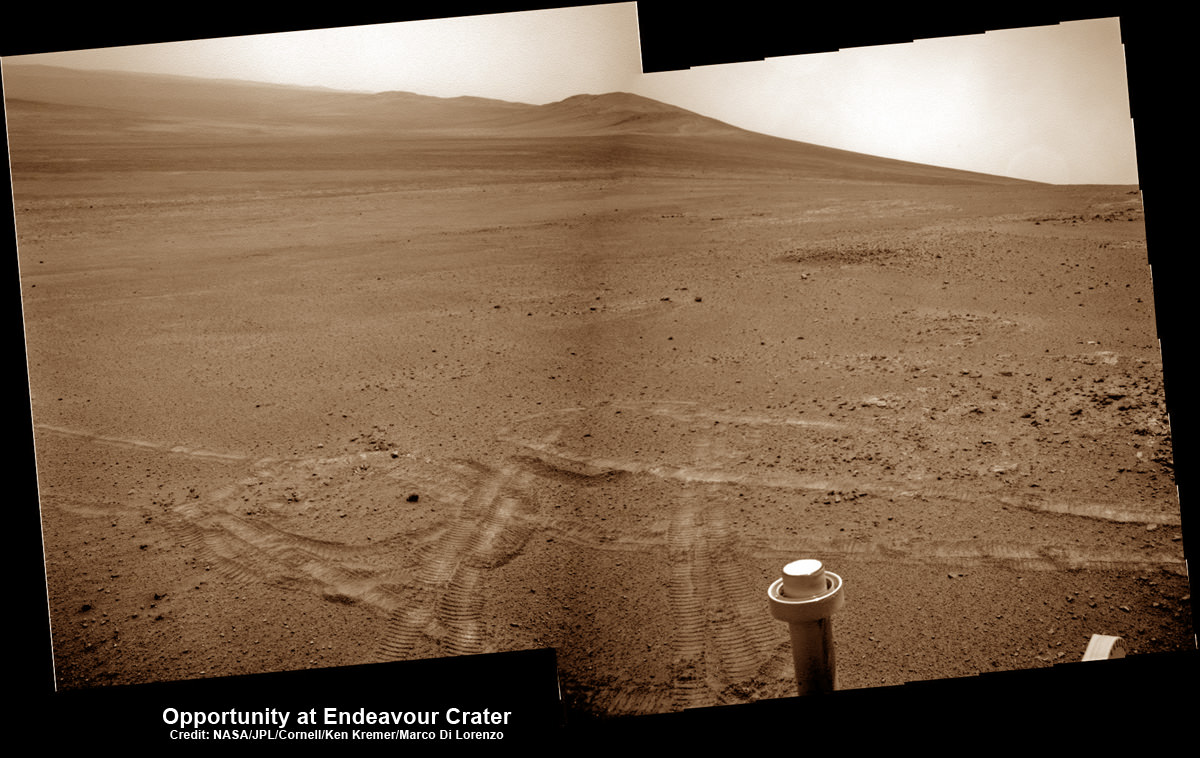
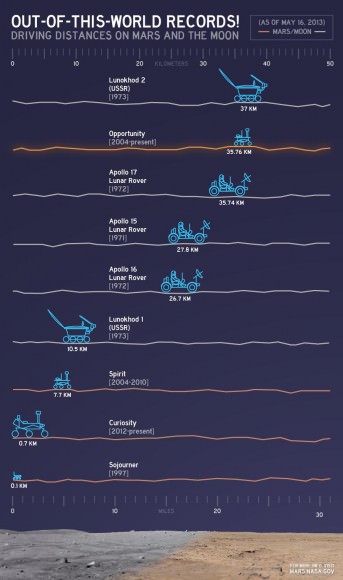
Meanwhile, Curiosity’s older sister rover Opportunity has likewise discovered clay minerals and a habitable zone on the opposite side of the Red Planet – details here.
And don’t forget to “Send Your Name to Mars” aboard NASA’s MAVEN orbiter- details here. Deadline: July 1, 2013
…………….
Learn more about Mars, Curiosity, Opportunity, MAVEN, LADEE and NASA missions at Ken’s upcoming lecture presentations
June 23: “Send your Name to Mars on MAVEN” and “CIBER Astro Sat, LADEE Lunar & Antares Rocket Launches from Virginia”; Rodeway Inn, Chincoteague, VA, 8 PM