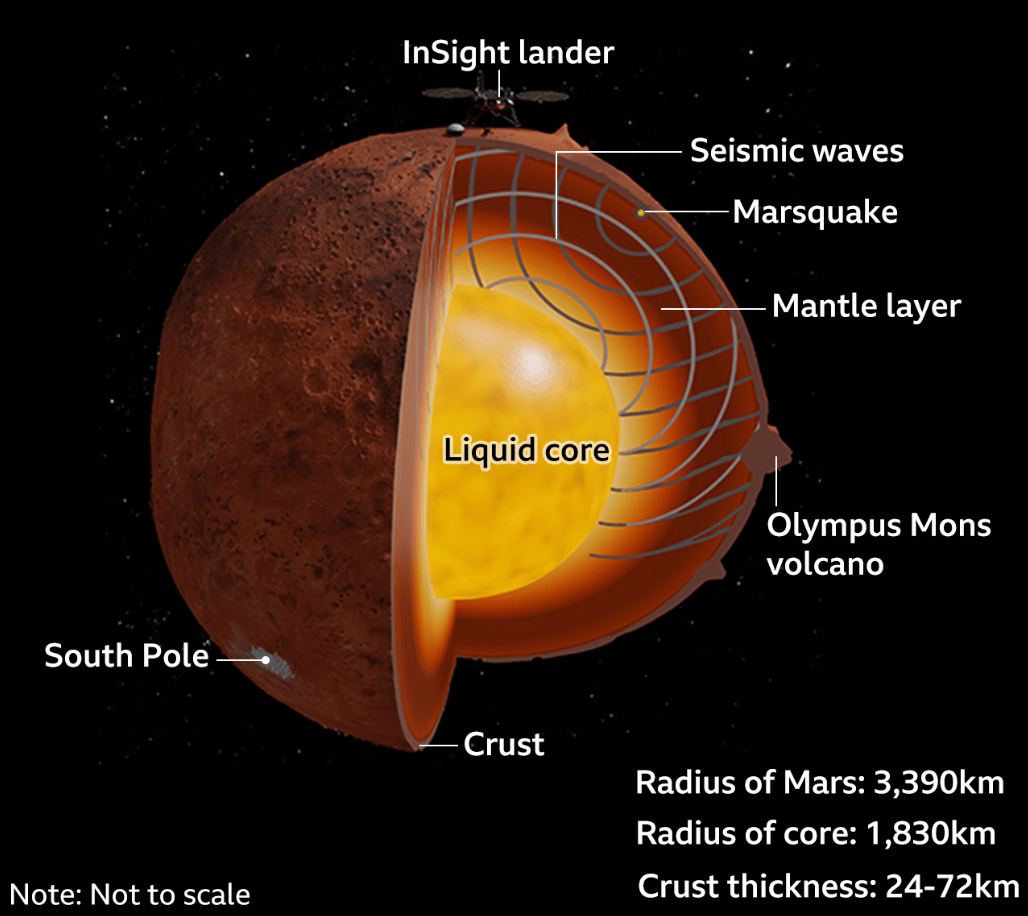
The InSight Mars lander will cease science operations sometime in the next few months due to a decreasing power supply, mission managers said at a news conference on May 17. Martian dust covering the solar panels has reduced the amount of power to roughly 500 watt-hours per Mars day or sol. When InSight landed in November of 2018, the solar panels produced around 5,000 watt-hours each sol.
“At the end of the calendar year, we do anticipate having to conclude all InSight operations,” said Kathya Zamora Garcia, InSight’s deputy project manager said at the briefing, “not because we want to turn it off but unfortunately we don’t have the energy to run it.”
Continue reading “InSight is Losing Power, it Probably Will be Shut Down in a Few Months”