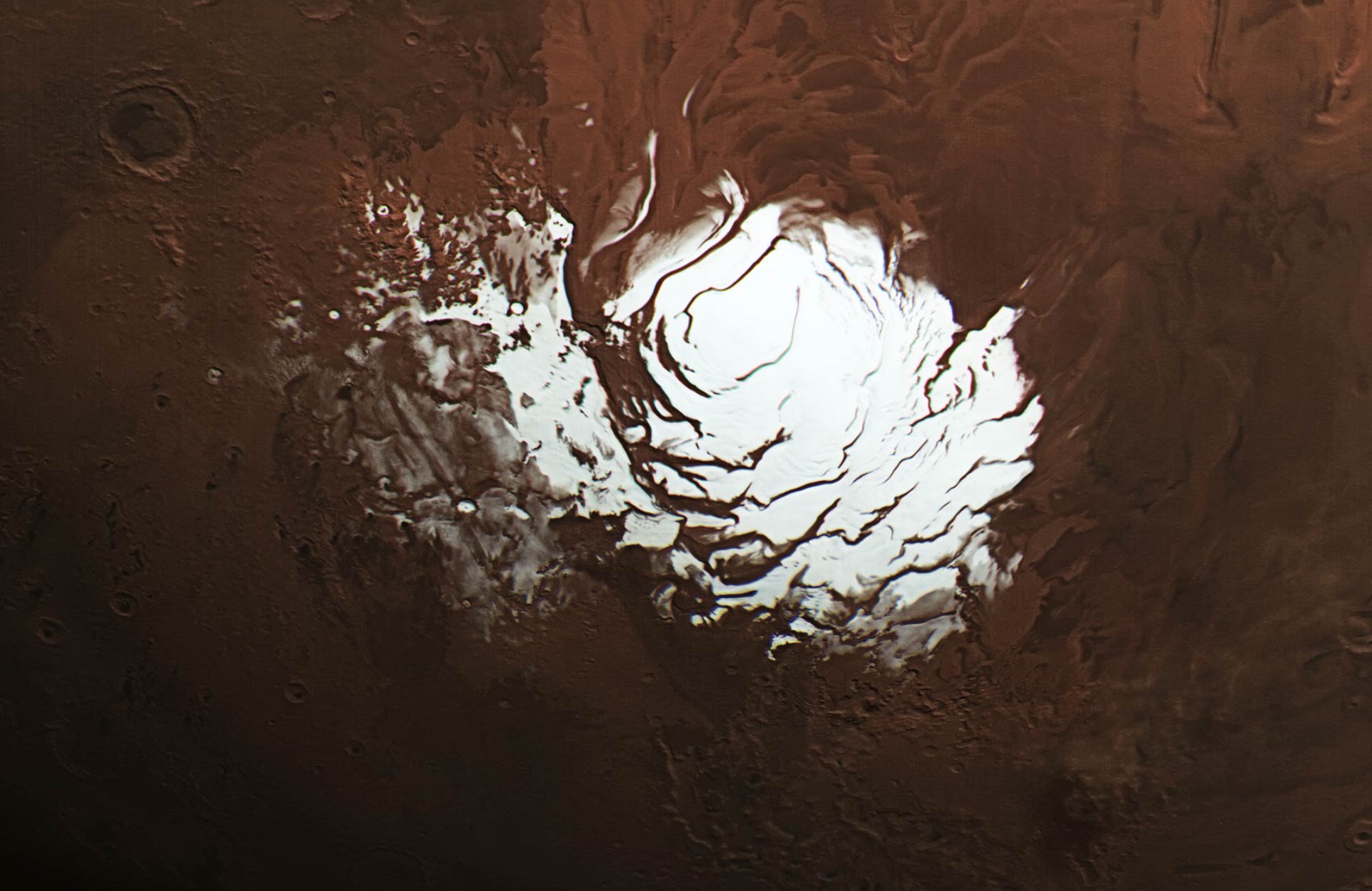
Like Earth, Mars experiences climatic variations during the course of a year because of the obliquity of its rotational axis. This leads to the annual deposition/sublimation of the CO2 ice/snow, which results in the formation of the seasonal polar caps. Similarly, these variations in temperature result in interaction between the atmosphere and the polar ice caps, which has a seasonal effect on surface features.
On Mars, however, things work a little differently. In addition to water ice, a significant percentage of the Martian polar ice caps are made up of frozen carbon dioxide (“dry ice”). Recently, an international team of scientists used data from NASA’s Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) mission to measure how the planet’s polar ice caps grow and recede annually. Their results could provide new insights into how the Martian climate varies due to seasonal change.
Continue reading “How Much Carbon Dioxide Snow Falls Every Winter on Mars?”