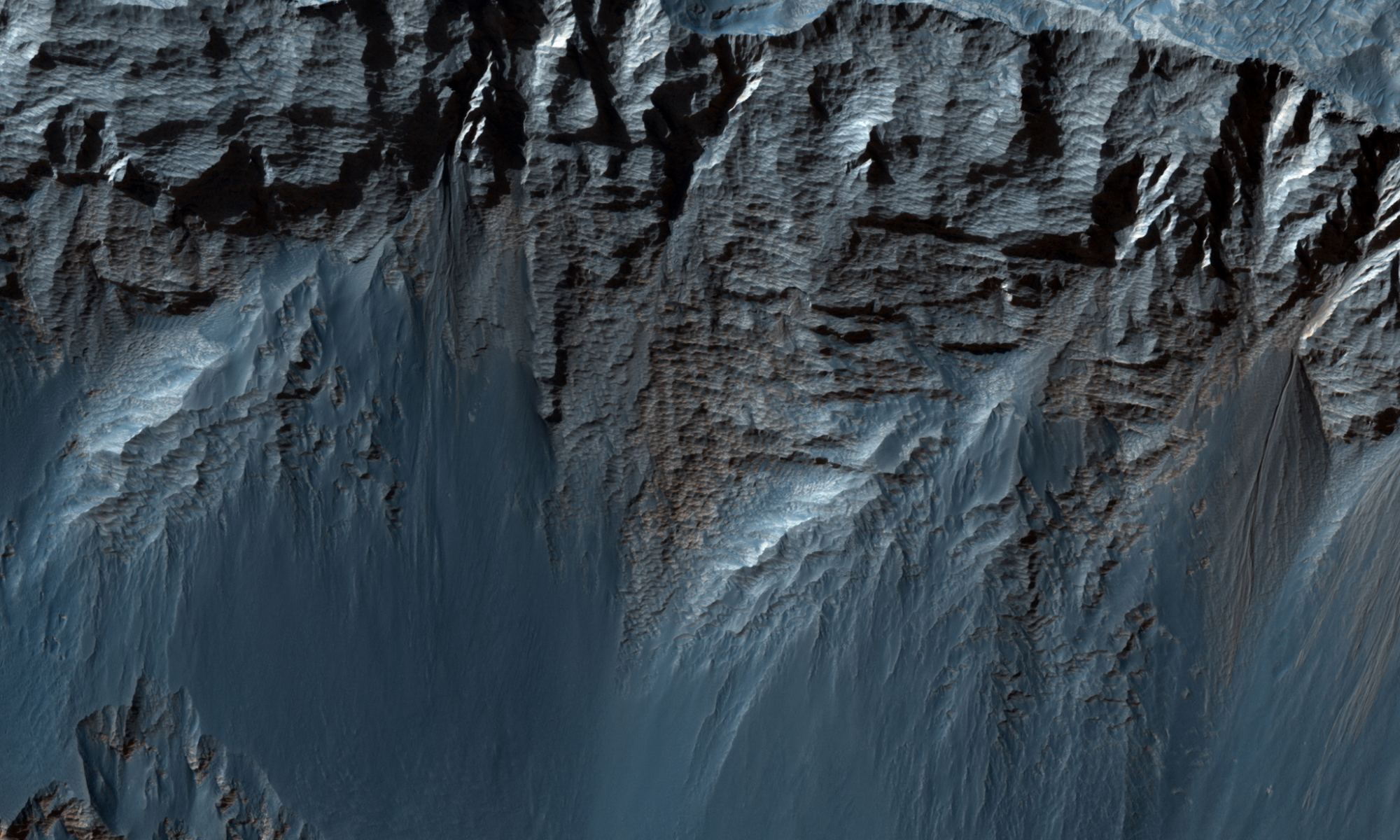
In many ways, Mars is the planet that is most similar to the Earth. The red world has polar ice caps, a nearly 24-hour rotation period (about 24 hours and 37 minutes), mountains, plains, dust storms, volcanoes, a population of robots, many of which are old and no longer work, and even a Grand Canyon of sorts. The ‘Grand Canyon’ on Mars is actually far grander than any Arizonan gorge. Valles Marineris dwarfs the Grand Canyon of the southwestern US, spanning 4,000 km in length (the distance between LA and New York City), and dives 7 kilometers into the Martian crust (compared to a measly 2km of depth seen in the Grand Canyon). Newly released photos from the High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) aboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) reveal a stunning look at eroding cliff faces in Candor Chasma, a gigantic canyon that comprises a portion of the Valles Marineris system.
Continue reading “Layers Upon Layers of Rock in Candor Chasma on Mars”Planetary Scientists Have Created a Map of Mars’ Entire Ancient River Systems
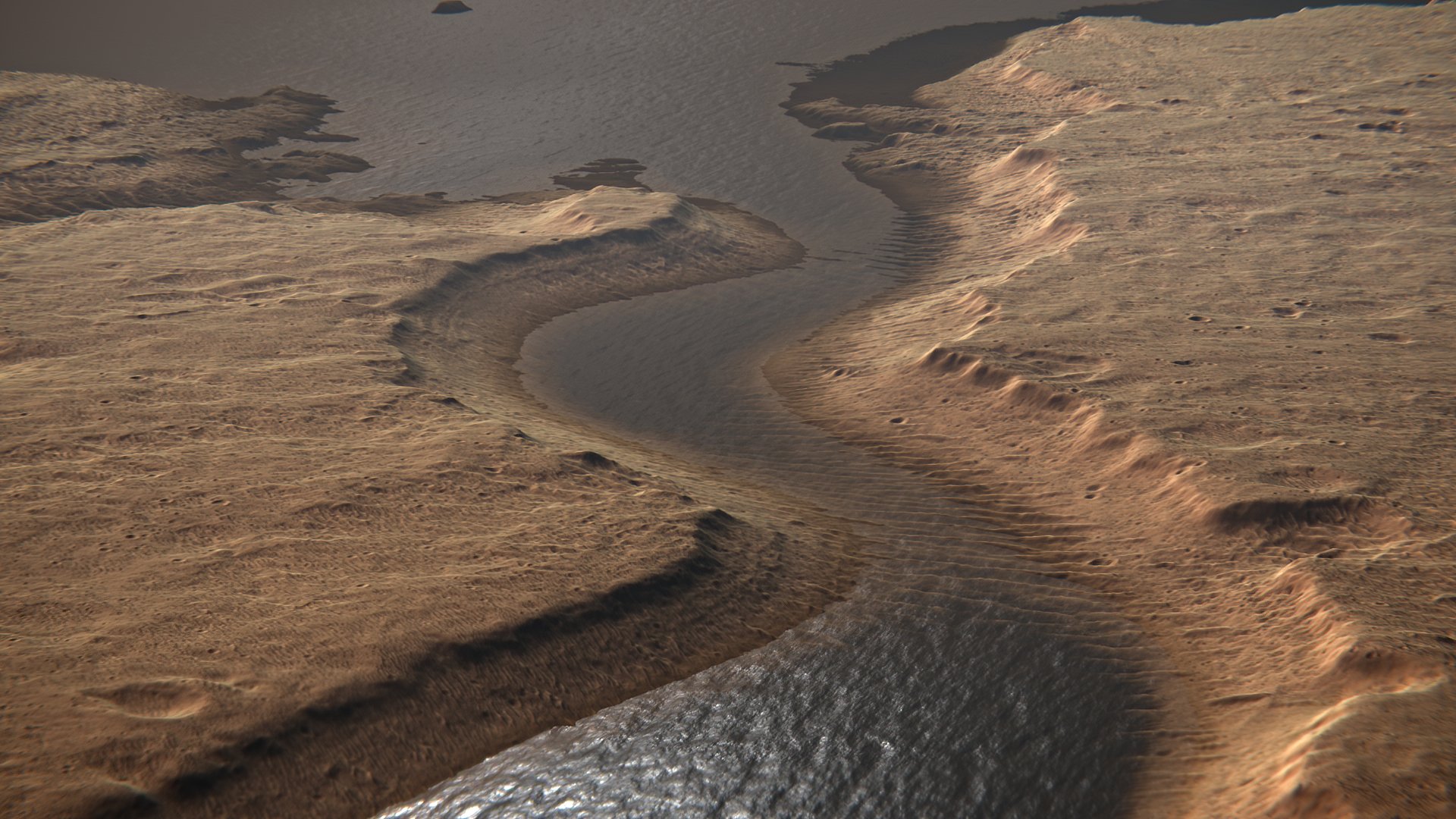
Navigating and mapping rivers has long been a central component in human exploration. Whether it was Powell exploring the Colorado’s canyons or Pizarro using the Amazon to try to find El Dorado, rivers, and our exploration of them, have been extremely important. Now, scientists have mapped out an entirely new, unique river basin. This one happens to be on an entirely different planet, and dried up billions of years ago.
Continue reading “Planetary Scientists Have Created a Map of Mars’ Entire Ancient River Systems”Brines Could be Present on the Surface of Mars for up to 12 Hours, Never for a Full day
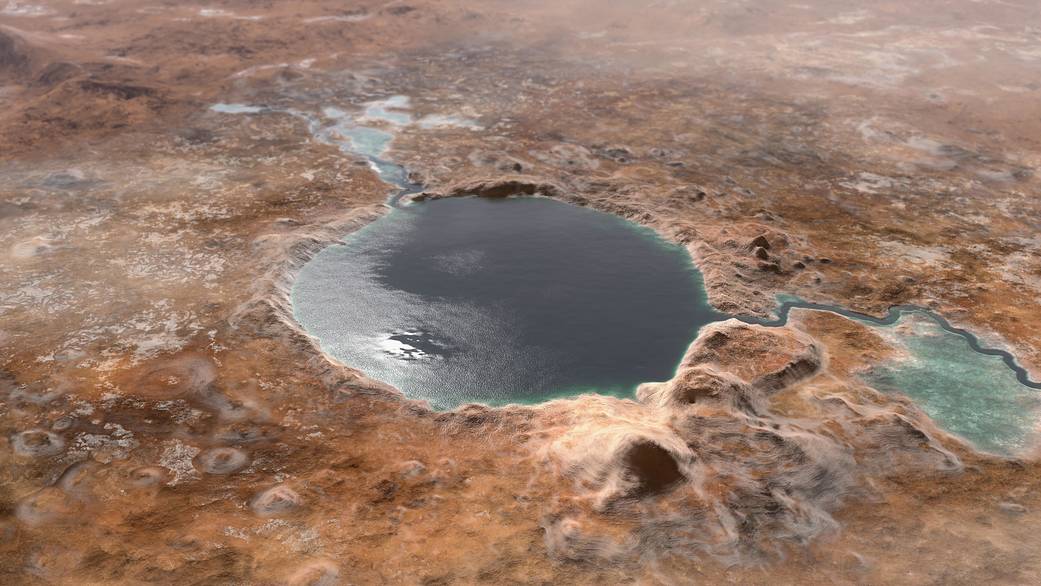

We are extremely interested in the possibility of water on Mars, because where there’s water, there’s the potential for life. But a new study throws a bit of a wet blanket (pun intended) on that tantalizing possibility. Unfortunately, it looks like even the saltiest of brines can only exist on the Martian surface for up to a few hours at a time.
Continue reading “Brines Could be Present on the Surface of Mars for up to 12 Hours, Never for a Full day”A Real River Valley on Mars, Filled With Virtual Water by @Kevinmgill
We are once again indebted to Kevin M. Gill, a science data visualization artist with a flair for the cosmos, for this beautiful rendering! The image first popped up on Kevin’s Twitter feed last week and can also be found (and downloaded) on his Flickr account. As he explained, the visual is his rendition of what the Hypanis Valles on Mars may have looked like back when water still flowed in the region. As he described it:
Continue reading “A Real River Valley on Mars, Filled With Virtual Water by @Kevinmgill”“A meandering river? Obvious and bad CGI? Based on a real place on Mars? All Three! Outflow location at Hypanis Valles With Flowing Water, via @HiRISE DTM data.”
You Can See the Spot Where Lava Broke Through the Wall of a Martian Crater and Began Filling it Up
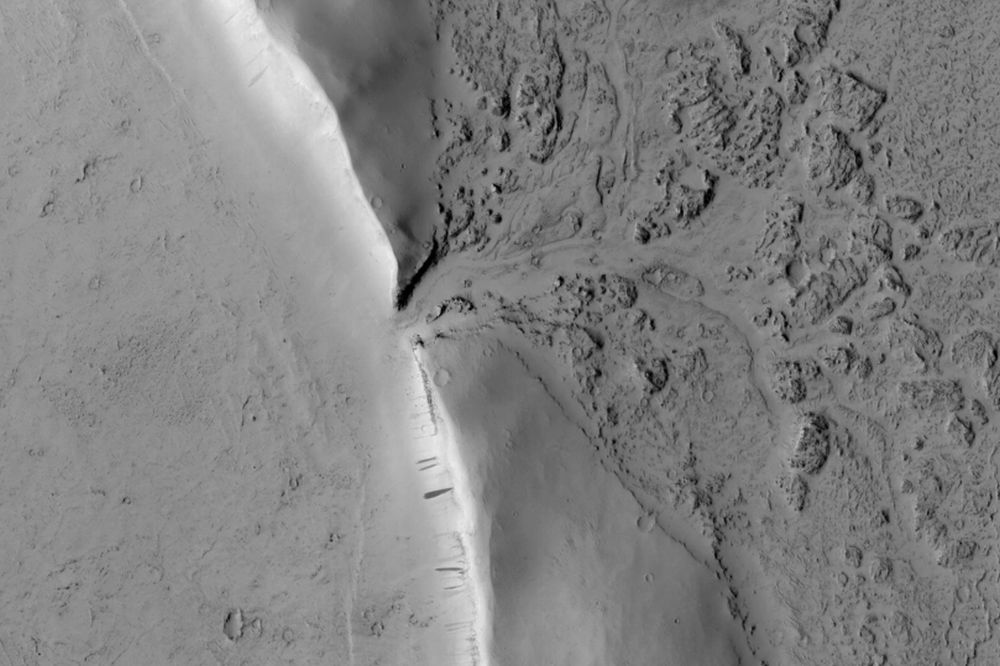

At a fundamental level, Mars is a volcanic planet. Its surface is home to the Solar System’s largest extinct volcano, Olympus Mons, and another trio of well-known volcanoes at Tharsis Montes. And those are just the highlights: there are many other volcanoes on the surface. Though that volcanic activity ceased long ago, the planet’s surface tells the tale of a world disrupted and shaped by powerful volcanic eruptions.
Continue reading “You Can See the Spot Where Lava Broke Through the Wall of a Martian Crater and Began Filling it Up”You’re Going to Need a Bigger Drill. The Best Place for Life on Mars is Deep, Deep Underground
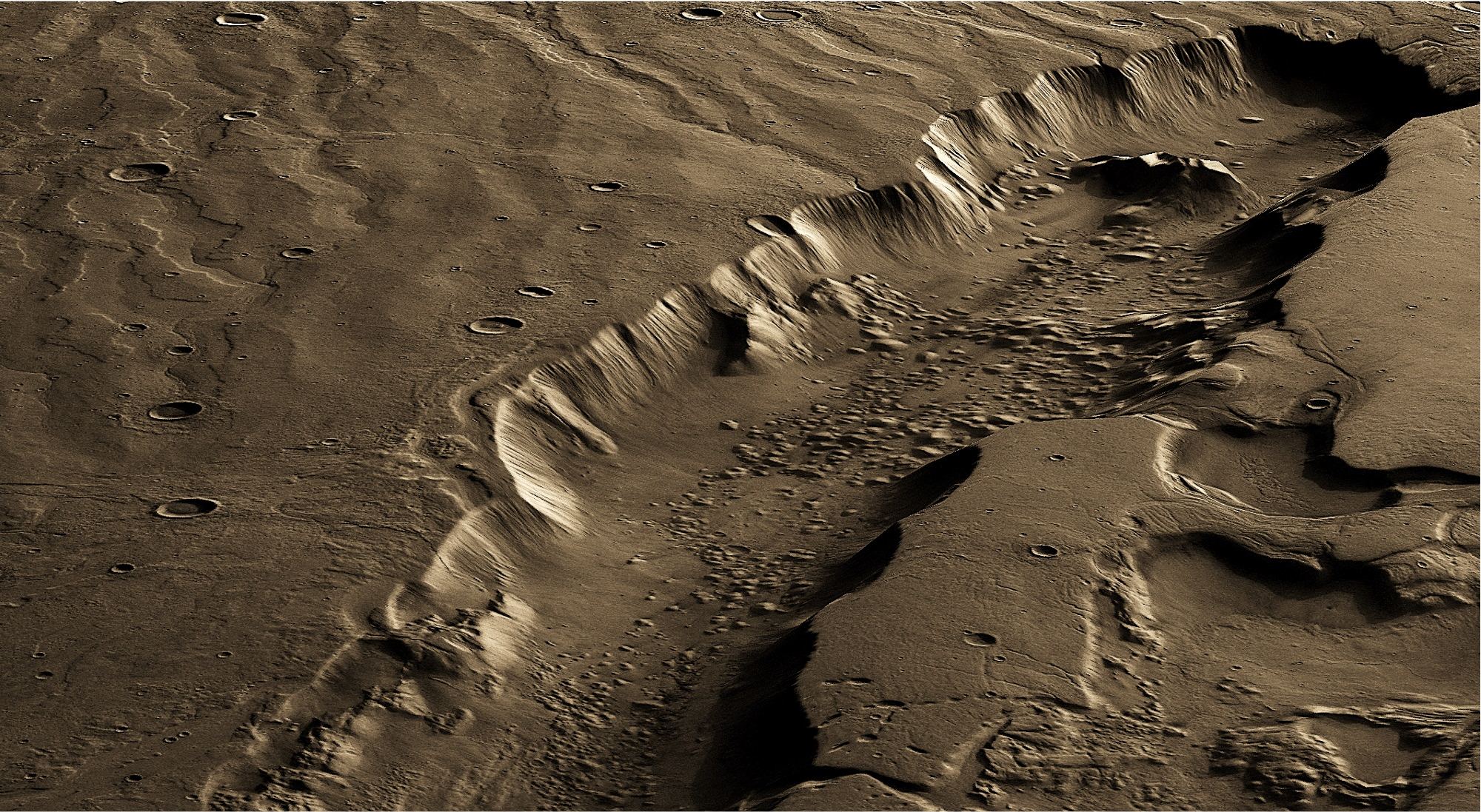

For decades, robotic missions have been exploring Mars to learn more about the planet’s geological and environmental history. Next year, the Perseverance rover will join in the hunt and be the first mission to send samples back to Earth and by the 2030s, the first crewed mission is expected to take place. All of these efforts are part of an ongoing effort to find evidence of past (and maybe even present) life on Mars.
According to a new study from Rutgers University-New Brunswick., the most likely place to find this evidence is located several kilometers beneath the surface. It is here (they argue) that water still exists in liquid form, which is likely the result of geothermal heating melting thick subsurface sheets of ice. This research could help resolve lingering questions like the faint young Sun paradox.
Continue reading “You’re Going to Need a Bigger Drill. The Best Place for Life on Mars is Deep, Deep Underground”If There’s Subsurface Water Across Mars, Where is it Safe to Land to Avoid Contamination?
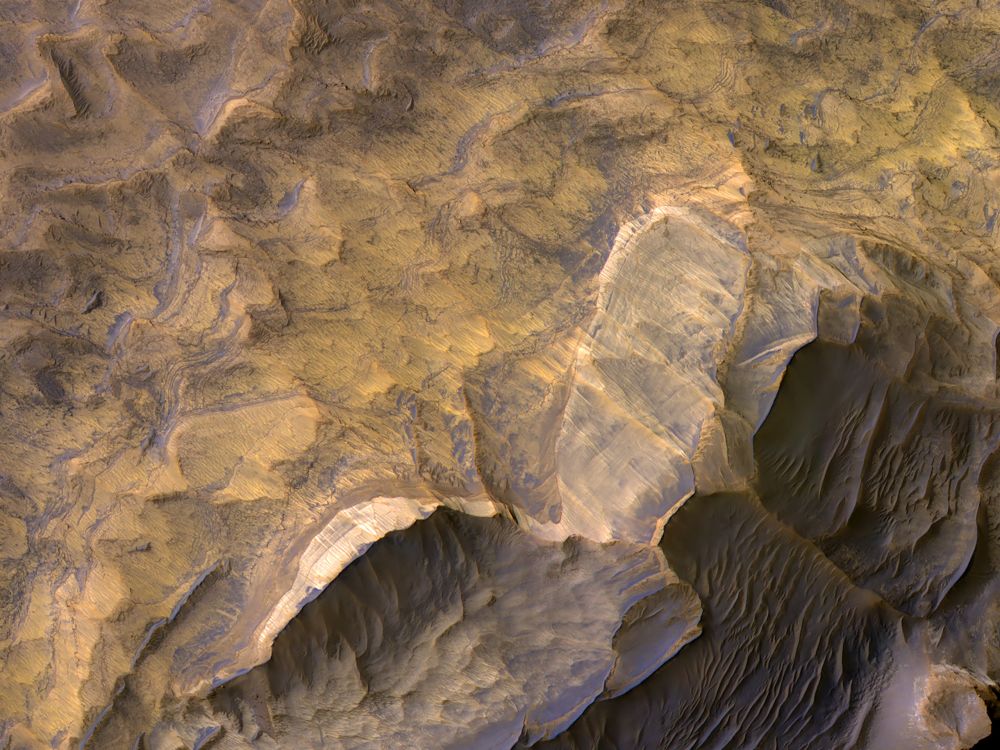

If Mars is a potential home for alien life, can we land safely anywhere on the surface without introducing contamination of Earth-born bacteria? A new study has some good news and some bad news. The good news is that Mars is likely completely inhospitable to life. The bad news is that Mars is…likely completely inhospitable to life.
Continue reading “If There’s Subsurface Water Across Mars, Where is it Safe to Land to Avoid Contamination?”Astronauts Will be Able to Extract Fuel, Air, and Water From Martian Brine

A little over a decade from now, NASA plans to send astronauts to Mars for the first time. This mission will build on decades of robotic exploration, collect samples from the surface, and return them to Earth for analysis. Given the immense distance involved, any operations on the Martian surface will need to be as self-sufficient as possible, which means sourcing whatever they can locally.
This includes using the local water to create oxygen gas, drinking water, and rocket fuel, which represents a challenge considering that any liquid water is likely to be briny. Luckily, a team of researchers from the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University at St. Louis (WUSTL) has created a new type of electrolysis system that can convert briny water into usable products while also being compact and lightweight.
Continue reading “Astronauts Will be Able to Extract Fuel, Air, and Water From Martian Brine”This is Mawrth Vallis on Mars, and it’s Positively Bursting with Evidence of Past Water Action on Mars
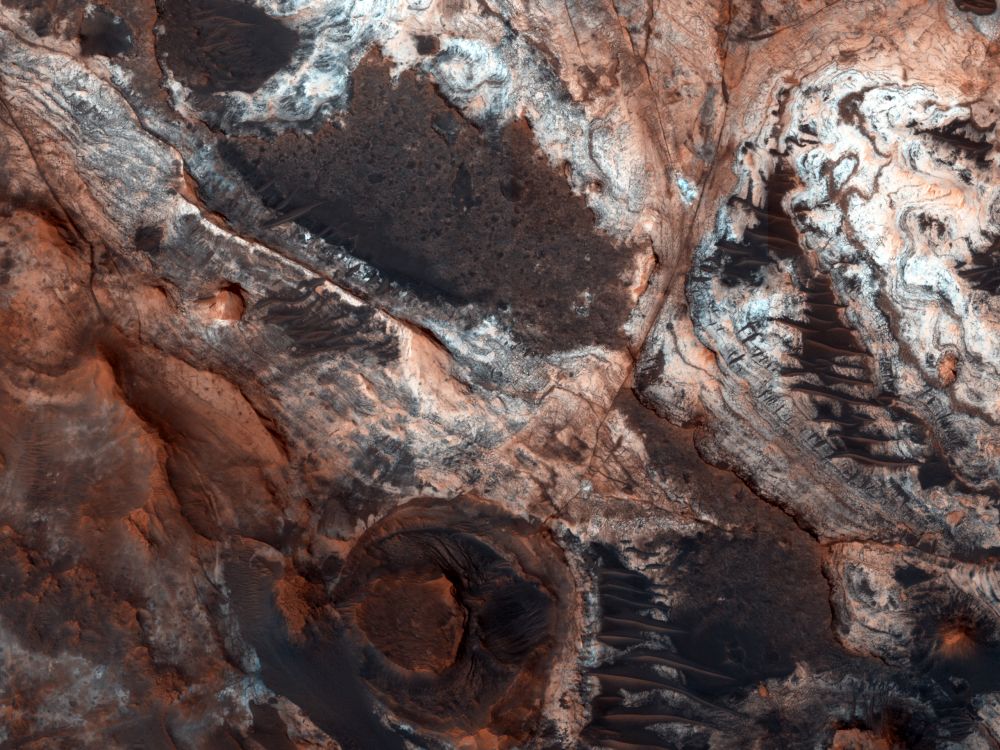

Here on Earth, geologists seek out deep channels into Earth’s rock, carved over the ages by flowing water. The exposed rock walls are like a visual timeline of a region’s geological history. On Mars, the surface water is long gone. But it flowed long enough to expose layers of rock just like here on Earth.
One of those water-exposed areas on Mars is Mawrth Vallis, an outflow channel that feeds into the Chryse Basin.
Continue reading “This is Mawrth Vallis on Mars, and it’s Positively Bursting with Evidence of Past Water Action on Mars”Mars Might Have Lost its Water Quickly

Mars is an arid place, and aside from a tiny amount of water vapour in the atmosphere, all water exists as ice. But it wasn’t always this arid. Evidence of the planet’s past wet chapter dots the surface. Paleolakes like Jezero Crater, soon to be explored by NASA’s Perseverance Rover, provide stark evidence of Mars’ ancient past. But what happened to all that water?
It disappeared into space, of course. But when? And how quickly?
Continue reading “Mars Might Have Lost its Water Quickly”