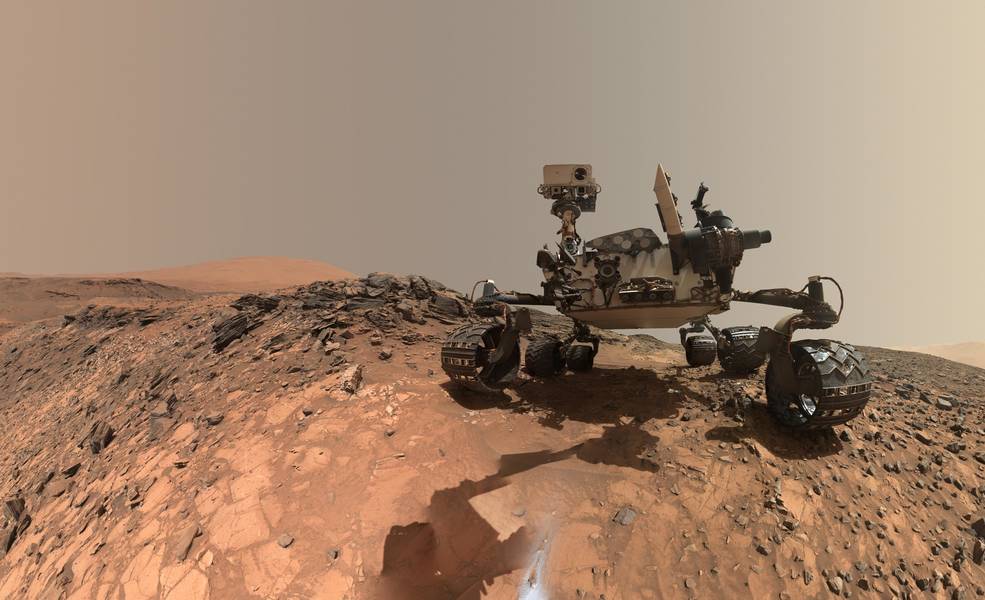
The idea of somehow terra-forming Mars to make it more habitable is a visionary, sci-fi dream. But though global terra-forming of Mars is out of reach, the idea persists. But now, a material called silica aerogel might make make the whole idea of terra-forming Mars slightly less impossible.
Continue reading “Blankets of Silica Aerogel Could Make Parts of Mars Habitable”Blankets of Silica Aerogel Could Make Parts of Mars Habitable